Local: EU-specific Time Value of Money
Lernziele der Lektion:
- Understand the importance of Present Value (PV) Und Future Value (FV) calculations in financial planning and investment analysis, specifically within the European market context where economic policies and inflation vary across member states.
- Learn how the European Central Bank’s (ECB) interest rates influence the discount rates used in PV calculations, affecting the valuation of future cash flows for investments and financial assessments.
- Explore the impact of inflation expectations on the Future Value (FV) of investments, particularly how regional differences in inflation within the EU can affect the real return on investments.
- Grasp the necessity of adjusting financial models to reflect local economic conditions in different EU countries, ensuring accurate valuation of investments based on current and projected economic data.
25.1 Present Value and Future Value
When calculating present value (PV) Und future value (FV) in the European Union, it is essential to consider EU-specific discount rates Und inflation expectations. These factors are influenced by European Central Bank (ECB) policies, individual country economic conditions, and the region’s inflation outlook. Given the interconnected economies within the Eurozone, discount rates and inflation expectations play a significant role in evaluating the value of future cash flows for European businesses and investors.
25.2 EU-Specific Discount Rates
Der discount rate used in PV and FV calculations in Europe often reflects the European Central Bank’s (ECB) monetary policy. The ECB sets interest rates to control inflation and stimulate or cool down the economy. These rates impact the cost of borrowing and the return on investments, which are directly linked to discount rates used by investors and financial professionals in present value calculations.
- Beispiel: If the ECB has set a low interest rate to stimulate economic growth, the discount rate for PV calculations will be lower, leading to a higher present value for future cash flows. Conversely, in times of high inflation or economic overheating, a higher ECB rate would increase the discount rate, reducing the present value of future cash flows.
Länder wie Deutschland, Frankreich, Und Italien often use discount rates that closely align with ECB rates, though local financial institutions may adjust them based on country-specific risk factors or market conditions. Investors in countries outside the Eurozone, such as Sweden oder Poland, will factor in local central bank policies, which may differ from ECB rates.
25.3 Inflation Expectations in the EU
Inflation expectations are critical in calculating future value (FV) as inflation erodes purchasing power over time. The Eurozone has experienced varying inflation rates across member states, making it necessary to adjust FV calculations based on regional inflation trends.
The ECB aims to keep inflation at or near 2%, but inflation may vary between countries. For example, Spanien oder Greece may experience higher inflation rates due to local economic factors, while Deutschland oder Niederlande might have lower inflation rates.
- Beispiel: If the inflation rate in the Eurozone is expected to be 2% annually, this will directly impact the FV of investments. For a business evaluating a long-term project, higher inflation in Southern European countries may necessitate higher expected future returns to offset the loss of purchasing power.
Inflation expectations also influence real returns, meaning that investors must adjust FV calculations to account for the impact of inflation on future cash flows. In high-inflation environments, a nominal return may look appealing, but the real return—after accounting for inflation—could be much lower.
`
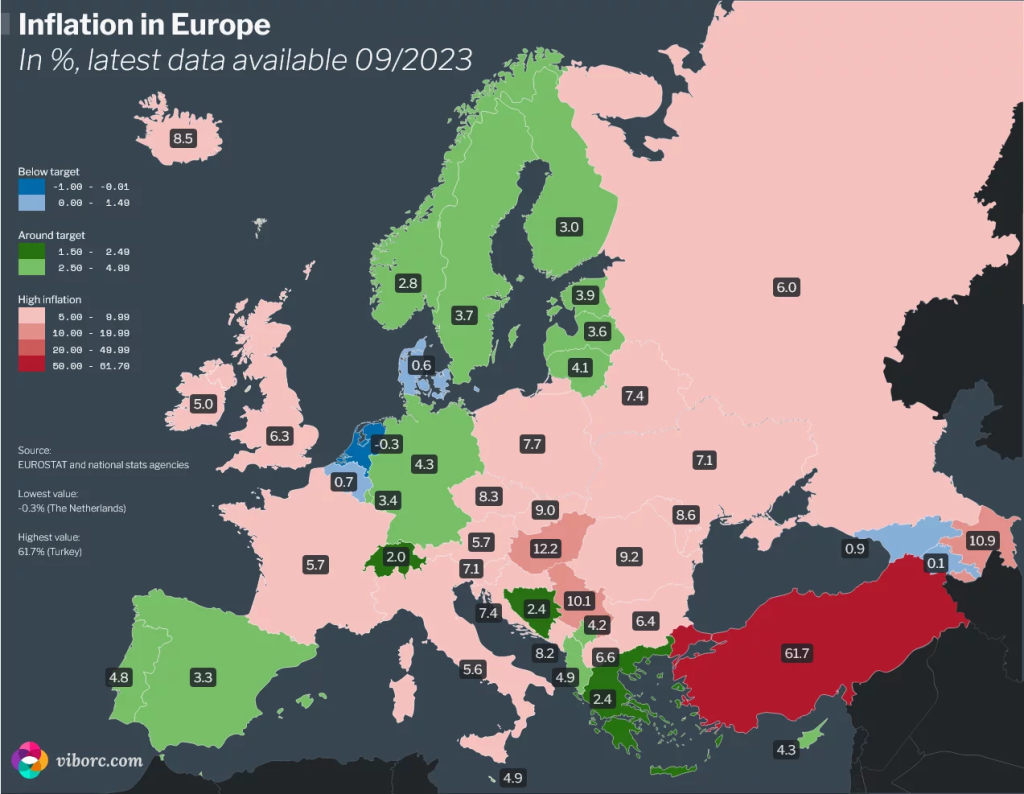
Figur: Inflation in Europe (09/2023)
Beschreibung:
This map displays inflation rates across Europe as of September 2023, with percentages indicating the inflation level in each country. The color gradient reflects inflation categories: below target (blue), around target (green), high inflation (pink), and very high inflation (red). For instance, countries like Niederlande have the lowest inflation rate at -0.3%, whereas Turkey shows the highest inflation rate at 61.7%. The map provides a visual comparison of inflation trends in various European countries, allowing users to quickly identify where inflation is highest or lowest.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Inflation rates vary significantly across Europe, ranging from -0.3% in the Netherlands Zu 61.7% in Turkey.
- The map uses color coding to classify inflation rates, making it easy to identify regions with low oder high inflation.
- Western and Central European countries generally experience lower inflation, während Eastern and Southeastern countries exhibit higher rates.
- Länder wie Deutschland Und Frankreich have moderate inflation rates around the target range, indicating relative stability.
Anwendung der Informationen:
Understanding regional inflation differences can help Investoren, Ökonomen, Und policy makers analyze economic conditions and make informed decisions. It provides a macroeconomic overview essential for evaluating market conditions, adjusting monetary policies, and formulating Anlagestrategien in the European context.
Abschluss
In Europe, present value Und future value calculations are significantly influenced by ECB policies Und country-specific inflation expectations. Low ECB interest rates lead to lower discount rates, increasing present value, while varying inflation expectations across the Eurozone impact the future value of investments. By considering these EU-specific factors, businesses and investors can make more accurate assessments of the value of future cash flows in European markets.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Present Value (PV) calculations are crucial for assessing the worth of future cash flows in today’s terms, influenced significantly by ECB interest rates which dictate the discount rates used across the EU.
- Future Value (FV) calculations help investors and businesses project the value of current investments into the future, taking into account regional inflation rates that can vary widely across the EU, from near zero in countries like the Netherlands to much higher in Eastern Europe.
- Understanding and applying the correct discount rates and adjusting for accurate inflation expectations are essential for financial analyses and investment decisions in Europe, as these factors critically impact the real returns of investments.
- The dynamic economic landscape of the EU, with its diverse inflation rates and economic policies, necessitates a tailored approach to financial valuation and investment planning, ensuring that strategies are robust against regional economic fluctuations and aligned with ECB monetary objectives.
Schlusserklärung:
Mastery of PV and FV calculations, with a keen understanding of ECB policies and inflation expectations, is crucial for financial professionals operating in the European Union. This knowledge enables accurate investment assessments and strategic financial planning in a region characterized by diverse economic conditions.

