Global: Überblick über globale Aktiensektoren
Lernziele der Lektion:
- Einführung: This section introduces the global stock sectors, providing a comprehensive overview of their roles and impacts on the global economy. Understanding these sectors is essential for investors to diversify their portfolios effectively and manage risk.
- Learn about the technology sector, focusing on key companies like Apple and Microsoft, and the innovations driving this sector such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. This knowledge is critical for identifying growth opportunities in a highly volatile environment.
- Explore the healthcare sector, which is influenced by demographic trends and advancements in medical technology. Companies like Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson lead this sector, which is crucial for understanding the long-term demand driven by an aging global population.
- Examine the consumer discretionary sector, recognizing how economic cycles affect companies like Amazon and Tesla. This sector’s performance is closely tied to consumer confidence and economic health, making it a vital area for cyclical investment strategies.
- Analyze the energy sector’s transition, noting the shift from traditional oil and gas operations to more sustainable energy practices. This transition impacts companies like ExxonMobil and Chevron, as well as pioneers in renewable energy like NextEra Energy.
A. Overview of Global Stock Sectors
Stock sectors can be grouped into broad categories based on the types of companies they include. These sectors play different roles in the global economy, and understanding them helps investors diversify their portfolios and manage risks.
- Technologiesektor: The technology sector includes companies involved in software, hardware, and IT services. Major players include Apple, Microsoft, Und Alphabet. This sector is known for its high growth potential but also for its volatility. Investors look at trends like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, Und cybersecurity to identify growth opportunities.
- Key Drivers: Innovation, consumer demand, and corporate IT spending.
- Major Industries: Software development, hardware manufacturing, and semiconductors.
- Healthcare Sector: The healthcare sector is made up of companies involved in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and healthcare services. Global pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer Und Johnson & Johnson dominate this sector, which is largely driven by demographic trends such as aging populations and rising healthcare expenditures.
- Key Drivers: Population aging, healthcare reforms, and R&D in drug development.
- Major Industries: Pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and healthcare facilities.
- Nicht-Basiskonsumgütersektor: This sector includes companies that sell non-essential goods and services, such as automobiles, entertainment, and luxury items. The sector is cyclical, meaning it tends to perform well during periods of economic expansion and poorly during recessions. Major players include Tesla, Nike, Und Amazon.
- Key Drivers: Consumer confidence, disposable income, and economic growth.
- Major Industries: Retail, entertainment, and automobiles.
- Energy Sector: The global energy sector includes companies involved in the exploration, production, and distribution of oil, gas, and renewable energy. As the world shifts toward greener energy solutions, this sector is evolving to include more companies focused on sustainability. ExxonMobil, Chevron, Und BP are major players in the oil & gas industry, while companies like NextEra Energy are leading in renewables.
- Key Drivers: Oil prices, environmental regulations, and technological advancements in renewable energy.
- Major Industries: Oil & gas, renewable energy, and utilities.
- Finanzsektor: The financial sector includes banks, insurance companies, and investment firms that provide financial services. This sector is crucial for the global economy, facilitating trade, investment, and consumer spending. JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Und Berkshire Hathaway are key players.
- Key Drivers: Interest rates, economic growth, and regulatory changes.
- Major Industries: Banking, insurance, and asset management.
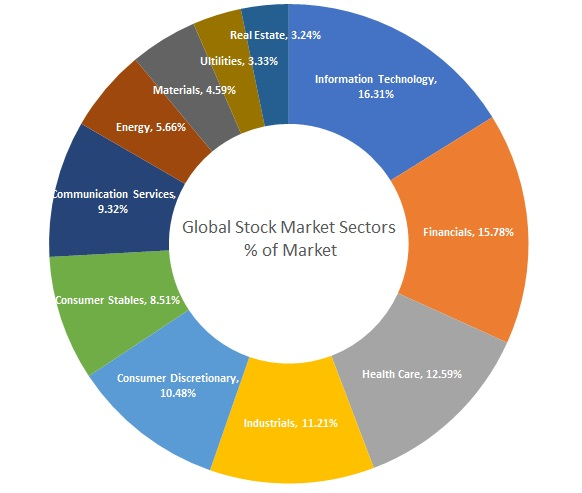
Figur: Global Stock Market Sectors % of Market
Beschreibung:
The figure shows the percentage share of different sectors in the global stock market. It is represented as a donut chart, where Information Technology holds the largest share at 16.31%, followed by Financials at 15.78%, and Gesundheitspflege at 12.59%. Other sectors include Industrials, Consumer Discretionary, Basiskonsumgüter, Communication Services, and smaller sectors like Dienstprogramme Und Immobilie. Each segment is clearly labeled with its corresponding percentage.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Information Technology dominates the global stock market, comprising 16.31% of the total market share.
- Financials Und Gesundheitspflege are also significant sectors, with 15.78% and 12.59% shares, respectively.
- Sectors like Dienstprogramme, Materials, Und Immobilie represent smaller portions of the market, indicating less influence in the global sector composition.
- The chart emphasizes the diverse allocation of sectors, highlighting potential areas for Diversifizierung.
Anwendung der Informationen:
This data helps investors understand the sectoral distribution within the global stock market, which is useful for making informed investment decisions. By knowing the largest sectors, investors can identify trends, focus on dominant sectors like Information Technology, or explore less represented areas for Diversifizierung. Understanding sector weights is essential for portfolio management and strategic asset allocation.
B. Stock Sectors: Drivers of Growth and Risk Factors
Understanding the key drivers and risk factors behind different global stock sectors helps investors make informed decisions when diversifying their portfolios:
- Key Drivers: Technological innovation, consumer trends, demographic shifts, and macroeconomic policies are the main drivers of growth across sectors. For example, the technology sector is driven by the rapid development of artificial intelligence, while the healthcare sector benefits from aging populations and increased healthcare spending.
- Risikofaktoren: Each sector faces unique risks. The energy sector, for instance, is highly sensitive to geopolitical tensions and fluctuations in oil prices, while the financial sector can be impacted by changes in interest rates and economic downturns. The technology sector, while fast-growing, faces the risk of rapid technological obsolescence and high competition.
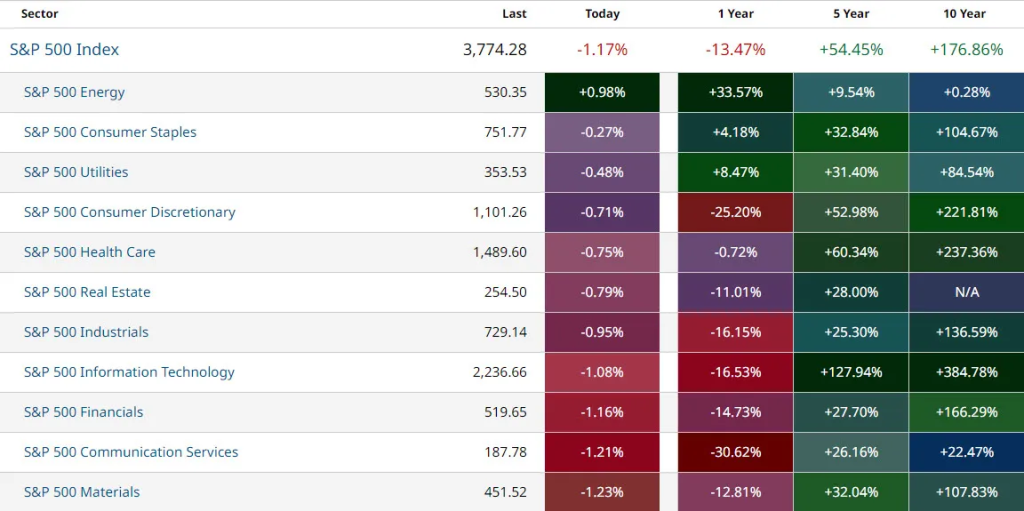
Figur: S&P 500 Sector Performance Overview
Beschreibung:
The figure presents the performance of various S&P 500 sectors over different timeframes: today, 1 year, 5 years, Und 10 years. Each sector is listed along with its latest value and corresponding percentage changes. The chart helps users compare how sectors like Energie, Basiskonsumgüter, Dienstprogramme, and others have performed recently and over longer periods, indicating trends in both short-term and long-term performance.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Energie shows the highest 1-year growth (+33.57%), while most other sectors experienced declines.
- Information Technology had a significant 5-year growth (+127.94%) and 10-year growth (+384.78%), highlighting its consistent long-term performance.
- Consumer Discretionary leads in the 10-year category with +221.81% growth, demonstrating strong growth potential over the decade.
- Real estate lacks a 10-year performance figure, possibly due to missing historical data.
- Sectors like Communication Services Und Materials show mixed performance, with notable 1-year declines but positive returns over longer periods.
Anwendung der Informationen:
This data is useful for investors analyzing sector trends and identifying potential investment opportunities within the S&P 500. By understanding which sectors have shown consistent growth, investors can make fundierte Entscheidungen about sector allocations in their portfolios. The figure can also help in tracking market cycles, identifying which sectors may be more resilient during downturns or periods of volatility.
Abschluss
Exploring stock sectors and industries provides investors with a roadmap for building a well-diversified portfolio. By understanding the key drivers of growth and the risks associated with each sector, investors can better position themselves for long-term success. Both local and global sectors play unique roles in shaping the economy, and knowing how to analyze them is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Der technology sector dominates the global stock market, with significant growth potential but also high volatility, reflecting rapid technological advancements and investor interest in innovation-driven companies.
- Der healthcare sector remains robust, driven by an aging population and increased healthcare spending, which supports ongoing demand for pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and healthcare services.
- Consumer discretionary spending is closely linked to economic cycles, with companies in this sector performing well during economic expansions due to increased consumer spending on non-essential goods and services.
- Der energy sector is experiencing a significant transformation, with a shift towards sustainability and renewable energy sources, reflecting changes in consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
- Der financial sector is essential for economic stability, influenced by factors like interest rates and economic growth, which dictate the operational dynamics of banks and financial institutions.
Schlusserklärung:
A thorough understanding of the different global stock sectors and their driving factors enables investors to make informed decisions, diversify their portfolios, and effectively manage risks associated with global economic fluctuations. This knowledge is crucial for strategic investment planning and achieving long-term financial goals.

