Τοπικό: Κατανόηση του Χρηματοοικονομικού Αλφαβητισμού και των Δικαιωμάτων των Καταναλωτών στην ΕΕ
Στόχοι Μαθήματος:
Εισαγωγή:
This section focuses on financial literacy, consumer rights, and personal data management in the EU. By understanding these concepts, users can manage financial data securely, assert their rights as consumers, and build confidence in financial decisions.
- Securely Manage Personal Financial Data: Learn how to protect personal financial information in digital environments by understanding the risks of data breaches, χρησιμοποιώντας encryption, and implementing strong access controls. This helps users prevent unauthorized access and maintain privacy.
- Understand Consumer Rights in Financial Services: Gain knowledge of consumer rights in the EU, including data privacy, e-commerce protections, και redress mechanisms. This enables users to identify unfair practices, request corrections, and use available dispute resolution tools.
- Enhance Financial Literacy through Tools and Resources: Εξερευνήστε διάφορα financial tools (e.g., budget calculators, investment platforms) and educational resources to improve decision-making. This objective emphasizes using reliable tools and resources to plan budgets, manage debts, and increase savings.
- Build Confidence in Financial Decision-Making: Understand how to critically assess financial advice, use digital advisory tools, and share financial knowledge with others. This helps users make informed financial choices and positively influence others’ financial literacy.
Εισαγωγή
Understanding financial literacy, consumer rights, and data management are critical skills in today’s digital financial landscape. As the use of digital financial services grows, it becomes increasingly important to stay informed about the tools, resources, and protections available. This chapter focuses on managing personal financial information securely, knowing your rights as a consumer in the EU, improving financial literacy, and building confidence in financial decision-making through both local and global perspectives.
Security and Personal Data Management in Financial Services
In today’s digital world, managing personal financial data securely is essential. Financial consumers must be aware of the security implications of storing sensitive financial documents and personal data online.
- Storing Financial Documents Online: Consumers should understand the risks of storing financial documents on cloud platforms or personal devices. These risks include the potential for data breaches, cyberattacks, or unauthorized access to sensitive information. It is crucial to use secure storage options that provide encryption and multi-factor authentication to protect personal data.
- Παράδειγμα: When storing bank statements ή loan documents online, individuals should ensure that their storage service uses industry-standard encryption and that access is limited to authorized users only.
- Παράδειγμα: When storing bank statements ή loan documents online, individuals should ensure that their storage service uses industry-standard encryption and that access is limited to authorized users only.
- Personal Information Used by Financial Service Providers: Financial companies may collect and store personal data for several reasons, including personalizing offers, tracking behavior (e.g., loan repayment history), or assessing risk. Consumers need to understand that financial institutions can use personal data, such as driving behavior in telematics insurance, to infer price sensitivity or tailor product offers.
- Παράδειγμα: An individual using a telematics-based car insurance policy should be aware that the insurer collects data on their driving habits to adjust premiums based on driving behavior.
- Παράδειγμα: An individual using a telematics-based car insurance policy should be aware that the insurer collects data on their driving habits to adjust premiums based on driving behavior.
- Consequences of Disclosing Personal Data: Sharing personal data—such as identification numbers, bank account details, or addresses—carries significant financial risks, especially when done through unsecured digital channels. This data can be used for fraudulent purposes if intercepted by cybercriminals. Individuals should carefully assess the necessity of disclosing personal data and ensure they are dealing with reputable financial service providers.
- Tip: Always verify the identity of any financial institution before providing personal data and avoid sharing sensitive information via unencrypted emails or unsecured websites.

Figure: Safeguarding Personal Information in Financial Institutions
Περιγραφή:
The figure illustrates five key strategies financial institutions should adopt to safeguard personal information. Starting with the implementation of strong access controls, it emphasizes the importance of encrypting sensitive data και regularly updating systems to maintain security. The image also highlights the need for employee training to ensure awareness and regular security audits to identify potential risks and maintain data integrity.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Strong access controls are essential to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Encryption helps protect data by making it unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Regular updates and patches keep systems secure from vulnerabilities.
- Employee training raises awareness and prepares staff to handle data safely.
- Security audits help detect weaknesses and ensure continuous improvement in data security measures.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
These practices are crucial for financial institutions to protect customer data and build trust. By understanding these strategies, businesses can minimize risks associated with data breaches and comply with regulatory standards. This information is valuable for anyone learning about κυβερνοασφάλεια in the financial sector.
Financial Consumer Rights and Responsibilities
As a financial consumer in the EU, individuals have several rights that protect them when purchasing financial products or using financial services. At the same time, consumers also have certain responsibilities to ensure they make informed decisions.
- Rights to Data and Privacy: Consumers have the right to control their personal data, especially in a financial context. This includes the right to revoke authorizations for financial service providers to access or store data when no longer necessary.
- Παράδειγμα: If an individual has closed an account with a financial provider, they should ensure the provider no longer retains unnecessary personal information, such as bank account details or transaction history.
- Παράδειγμα: If an individual has closed an account with a financial provider, they should ensure the provider no longer retains unnecessary personal information, such as bank account details or transaction history.
- Consumer Protection in E-Commerce: With the rise of online transactions, consumers should be aware of their rights in digital commerce. This includes the right to full price disclosure, return policies, και refund conditions. Consumers should carefully review the terms and conditions before making any online purchases.
- Payment and Bill Management: In case of unauthorized payments or errors in billing, consumers have the right to request corrections or refunds. Additionally, individuals should be aware of their rights and responsibilities when they fail to pay bills, such as utilities or taxes, including the consequences and available dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Παράδειγμα: A consumer in the EU who finds an unauthorized payment on their bank statement should report it to their bank immediately and request a refund or investigation into the issue.
- Παράδειγμα: A consumer in the EU who finds an unauthorized payment on their bank statement should report it to their bank immediately and request a refund or investigation into the issue.
- Redress Mechanisms: If a consumer feels they have been treated unfairly by a financial service provider, they have access to redress mechanisms, συμπεριλαμβανομένων out-of-court dispute resolution services και online dispute resolution (ODR) tools. These resources help resolve conflicts without the need for costly legal procedures.

Figure: The Dispute Resolution Journey
Περιγραφή:
The figure outlines the six key steps in the process of resolving a dispute related to financial transactions. Starting with discovery, where a customer notices an issue, it progresses through merchant contact και complaint filing if the problem isn’t resolved. The process involves collecting evidence, an investigation by the card issuer, and concludes with a resolution. Each step reflects a common sequence followed to address disputes, showing how emotions and actions evolve throughout the journey.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Discovery begins when a customer identifies a charge issue, sparking the need for resolution.
- Merchant contact can prevent disputes if issues are resolved early between the customer and retailer.
- Filing a complaint is necessary if direct contact fails, moving the issue to a formal dispute stage.
- Providing evidence is critical, as customers must substantiate their claims to move forward.
- Resolution determines the final outcome, impacting customer satisfaction and business relationships.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding this dispute resolution process is essential for consumers and businesses alike. Customers can learn how to effectively raise disputes, while businesses can improve their handling of transaction issues to maintain trust and reduce chargebacks. This process is valuable knowledge for anyone managing financial transactions and aiming to ensure smooth, fair dealings.
Improving Financial Literacy
Improving financial literacy is an ongoing process that can significantly enhance financial well-being. Individuals need access to reliable information, educational resources, and tools to make informed financial decisions.
- Financial Education Sources: There are numerous sources of financial education, συμπεριλαμβανομένων government websites, independent financial advisors, και non-profit organizations focused on financial literacy. However, consumers should verify the impartiality of these sources before relying on them, as some financial education materials may contain marketing or promotional content disguised as educational resources.
- Financial Tools: Digital tools, such as budget calculators, αριθμομηχανές στεγαστικών δανείων, και επενδυτικές πλατφόρμες, can help consumers plan and manage their finances. Using these tools empowers individuals to make better financial decisions by providing real-time insights into spending patterns, loan repayment schedules, και επενδυτικές αποδόσεις.
- Παράδειγμα: An individual in the Netherlands might use a mortgage calculator to determine how changes in interest rates would impact their monthly mortgage payments, allowing them to make informed decisions about refinancing.
- Παράδειγμα: An individual in the Netherlands might use a mortgage calculator to determine how changes in interest rates would impact their monthly mortgage payments, allowing them to make informed decisions about refinancing.
- Life-Long Financial Learning: Financial literacy is not a one-time activity but rather a life-long learning process. Consumers should develop the habit of staying informed about changes in financial products, services, and regulations. Building personal financial knowledge helps individuals adapt to new challenges, such as changing market conditions, tax reforms, or technological advancements in financial services.
- Seeking Financial Advice: Sometimes, it is necessary to seek professional financial advice, especially for complex financial decisions like investing, tax planning, or retirement savings. Consumers should know the difference between independent advice (which is objective and not influenced by product commissions) and non-independent advice (which may be influenced by incentives or partnerships with product providers).
- Παράδειγμα: A consumer may consult a financial advisor to help them navigate their retirement savings options. They should clarify whether the advisor is providing independent advice to ensure objectivity.

Figure: The Useful Resources and Tools to Help You with Asset Selection
Περιγραφή:
The figure lists seven essential resources and tools for effective asset selection. These include financial planning software, risk assessment tools, fundamental analysis resources, technical analysis tools, asset allocation models, investment research platforms, και robo-advisors. Each tool serves a specific purpose, from understanding risks to analyzing market trends, and can be instrumental in making informed investment decisions.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Financial planning software helps create comprehensive investment strategies based on individual financial goals.
- Risk assessment tools are crucial for evaluating the risk associated with various assets.
- Fundamental and technical analysis tools enable deeper insights into market trends and asset performance.
- Asset allocation models assist in diversifying investments, optimizing returns, and minimizing risks.
- Ρομποτικοί σύμβουλοι provide automated investment guidance, making it easier for users to manage portfolios.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
These tools can be used by επενδυτές to build diversified and well-analyzed portfolios. By leveraging the right resources, investors can make more informed decisions, minimize risks, and align their investments with their οικονομικοί στόχοι. These tools are also beneficial for beginners to get a structured start in asset selection and management.
Confidence in Financial Decision-Making
Building εμπιστοσύνη in financial decision-making is a key goal of financial education. Consumers should be empowered to take control of their financial future by applying lessons learned from previous experiences and making informed choices.
- Critical Thinking and Evaluation: Consumers should critically assess financial advice και educational resources before acting on them. This involves verifying the source, checking for potential biases, and comparing multiple sources of information to get a complete picture.
- Sharing Financial Knowledge: Financially literate individuals are not only able to manage their own finances effectively but can also pass on their knowledge to others. Whether it’s advising family members, discussing financial options with friends, or engaging in financial education communities, sharing knowledge contributes to broader financial literacy.
- Using Digital Advice Tools: In addition to traditional financial advice, consumers now have access to robo-advisors και hybrid financial advisory tools. These platforms combine automated investment algorithms with human advice to provide cost-effective, tailored financial guidance. Consumers should feel confident in using these tools while understanding their limitations and the importance of independent verification.
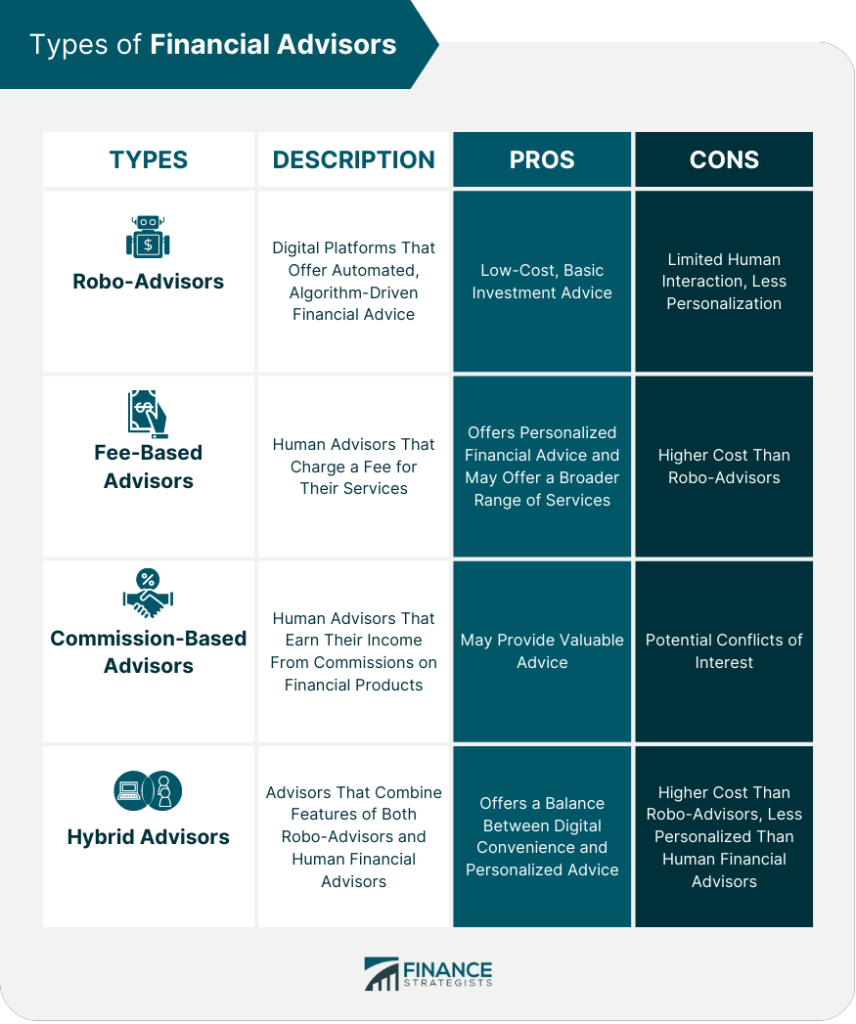
Figure: Types of Financial Advisors
Περιγραφή:
The figure provides an overview of four types of financial advisors: Robo-Advisors, Fee-Based Advisors, Commission-Based Advisors, και Hybrid Advisors. It highlights the description, pros, and cons of each type, allowing readers to understand their differences. Robo-Advisors are automated platforms, while Fee-Based and Commission-Based Advisors are human advisors with different payment models. Hybrid Advisors offer a combination of both automated and human elements, providing a balance between cost, convenience, and personalization.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Robo-Advisors προμηθεύω low-cost, automated financial advice but may lack personalized interaction.
- Fee-Based Advisors προσφορά personalized advice with a wider range of services, though they tend to have υψηλότερο κόστος.
- Commission-Based Advisors can offer valuable advice, but πιθανές συγκρούσεις συμφερόντων may arise due to commission structures.
- Hybrid Advisors combine the benefits of digital tools and human interaction, though they may be more expensive than pure Robo-Advisors.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Κατανοώντας το types of financial advisors helps individuals choose the right advisory model based on their επενδυτικοί στόχοι και προϋπολογισμός. Investors can weigh the benefits of automation vs. human interaction to determine which option provides the most value for their needs.
Βασικές πληροφορίες μαθήματος:
- Managing Personal Data: Financial data should be stored securely with strong access controls και encryption. Avoid sharing personal information over unsecured channels to prevent fraud or identity theft. By being aware of data risks and using protective measures, users can maintain privacy and security.
- Consumer Rights and Protections: EU consumers have rights related to data privacy, full price disclosure, and access to dispute resolution for financial transactions. These rights help ensure fairness and transparency in financial services, empowering consumers to act confidently and responsibly.
- Using Financial Tools: Εργαλεία όπως budget calculators, αριθμομηχανές στεγαστικών δανείων, και επενδυτικές πλατφόρμες provide practical insights into personal finances. These tools enable users to understand spending patterns, estimate loan repayments, and plan for future financial goals effectively.
- Improving Financial Literacy: Ongoing education and reliable financial advice are crucial for making informed decisions. Consumers should verify the source of information to avoid biases, use multiple resources, and adapt to changes in financial products and services.
- Building Confidence in Decisions: Users can build confidence by understanding different types of οικονομικούς συμβούλους (e.g., robo-advisors, fee-based, commission-based, hybrid). By choosing the right advisory model and sharing knowledge with others, individuals can strengthen their financial literacy and influence positive outcomes in personal finance.
Τελική δήλωση:
Understanding financial literacy, consumer rights, and data management is essential for navigating today’s digital financial landscape. By applying these concepts, users can make secure, informed, and confident financial decisions.

