Global: Understanding Tax Systems and Strategic Planning
Στόχοι Μαθήματος:
Εισαγωγή:
This section covers the fundamentals of global tax systems, exploring common types of taxes, basic income tax essentials, and advanced strategies for optimizing tax obligations. Understanding these concepts is crucial for managing personal finances efficiently and making informed financial decisions.
- Understand the different types of taxes applied globally, such as income tax, sales tax (or VAT), corporate tax, and capital gains tax. This knowledge will help individuals navigate tax laws and fulfill tax obligations, ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties.
- Gain insights into income tax essentials, including tax brackets, deductions, credits, and withholding taxes. This understanding allows users to plan their finances better, potentially lowering their tax liabilities by using available deductions and credits.
- Learn advanced tax strategies such as tax-deferred investments, managing capital gains, and estate planning. These strategies can help users reduce their tax burdens, maximize savings, and prepare effectively for retirement and wealth transfer.
- Explore international tax planning techniques, including double taxation agreements (DTAs) and charitable giving options. This knowledge is especially useful for individuals with income from multiple countries, enabling them to optimize taxes on global income.
Α. Βασικά Φορολογικά
Φόροι are a universal tool used by governments around the world to generate revenue for public services and infrastructure. While tax structures vary between countries, common types of taxes include:
- Income tax: A tax on earned income from employment or investments.
- Sales tax (or VAT): A consumption tax applied to goods and services, common across both developed and developing countries.
- Corporate tax: A tax on the profits of businesses.
- Φόρος υπεραξίας: Levied on the profit made from the sale of assets like stocks, real estate, or other investments.
Κατανοώντας το basics of taxation is essential for individuals to comply with tax laws and manage their financial responsibilities efficiently. Taxes fund critical services such as healthcare, education, public transportation, and social programs, making them a vital aspect of societal functioning.
Global Example: In the United States, federal income tax is progressive, meaning that higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. In contrast, countries like Singapore have lower income tax rates but rely more heavily on indirect taxes like goods and services tax (GST).
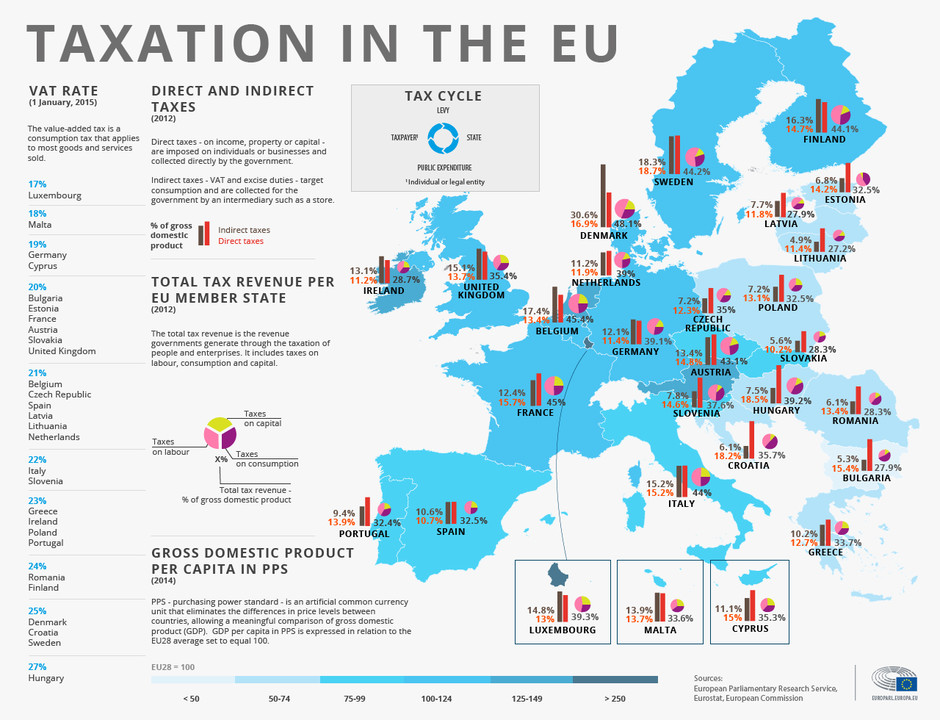
Figure: Taxation in the EU
Περιγραφή:
The figure presents a comprehensive overview of taxation within the European Union (EU), highlighting VAT rates, direct and indirect tax contributions, and total tax revenue per EU member state. It also visualizes the tax cycle, showing how taxes are levied and spent, and the gross domestic product (GDP) per capita across the EU. Each country’s tax revenue is broken down by labor, consumption, and capital, helping to illustrate how different nations balance their tax systems.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- VAT rates vary across the EU, with lower rates observed in Luxembourg (17%) and higher rates in Hungary (27%).
- Direct and indirect taxes differ significantly, showing how governments generate revenue from income, consumption, and other sources.
- Tax revenue as a percentage of GDP reveals how much each country relies on taxes for its budget.
- GDP per capita provides context on the economic strength and living standards of each EU nation.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding the differences in tax structures and VAT rates can help investors and businesses make informed decisions about where to operate or invest within the EU. By analyzing GDP per capita and tax revenue data, individuals can better assess the economic health and fiscal strategies of different EU countries, allowing for smarter investment planning and business strategies.
Β. Βασικά στοιχεία φορολογίας εισοδήματος
Income tax is one of the most common and important taxes that individuals face globally. It is generally imposed on κερδισμένο εισόδημα, such as wages and salaries, and unearned income, such as dividends, interest, and rental income. The key elements to understand about income tax include:
- Tax brackets: Most countries use a progressive tax system, where tax rates increase as income rises. Each portion of income is taxed at a different rate, with higher earners paying a greater percentage of their income in taxes.
- Deductions and allowances: Many tax systems offer deductions, such as mortgage interest or education expenses, that reduce taxable income. Allowances may also be granted for dependents or other factors, helping to reduce the overall tax burden.
- Tax credits: Unlike deductions, which reduce taxable income, tax credits reduce the amount of tax owed directly. For example, child tax credits ή energy-efficiency credits can lower the final tax bill.
- Withholding taxes: In many countries, employers deduct income tax directly from an employee’s paycheck, ensuring that taxes are paid throughout the year. If more taxes were withheld than necessary, individuals are eligible for a refund after filing their tax return.
Global Example: In the UK, the PAYE (Pay As You Earn) system allows income tax to be deducted directly from an employee’s salary before they receive it. The same model applies in countries like Australia and Canada, simplifying the tax process for employees.
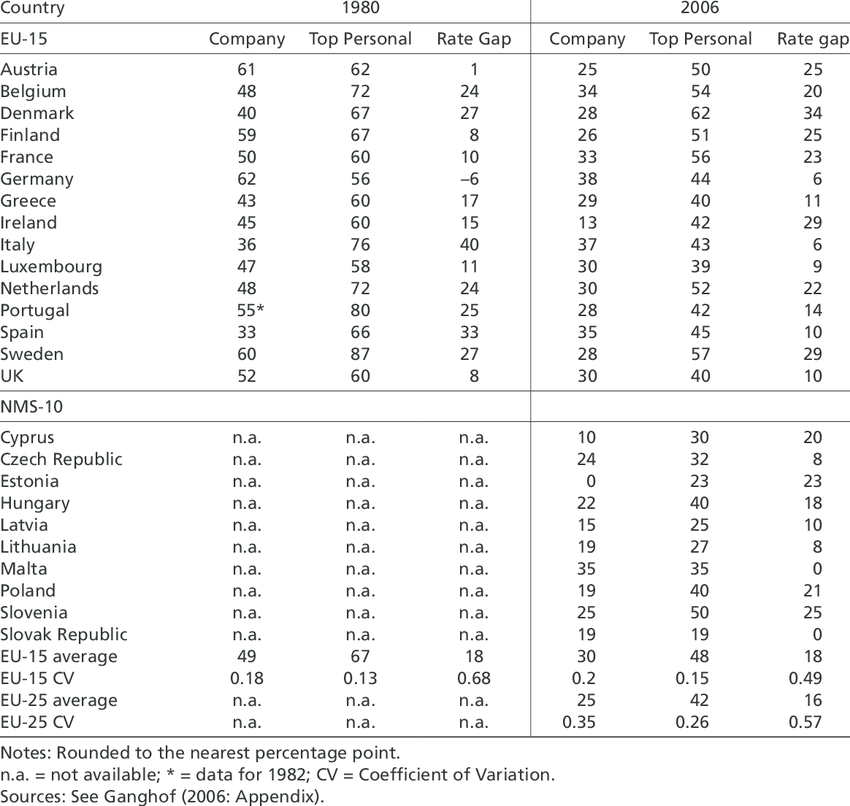
Εικόνα: Company and Personal Income Tax Rates in the EU (1980 vs. 2006)
Περιγραφή:
The figure compares company and top personal income tax rates across EU-15 countries between 1980 and 2006. It also includes data from new member states (NMS-10) as of 2006. The table shows changes in tax policies, illustrating how rates have generally decreased over time. It highlights the “rate gap,” which is the difference between corporate and personal tax rates, reflecting variations in tax strategies among countries.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Corporate tax rates decreased significantly across most EU-15 countries between 1980 and 2006, indicating a trend toward lower business taxes.
- Top personal income tax rates also declined, though not as dramatically as corporate taxes.
- Rate gap changes illustrate how some countries, like Germany, adjusted tax policies to narrow or widen the gap between personal and corporate taxes.
- NMS-10 countries, which joined the EU more recently, generally have lower corporate and personal tax rates compared to the EU-15.
- The Coefficient of Variation (CV) indicates reduced variation in tax rates among EU-15 countries over time.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
This data helps investors understand tax policy trends across Europe, enabling them to assess which countries have become more tax-friendly for businesses over time. Lower corporate tax rates can attract investment, while differences in the rate gap might affect decisions on where to set up businesses. Comparing historical and current tax rates can guide strategic business planning και investment analysis.
C. Advanced Tax Strategies
Once the basics of taxation are understood, individuals can explore advanced tax strategies to optimize their tax liability and increase financial efficiency. These strategies can include:
- Tax-deferred investments: Some investments, like retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k) in the U.S., RRSP in Canada, or superannuation in Australia), offer tax deferral benefits. Contributions to these accounts reduce taxable income in the present, and taxes are only paid upon withdrawal in retirement, when an individual may be in a lower tax bracket.
- Capital gains tax optimization: Managing capital gains is a key part of advanced tax strategy. For example, by holding investments for over a year, individuals can benefit from long-term capital gains tax rates, which are generally lower than short-term rates. Additionally, strategies like tax-loss harvesting—selling losing investments to offset gains—can help minimize capital gains tax liabilities.
- Estate planning: Inheritance taxes και estate taxes can significantly reduce the amount of wealth passed down to heirs. Trusts και gifting strategies are often used in estate planning to reduce the taxable value of an estate and ensure that assets are distributed efficiently.
- International tax planning: For individuals or businesses with international income, understanding double taxation agreements (DTAs) is essential. DTAs help prevent individuals from being taxed on the same income by two countries, and they are a common feature in global tax systems.
- Charitable giving: Donations to charitable organizations can offer significant tax benefits, especially in countries where charitable contributions are tax-deductible. This strategy allows individuals to support causes they care about while reducing their taxable income.
Global Example: In the U.S., individuals can reduce taxable income by contributing to 401(k) retirement plans or IRA accounts, while in Canada, contributions to Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSPs) can be deducted from income, lowering the overall tax burden.
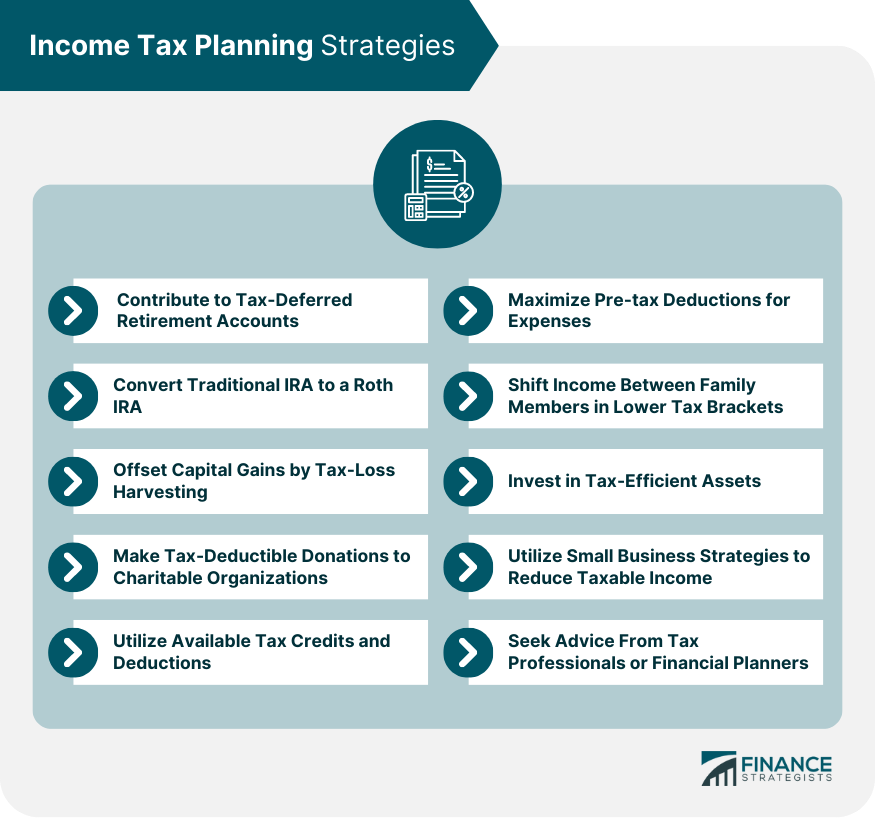
Figure: Income Tax Planning Strategies
Περιγραφή:
The figure presents various strategies that individuals can use to plan their income taxes effectively. It includes methods such as contributing to tax-deferred accounts, converting IRAs, offsetting capital gains, maximizing pre-tax deductions, and utilizing tax credits. Additionally, it suggests shifting income within family members, investing in tax-efficient assets, and seeking professional advice to optimize tax planning.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Contributing to tax-deferred accounts helps reduce taxable income now, deferring taxes until later.
- Tax-loss harvesting can be used to offset capital gains and lower tax liability.
- Shifting income and making charitable donations are effective methods to utilize lower tax brackets and deductions.
- Seeking professional advice ensures that all available tax benefits and strategies are considered.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
By understanding these tax planning strategies, individuals can effectively manage their tax obligations and increase savings. Investors can maximize tax deductions, credits, and savings plans to lower overall tax liability, making it easier to plan for future financial goals.
Βασικές πληροφορίες μαθήματος:
Τελική δήλωση:
A solid understanding of tax systems and planning is essential for financial success. By learning about different taxes and applying strategic planning, users can manage their finances efficiently, reduce tax burdens, and achieve long-term financial stability.
- Different types of taxes, such as income tax, sales tax (VAT), corporate tax, and capital gains tax, play vital roles in government revenue generation. These taxes fund public services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure, making them crucial for societal welfare.
- Income tax essentials include progressive tax brackets, deductions, and credits, which affect the amount of tax individuals owe. Properly using deductions and credits, such as those for mortgage interest or charitable donations, can reduce taxable income and lower tax bills.
- Advanced tax strategies like tax-deferred accounts (e.g., 401(k) in the U.S., RRSP in Canada) allow individuals to save more effectively by deferring taxes until withdrawal in retirement. Managing capital gains, estate planning, and utilizing charitable contributions also contribute to lower tax liabilities.
- International tax planning is important for individuals with global income sources. Double taxation agreements help avoid paying taxes twice on the same income, while strategic charitable giving can reduce taxable income and support personal causes.
- Professional advice and digital tools can enhance tax planning. Consulting tax professionals and using online tools can simplify the process, ensuring that users take full advantage of available tax benefits and stay compliant with global tax regulations.