Global: Understanding Risk and the Role of Insurance
Στόχοι Μαθήματος:
Εισαγωγή:
This section explores the fundamental concepts of risk and insurance, highlighting how they work together to protect individuals and businesses from financial loss. By understanding how insurance helps manage risk and how to evaluate insurance options, users can make better financial decisions to safeguard their assets and financial stability.
- Understand the Nature of Risk and Insurance. Learn how insurance functions as a risk transfer tool, shifting financial responsibility from individuals to insurance providers. This helps users grasp how insurance minimizes financial losses from unexpected events like health issues, accidents, or property damage.
- Learn How to Evaluate and Choose Insurance. Discover different types of insurance (health, life, property, etc.) and understand how to select the right policies based on coverage, premiums, deductibles, and providers. This will help users make informed choices to ensure they have adequate protection tailored to their financial situation.
- Understand Insurance Cost Management. Learn strategies for managing insurance costs effectively, such as bundling policies, adjusting deductibles, and regularly reviewing policies. This knowledge enables users to balance insurance costs and coverage to achieve financial efficiency.
- Recognize the Role of Digital Insurance Tools. Explore digital insurance options like peer-to-peer and on-demand insurance, understanding how they offer affordable alternatives for coverage. This will help users evaluate new insurance models that may be better suited to their needs.
Α. Η φύση του κινδύνου και της ασφάλισης
At its core, κίνδυνος refers to the possibility of an uncertain event or loss. In financial contexts, risk can be related to market fluctuations, unforeseen personal circumstances, or external factors such as natural disasters. ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΗ is a tool designed to manage risk by transferring the financial burden from the individual to an insurance provider. In exchange for regular payments, called premiums, the insurer agrees to cover specific losses or damages outlined in the policy.
The primary role of insurance is to provide financial protection against risks that individuals or businesses may not be able to cover on their own. For instance, health insurance helps cover the cost of medical care, while life insurance ensures that beneficiaries are financially supported in the event of the policyholder’s death.
Insurance plays a key role in διαχείριση κινδύνου strategies worldwide, helping people mitigate the financial impact of unexpected events such as medical emergencies, accidents, or property damage. For example, in the Eurozone, various forms of mandatory insurance exist (such as health and car insurance) to ensure that citizens have basic coverage against significant financial risks.
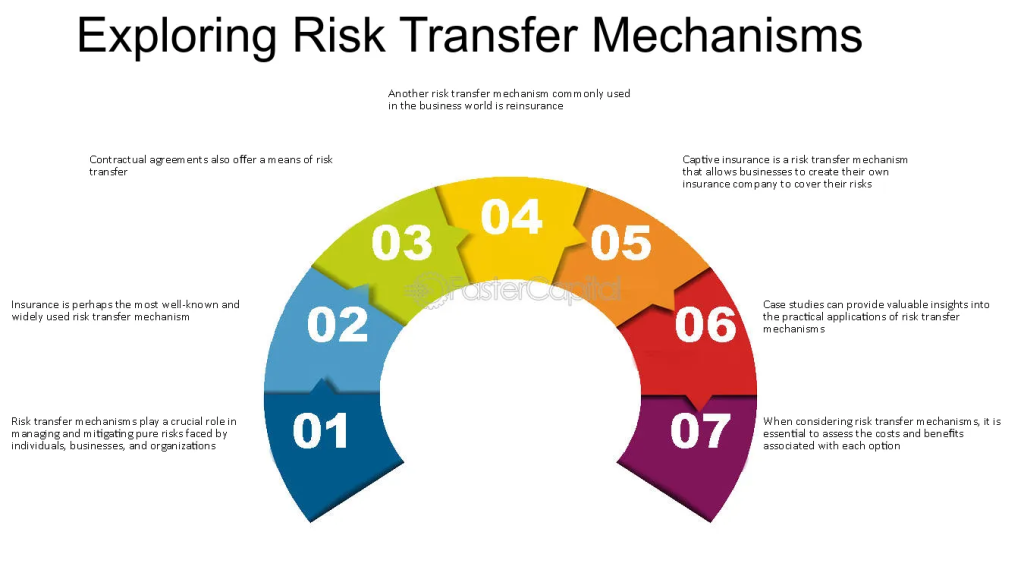
Figure: Exploring Risk Transfer Mechanisms
Περιγραφή:
The figure outlines various risk transfer mechanisms that help manage and mitigate risks for individuals and businesses. It highlights that insurance is one of the most well-known forms of risk transfer, along with contractual agreements, reinsurance, και captive insurance. The graphic emphasizes the importance of considering costs, benefits, and practical examples through case studies to understand the effective application of these mechanisms.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΗ is a widely used and essential method for transferring risk, providing coverage against unforeseen events.
- Contractual agreements can also be a means of shifting risk responsibilities between parties.
- Reinsurance helps insurance companies mitigate risks by sharing them with other insurers.
- Captive insurance allows businesses to create their own insurance to manage specific risks.
- Case studies provide insights into the real-world application of risk transfer methods.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding various risk transfer mechanisms allows users to evaluate and choose the right strategies to manage potential financial threats. For businesses, knowing the different options can help in mitigating risks effectively και planning for contingencies, ensuring stability and sustainability.
Β. Αξιολόγηση και Επιλογή Ασφάλισης
Selecting the right insurance product requires a careful evaluation of one’s financial needs and potential risks. Different types of insurance policies serve different purposes, and the choice depends on factors like income, lifestyle, assets, and future financial goals.
- Είδη Ασφάλισης: Common types of insurance include:
- Health insurance: Covers medical expenses.
- Ασφάλεια ζωής: Provides financial support to dependents after the policyholder’s death.
- Property insurance: Protects assets like homes and cars from damage or theft.
- Disability insurance: Offers income protection if the policyholder becomes unable to work due to illness or injury.
- Policy Coverage: When evaluating insurance, it’s essential to understand the coverage provided by each policy, including what is covered and what is excluded. Policies may cover events like accidental damage, natural disasters, or medical emergencies, but they often come with specific conditions or exclusions.
- Premiums and Deductibles: Insurance policies come with premiums (regular payments) and deductibles (the amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before coverage kicks in). Lower premiums generally mean higher deductibles, and vice versa. For example, a low-premium health insurance policy may have a high deductible, requiring the policyholder to cover more of the costs before receiving benefits.
- Evaluating Providers: It’s also important to evaluate the insurance provider. Reputable providers with a strong financial standing are more likely to honor claims promptly and fully. In the Eurozone, the Solvency II Directive regulates insurance companies to ensure that they maintain adequate capital to protect policyholders from financial loss.
Example: A family in Germany might opt for a life insurance policy with lower premiums and higher coverage limits to ensure their children are financially supported in the case of the parents’ death, but they must carefully check the policy’s exclusions, such as for pre-existing medical conditions.
Είδος Ασφάλισης | Κάλυψη | Κόστος | Παράδειγμα |
Υγεία | Επισκέψεις γιατρού, συνταγογραφούμενα φάρμακα, επείγουσες ιατρικές υπηρεσίες | Διαφέρει ευρέως. τυπικά $200-$500/μήνα | Το μηνιαίο premium της Μαρίας είναι $350 για ολοκληρωμένη κάλυψη. |
Ζωή | Επίδομα θανάτου στους δικαιούχους. | $15-$30/μήνα για πολιτική $250.000 | Ο Γιάννης πληρώνει $25/μήνα για συμβόλαιο διάρκειας ζωής. |
Αναπηρία | Αντικατάσταση εισοδήματος σε περίπτωση αναπηρίας | 1-31ΤΠ3Τ ετήσιου μισθού | Η Τίνα λαμβάνει 601 TP3T του μισθού της μέσω ασφάλισης αναπηρίας. |
Αυτο | Ζημιές οχημάτων, ευθύνη για τραυματισμούς και υλικές ζημιές σε άλλους | Διαφέρει ανάλογα με το ιστορικό οχήματος και οδηγού. περίπου $100-$200/μήνα | Η ασφάλιση αυτοκινήτου του Liam κοστίζει $150/μήνα με έκπτωση $500. |
Ιδιοκτήτες σπιτιού | Ζημιές σε σπίτι και προσωπική περιουσία, προστασία αστικής ευθύνης | Εξαρτάται από την αξία του ακινήτου. μέσος όρος $1000/έτος | Η ασφάλιση ιδιοκτητών σπιτιού της Ava κοστίζει $1200/έτος με κάλυψη $250.000. |
Ενοικιαστές | Προσωπική ιδιοκτησία σε ενοικιαζόμενους χώρους κατοικίας, ευθύνη | $15-$30/μήνα | Ο Noah πληρώνει $20/μήνα για ενοικιαστές ασφάλισης που καλύπτει $30.000 σε προσωπική περιουσία. |
Ευθύνη | Προστασία έναντι αξιώσεων υλικών ζημιών ή σωματικών βλαβών που προκλήθηκαν σε άλλους | Διαφέρει σημαντικά ανάλογα με το επίπεδο κάλυψης. Συχνά μέρος της πολιτικής των ιδιοκτητών σπιτιού ή των ενοικιαστών | Η ασφάλεια αστικής ευθύνης μικρών επιχειρήσεων της Emily κοστίζει $500/έτος. |
Γ. Διαχείριση Κόστους και Αποτελεσματικότητα Ασφάλισης
Managing the cost of insurance is an essential part of maximizing financial efficiency. Insurance costs vary depending on factors such as the type of coverage, the level of risk, and personal circumstances (age, health, income). To maintain insurance efficiency, it’s important to ensure that one is not underinsured (lacking sufficient coverage) or overinsured (paying for coverage that exceeds actual needs).
- Tailored Policies: Individuals should seek insurance policies that are tailored to their specific needs and risks. For example, someone who owns a home in a region prone to natural disasters may want to prioritize comprehensive property insurance, while someone with minimal health risks may opt for a more basic health insurance plan with lower premiums.
- Bundling and Discounts: Many insurance providers offer discounts when multiple policies (such as home and auto insurance) are bundled together. Bundling can reduce overall premiums, making insurance more cost-efficient.
- Regular Policy Reviews: It’s also important to review insurance policies regularly to ensure that they continue to meet one’s needs as circumstances change. For example, if a person’s income increases, they may want to adjust their life insurance coverage to provide better protection for their dependents.
- Evaluating Deductibles and Premiums: Balancing deductibles και premiums can also help manage insurance costs. A higher deductible results in lower premiums but requires the policyholder to bear more upfront costs in the event of a claim. Conversely, low deductibles lead to higher premiums but offer greater financial protection when filing claims.
Example: A homeowner in Spain could reduce their insurance costs by increasing their property insurance deductible, lowering their monthly premium. However, they would need to ensure they have enough savings to cover the higher deductible in case of an emergency.
5. Using Digital Tools: In many countries, including the Eurozone, digital insurance providers offer innovative products such as peer-to-peer insurance, on-demand insurance, και usage-based insurance. These services often come with lower overhead costs and can be more affordable than traditional insurance models, especially for younger and tech-savvy consumers. However, users must be aware that digital products may differ from traditional policies in terms of regulation, claims processing, and risk management.
Figure: Steps to Minimize Insurance Costs
Περιγραφή:
The figure outlines eight practical steps that can help businesses and individuals reduce insurance expenses. These steps include conducting regular risk assessments, implementing safety procedures, providing training, maintaining documentation, και collaborating with insurance providers. Each step aims to minimize risks, ensure safety, and optimize insurance premiums through careful planning and management.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Regular risk assessments help identify and mitigate potential hazards before they become costly issues.
- Proper safety policies and training can reduce the likelihood of accidents and claims.
- Accurate documentation and updated policies are essential for compliance and efficient claims processing.
- Collaborating with insurance providers can lead to customized policies and potential cost savings.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
By applying these cost-saving measures, businesses can optimize their insurance plans, reducing premiums while maintaining adequate coverage. For individuals and companies, understanding these steps can lead to more informed decision-making when selecting and managing insurance policies, ultimately lowering financial risk.
Βασικές πληροφορίες μαθήματος:
- Insurance as a Risk Transfer Tool helps manage financial risks by shifting potential losses to insurance providers. By paying regular premiums, individuals and businesses can ensure they are covered for specific events, such as medical emergencies or property damage, reducing the financial burden of unforeseen circumstances.
- Evaluating Insurance Coverage involves understanding what each policy covers, the premiums, and the deductibles. For example, health insurance may cover hospital visits but exclude certain procedures, while a life insurance policy might have a lower premium but higher deductible. Knowing these details ensures users select the right policies for their needs.
- Cost Management in Insurance is achieved by tailoring policies, bundling coverage, and balancing premiums with deductibles. For instance, a homeowner can save on costs by increasing the deductible on their property insurance, which lowers monthly premiums. This approach enables users to maintain financial efficiency while ensuring adequate protection.
- Digital Insurance Options offer new ways to manage risk affordably, with features like peer-to-peer models and usage-based premiums. While these models often have lower costs, users should be aware of potential differences in claims processing and coverage compared to traditional insurance. Understanding these digital tools can help users find cost-effective coverage that suits their needs.
- Regular Policy Reviews are essential to ensure insurance coverage remains relevant as personal circumstances change. For example, an increase in income may require more life insurance coverage, while selling a car might reduce the need for auto insurance. Regular reviews help users adjust their insurance to meet current needs.