Global: Budgetierungsstrategien für finanziellen Erfolg
Lesson Learning Objectives:
Einführung:
This section introduces budgeting as a fundamental part of financial success. It emphasizes the importance of managing income, tracking expenses, and planning for both short-term and long-term goals. By learning effective budgeting strategies, individuals can better allocate their money, reduce debt, and build financial stability.
- Understand the importance of budgeting for financial planning. Learn how budgeting helps in tracking expenses, managing income, and setting savings targets, allowing for better financial control and decision-making.
- Differentiate between fixed and variable expenses in a budget. This will help prioritize spending and identify which costs can be adjusted to free up funds for savings or investments.
- Identify needs versus wants when budgeting. Knowing how to categorize expenses helps individuals focus on essential spending while managing discretionary expenses, promoting better financial habits.
- Develop flexible budgeting strategies to adapt to changes in income or unexpected expenses. This ensures financial stability even when facing life changes or economic shifts.
A. Introduction to Budgeting and Expense Management
Budgeting is one of the foundational elements of financial planning. It involves creating a plan for how income will be allocated to cover both essential expenses Und discretionary spending, with a focus on ensuring there is enough left over for savings Und investment. Effective budgeting is key to achieving financial goals and maintaining control over personal or household finances.
By consistently managing expenses and tracking income, individuals can avoid overspending, reduce debt, and work towards financial stability. Budgeting helps people make informed spending decisions, allowing them to understand where their money is going and how they can better allocate it.

Figur: 7 Budget Process Steps
Beschreibung:
This figure outlines the seven key steps involved in the budget creation process. It starts with setting realistic goals to determine the purpose and targets, followed by choosing the type of budget suited to the needs. The process includes projecting revenue and identifying both fixed and variable costs, which help in planning accurate budget estimates. Capital expenditure (CapEx) spends Und contingencies are also included to address major purchases and unexpected costs, ensuring the budget is comprehensive and adaptable.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Setting realistic goals is the first step, which ensures the budget aligns with organizational or personal financial objectives.
- Inclusion of fixed and variable costs helps to estimate accurate expenditures and manage resources effectively.
- CapEx spends focus on investments in long-term assets, while contingencies prepare for unforeseen expenses.
- Following a structured budgeting process ensures better financial planning and efficient allocation of resources.
Application of Information:
These budget process steps can help individuals and organizations plan their finances effectively by setting clear goals, estimating revenues, and preparing for fixed, variable, and unforeseen expenses. Understanding these steps allows for better resource management and can lead to more informed financial decisions.
B. Developing a Budget
The process of developing a budget begins by assessing both income Und expenses. Start by calculating total monthly income, which could include salaries, freelance earnings, investment income, and any government benefits. Then, list out all expenses, including:
- Fixed expenses: Rent, mortgage, insurance, utilities.
- Variable expenses: Groceries, transportation, entertainment, clothing.
- Savings goals: Emergency funds, retirement contributions, investments.
Once all expenses are identified, categorize them as needs oder wants to prioritize where to allocate funds. The key to a successful budget is ensuring that essential expenses are covered before discretionary spending is considered. Additionally, setting aside a portion of income for savings Und investment goals helps ensure financial growth and security.
C. Creating and Revising Budgets
Creating a budget is not a one-time activity—it is an ongoing process that requires monitoring, evaluation, Und revision. After creating an initial budget, it’s important to track actual spending and compare it to the budgeted amounts. This will help identify any overages oder underspending, enabling adjustments where needed.
If actual expenses consistently exceed the budget, it may be necessary to:
- Cut discretionary spending (e.g., dining out, entertainment).
- Adjust variable expenses (e.g., groceries, clothing).
- Seek additional income through side jobs or selling unused items.
Regularly revising the budget ensures that it remains relevant and reflects changes in financial circumstances, such as income increases, unexpected expenses, or changing financial goals. This flexibility is key to maintaining financial control and achieving long-term objectives.
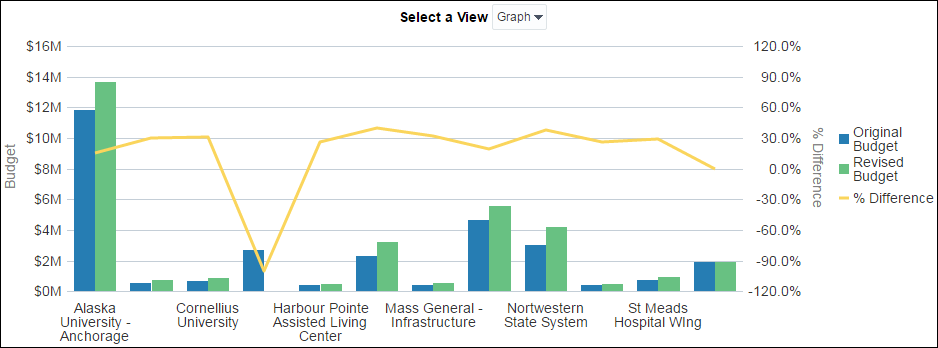
Figur: Budget Comparison Across Institutions
Beschreibung:
This graph compares the original budget Und revised budget for various institutions, with a line showing the percentage difference between them. The vertical bars represent budget values, while the line indicates how much the revised budget has changed from the original. Institutions such as Alaska University – Anchorage have significant budget revisions, while others like St Meads Hospital Wing show less variance.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Alaska University – Anchorage had the largest budget, with a notable difference between the original and revised figures.
- Percentage difference shows how much each institution’s budget was adjusted, which can be either an increase or a decrease.
- Smaller institutions like Cornelius University had minimal adjustments compared to larger ones.
- Understanding budget revisions can help identify areas where additional funding oder cost-cutting measures were necessary.
Application of Information:
This data helps users understand how budgets are managed and adjusted over time, showing the importance of monitoring financial plans. By analyzing percentage differences, users can gain insights into which projects or institutions required more funding than initially planned and adjust their financial strategies accordingly.
D. Impact of External Factors on Budgeting
External factors, such as economic conditions, inflation, or market fluctuations, can significantly affect personal budgets. For instance, inflation can drive up the cost of necessities like groceries, utilities, and fuel, leaving less disposable income for discretionary spending or savings. Economic downturns may lead to income loss oder reduced work hours, forcing individuals to adjust their budgets to cover essential expenses with a lower income.

In such cases, individuals may need to:
- Prioritize savings for emergency funds to cover unforeseen financial setbacks.
- Cut back on non-essential spending to compensate for rising prices.
- Reallocate funds to essential areas like housing, healthcare, and groceries.
Additionally, global events—such as pandemics oder natural disasters—can disrupt income sources or increase costs in unexpected ways. Individuals who are flexible with their budgets and able to adapt to these changes will be better positioned to maintain financial stability during challenging times.
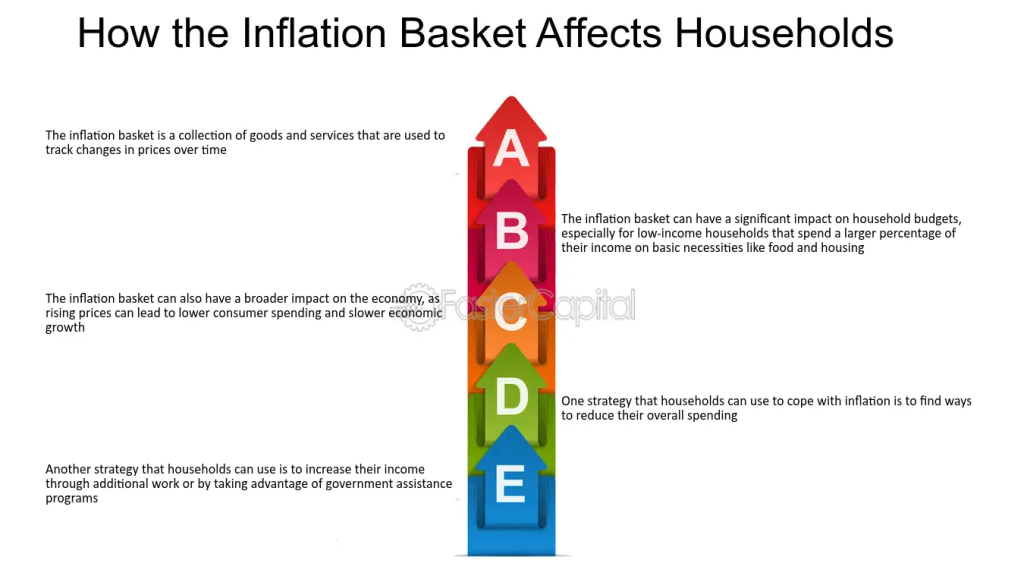
Figur: How the Inflation Basket Affects Households
Beschreibung:
The image explains the concept of the inflation basket, which is a collection of goods and services used to track changes in prices over time. It highlights how inflation affects household budgets, particularly for low-income households that allocate a larger part of their income to essential goods. Additionally, it mentions broader economic impacts, such as reduced consumer spending, and offers strategies for households to cope with rising prices.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Inflation baskets track price changes, helping to measure inflation’s impact on consumers.
- Low-income households are more affected, as they spend a higher percentage of their income on essentials.
- Rising prices can lead to decreased consumer spending, affecting economic growth.
- Household strategies to cope with inflation include reducing expenses and increasing income.
Application of Information:
Understanding how inflation baskets work helps users see the importance of budgeting Und monitoring spending. For investors, it can indicate shifts in consumer behavior, offering insights into market trends. Additionally, knowing how inflation affects various income groups can help people plan better and develop financial resilience.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Budgeting is a crucial part of financial planning, as it helps manage both income and expenses effectively. By creating a budget, individuals can track spending, allocate funds wisely, and achieve financial goals.
- Fixed expenses are consistent monthly costs, such as rent, mortgage, or insurance, while variable expenses fluctuate and include groceries, entertainment, and utilities. Understanding this distinction helps prioritize essential spending over non-essential expenses.
- Prioritizing needs over wants is essential for effective budgeting. Needs are necessary for daily living (e.g., food, housing), while wants are non-essential items (e.g., dining out, luxury goods). Focusing on needs first ensures financial security before spending on discretionary items.
- Flexibility in budgeting allows for adjustments when income changes or unexpected expenses arise. By regularly reviewing and revising the budget, individuals can maintain control over their finances and adapt to new financial circumstances.
- External factors, like inflation or economic changes, can impact budgeting. For instance, rising prices may require adjustments in spending or saving patterns. Understanding these factors helps individuals create a resilient budget that can handle unexpected financial challenges.
- Consistent budget management leads to long-term financial success by promoting better spending habits, reducing debt, and increasing savings. It is essential to revisit and revise the budget regularly to ensure it aligns with changing financial goals and circumstances.
Schlusserklärung: Budgeting is not just about tracking expenses—it’s about creating a roadmap for financial success. By mastering these budgeting strategies, users can achieve better financial outcomes, maintain stability, and work toward long-term goals with confidence.