Παγκόσμια: Μέτρηση Μεταβλητότητας, Διαχείριση Κινδύνου και Διαφοροποίηση
Στόχοι Μαθήματος:
- Understand how volatility is measured using tools like standard deviation and beta. You’ll learn how these numbers show how much an investment’s price moves and what that means for your portfolio’s risk level.
- Explore the role of diversification in managing risk. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, και countries, you reduce your chances of losing money due to problems in one area.
- Learn why rebalancing your portfolio is important. This helps you stay on track with your goals and risk level, especially after big market changes.
- Discover how global ETFs can simplify diversification. You’ll see how different types of ETFs—broad market, sector-specific, regional, and bond ETFs—can help you create a strong, balanced investment portfolio.
- Gain insight into global market hours. Understanding how different countries’ stock market times compare to U.S. trading hours can help you better manage your investments across time zones.
A. Volatility Measurement, Risk Management, and Diversification
Διαποικίληση is one of the most effective strategies for managing volatility and mitigating risk in global stock markets. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors reduce their exposure to the risks associated with any single stock or market. This strategy is essential for long-term portfolio stability and growth, especially in the face of unpredictable market fluctuations.
- Volatility Measurement: Volatility is a key consideration when assessing the risk associated with different investments. Investors use metrics like standard deviation και beta to gauge the potential price fluctuations of individual stocks or broader markets:
- Τυπική απόκλιση: A statistical measure that indicates how much a stock’s returns deviate from its average return. A high standard deviation suggests greater volatility.
- Βήτα: A metric that compares a stock’s volatility to the overall market. Stocks with a beta greater than 1 are more volatile than the market, while those with a beta less than 1 are less volatile.
- Risk Management Principles:
- Diversification Across Asset Classes: By holding a mix of αποθέματα, δεσμούς, εμπορεύματα, and other asset classes, investors can protect their portfolios from the volatility of any single market. For instance, when stock markets experience a downturn, bonds may provide a more stable return.
- Geographic Diversification: Investing across global markets further reduces risk, as economic conditions vary between regions. For example, an economic slowdown in one country may be offset by growth in another, balancing portfolio performance.
- Sector Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple sectors—such as technology, healthcare, and energy—protects investors from industry-specific risks. For example, if the technology sector underperforms, gains in the healthcare or energy sectors can help stabilize the portfolio.
- Επανεξισορρόπηση: Regularly adjusting the portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation helps mitigate risk, particularly after significant market fluctuations. This ensures the portfolio remains aligned with the investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Global ETFs for Diversification: Διαπραγματεύσιμα Αμοιβαία Κεφάλαια (ETF) are powerful tools for achieving diversification across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. Global ETFs provide exposure to a wide range of assets, allowing investors to diversify their portfolios with ease:
- Broad Market ETFs: These track major indices like the MSCI World Index ή FTSE All-World Index, offering exposure to companies across multiple countries and sectors.
- Sector-Specific ETFs: Investors can target specific sectors, such as technology, financial services, ή healthcare, through ETFs that focus on these industries globally.
- Regional ETFs: Investors can diversify across different regions by using ETFs that focus on specific areas, such as Asia-Pacific, Europe, ή emerging markets.
- Bond ETFs: In addition to stock ETFs, bond ETFs allow investors to diversify into fixed-income assets, reducing overall portfolio risk, especially during periods of stock market volatility.
- Volatility and Diversification: While individual stocks may experience significant volatility, diversification through global ETFs helps reduce overall portfolio volatility. By holding a variety of assets that don’t move in the same direction at the same time, investors can smooth out returns and reduce the impact of any single market downturn.
- ETFs vs. Individual Stocks: Unlike individual stock investments, which are highly concentrated and susceptible to market volatility, ETFs provide instant diversification by holding a basket of securities. This makes them an ideal investment vehicle for risk-averse investors who want to minimize the impact of market fluctuations.
Benefits of Global Diversification:
- Reduced Risk: Spreading investments across different regions and sectors limits exposure to country-specific or sector-specific risks.
- Improved Return Potential: Global diversification enables investors to capture growth from various parts of the world, including emerging markets, which often have higher growth rates than developed economies.
- Currency Diversification: Investing globally also exposes portfolios to different currencies, which can act as a hedge against local currency devaluation.
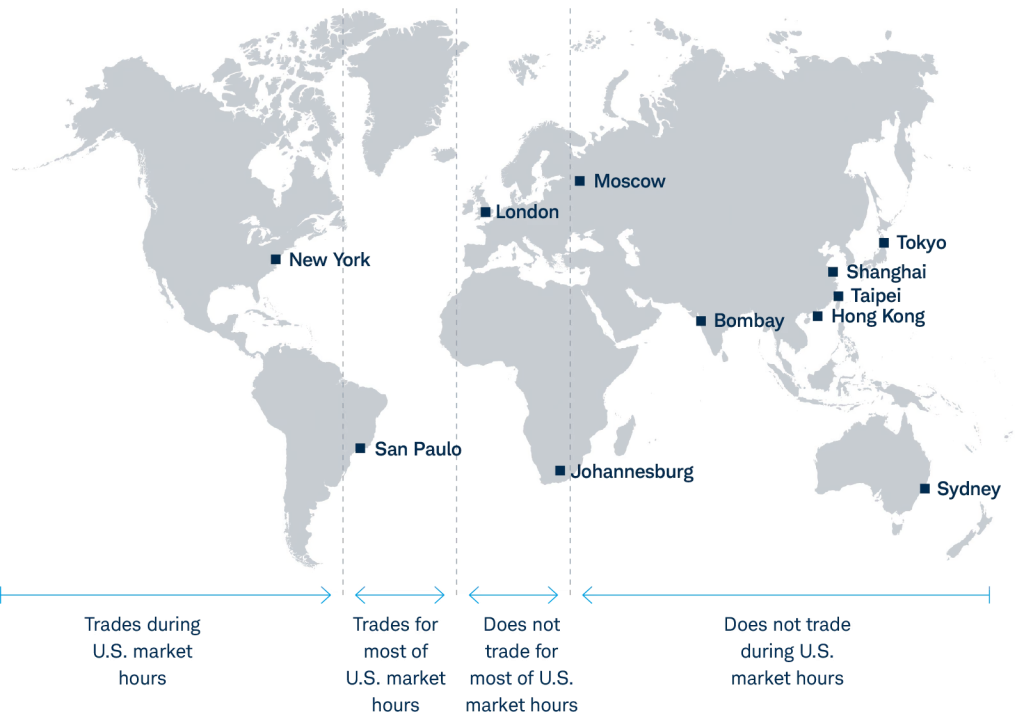
Εικόνα: Global Stock Markets and U.S. Market Trading Hours
Περιγραφή:
The map presents a global view of major stock markets and their relation to U.S. market trading hours. It categorizes the world’s financial centers into three groups based on their trading times relative to U.S. market hours: markets that trade during U.S. hours, markets that trade for most of U.S. hours, and markets that do not trade for most of U.S. hours. For example, New York και São Paulo trade during U.S. market hours, while Λονδίνο overlaps significantly with U.S. hours. Conversely, Tokyo, Shanghai, και Sydney do not overlap with U.S. market hours.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- New York και São Paulo fully align with U.S. market hours, making them prime locations for real-time trading.
- Λονδίνο overlaps with U.S. trading hours, allowing for partial coordination.
- Asian markets σαν Tokyo, Shanghai, και Sydney do not trade during U.S. hours, indicating separate trading cycles.
- Understanding these time zone differences is crucial for investors interested in global market dynamics.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
This map is useful for investors who engage in global trading and want to understand how different stock market hours overlap with U.S. trading times. It provides insights into market accessibility, helping investors plan trading strategies that account for time zone differences and potential price movements in international markets.
συμπέρασμα
Diversification is a key strategy for managing volatility and risk in both global and European stock markets. While global markets follow universal risk management principles, such as asset allocation and volatility measurement, European investors must also consider region-specific factors like ECB policies and political risks. By incorporating diversified ETFs and applying effective risk management techniques, investors can navigate market volatility and enhance the stability of their portfolios, ensuring long-term growth despite economic fluctuations.
Βασικές πληροφορίες μαθήματος:
- Volatility is measured using standard deviation and beta. Standard deviation shows how much an investment’s return moves from its average, while beta compares the investment’s risk to the whole market. These tools help you understand how risky your investments are.
- Diversification reduces the risk of big losses. By investing in different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and commodities, and across various sectors και countries, you avoid putting all your money in one place. This can help your portfolio stay stable even when one area performs poorly.
- Rebalancing keeps your investments aligned with your goals. When some investments grow or shrink faster than others, rebalancing helps you return to your target mix of assets. This is especially important after major market swings.
- Global ETFs are a smart way to diversify. You can invest in broad market ETFs that cover many countries, sector ETFs for specific industries, or regional ETFs that focus on areas like Europe or Asia. Bond ETFs also provide more stable income, especially during times of stock market volatility.
- ETFs are less risky than individual stocks. Unlike a single stock that can rise or fall sharply, ETF include many investments in one, making them better suited for people who want to reduce volatility.
Τελική δήλωση:
Managing risk and reducing volatility are key parts of long-term investing. This section shows how using διαποικίληση, volatility tools, και global ETFs can help you build a safer and more stable portfolio.

