عالميًا: فهم الضرائب والرسوم
أهداف تعلم الدرس:
- Understand different types of taxes related to stock trading, including capital gains tax, dividend tax, and withholding tax, and how they vary by country and investment type.
- استكشف مختلف types of trading fees such as brokerage fees, transaction costs, and custodian fees, and how these can differ among financial service providers.
- Learn strategies to minimize taxes, such as utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, holding investments long-term for favorable capital gains rates, and employing tax-loss harvesting to offset gains.
- Discover methods to reduce trading fees through careful selection of brokerage services, opting for low-cost investment vehicles, and trading prudently to avoid excessive transaction costs.
A. Introduction
When investing in stocks, understanding الضرائب و مصاريف is crucial for maximizing returns and managing the overall cost of your portfolio. Taxes on capital gains, dividends, and transaction fees can erode your profits, making it essential to develop strategies to manage these expenses. In this chapter, we’ll explore the different types of taxes and fees involved in stock trading and discuss strategies for reducing their impact on your investments.
B. Managing Taxes and Fees in Stock Trading
Investors need to account for both الضرائب و مصاريف when making trades or holding stocks in their portfolios. These costs vary by country and can significantly affect long-term returns if not managed properly.
مقدمة عن الضرائب والرسوم
Taxes and fees are inherent costs of investing that can vary by jurisdiction and the type of investment you make. It’s important to be aware of these costs to develop strategies that can help mitigate their impact on your investment performance.
أنواع الضرائب:
- ضريبة الأرباح الرأسمالية: This tax applies when you sell a stock at a higher price than you paid for it. The rate varies depending on how long you held the stock and your country’s tax laws. Short-term capital gains (for assets held less than a year) are often taxed at a higher rate than long-term gains.
- Dividend Tax: If you hold dividend-paying stocks, you may be required to pay taxes on the dividends received. Some countries offer lower tax rates on dividends, while others may tax them at the same rate as ordinary income.
- Withholding Tax: For international investors, withholding taxes may be levied on dividends paid by foreign companies. These taxes are withheld at the source and may require tax treaties between countries to reduce or reclaim part of the tax.
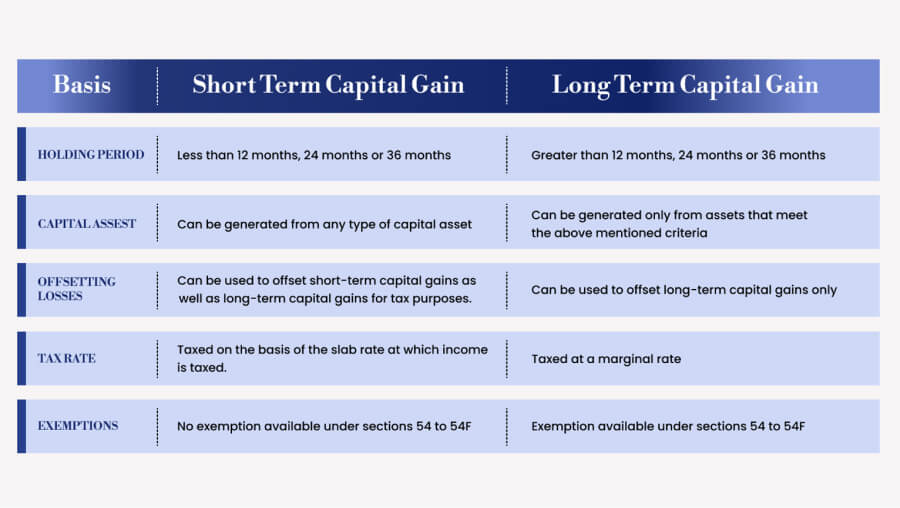
شكل: Short-Term Capital Gain vs. Long-Term Capital Gain
وصف:
This table outlines the differences between short-term و long-term capital gains based on key factors such as holding period, capital asset, offsetting losses, tax rate، و exemptions. Short-term gains apply to assets held for less than 12, 24, or 36 months, while long-term gains are for assets held longer than these periods. Short-term capital gains are generally taxed at slab rates, while long-term gains are taxed at marginal rates. Exemptions are available for long-term gains under Sections 54 to 54F, while short-term gains have no exemptions under these sections.
الماخذ الرئيسية:
- Holding Period: Short-term applies to assets held less than 36 months, while long-term applies to assets held for more than 36 months.
- Tax Rate: Short-term gains are taxed based on income slab rates, whereas long-term gains have marginal tax rates.
- Offsetting Losses: Both gains can offset capital losses, but short-term gains can offset both short and long-term losses, while long-term gains offset only long-term losses.
- Exemptions: Only long-term gains qualify for exemptions under Sections 54 to 54F.
تطبيق المعلومات:
This information helps investors understand the الآثار المترتبة على الضرائب of selling assets at different holding periods. Knowing the differences can guide decisions on asset holding duration to optimize tax benefits. For instance, an investor may choose to hold an asset longer to qualify for lower long-term tax rates or to benefit from tax exemptions.
أنواع الرسوم:
- رسوم الوساطة: These are fees charged by brokers for executing buy or sell orders. Fees may vary depending on the broker and the size or type of transaction.
- Transaction Fees: Some brokers or exchanges charge a flat fee or a percentage-based commission for each trade executed. This can include fees for market access or electronic communication networks (ECNs).
- رسوم الإدارة: If you use a financial advisor or invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), you may be charged a management fee, which is typically a percentage of the assets under management (AUM).
- Custodian Fees: Some brokers charge fees for maintaining and safeguarding your securities, especially for international stocks or complex instruments.
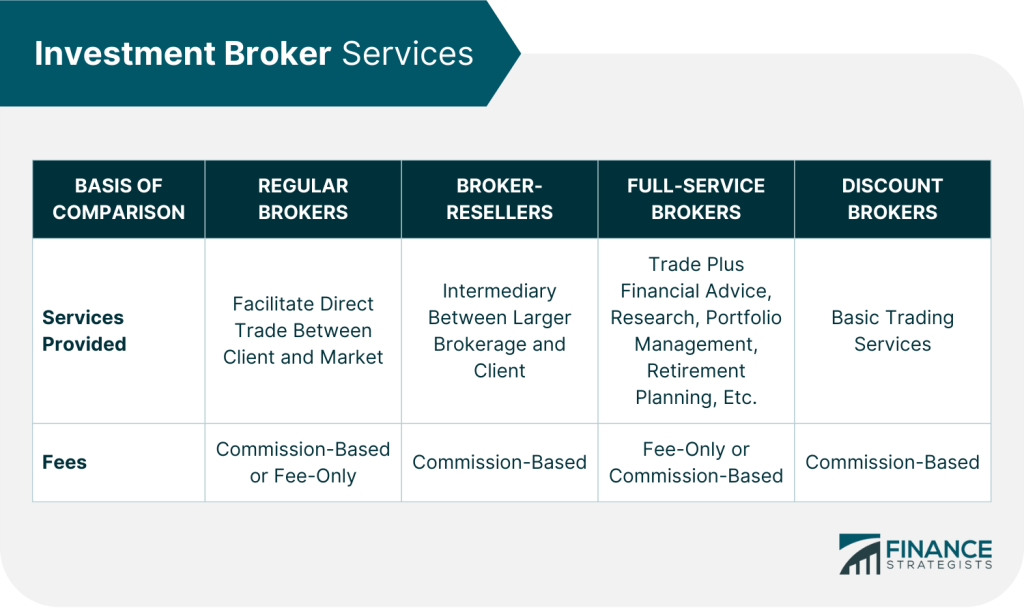
شكل: Investment Broker Services
وصف:
This table compares four types of investment brokers: Regular Brokers, Broker-Resellers, Full-Service Brokers، و Discount Brokers. It details the services provided و مصاريف associated with each type. Regular brokers facilitate direct trades between clients and the market, while broker-resellers act as intermediaries between larger brokerages and clients. Full-service brokers offer additional services like financial advice, portfolio management, and research. Discount brokers provide basic trading services. Fee structures range from commission-based ل fee-only, depending on the broker type.
الماخذ الرئيسية:
- Regular Brokers: Facilitate direct trade with fees based on commission أو fee-only.
- Broker-Resellers: Act as intermediaries, charging commission-based fees.
- Full-Service Brokers: Offer a range of financial services with fees either fee-only أو commission-based.
- Discount Brokers: Provide only basic trading services and typically charge commission-based fees.
تطبيق المعلومات:
فهم different types of brokers helps investors choose a service that matches their needs and budget. For those seeking basic trading, discount brokers may be suitable. In contrast, investors requiring comprehensive advice أو إدارة المحافظ may benefit from full-service brokers. Awareness of fee structures can also guide investors in optimizing costs and selecting a broker that aligns with their trading strategy.
C. Strategies to Reduce or Manage Tax
There are various strategies that investors can employ to minimize their tax liabilities when trading stocks. Proper tax planning can help ensure that you keep more of your profits.
Use of Tax-Advantaged Accounts
One of the most effective ways to reduce taxes on stock gains and dividends is by using حسابات ذات امتيازات ضريبية. In many countries, retirement accounts or investment accounts like Roth IRAs (in the U.S.) or ISAs (in the UK) allow you to invest in stocks while deferring or avoiding taxes.
- مثال: In a حساب روث الفردي للتقاعد, investments grow tax-free, and withdrawals in retirement are also tax-free, making it a powerful tool for long-term investors.
Hold Investments for the Long Term
Holding stocks for more than a year generally qualifies your profits for long-term capital gains rates, which are usually lower than short-term rates. Long-term investing can be a simple and effective strategy for reducing tax liabilities.
- مثال: In many countries, long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate (e.g., 0%, 15%, or 20% in the U.S.), whereas short-term gains can be taxed at your regular income tax rate.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Investors can offset capital gains by strategically selling underperforming stocks to realize a loss, a technique known as حصاد الخسائر الضريبية. This allows you to reduce taxable gains by the amount of your realized losses.
- مثال: If you sold a stock for a $5,000 profit and sold another stock for a $3,000 loss, you could offset $3,000 of your gains, reducing your tax liability.
D. Managing Fees and Expenses in Investing
Fees can accumulate over time, eating into your investment returns. Investors should focus on minimizing these expenses to enhance overall portfolio performance
Compare Brokerage Fees
One of the simplest ways to reduce costs is by comparing fees across different brokerage platforms. Discount brokers tend to offer lower fees than full-service brokers, though they may provide fewer services.
- مثال: Platforms like Robinhood و إي تورو offer commission-free trading for stocks, making them popular choices for cost-conscious investors.
Use Low-Cost ETFs and Index Funds
Investing in low-cost ETFs أو index funds can significantly reduce management fees. These passive funds typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds, allowing you to keep more of your returns.
- مثال: Many index funds, such as those tracking the ستاندرد آند بورز 500, have expense ratios below 0.10%, meaning more of your money stays invested in the market.
Avoid Overtrading
Frequent trading can lead to higher transaction costs, especially if your broker charges per trade. Reducing the number of trades you make can help minimize fees and improve long-term returns.
- مثال: If your broker charges a $10 fee per trade and you make 50 trades a year, you could save $500 annually by cutting your trades in half.
خاتمة
Understanding and managing الضرائب و مصاريف are critical components of successful investing. By leveraging strategies such as using حسابات ذات امتيازات ضريبية, practicing حصاد الخسائر الضريبية, and choosing low-cost investment vehicles, you can significantly reduce the costs associated with stock trading. Additionally, minimizing brokerage and management fees can help maximize your investment returns over time, allowing you to build wealth more efficiently.
معلومات الدرس الرئيسية:
- Tax Implications: Capital gains and dividend taxes can take a significant portion of your investment returns if not managed properly. Knowing the specific tax rules in your jurisdiction and how they apply to different types of investments is crucial for effective tax planning.
- Fee Management: Fees can erode investment gains subtly over time. Investors should choose brokers and trading platforms that align with their trading frequency and investment style to minimize costs.
- Strategies for Tax Reduction: Utilizing accounts that offer tax advantages can greatly reduce the tax burden on investments. Strategies like holding investments for longer periods to benefit from lower long-term capital gains rates, and tax-loss harvesting to offset gains with losses, are effective ways to reduce taxable income.
- Cost-Efficient Investing: Opting for low-cost ETFs and index funds can significantly reduce management fees. Comparing brokerage fees and understanding the cost structure of each trade or investment can help in choosing the most cost-effective platforms.
كلمة الختام:
Effective management of taxes and trading fees is crucial for maximizing investment returns. By understanding the implications of these financial obligations and implementing strategic measures to mitigate them, investors can enhance the overall performance of their investment portfolios.

