Lokal: Finanzielle Risiken verstehen und Kredite verwalten
Lernziele der Lektion:
Einführung:
This section emphasizes the importance of understanding financial risks and credit management to maintain financial stability. By learning how to assess risks and manage credit effectively, you can make better financial decisions and achieve your goals.
- Recognize different types of financial risks: Understand common financial risks associated with credit, loans, and investments. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions about borrowing and saving, protecting your financial well-being.
- Assess personal risk tolerance: Learn to identify your own comfort level with risk, ranging from conservative to aggressive approaches. Knowing your risk tolerance is essential for choosing the right financial products and strategies that align with your goals.
- Evaluate credit products and costs: Discover how to analyze various credit options, such as fixed vs. variable interest rates, and consider factors like repayment periods and potential currency risks. This helps you select the best credit products and avoid costly mistakes.
- Adopt strategies to manage financial risks: Develop skills to mitigate risks, such as diversifying investments, saving for emergencies, and using insurance effectively. These strategies help maintain financial stability, even during uncertain times.
Einführung
Credit management is a critical aspect of financial health, encompassing the ability to responsibly use and repay borrowed money. Understanding the risks and benefits associated with credit can help individuals make informed decisions, whether they are using credit for everyday purchases, major life events, or investments. This chapter explores various financial risks, personal risk tolerance, and the importance of evaluating the costs and implications of credit products. It also delves into managing credit commitments, avoiding over-indebtedness, and confidently navigating the complex world of credit and loans to maintain financial stability.
Awareness of Risks in a Financial Context
In any financial decision, it is important to be aware of financial risks—the potential for negative financial outcomes due to unforeseen circumstances or choices. These risks are inherent in various financial products, such as loans, investments, and credit options, and can significantly affect personal financial well-being. For example, taking out a loan with a variable interest rate may expose the borrower to rising costs if interest rates increase unexpectedly.
Certain risks, however, can be hedged oder insured against, such as purchasing insurance to protect against health emergencies or job loss. Similarly, some financial products come with capital guarantees, ensuring that the initial investment or capital is protected, even if the market fluctuates.
Identifying and Managing External Risks
External issues, such as environmental disasters, economic downturns, or technological changes, can significantly impact personal finances. For example, a major recession might lead to job loss, while climate-related events could affect the value of real estate or investments.
Individuals should stay aware of low-probability, high-cost events—events that may be unlikely but could have devastating financial consequences. Preparing for such events by using appropriate financial tools, such as well-diversified investments oder Notfallersparnisse, helps reduce potential negative impacts.
Personal Risk Tolerance and Financial Decision-Making
Every person has a different level of Risikotoleranz—the degree of financial risk they are willing to take. Some may be comfortable with high-risk, high-reward financial products, while others may prefer safer options with lower returns. Identifying one’s Risikotoleranz is key to making informed financial decisions that align with personal goals and comfort levels.
Being confident in making independent risk assessments is crucial, especially in a world where marketing Und news media can create availability bias. Availability bias occurs when individuals place too much emphasis on recent or highly publicized events (e.g., a sudden drop in the stock market), which can lead to emotional and impulsive financial decisions.
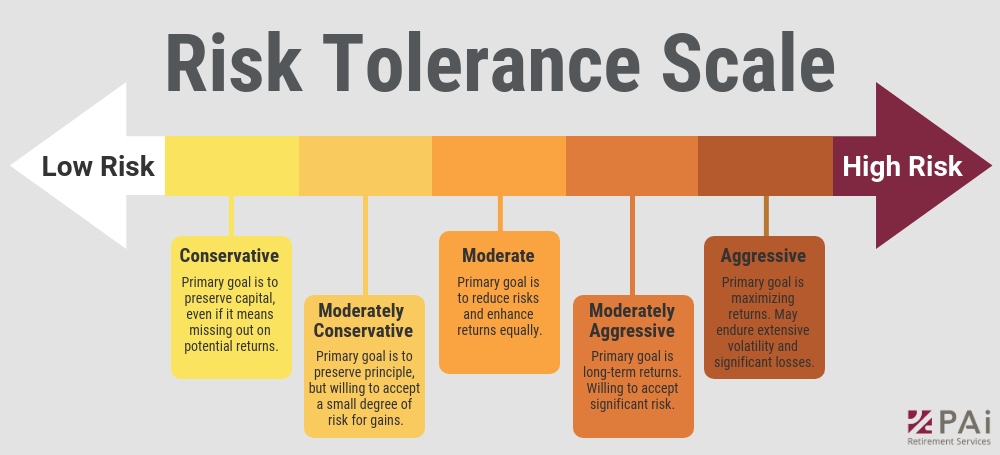
Figure: Risk Tolerance Scale
Beschreibung:
The image illustrates a risk tolerance scale, ranging from low to high risk. It categorizes different investment approaches based on risk preference, starting from “Conservative” (low risk) to “Aggressive” (high risk). Each category, such as “Moderate” or “Moderately Aggressive,” explains the primary goal of that risk level, whether it is to preserve capital, seek balanced returns, or aim for maximum gains, acknowledging the associated risk levels.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Conservative investors focus on capital preservation and are not willing to take risks that might lead to losses.
- Moderate risk investors aim to balance risk and reward, seeking reasonable returns while managing risks.
- Aggressive investors prioritize high returns and are prepared to accept significant volatility and potential losses.
- The scale helps understand risk preferences and align them with investment strategies.
Anwendung der Informationen:
Understanding one’s Risikotoleranz is crucial in selecting suitable investments. Investors can use this scale to identify which category they fall into, helping them make informed decisions about their portfolio allocation. Knowing your risk tolerance helps in choosing investments that match your financial goals and comfort with risk.
Evaluating Risks of Financial Products
It is critical to be aware of the risks associated with different financial products, including the type of interest rates, currency risks, and commitment periods. For example:
- Variable interest rates: Loans with variable rates may become more expensive if interest rates rise.
- Fixed interest rates: Locking in a fixed rate can be costly if interest rates fall, as the borrower may miss out on potential savings.
- Foreign currency products: Taking out loans in foreign currencies can expose individuals to currency exchange risks, especially if exchange rates fluctuate.
When making major purchases or significant financial commitments, it’s essential to assess the long-term risks, including the potential for Arbeitsplatzverlust, increased financial responsibilities, or economic changes that could affect income or expenses.
Risks of Income Loss and Life Changes
Personal decisions and life choices often carry financial risks. For example, the decision to buy a house or start a family can have long-term financial implications. It’s important to consider the possibility of losing household income due to events such as ill-health, disability, or the death of a family member. Planning for these risks by acquiring the appropriate insurance or building an Notfallfonds can protect individuals from severe financial distress.
Figure: Strategies for Mitigating Financial Risks
Beschreibung:
The image outlines ten key strategies for managing and reducing financial risks. It includes measures such as diversification, insurance, and liquidity management. Each strategy plays a distinct role, from assessing and measuring risk to ensuring compliance and conducting due diligence. These strategies help individuals and businesses prepare for and mitigate potential financial uncertainties.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Diversifizierung spreads risk by investing in different assets.
- Versicherung provides protection against specific financial losses.
- Liquidity management ensures that there is sufficient cash flow to meet short-term obligations.
- Risk assessment and measurement help in identifying potential threats and quantifying risks.
- Notfallfonds serve as a financial buffer during unexpected situations.
Anwendung der Informationen:
Understanding and implementing these risk mitigation strategies can help investors and businesses protect their assets and finances. By adopting a combination of these practices, users can create a more robust financial plan that prepares them for uncertainties, reducing the impact of potential losses.
Digital Financial Products and Emerging Technologies
As the financial world increasingly moves online, digital financial products and services—such as mobile banking, peer-to-peer lending, Und cryptocurrency investments—come with unique risks. These digital products, especially those based on emerging technologies wie blockchain, can be more volatile and less regulated than traditional financial products.
For instance, investing in Krypto-Assets or participating in an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) is often riskier because these products lack the same regulatory oversight as established financial markets. Individuals must be aware of the heightened risks when dealing with these digital products and ensure they fully understand the potential financial consequences before committing funds.
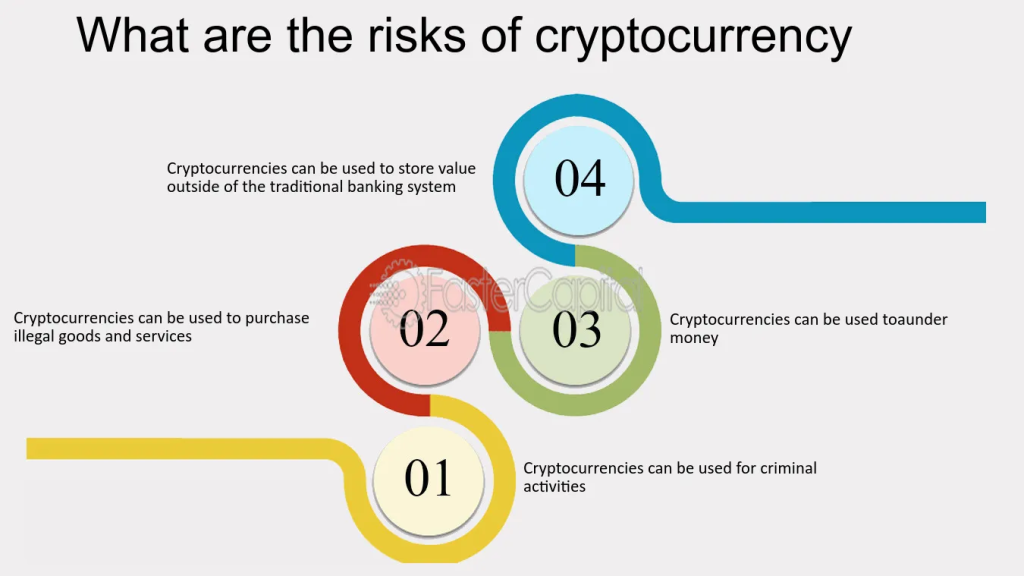
Figur: What are the risks of cryptocurrency
Beschreibung:
The image highlights four major risks associated with using cryptocurrencies. It mentions that cryptocurrencies can be used to purchase illegal goods and services, engage in criminal activities, and launder money. Additionally, cryptocurrencies can store value outside the traditional banking system, which might raise regulatory concerns. Each of these points emphasizes potential misuse and risks in the context of digital currency usage.
dq
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Cryptocurrencies can facilitate illegal transactions, making it easier to purchase illicit goods.
- Digital currencies can be exploited for money laundering, bypassing traditional banking checks.
- Storing value outside the banking system could pose regulatory and security risks.
- Criminal activities may increase due to the anonymity and decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies.
Anwendung der Informationen:
diese verstehen risks associated with cryptocurrencies is essential for investors, regulators, and users. Awareness can lead to better risk management strategies and more informed decisions about investing or using digital currencies. Investors should be cautious and consider the potential regulatory implications before engaging in cryptocurrency transactions.
Confidence in Managing Risks
Finally, individuals should be motivated to mitigate risks whenever necessary. Whether it’s purchasing insurance, diversifying investments, or saving for emergencies, actively managing financial risks helps protect personal wealth and reduce stress. Confidence in making well-informed decisions, especially when risks become apparent, ensures that individuals can navigate financial challenges effectively.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Financial risks affect decisions: Financial risks, such as fluctuating interest rates or unexpected life changes, can impact your overall financial health. Being aware of these risks helps you prepare better and make smarter choices.
- Risk tolerance guides your strategy: Your comfort level with financial risk should guide your investment and credit decisions. For example, conservative investors focus on safety, while aggressive investors accept more volatility for potentially higher returns.
- Credit products have different costs: Credit options come with various costs, from interest rates to fees. Fixed rates offer predictability, while variable rates may fluctuate, impacting your total costs. Evaluating these options helps you choose wisely.
- Prepare for external events: Unexpected events like economic downturns or job loss can affect your finances. Strategies such as having an Notfallfonds or insurance can help protect against these risks and ensure stability.
- Be cautious with digital financial products: Emerging digital financial products, such as cryptocurrencies, come with unique risks, including high volatility and limited regulation. Understanding these risks is crucial before investing or using these products.
Schlusserklärung: Understanding financial risks and managing credit effectively are essential skills for maintaining financial stability. By knowing your risk tolerance, evaluating credit costs, and preparing for unexpected events, you can make better decisions and protect your financial future.