Global: IPO versus Public Companies
Lernziele der Lektion:
- Grasp the differences between IPOs and public companies, focusing on the transformation that occurs when a private company goes public and the subsequent stability offered by established public companies.
- Understand the importance of the ownership structure of a company, including the influence of institutional investors, insider ownership, and retail investors on stock stability and company governance.
- Learn about the IPO process, from filing with regulatory bodies to becoming a publicly traded entity on stock exchanges, and the role this process plays in a company’s ability to raise capital and expand its market presence.
- Explore methods for checking the ownership structure of a company, using tools like annual reports, financial news websites, stock exchange filings, and brokerage platforms to gather and analyze crucial shareholder information.
A. Introduction
When investing in stocks, it’s essential to understand more than just price movements and financial ratios. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) and the ownership structure of companies can significantly influence stock performance and investor decisions. This section covers the differences between IPOs Und public companies, as well as the importance of understanding a company’s ownership structure, and how to check it.
B. IPO versus Public Companies
Ein Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process through which a private company first offers shares to the public. After an IPO, a company becomes a publicly traded company listed on a stock exchange, allowing investors to buy and sell its shares.
B.1 IPO (Initial Public Offering)
Ein Börsengang represents a company’s first public sale of shares, often to raise capital for expansion, research, or paying off debt. IPOs provide investors with the opportunity to invest in a company’s early growth phase, but they also come with higher risks due to uncertainty about the company’s future performance.
- IPO Process: Companies must go through a rigorous regulatory process before going public, including filing documents with regulators like the SEC (U.S.) or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK. Investment banks often underwrite the offering, setting the initial share price.
- Volatilität: Stocks of newly public companies tend to be more volatile as the market establishes a fair value for the shares. High-profile IPOs like Airbnb oder Uber saw significant price fluctuations in the early days of trading.
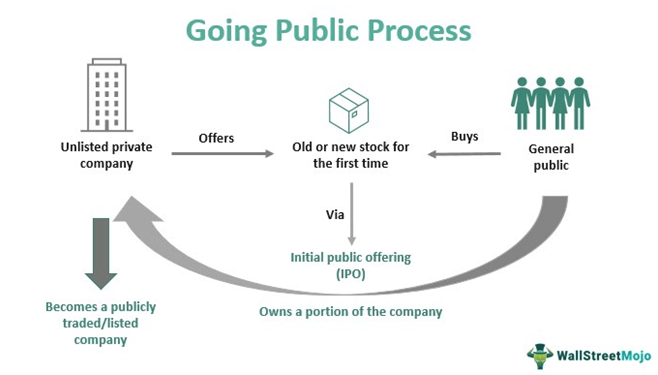
Figur: Going Public Process
Beschreibung:
This diagram outlines the going public process through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). It starts with an unlisted private company that offers new or existing shares to the general public for the first time. The public buys these shares via the IPO, leading to the company’s transition into a publicly traded entity. In this process, the public becomes shareholders, effectively owning a part of the company.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Ein unlisted private company initiates the IPO to raise funds or expand ownership.
- The public can purchase old or new shares offered in the IPO, making the company publicly traded.
- Through the IPO, the public gains ownership in the company, represented by shares.
Anwendung der Informationen:
Das verstehen going public process ist entscheidend für business owners, Investoren, Und financial analysts. For companies, an IPO is a method to raise capital Und increase visibility. For investors, IPOs offer an opportunity to invest early in a company’s growth. For learners, grasping this process helps in analyzing investment opportunities and understanding the implications of equity ownership in a public company.
B.2 Public Companies
Once a company has completed its IPO, it becomes a public company, which means its shares can be freely traded on a stock exchange by the general public. Public companies are subject to strict regulatory requirements, including regular financial reporting and governance standards.
- Reporting Requirements: Public companies must file quarterly and annual reports detailing their financial performance. This transparency provides investors with the information needed to make informed decisions.
- Stability: Public companies, especially well-established ones, tend to have less volatility compared to IPOs. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, Und Nestlé have been public for decades, offering stability and more predictable performance.
C. Checking the Ownership Structure of a Stock
Der ownership structure of a company reveals who holds significant shares in the company, such as institutional investors, company insiders, or retail investors. Understanding this structure is crucial because it can affect stock performance, voting power, and the company’s strategic direction.
C.1 Why is Ownership Structure Important?
- Institutionelle Anleger: If a large portion of a company’s shares is held by institutional investors like mutual funds, pension funds, or hedge funds, this can signal confidence in the company’s future performance. However, large institutional ownership can also lead to increased volatility if these investors decide to buy or sell significant amounts of stock at once.
- Insider Ownership: A high level of insider ownership (where company executives, founders, or board members hold a significant stake) can be seen as a positive indicator because it suggests that the leadership has a vested interest in the company’s success. However, it can also concentrate decision-making power within a small group, potentially limiting broader shareholder influence.
- Retail Investors: Companies with a high proportion of shares held by retail investors may experience greater volatility, as individual investors tend to react more emotionally to news and stock price movements than institutional investors.
- Beispiel: Companies like Tesla have significant retail investor ownership, contributing to its stock price volatility. Meanwhile, large institutional investors dominate the ownership of companies like Johnson & Johnson.
C.2 How to Check Ownership Structure
There are several ways to check the ownership structure of a publicly traded company:
- Annual Reports and Proxy Statements: Public companies are required to disclose significant ownership stakes in their annual reports and proxy statements. These documents list major shareholders and indicate the percentage of shares they own.
- Financial News Websites and Platforms: Many financial websites, such as Yahoo Finance, Morgen Stern, Und Bloomberg, provide details on the ownership breakdown of public companies. These platforms often categorize ownership into institutional, insider, and retail segments, making it easy to assess how the company’s shares are distributed.
- Stock Exchange Filings: In the U.S., companies must file Form 13F with the SEC, which discloses the holdings of institutional investors managing more than $100 million in assets. In Europe, similar filings are required by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
- Brokerage Platforms: Some brokerage platforms offer detailed insights into a company’s ownership structure, allowing investors to see real-time updates on institutional buying or selling activity.
Abschluss
die Unterschiede verstehen zwischen IPOs Und public companies is key to making informed investment decisions. While IPOs offer opportunities for early-stage growth, they come with higher risks and volatility. Public companies, on the other hand, tend to offer more stability but can still be influenced by their ownership structure, which impacts stock performance and corporate governance. By learning how to check the ownership breakdown of a stock, investors can gain deeper insights into who controls the company and how it might affect their investment.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- IPOs offer companies a path to raise capital through public investment but come with challenges, including regulatory compliance and market volatility. Investors in IPOs potentially gain from early investments but must be aware of the risks associated with new public listings.
- Public companies provide more stability and are subject to rigorous financial reporting and governance standards, making their stocks generally less volatile and more attractive to conservative investors.
- Der ownership structure of a company can significantly impact its governance, strategic direction, and stock volatility. High insider ownership might align interests with shareholders, while substantial institutional ownership could indicate robust confidence in the company’s prospects.
- Investors can check a company’s ownership structure through various resources, including regulatory filings, financial news platforms, and brokerage services, which provide comprehensive data on major shareholders and their influence on the company.
Schlusserklärung:
Understanding IPOs and the dynamics of public companies, along with the significance of ownership structures, is crucial for anyone involved in the stock market, whether they are investors, financial analysts, or corporate managers. This knowledge aids in making informed investment decisions and understanding market behaviors.