Global: Investment Fees & Expenses
Lesson Learning Objectives:
- Understand the Impact of Investment Fees and Expenses: Learn how transaction fees Und management expenses (for active vs. passive ETFs) can affect the overall returns of your investments. Understand the cost implications of both stock investing and ETF management strategies.
- Explore Buy & Hold vs. Active Trading: Compare the buy-and-hold strategy for long-term growth versus the active trading strategy for short-term gains. Understand the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches, including transaction costs, tax implications, Und emotional decision-making.
- Learn About Dollar-Cost Averaging: Understand the dollar-cost averaging (DCA) strategy, which helps mitigate the impact of market volatility. This approach is useful for both passive and active investors seeking to enter the market gradually over time.
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis: Understand the difference between fundamental analysis (evaluating company financials) and technical analysis (using price patterns and market trends) to make investment decisions. Learn how both methods can complement each other in crafting an investment strategy.
A. Investment Fees & Expenses
One of the most significant factors to consider when comparing stocks and ETFs (both active and passive) is the cost.
- Stocks: When investing in individual stocks, you typically pay transaction fees for buying and selling. However, once you own the stock, there are no ongoing management fees, unless you’re using a managed account.
- Active ETFs: Active ETFs are managed by professionals who make investment decisions on behalf of investors, attempting to outperform the market. These funds typically have higher management fees, called expense ratios, due to the active management and frequent trading involved.
- Passive ETFs: Passive ETFs track a specific index, such as the S&P 500 oder FTSE 100, and are not actively managed. As a result, they have lower expense ratios compared to active ETFs, making them a cost-effective option for investors seeking broad market exposure.
B. Buy & Hold vs. Active Trading
Investment strategies vary significantly between buy-and-hold investors Und active traders, especially when comparing stocks with active and passive ETFs.
- Buy & Hold (Passive Strategy): This strategy involves purchasing investments with the intention of holding them for the long term, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. This approach is popular with passive ETF investors and those who purchase individual stocks of stable companies. The goal is to benefit from long-term growth and compounding returns.
- Advantages: Lower transaction costs, fewer taxes on capital gains, and reduced emotional decision-making.
- Disadvantages: Potential for missed opportunities during short-term market trends.
- Advantages: Lower transaction costs, fewer taxes on capital gains, and reduced emotional decision-making.
- Active Trading (Active Strategy): Active trading involves frequent buying and selling of securities to capitalize on short-term market movements. Active ETF managers and individual traders use this strategy to outperform market indices, but it requires constant monitoring and a higher level of market expertise.
- Advantages: Potential for higher returns if market timing is successful.
- Disadvantages: Higher transaction costs, greater tax liabilities, and increased risk from short-term market volatility.
- Advantages: Potential for higher returns if market timing is successful.
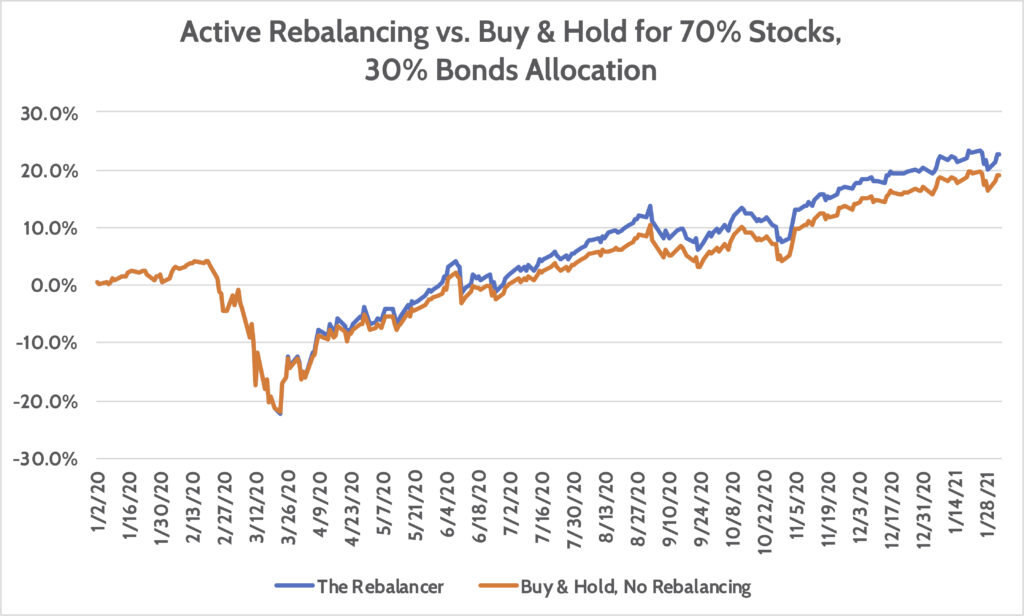
Figur: Active Rebalancing vs. Buy & Hold for 70% Stocks, 30% Bonds Allocation
Beschreibung:
This line chart compares the performance of active rebalancing versus a buy-and-hold strategy with a 70% stocks and 30% bonds allocation over a period spanning from January 2, 2020, to January 28, 2021. The blue line represents “The Rebalancer,” which indicates active rebalancing of the portfolio, while the orange line represents “Buy & Hold, No Rebalancing,” showing a static portfolio strategy. Throughout the observed period, the rebalanced portfolio shows a slight edge in performance, especially during volatile phases such as the March 2020 market downturn. Over time, the active rebalancer demonstrates a consistently higher return compared to the buy-and-hold approach, particularly noticeable from mid-2020 onwards.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Active rebalancing tends to yield higher returns compared to the buy-and-hold strategy, especially during volatile market conditions.
- Der March 2020 market downturn demonstrates the value of active rebalancing, as the strategy recovers more effectively.
- By the end of the period, the actively rebalanced portfolio maintains a higher total return than the buy-and-hold strategy.
- The gap between the two strategies increases over time, highlighting the potential benefits of rebalancing in a diversified portfolio.
Application of Information:
This comparison illustrates the potential advantages of implementing an active rebalancing strategy for investors aiming to maintain their desired asset allocation and enhance returns. By regularly adjusting the portfolio, investors can mitigate risks during market volatility and potentially improve their overall returns. Understanding this concept can help investors decide whether to adopt a rebalancing approach in their long-term investment strategies, balancing Risiko Und zurückkehren more effectively.
C. Dollar-Cost Averaging Strategy
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is a popular investment strategy that involves investing a fixed amount of money into a particular stock, ETF, or other asset at regular intervals, regardless of its price. This strategy works well for both stocks and ETFs (active and passive) and helps investors mitigate the risks of market volatility.
- How it works: By investing the same amount regularly, investors buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, effectively lowering the average cost per share over time.
- Anwendung: DCA is particularly effective in passive ETFs, where investors are looking for long-term, steady growth. It can also be applied to stocks Und active ETFs but may yield less predictable results due to market fluctuations and the higher volatility associated with active management.
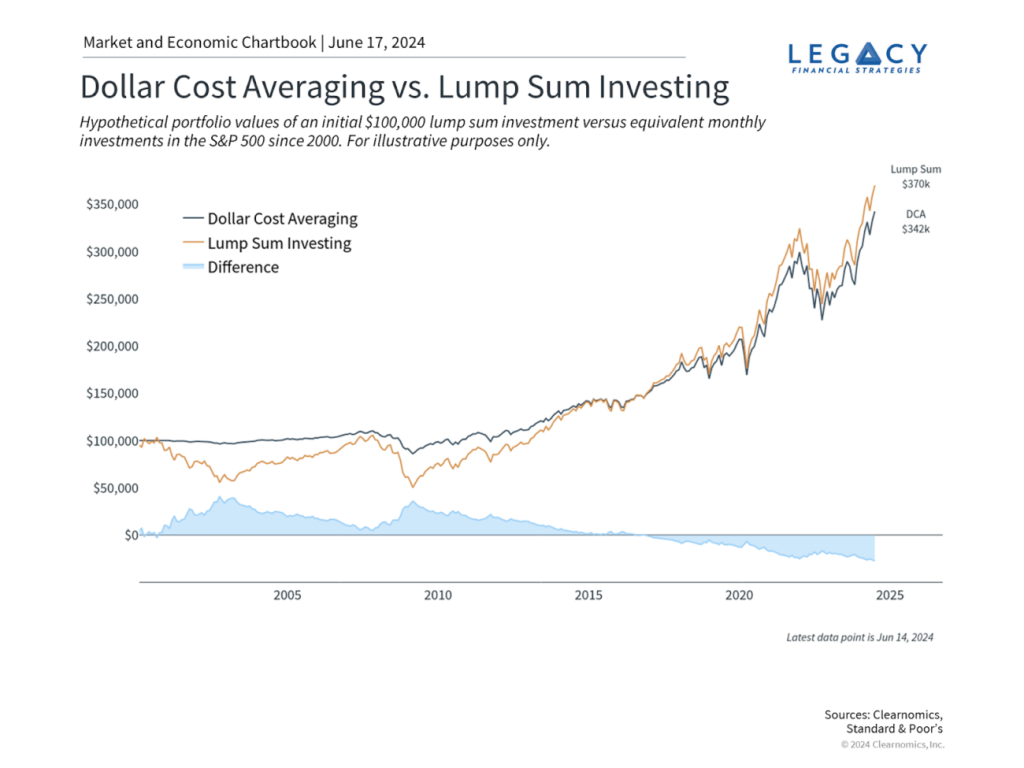
Figur: Dollar Cost Averaging vs. Lump Sum Investing
Beschreibung:
This line chart compares the outcomes of Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA) Und Lump Sum Investing using hypothetical portfolio values based on an initial $100,000 investment in the S&P 500 from 2000 to 2024. The orange line shows the performance of a lump sum investment, while the black line represents dollar cost averaging, where equivalent monthly investments are made. The blue shaded area illustrates the difference in value between the two strategies. By 2024, the lump sum investment reaches around $370k, while DCA ends at approximately $342k.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Lump sum investing generally achieves higher returns over time compared to Dollar Cost Averaging.
- The gap between the two strategies widens over the long term, with lump sum benefiting more during sustained bull markets.
- Both strategies are impacted by market downturns, but DCA shows less volatility during bear markets.
- Der difference in returns between the two strategies is most evident during prolonged bull markets, where lump sum investing capitalizes more on early market gains.
Application of Information:
Investors can use this comparison to understand the potential benefits and risks of both Dollar Cost Averaging Und Lump Sum Investing. While lump sum investing might yield higher returns over time, it also involves greater initial risk. DCA is useful for those looking to minimize risk and gradually enter the market, making it a good choice during periods of uncertainty. Understanding these strategies helps investors align their investment approach with their risk tolerance Und market outlook.
D. Fundamental Analysis: Valuation of Stocks
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial health to determine whether its stock is undervalued or overvalued. This type of analysis is primarily used for stock investing, but it can also inform decisions regarding active ETFs, especially those focused on individual sectors or industries.
Key components of fundamental analysis:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Compares a company’s current share price to its earnings per share. A low P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: Measures a company’s market value relative to its book value. A lower ratio can signal a potential buying opportunity.
- Dividend Yield: Indicates the income generated by a stock relative to its price. Higher yields are attractive to income-focused investors.
Fundamental analysis allows stock investors to assess whether a company is a good long-term investment based on its financial metrics, industry position, and growth potential.
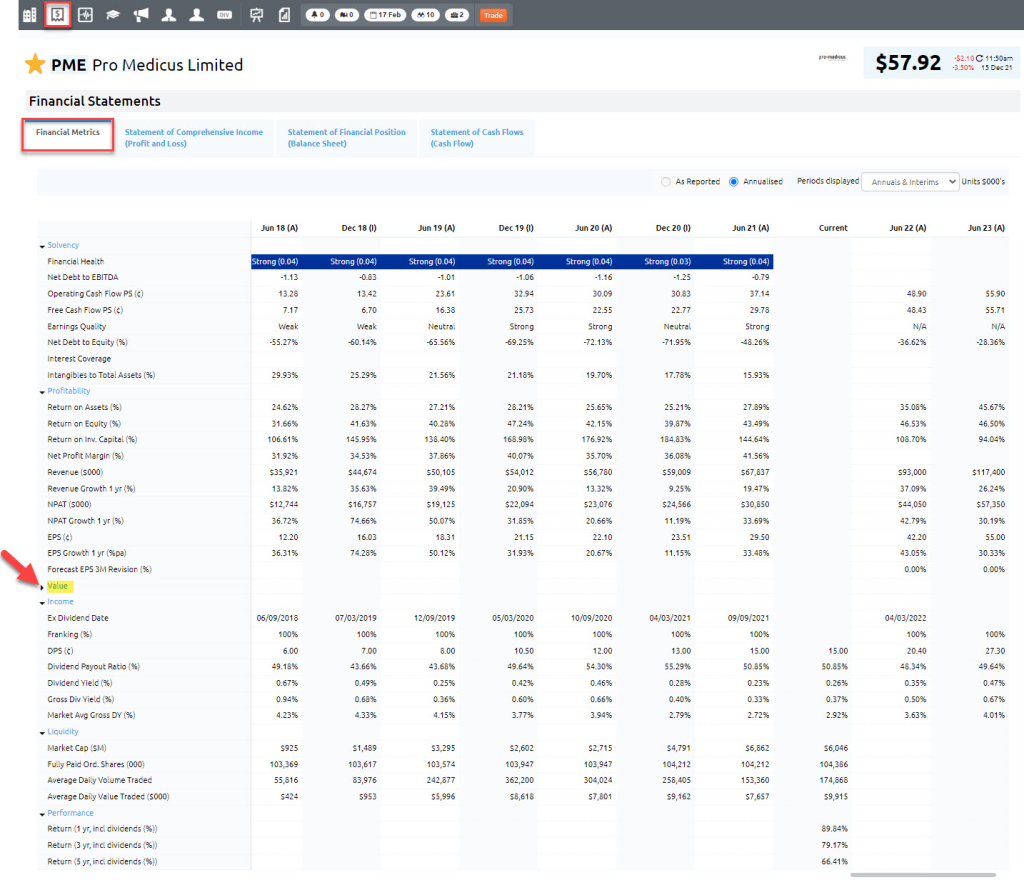
Figur: PME Pro Medicus Limited – Financial Metrics Overview
Beschreibung:
The image displays the financial metrics table for PME Pro Medicus Limited, highlighting various performance indicators over several reporting periods, including annual and semi-annual data. Metrics include key financial ratios, profitability, returns, and earnings metrics. The table is segmented into sections like financial health, profitability, return on assets/equity, EPS growth, dividend payout ratio, and more, helping users assess the company’s financial performance over time. A red arrow points to the revenue section, emphasizing its importance in evaluating business growth.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- The table provides a comprehensive view of PME’s financial performance across multiple years, facilitating trend analysis.
- Metrics such as ROA, ROE, EPS growth, Und dividends offer insights into profitability, returns, Und shareholder value.
- Consistent monitoring of financial metrics can help users understand financial stability and predict potential growth or risks.
- The highlighted revenue metric is crucial for analyzing sales trends and business expansion.
Application of Information:
Investors can use this financial metrics table to perform fundamental analysis on PME Pro Medicus Limited. By examining historical trends, users can assess the company’s financial health, profitability, Und earnings growth over time. This analysis helps in making informed investment decisions, understanding dividend sustainability, and projecting future earnings potential.
E. Technical Analysis Introduction
Technical analysis focuses on studying historical price movements and market trends to make investment decisions. This method is often used by active traders Und active ETF managers who aim to take advantage of short-term price movements. Technical analysis involves examining charts, patterns, Und indicators to predict future price movements.
Key tools in technical analysis:
- Gleitende Durchschnitte: The average price of a stock or ETF over a specific period, used to identify trends and potential entry or exit points.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements to determine whether an asset is overbought or oversold.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Price levels where a stock or ETF tends to encounter buying (support) or selling (resistance), which can signal potential turning points in the market.
While technical analysis is more commonly used in active trading, it can also complement fundamental analysis for long-term investors looking to time their entry and exit points.
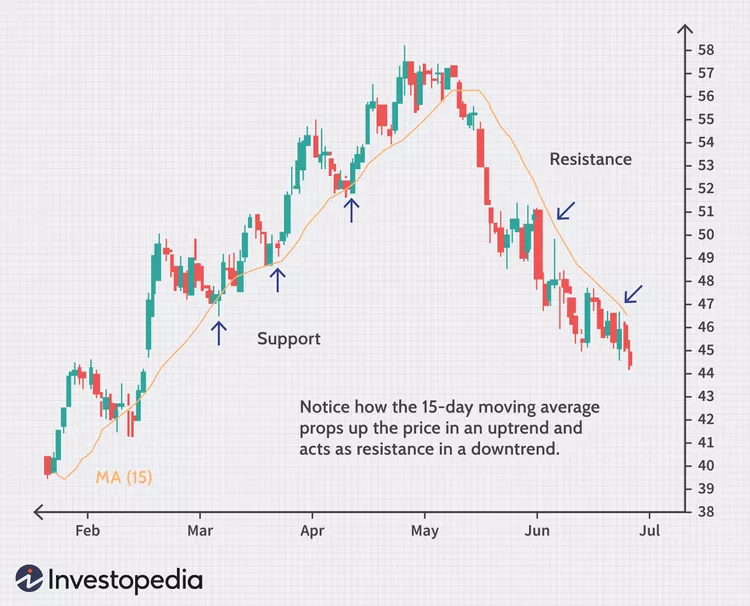
Figur: Support and Resistance with 15-Day Moving Average
Beschreibung:
This chart illustrates how a 15-day moving average acts as both Unterstützung Und resistance in a stock’s price movement. In an uptrend, the moving average serves as a support level, meaning the stock price tends to bounce off the line as it rises. In a downtrend, the same moving average becomes a resistance level, preventing the stock price from moving higher. Arrows on the chart indicate where the moving average either supports or resists the price action.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Der 15-day moving average is a popular tool to identify Unterstützung Und resistance levels.
- It acts as a support level in an uptrend, helping prices maintain their upward momentum.
- Conversely, it becomes a resistance level during a downtrend, hindering price increases.
- Using moving averages can help traders identify potential entry Und exit points in trades.
Application of Information:
Traders can use the 15-day moving average as a tool for trend analysis and identifying support and resistance levels. It helps in making buying decisions when the price is near the support in an uptrend and selling decisions when the price meets resistance in a downtrend. Understanding these levels can assist investors in managing their Risiko and planning trade strategies.
Abschluss
When comparing stocks, active ETFs, Und passive ETFs, investors must consider factors such as investment fees, strategy (buy-and-hold vs. active trading), and their approach to analysis. Each option offers different opportunities and risks, depending on an investor’s financial goals and risk tolerance. For those looking to minimize costs and take a long-term approach, passive ETFs Und buy-and-hold strategies may be ideal. In contrast, active trading with stocks oder active ETFs can offer higher returns but requires more frequent monitoring and a higher level of expertise. Ultimately, a combination of fundamental Und technical analysis, paired with strategies like dollar-cost averaging, can help investors make informed decisions across different asset types.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Investment fees significantly impact your returns, with active ETFs generally having higher management fees due to professional management, while passive ETFs offer lower fees due to their simple, index-tracking nature. Stocks typically involve transaction fees but no ongoing management fees once purchased.
- Der buy-and-hold strategy is suitable for investors seeking long-term growth, with lower transaction costs and reduced tax liabilities. However, active trading offers the potential for higher short-term returns but comes with higher costs, greater tax implications, Und increased risk due to constant market monitoring.
- Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) allows investors to reduce the impact of market volatility by regularly investing a fixed amount, regardless of market conditions. This strategy can smooth out the purchase price over time and is especially useful for long-term growth through passive ETFs.
- Fundamental analysis involves assessing a company’s financial health through metrics like the P/E ratio, P/B ratio, Und dividend yield to determine if a stock is undervalued oder overvalued. Technical analysis, on the other hand, focuses on price movements Und Markttrends using tools like moving averages Und RSI to predict future price movements.
Schlusserklärung:
By understanding the key investment strategies and techniques covered in this section, investors can make informed decisions about their portfolios, align their approach with their financial goals, and manage risks effectively. Whether you’re interested in long-term growth, income generation, or short-term gains, these concepts will guide you toward creating a successful trading plan.