Local (European-Specific) Content : Keeping Track of Income and Expenses in Europe
Lesson Learning Objectives:
- Accurate Financial Tracking is essential for managing cash flow, preparing for taxes, and avoiding legal issues. You’ll learn how to track income, expenses, Und property-related costs across countries with different tax systems and housing laws.
- Legal Compliance is a requirement across European nations. You’ll understand how countries like Germany Und France enforce strict record-keeping standards, and how good bookkeeping can help you avoid penalties and claim tax benefits.
- Using Accounting Tools and Best Practices helps real estate investors stay organized. You’ll learn how software tools, bank reconciliation, Und cloud storage can simplify financial tracking and ensure accuracy in different European tax systems.
- Understanding Real Estate Taxation gives you a financial advantage. This section teaches you how to reduce your tax burden using tools like mortgage interest deductions, depreciation, Und rental income tax deductions in countries like Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands.
- Applying Tax Planning Strategies such as double taxation treaties, setting up holding companies, and preparing for inheritance taxes will help you protect your investments, improve returns, and plan for the long term.
16.1 Keeping Track of Income and Expenses in Europe
Importance of Tracking Income and Expenses
Effective bookkeeping is essential for real estate investors to monitor cash flow, profitability, and tax liabilities. In Europe, with diverse tax regulations and complex property laws across different countries, maintaining accurate financial records is crucial to ensure compliance and optimize tax benefits.
- Legal Compliance: European countries, such as Germany Und France, require real estate investors to maintain detailed financial records for auditing and taxation purposes. Failure to comply with record-keeping requirements can result in penalties, fines, or disallowed tax deductions.
- Monitoring Cash Flow: Proper tracking of rental income, expenses, and property-related costs helps investors maintain positive cash flow. In high-cost cities like Paris Und London, where expenses such as property taxes, maintenance, and management fees are high, tracking these expenses is vital to ensuring the property remains profitable.
- Tax Deductions: Keeping accurate records allows investors to claim deductions on property expenses such as mortgage interest, maintenance costs, and property management fees. In countries like Italy oder Spain, claiming allowable deductions can significantly reduce taxable income and increase net returns.

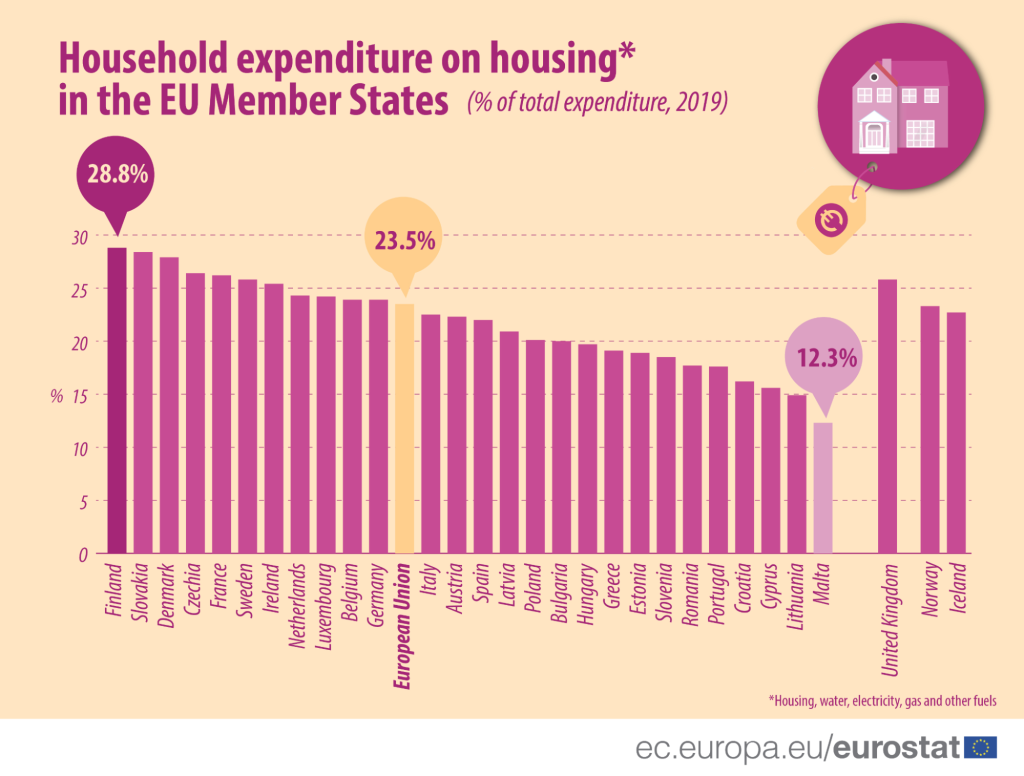
Figur: Household Expenditure on Housing in the EU Member States (2019)
Beschreibung:
This bar chart compares the proportion of household expenditure spent on housing, including utilities like water, electricity, and gas, across EU Member States in 2019. Finland ranks the highest with 28.8% of total household expenditure dedicated to housing, while Malta spends the least at 12.3%. The European Union average stands at 23.5%, highlighting significant disparities in housing-related costs across member states.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Finland has the highest household expenditure on housing at 28.8%, reflecting significant housing costs in the region.
- Malta records the lowest spending at 12.3%, indicating relatively lower housing-related expenses.
- Der European Union average of 23.5% shows a baseline against which individual countries can compare.
- Other countries like Slovakia, Denmark, and the Czech Republic also show above-average expenditures, suggesting housing costs are a key burden in these nations.
- Significant disparities indicate different economic factors, housing policies, and income levels across countries.
Application of Information:
This data is essential for policy analysts, investors, Und economists to understand the economic burden of housing in different EU countries. It provides insights into affordability, helps identify regions with high investment potential in housing infrastructure, and supports the design of housing policies to reduce financial strain. For individuals, this information offers a guide to cost-of-living comparisons across countries.
Implementing a System
To ensure efficiency and accuracy in record-keeping, investors should implement a reliable system for tracking income and expenses. In Europe, where tax regulations can vary significantly by country, investors should use tools that allow them to meet local compliance requirements.
- Accounting Software: In Europe, property management software like Xero, QuickBooks, or real estate-specific platforms such as Arthur oder Rentila can simplify the process of tracking income and expenses. These tools are particularly useful in countries with complex tax systems, like France oder Germany, where different expenses are deductible depending on the type of property and rental structure.
- Bank Reconciliation: Ensuring that bank accounts are reconciled with bookkeeping records is essential. In countries like the U.K., where landlords may manage multiple properties with different tax obligations, using accounting software that integrates with bank accounts helps avoid discrepancies and improves accuracy.
- Document Storage: Real estate investors must store invoices, receipts, and other financial documents for several years, depending on local regulations. In the Netherlands, for example, tax authorities may request records dating back five to seven years. Cloud-based document storage systems, such as Google Drive oder Dropbox, allow investors to securely store these records and access them as needed.
Figur: Real Estate Accounting Best Practices
Beschreibung:
This infographic highlights five best practices for managing real estate accounting effectively. These include updating accounting books regularly, keeping business and personal accounts separate, Und tracking and classifying expenses accurately. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of using specialized accounting software and staying updated on the latest tax laws. Each practice ensures smooth financial management and compliance for real estate professionals.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- Update records regularly to ensure accurate and timely financial tracking.
- Separate business and personal accounts to avoid financial mismanagement and simplify tax filing.
- Track and classify expenses correctly, ensuring better control over costs and easier audits.
- Use specialized accounting software for increased efficiency and accuracy.
- Stay informed about tax laws to maintain compliance and take advantage of potential deductions.
Application of Information:
These best practices provide real estate professionals with a framework to manage finances systematically. Following these steps ensures compliance with regulations, helps identify cost-saving opportunities, and enhances financial decision-making. Investors and landlords can use this approach to streamline property management and optimize profitability.
16.2 Real Estate Taxation in Europe
Tax Benefits of Owning Real Estate Investments in Europe
Owning real estate in Europe offers various tax benefits, depending on the country and type of property. Investors must understand the local tax implications to maximize their returns and avoid unnecessary tax liabilities.
- Mortgage Interest Deductions: In many European countries, mortgage interest on loans used to purchase rental properties can be deducted from taxable income. In France Und Italy, for example, this deduction helps reduce the overall tax burden for property owners, especially those with high-interest mortgages.
- Depreciation: European countries like Germany Und Spain allow property owners to depreciate the value of their buildings over time. This allows investors to reduce their taxable income by accounting for the property’s wear and tear. However, depreciation rates and rules vary widely across Europe, making it important for investors to work with tax professionals familiar with local regulations.
- Capital Gains Tax: When selling a property, capital gains tax may apply to the profit earned. In Germany, for instance, properties held for more than 10 years are exempt from capital gains tax, while in the U.K., the rate depends on the investor’s income level. Understanding these rules can help investors decide when to sell a property to minimize tax liabilities.
- Rental Income Tax: Most European countries tax rental income, though tax rates and exemptions vary. In the Netherlands, rental income from property investments is considered part of an investor’s wealth and is taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income. In contrast, France taxes rental income as part of the regular income tax system, but with allowable deductions for property expenses.
Tax Planning Strategies
- Double Taxation Treaties: For investors holding properties across different European countries, double taxation treaties help prevent being taxed in two jurisdictions on the same income. For example, a German investor with property in Spain can benefit from tax treaties that reduce the overall tax burden by avoiding double taxation on rental income.
- Holding Structures: In some cases, forming a company or holding entity to own properties may offer tax advantages. In Luxembourg Und the U.K., setting up a holding company for real estate investments can provide tax benefits, such as lower corporate tax rates or exemptions on certain types of income.
- Inheritance and Gift Taxes: Property inheritance can be subject to significant taxes in Europe. For example, France has high inheritance taxes on real estate, but tax planning strategies, such as gifting property to family members, can reduce these taxes over time.
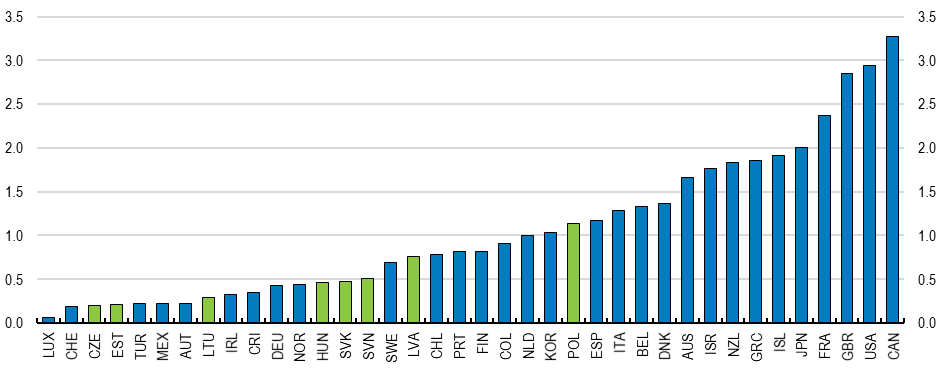
Figur: GDP per Capita Growth in Central and Eastern European (CEE) Countries
Beschreibung:
This bar chart compares GDP per capita growth across Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries. The bars represent individual countries, with blue bars showing higher growth rates and green bars indicating lower rates. The data reflects varying economic performance among nations in the region, showcasing significant disparities in GDP growth.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse:
- CEE countries exhibit diverse growth rates, with some nations experiencing robust GDP per capita growth while others show more modest increases.
- Top-performing countries have significantly higher GDP per capita, demonstrating better economic conditions.
- The variation highlights differences in economic policy, investment climates, and resource management across the region.
- Economic disparities may affect regional stability and collaborative efforts.
- Countries with slower growth may require targeted policies to improve economic performance.
Application of Information:
This data provides insight into economic trends in Central and Eastern Europe, helping investors identify markets with high growth potential. Policymakers can use this information to address gaps and foster regional economic equality. Understanding these trends aids in investment decision-making and economic forecasting for businesses and governments.
Wichtige Unterrichtsinformationen:
- Keeping Accurate Records is required in many European countries. Countries like Germany Und France demand proper documentation for audits and taxes. Staying organized helps prevent fines and ensures you’re claiming all allowable deductions.
- Monitoring Cash Flow and Expenses is key for property profitability. Tracking rental income, maintenance, taxes, Und fees helps investors make smart decisions, especially in high-cost cities like London Und Paris.
- Using Accounting Software and Best Practices improves efficiency. Tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or real estate platforms like Rentila help you manage finances accurately. Bank reconciliation and separating personal and business accounts further strengthen your records.
- Claiming Deductions like mortgage interest, maintenance costs, Und property management fees can significantly reduce your taxable income. These deductions are common in countries like Italy, France, Und Spain.
- Capital Gains Tax and Rental Income Tax rules vary by country. For example, Germany offers capital gains tax exemption after 10 years, while France treats rental income as regular income but allows deductions. Understanding these rules helps you plan when to sell or rent.
Schlusserklärung:
By learning how to manage real estate income, expenses, and taxes in Europe, you can protect your investments, maximize returns, and avoid costly mistakes. These practices build a strong foundation for long-term success.