Lokal: Budgetierungsstandards und Best Practices
Lesson Learning Objectives:
Einführung:
This section focuses on budgeting standards and the best practices for managing expenses. It guides users on creating budgets, differentiating between fixed Und variable expenses, and prioritizing needs over wants to ensure financial stability. The section emphasizes strategies for maintaining a budget that aligns with both short-term and long-term financial goals.
- Understand the Basics of Budgeting: Learn how to create a budget that effectively manages income and tracks expenses. This helps users allocate funds properly, avoid overspending, and build a foundation for both short-term Und long-term financial stability.
- Differentiate Between Fixed and Variable Expenses: Gain a clear understanding of fixed expenses (consistent costs like rent or insurance) and variable expenses (fluctuating costs like groceries or entertainment). Knowing this distinction allows users to better prioritize essential expenses and reduce discretionary spending.
- Prioritize Needs Over Wants: Identify the difference between needs (e.g., housing, food) and wants (e.g., dining out, vacations). This helps users allocate their income more wisely, ensuring essential expenses are covered before considering discretionary spending.
- Adapt Budgeting Strategies as Needed: Understand how to use budgeting tools and develop the flexibility to adjust the budget in response to unexpected expenses, changes in income, or new financial goals. This ensures the budget remains realistic and achievable.
Einführung
Budgeting and expense management are crucial components of personal financial planning. By creating a detailed budget, individuals can effectively manage their income, allocate funds to essential and non-essential expenses, and set aside money for savings and investments. This chapter focuses on the importance of budgeting, differentiating between fixed and variable expenses, and developing strategies to maintain flexibility in managing both short-term and long-term financial goals. Understanding how to prioritize needs versus wants and use reliable budgeting tools is essential for achieving financial stability and long-term success.
Understanding the Importance of Budgeting
A budget is a financial plan that helps individuals manage their income, expenses, Und savings. Creating and maintaining a budget is essential for achieving both short-term and long-term financial goals. It provides a clear picture of how money is being spent and helps individuals identify areas where they can cut costs or increase savings.
Budgeting requires regular tracking of expenses to ensure that spending aligns with the plan. It’s also important to note that recent transactions may not immediately appear in financial statements, so keeping an up-to-date record of spending is critical for accurate budgeting.
Fixed vs. Variable Expenditure
A key element of budgeting is understanding the difference between fixed Und variable expenses:
- Fixed expenses: These are regular, consistent costs such as rent, mortgage payments, utilities, and insurance. They remain relatively constant each month.
- Variable expenses: These fluctuate depending on usage or needs, such as groceries, entertainment, or travel.
Recognizing the distinction between these two types of expenses allows individuals to prioritize essential spending—such as housing, food, and healthcare—over discretionary purchases like dining out or entertainment. Essential spending should always take precedence when allocating funds in a budget.
Prioritizing Needs vs. Wants
When budgeting, it’s crucial to identify needs Und wants. Needs are essential for survival or well-being, such as housing, utilities, and groceries, while wants are non-essential items or services, such as luxury goods, vacations, or dining out.
By distinguishing between these categories, individuals can allocate their income more effectively and ensure that essential expenses are covered before spending on discretionary items. This process helps avoid overspending and encourages long-term financial stability.

Figur: 50-30-20 Budgeting Rule
Beschreibung:
This figure represents the 50-30-20 budgeting rule, a widely recommended framework for managing personal finances. It suggests dividing income into three categories: 50% for needs (essential expenses like rent and utilities), 30% for wants (non-essential, nice-to-have purchases), and 20% for savings (money set aside for future goals or emergencies). This breakdown helps individuals ensure a balanced approach to spending and saving.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- 50% of income should be allocated to needs, covering essential living expenses.
- 30% of income can be used for wants, such as entertainment, dining out, or hobbies.
- 20% of income should be put into savings, helping build financial security for the future.
- Der 50-30-20 rule offers a simple yet effective approach to financial planning.
- It encourages individuals to live within their means while building long-term savings.
Application of Information:
Der 50-30-20 rule is a useful tool for individuals looking to manage their finances efficiently. It helps people balance their spending between essential needs and discretionary wants, while also prioritizing savings for future financial security. This framework is particularly useful for those beginning their financial journey or looking for a simple method to stay on top of their budget.
Using Reliable Budgeting Tools
Budgeting tools, such as mobile apps Und digital platforms, are invaluable for tracking income, expenses, and savings in real-time. These tools allow individuals to set spending limits, receive alerts for upcoming bills, and monitor progress toward financial goals. It is important to choose reliable budgeting tools developed by impartial providers, ensuring that they are trustworthy and secure.
Many tools also allow for automatic tracking of expenses by linking bank accounts, making it easier to maintain an accurate budget. For individuals who prefer manual methods, creating a simple spreadsheet can be just as effective.
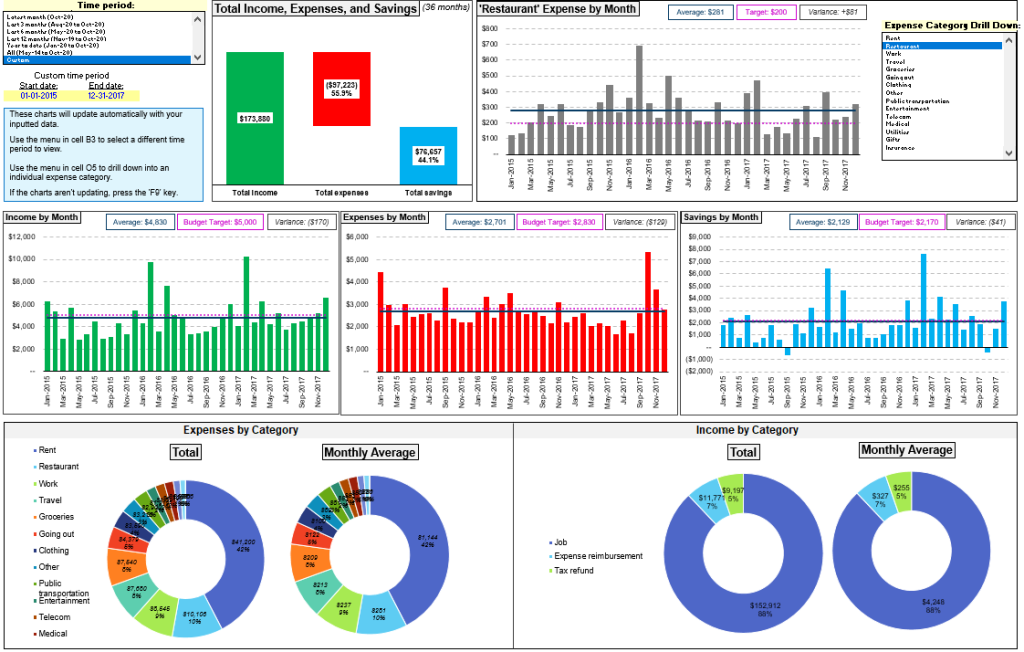
Figur: Total Income, Expenses, and Savings Dashboard
Beschreibung:
This figure displays a comprehensive budget dashboard showing income, expenses, and savings over a 36-month period. It includes various charts, such as bar graphs for monthly income, expenses, and savings, as well as pie charts showing expenses by category Und income by category. Users can see a breakdown of average expenses and income, budget targets, and variances, helping to track spending patterns and saving habits over time.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- The dashboard provides a clear comparison of total income, expenses, and savings, making it easier to analyze financial health.
- Monthly bar graphs help track trends in income, spending, and savings, revealing patterns over a 3-year period.
- Pie charts categorize income and expenses, showing where most money is earned and spent.
- Budget targets Und variances highlight areas where spending exceeded or stayed within budget, helping users identify financial habits.
- Users can filter time periods Und drill down into specific expense categories for a more detailed analysis.
Application of Information:
This dashboard is an effective tool for individuals looking to monitor and control their finances. It helps users identify trends, set budget goals, Und track spending behavior over time. For investors, understanding personal spending patterns can be essential for making informed financial decisions and allocating funds effectively.
Business and Household Budgeting
Budgeting tools, such as mobile apps Und digital platforms, are invaluable for tracking income, expenses, and savings in real-time. These tools allow individuals to set spending limits, receive alerts for upcoming bills, and monitor progress toward financial goals. It is important to choose reliable budgeting tools developed by impartial providers, ensuring that they are trustworthy and secure.
Many tools also allow for automatic tracking of expenses by linking bank accounts, making it easier to maintain an accurate budget. For individuals who prefer manual methods, creating a simple spreadsheet can be just as effective.
Medium- and Long-Term Budgeting
While budgeting for immediate expenses is essential, it’s equally important to consider medium- and long-term financial goals. This includes saving for retirement, purchasing a home, or building an emergency fund. When creating a budget, individuals should ensure that they allocate funds for both short-term needs and future objectives.
A well-rounded budget takes into account both immediate priorities and future financial goals, allowing individuals to prepare for emergencies Und build wealth over time.
Flexibility in Budgeting
One of the keys to successful budgeting is being flexible. Life circumstances and financial situations can change, such as unexpected expenses, changes in income, or new financial goals. When these changes occur, it’s important to be confident in adjusting the budget to accommodate the new circumstances. This may involve cutting back on non-essential spending or finding ways to increase income.
Being motivated to regularly review Und adjust the budget helps individuals stay on track and make informed financial decisions, even when facing unexpected challenges.

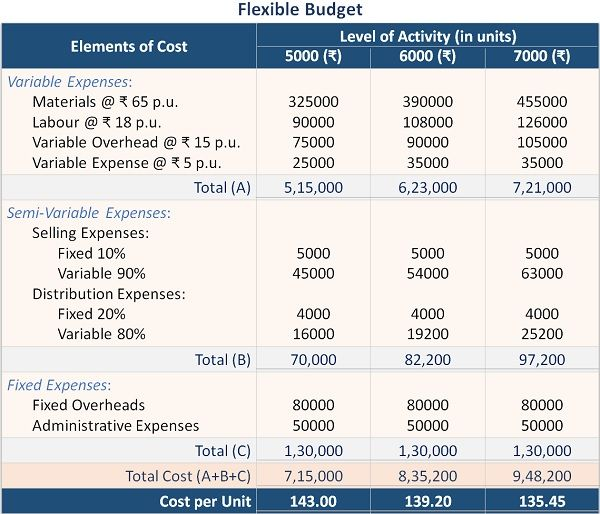
Figur: Flexible Budget
Beschreibung:
This figure shows a flexible budget outlining costs at different levels of production: 5,000, 6,000, and 7,000 units. It divides expenses into three main categories: Variable Expenses, Semi-Variable Expenses, Und Fixed Expenses, showing how costs change with production volume. Variable costs increase directly with the level of activity, while fixed costs remain constant, and semi-variable expenses have both fixed and variable components. The cost per unit decreases as production volume rises, indicating economies of scale.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Variable expenses increase proportionally with production, reflecting costs that vary per unit produced.
- Fixed expenses remain unchanged regardless of the production volume, contributing to consistent overheads.
- Semi-variable expenses show a mix of fixed and variable characteristics, adjusting partially with activity levels.
- Cost per unit decreases as production increases, highlighting economies of scale and more efficient cost distribution.
- The flexible budget helps in planning and decision-making, providing insights into how different production levels affect costs.
Application of Information:
Understanding a flexible budget is essential for businesses to adjust to changes in production volume without compromising cost control. It allows managers to predict how costs will behave at different levels of activity, making it easier to plan, allocate resources, Und identify areas for cost savings. For investors, this helps in assessing how well a company can manage its costs and maintain profitability under different operating conditions.
Long-Term Motivation in Budgeting
Successful budgeting goes beyond managing day-to-day expenses—it requires a long-term perspective. Individuals should be motivated to look beyond immediate needs and wants when creating a budget, and instead focus on achieving long-term financial well-being.
For example, consistently setting aside money for an emergency fund or a retirement account, even when there are tempting short-term spending opportunities, builds long-term financial security.
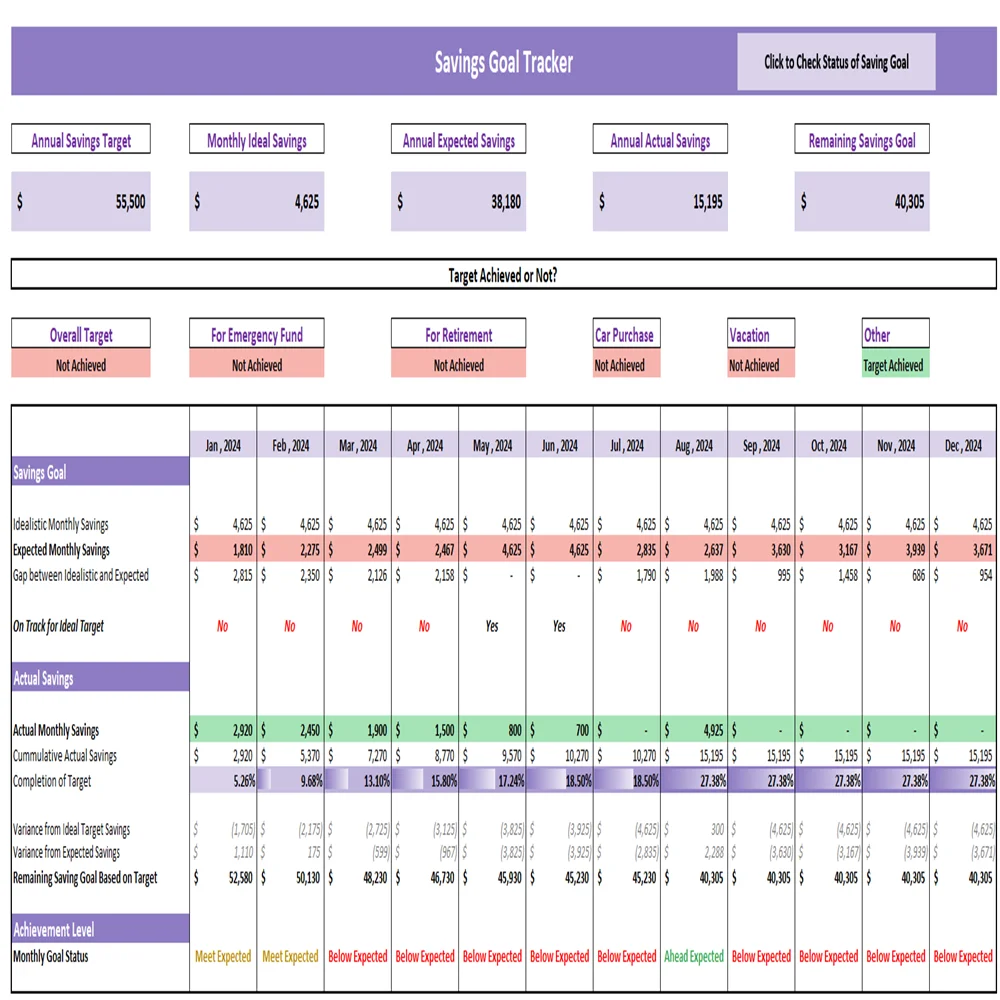
Figur: Savings Goal Tracker
Beschreibung:
This figure displays a Savings Goal Tracker that monitors monthly and annual savings progress. It includes key figures such as monthly ideal savings, annual expected savings, and actual annual savings. The table categorizes various savings targets like emergency funds, retirement, car purchases, and vacations, indicating whether the savings goal has been achieved or not each month. The tracker provides a comparison between expected Und actual savings, highlighting gaps and whether the performance is meeting or falling short of the goals.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- The tracker helps users monitor savings goals by setting monthly and annual targets.
- Achievement level is displayed clearly, showing if savings are meeting, ahead of, or below expectations.
- Different savings categories like retirement, emergency funds, and vacations are tracked separately to focus on specific financial objectives.
- The visual breakdown aids in understanding where gaps exist and which months performed better or worse.
- Consistently below expected savings may indicate a need to reassess budget strategies or saving practices.
Application of Information:
Using a savings tracker like this allows individuals to plan effectively by setting clear goals and monitoring progress. It helps users adjust their financial behaviors, make informed decisions about spending, and ensure they are on track for major financial milestones. For investors or learners, this shows the importance of regular savings planning and tracking to achieve long-term financial stability.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Budgeting helps manage spending effectively. A budget serves as a financial plan that tracks income, expenses, and savings. It allows users to allocate funds for essentials while setting aside money for savings and future goals.
- Fixed and variable expenses require different budgeting strategies. Fixed expenses like rent, insurance, and utilities remain constant, while variable expenses such as groceries or entertainment fluctuate. Differentiating between these helps users prioritize essential spending and make informed adjustments to discretionary costs.
- The 50-30-20 rule offers a balanced approach to budgeting. Allocate 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, Und 20% to savings. This method provides a simple yet effective way to manage spending, save money, and build financial security over time.
- Reliable budgeting tools support financial planning. Tools like apps, digital dashboards, or spreadsheets allow users to monitor income, expenses, and savings in real-time. These tools help users track financial habits, adjust spending, and achieve both short-term and long-term goals.
- Flexibility in budgeting is essential. Being open to adjusting the budget based on changes in income or unexpected expenses helps maintain financial stability. This adaptability ensures that users can continue working toward their financial goals despite challenges.
- Long-term motivation drives budgeting success. Consistently setting aside funds for emergency savings oder retirement accounts, even when tempted by short-term spending opportunities, builds financial security over time.
Schlusserklärung: A well-maintained budget is essential for achieving financial stability. By understanding the difference between fixed and variable expenses, using effective budgeting tools, and adapting to changes, users can build both short-term and long-term financial success. Applying these budgeting standards and best practices creates a pathway to a secure and prosperous financial future.


