Erkundung von Aktiensektoren und Industrien
Wichtigste Lernziele:
Einführung: This section delves into the importance of understanding stock sectors and industries in achieving portfolio diversification. By exploring the unique characteristics and business cycle performance of various stock sectors, you will be better equipped to tailor your investments according to market conditions.
- Understand the Significance of Stock Sectors and Industries: Grasp the role they play in portfolio diversification.
- Learn the Characteristics and Business Cycle Performance: Delve into eight major stock sectors and their respective industries to understand their behavior across different phases of the business cycle.
- Apprehend Sectoral Response to Business Cycle Phases: Understand how sectors respond differently to business cycle phases, enabling better prediction of potential performance shifts.
Einführung:
Understanding stock sectors and industries is crucial for investors looking to build a well-diversified portfolio. Each sector and industry has its unique characteristics and performance patterns, which can help investors make better-informed decisions. In this chapter, we’ll explore eight stock sectors and eight industries, their characteristics, and how they perform during different phases of the business cycle.

Figure title: Stock Market Sectors
Quelle: MarketBeat
Beschreibung:
The image lists the following sectors in the stock market:
- Information Technology
- Healthcare
- Financials
- Consumer Discretionary
- Industrials
- Communication Services
- Basiskonsumgüter
- Energie
- Dienstprogramme
- Materials
- Immobilie
These sectors represent the broad range of industries within the stock market, each with its unique characteristics and performance metrics.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- The stock market is organized into sectors to categorize companies based on their primary business activities.
- Understanding these sectors can help investors diversify their portfolios and target specific areas of the economy.
Anwendung: Investors can use this categorization to diversify their portfolios by investing in different sectors. This diversification can help mitigate risks and achieve a more balanced investment strategy. Additionally, understanding the different sectors can help investors identify trends and opportunities within specific areas of the market.
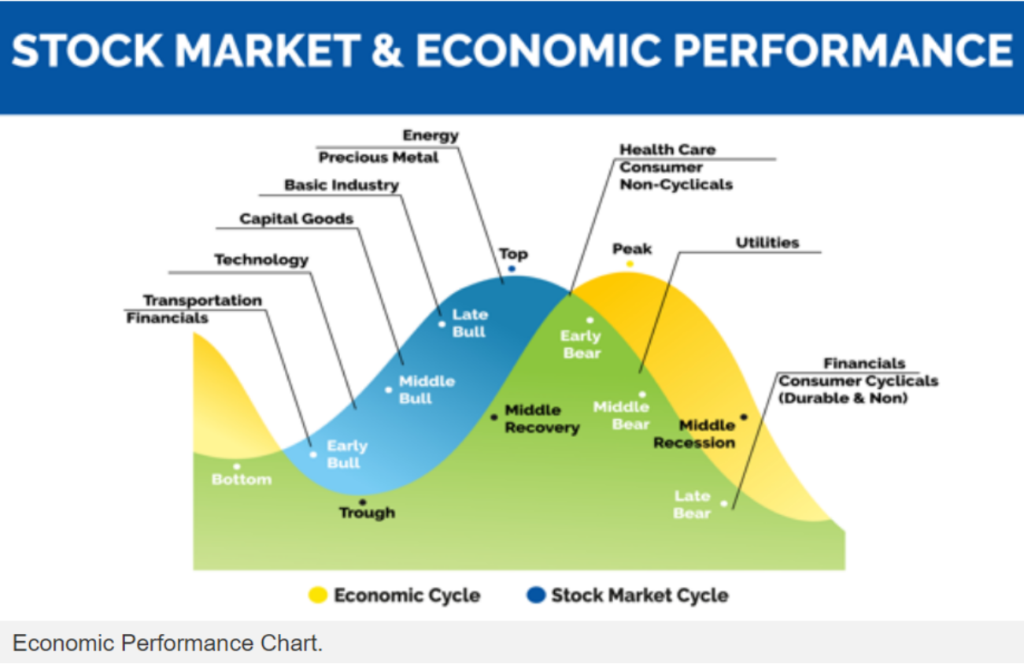
Abbildungstitel: Stock Market & Economic Performance
Source: Investing.com
Beschreibung:
The image illustrates the correlation between the economic cycle and the stock market cycle. Although the exact details are not clear from the OCR result, it’s common knowledge that the stock market and economic cycles are interconnected. The stock market often reacts to changes in the economy, and vice versa. The cycles typically have phases like expansion, peak, contraction, and trough, which reflect the state of the economy and the stock market.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Understanding the relationship between the economic cycle and the stock market cycle can help investors make informed decisions.
- Both cycles have phases that can impact investment strategies and financial planning.
Anwendung:
Investors can use the knowledge of these cycles to better understand market trends and potentially make more informed investment decisions. By recognizing the phase of the economic and stock market cycles, investors may be able to better predict market movements and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
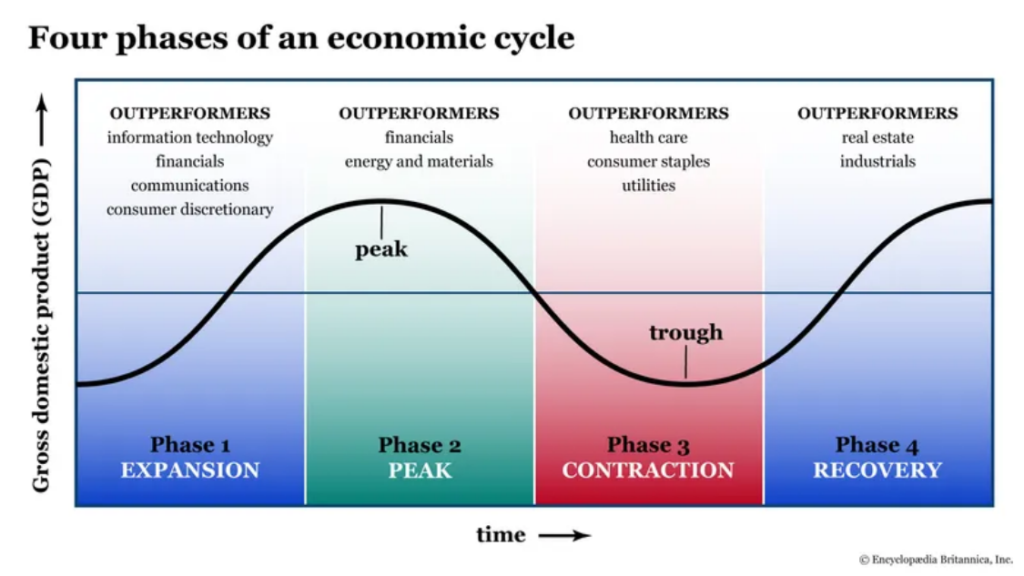
Abbildungstitel: Sector Performance Across Business Cycle Phases
Quelle: Britannica
Beschreibung: This illustration portrays the different phases of the business cycle and the particular sectors that thrive in each phase. By understanding which sectors excel at different times, users gain a clearer perspective of potential investment avenues.
Die zentralen Thesen:
- Expansionsphase: Dominated by sectors like information technology, financials, communications, consumer discretionary, and growth stocks.
- Peak Phase: Financials, energy, and materials tend to have the upper hand.
- Contraction Phase: Healthcare, consumer staples, and utilities often stand out as strong contenders.
- Recovery Phase: The limelight is on real estate and industrials.
Anwendung: Leveraging this information, investors can strategically allocate their resources in sectors likely to prosper in the current business cycle phase. But remember, while concentration in promising sectors can be beneficial, maintaining overall diversification safeguards against the unpredictability of markets.
Discussion of different stock market sectors:
Understanding the variety of sectors within the stock market is crucial for investors to diversify their portfolios effectively and manage risk. Each sector has unique characteristics and is impacted by different economic variables. In this chapter, we will delve into various stock market sectors, including the newly added Real Estate and Materials sectors, shedding light on their industry focus, characteristics, business cycle performance, and some sector-specific considerations for investors.
Technologiesektor
- Industry Focus: Software & Services
- Characteristics: High growth potential, significant R&D expenses, relatively low dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Generally strong during economic expansions but weaker during contractions.
- Additional Information: Innovations and technological advancements often drive growth in this sector, but susceptibility to obsolescence and fierce competition are risks to consider.
Gesundheitssektor
- Industry Focus: Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology
- Characteristics: High growth, substantial R&D expenditures, stable cash flows, moderate dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Defensive sector that remains relatively stable throughout all phases of the business cycle.
- Additional Information: Regulatory environments and patent protections are crucial factors impacting companies within this sector.
Finanzsektor
- Industry Focus: Banking & Insurance
- Characteristics: Cyclical nature, interest-rate sensitive, high assets, moderate to high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Performs well during economic expansions but faces challenges during contractions.
- Additional Information: Regulatory changes and interest rate environments significantly affect this sector’s performance.
Nicht-Basiskonsumgütersektor
- Industry Focus: Retail & Automobiles
- Characteristics: Cyclical, sensitive to consumer spending, moderate to high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Flourishes during expansions when consumer confidence and spending are high, weaker during contractions.
- Additional Information: E-commerce growth and changing consumer preferences are reshaping traditional retail dynamics within this sector.
Consumer Staples Sector
- Industry Focus: Food & Beverages
- Characteristics: Defensive, stable cash flows, high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Maintains stability across different phases of the business cycle due to the essential nature of products.
- Additional Information: This sector is often considered a safe haven during economic downturns.
Utilities Sector
- Industry Focus: Electricity & Gas
- Characteristics: Defensive, capital intensive, stable cash flows, high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Generally stable irrespective of business cycle phases.
- Additional Information: Regulatory environments and energy transition trends are notable factors for this sector.
Industrial Sector
- Industry Focus: Aerospace & Defense
- Characteristics: Cyclical, capital-intensive, moderate dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Strong during expansions but suffers during contractions.
- Additional Information: Global trade policies and geopolitical tensions can significantly influence this sector.
Energy Sector
- Industry Focus: Oil & Gas
- Characteristics: Cyclical, capital-intensive, commodity price-sensitive, high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Prospers during expansions, faces hardships during contractions.
- Additional Information: The transition towards renewable energy poses both challenges and opportunities for traditional energy firms.
Real Estate Sector
- Industry Focus: Residential and Commercial Real Estate, REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts)
- Characteristics: Capital intensive, steady cash flows from rental income, moderate to high dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Sensitive to interest rates and economic growth. Generally stable but can suffer during economic downturns.
- Additional Information: Location, property management, and interest rates are key considerations for investments in this sector.
Materials Sector
- Industry Focus: Metals, Mining, and Chemicals
- Characteristics: Cyclical, capital intensive, commodity price-sensitive, moderate dividend yields.
- Business Cycle Performance: Performs well during economic expansions but faces challenges during downturns due to decreased demand for materials
- Additional Information: Global supply chain dynamics and commodity prices significantly impact this sector.
Abschluss:
Diving into the landscape of stock market sectors unveils a rich tapestry of opportunities and risks. Each sector, embodying a distinct segment of the economy, exhibits unique characteristics influenced by a multitude of factors. From the innovative realms of the Technology sector to the foundational aspects of Utilities and Real Estate, investors traverse a diverse spectrum of investment avenues.
The cyclical nature of some sectors juxtaposed against the defensive posture of others presents a narrative of balance. Understanding this balance is essential in the quest for portfolio diversification and risk management. The economic tides ebb and flow, impacting each sector differently, and offering varying levels of resilience and growth potential.
Moreover, sector-specific considerations, like regulatory environments, global supply chain dynamics, and consumer preferences, among others, add layers of complexity and opportunity for discerning investors.
The Real Estate sector’s sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations and the Material sector’s tie to commodity prices are examples of how macroeconomic and sector-specific factors intertwine, influencing sector performance.
By delving into the characteristics and performance metrics of each sector, investors equip themselves with a knowledge arsenal. This knowledge, when applied judiciously, can pave the way for more informed investment decisions, potentially leading to better financial outcomes.
As the economic landscape evolves, so does the dynamic within and across sectors. Continuous learning and adapting to these shifts can position investors to navigate the vicissitudes of the market, making the journey through the investment world an enlightening and rewarding endeavor.
Die zentralen Thesen:
Schlusserklärung: The knowledge of stock sectors and their behavior during different phases of the business cycle is instrumental in crafting a well-diversified portfolio. This understanding is foundational in making informed investment decisions and minimizing risks associated with market fluctuations.
-
- Stock sectors and industries are crucial for understanding the stock market landscape and achieving portfolio diversification.
- Each sector has distinct characteristics and patterns during the business cycle, which significantly influence its performance.
- Recognizing the differences between sectors like the Technologiesektor with high growth and the Utilities Sector with stable cash flows can greatly impact investment decisions.
- Knowledge of sectors’ behavior across the business cycle aids in better portfolio management Und risk diversification.
