Τοπικά: Κατανόηση του Συνταξιοδοτικού Σχεδιασμού στο Πλαίσιο της ΕΕ
Στόχοι Μαθήματος:
Εισαγωγή: This section provides an overview of retirement planning in the EU, emphasizing the importance of early saving, understanding different pension systems, and how to balance compulsory and optional savings. The aim is to help individuals create a well-rounded plan for long-term financial security.
- Understand the importance of early retirement planning and how it benefits long-term financial security. You will learn how starting early can maximize the impact of compound interest, making it easier to reach retirement goals.
- Learn the differences between state, occupational, and individual pension schemes in the EU. By understanding these options, you will be better equipped to balance compulsory and optional savings to create a comprehensive retirement plan.
- Identify strategies for managing pension contributions and withdrawals. This will help you know when to adjust savings and how to optimize retirement income, considering factors like annuities and lump sum options.
- Explore sustainable investment options, such as ESG-focused funds, and how they can align with personal values while contributing to long-term financial growth.
Εισαγωγή
Retirement planning is an essential component of long-term financial security, especially in the EU, where public pension systems vary across countries. This chapter highlights the importance of early retirement planning and explores the different types of pensions available, including state pensions, occupational schemes, and individual retirement accounts. Understanding how to balance compulsory and optional savings, manage pension contributions, and leverage digital tools is crucial for creating a well-rounded retirement plan. Additionally, the chapter provides insights into managing retirement payouts, incorporating sustainability preferences, and exploring strategies like leveraging home equity to ensure financial stability throughout retirement.
Importance of Early Retirement Planning
Planning for οικονομική ασφάλεια beyond working age is crucial, and individuals should start saving for retirement as early as possible. By beginning to save in their youth, individuals can benefit from ανατοκισμός, which allows their savings to grow exponentially over time. The earlier individuals begin saving, the easier it becomes to achieve financial stability in retirement.
It’s essential to balance current spending with long-term retirement goals. While maintaining a certain standard of living during one’s working years is important, it’s equally important to set aside sufficient funds for the future.

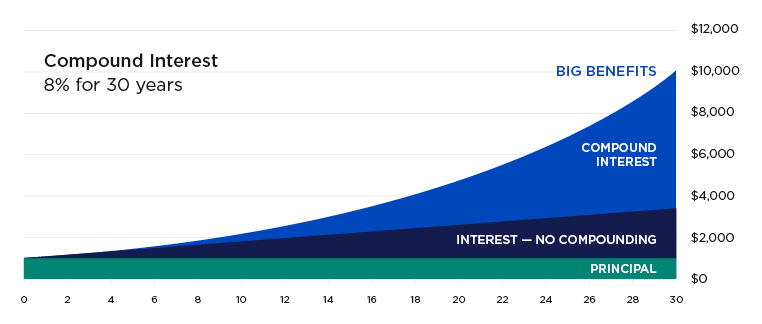
Figure: Compound Interest: 8% for 30 years
Περιγραφή:
The graph illustrates the growth of an initial investment over 30 years at an 8% interest rate. It compares the accumulation of wealth through ανατοκισμός έναντι simple interest (no compounding). The graph clearly shows how compound interest leads to significantly larger growth over time as both the principal and previously earned interest generate further interest.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Ανατοκισμός helps your money grow faster because it earns interest on both the principal and accumulated interest.
- ο longer the time period, the greater the benefits of compounding, shown by the curve’s steep increase over the years.
- Simple interest generates less overall growth since it only earns interest on the initial principal amount.
- Investing early allows more time for the benefits of compounding to accumulate, leading to much higher returns.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Κατανόηση ανατοκισμός is crucial for investors as it highlights the importance of starting early and allowing investments to grow over time. By reinvesting earnings, individuals can μεγιστοποίηση των αποδόσεων and build wealth more efficiently.
Understanding State and Private Pensions
In the EU, most countries offer a κρατική σύνταξη to ensure a basic level of income during retirement. The amount of the state pension is typically determined by the number of years of contributions and the level of earnings during one’s working life. However, relying solely on a state pension may not provide sufficient income to maintain the desired standard of living in retirement.
- State Pensions: Individuals should know who is entitled to a κρατική σύνταξη and how much they are likely to receive. This information is important for calculating how much additional savings or pension income will be required to achieve financial security.
- Ιδιωτικές Συντάξεις: Besides state pensions, there are private pension schemes available, such as επαγγελματικές συντάξεις (provided through employers) and individual pension plans (chosen by individuals). Occupational schemes may be compulsory in some countries, or employees may be automatically enrolled with the option to opt out, depending on local laws. Individual schemes offer more flexibility but require personal responsibility to manage and contribute.
It’s important to understand the difference between compulsory και optional retirement savings as well as between occupational schemes (through employers) and individual schemes. For example, in countries like the UK and Germany, employees are often automatically enrolled in workplace pension schemes, which can help ensure retirement savings.
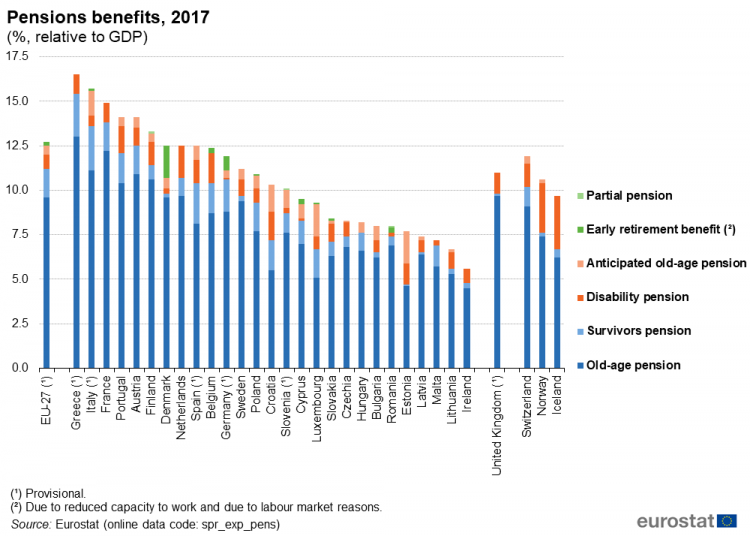
Figure: Pensions benefits, 2017 (% relative to GDP)
Περιγραφή:
The graph illustrates the proportion of GDP that various EU countries, as well as some non-EU nations, allocate to different types of pension benefits in 2017. The categories include old-age pensions, disability pensions, survivor pensions, anticipated old-age pensions, early retirement benefits, και partial pensions. Countries like Greece, Italy, and France have the highest percentage of GDP dedicated to pension benefits, while nations such as Iceland and Ireland have much lower allocations.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Old-age pensions are the largest component of pension spending across most countries, indicating a significant focus on retirement benefits.
- Χώρες όπως Ελλάδα και Ιταλία have pension expenditures over 15% of their GDP, the highest among those shown.
- Non-EU countries σαν Ισλανδία και Ελβετία allocate lower percentages of GDP to pensions compared to many EU states.
- Early retirement benefits και partial pensions are less common, with small contributions to overall pension expenditure.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding the allocation of GDP to pension benefits helps investors gauge economic priorities και οικονομική σταθερότητα in different regions. Higher pension spending can indicate an aging population and potential future economic pressures. This data is useful for evaluating long-term investment opportunities and assessing the οικονομική υγεία of countries.
Compulsory vs. Optional Retirement Savings

In many countries, individuals are required by law to participate in compulsory retirement savings schemes, either through their employment or as part of national social security programs. However, there are also optional retirement savings plans that individuals can voluntarily contribute to in addition to these compulsory schemes. Understanding the difference between the two is essential for effective retirement planning.
- Compulsory Retirement Savings: In countries with compulsory pension systems, individuals must contribute a portion of their income to a national pension scheme ή occupational pension scheme through their employer. The contributions are usually deducted automatically from salaries, with both employees and employers contributing to the pension fund.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Γερμανία, employees are required to contribute to the statutory pension insurance scheme, which provides basic retirement benefits. Both employers and employees make contributions based on the employee’s earnings.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Γαλλία, contributions to the mandatory pension system are deducted from wages and managed by the social security system (Caisse Nationale d’Assurance Vieillesse – CNAV).
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Γερμανία, employees are required to contribute to the statutory pension insurance scheme, which provides basic retirement benefits. Both employers and employees make contributions based on the employee’s earnings.
- Optional Retirement Savings: These are additional voluntary contributions made by individuals to private or individual retirement accounts. Optional plans allow individuals to supplement the compulsory pension with additional savings, often benefiting from tax advantages. Optional savings are typically more flexible, allowing individuals to choose how much to contribute and which financial products to invest in.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα the UK, while employees are automatically enrolled in an occupational pension (which they can opt out of), they can also open a private pension like a Self-Invested Personal Pension (SIPP), where they have more control over investment choices.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Ισπανία, individuals can voluntarily contribute to private pension plans in addition to the public pension system to boost retirement income. These contributions often receive tax benefits.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα the UK, while employees are automatically enrolled in an occupational pension (which they can opt out of), they can also open a private pension like a Self-Invested Personal Pension (SIPP), where they have more control over investment choices.
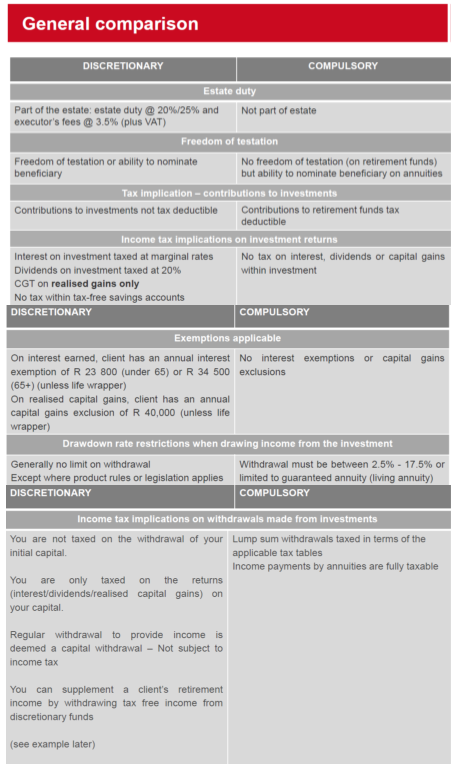
Figure: General Comparison Between Discretionary and Compulsory Investments
Περιγραφή:
This table compares discretionary and compulsory investment types, highlighting differences across aspects such as estate duty, freedom of testation, φορολογικές επιπτώσεις, και income tax on investment returns. Discretionary investments are part of the estate and incur estate duties, while compulsory investments are not. Contributions to discretionary investments are not tax deductible, unlike compulsory retirement funds. Income generated from discretionary investments is subject to taxes, whereas compulsory investments may benefit from tax exemptions.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Estate duty applies to discretionary investments but not to compulsory ones.
- Freedom of testation allows investors in discretionary funds to nominate beneficiaries freely, whereas this is restricted for compulsory funds.
- Tax deductibility is only available for contributions to compulsory retirement funds.
- Income from discretionary investments is subject to taxes, while compulsory investments can enjoy tax benefits on interest, dividends, and capital gains.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding these differences helps investors make τεκμηριωμένες αποφάσεις about where to allocate their money, depending on φορολογικά οφέλη, estate planning, και επενδυτικοί στόχοι. This knowledge is useful for structuring investments to minimize tax liabilities και μεγιστοποίηση των αποδόσεων με την πάροδο του χρόνου.
Occupational vs. Individual Retirement Schemes
- Occupational Pension Schemes: These are employer-sponsored pension plans where employees and employers make regular contributions toward the employee’s retirement. Occupational pension schemes are either compulsory or voluntary depending on the country. In some countries, employees are automatically enrolled in a workplace pension but have the option to opt-out if they choose. These schemes often include αντίστοιχες συνεισφορές from the employer, which incentivizes employees to participate.
- Defined Benefit Plans: Some occupational pensions, like defined benefit (DB) schemes, guarantee a specific monthly payment in retirement based on factors like salary and years of service. These plans are typically found in the public sector or large companies.
- Defined Contribution Plans: Others, like defined contribution (DC) plans, do not guarantee a specific payout but instead accumulate contributions that are invested to grow over time. The retirement income from these plans depends on the amount contributed and the investment performance.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα the Netherlands, employers are required to provide employees with επαγγελματικές συντάξεις, which are often defined benefit schemes. Employees cannot opt out, and both employers and employees contribute to the pension.
- Defined Benefit Plans: Some occupational pensions, like defined benefit (DB) schemes, guarantee a specific monthly payment in retirement based on factors like salary and years of service. These plans are typically found in the public sector or large companies.
- Individual Pension Schemes: These are personal retirement savings plans that individuals set up independently of their employer. Individual pension plans allow for more flexibility and control, as individuals can choose their own contribution levels and investment options. These plans are particularly useful for self-employed individuals or for those who want to supplement their occupational pensions.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Γερμανία, individuals can contribute to a Riester pension ή Rürup pension, both of which offer tax incentives to encourage retirement savings. These are especially useful for people who are self-employed or looking to enhance their retirement income beyond compulsory schemes.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Ιρλανδία, individuals can open a Personal Retirement Savings Account (PRSA), a type of individual pension plan that allows them to contribute as much or as little as they wish. These accounts are portable, meaning individuals can continue contributing even if they change jobs.
- Παράδειγμα: Μέσα Γερμανία, individuals can contribute to a Riester pension ή Rürup pension, both of which offer tax incentives to encourage retirement savings. These are especially useful for people who are self-employed or looking to enhance their retirement income beyond compulsory schemes.
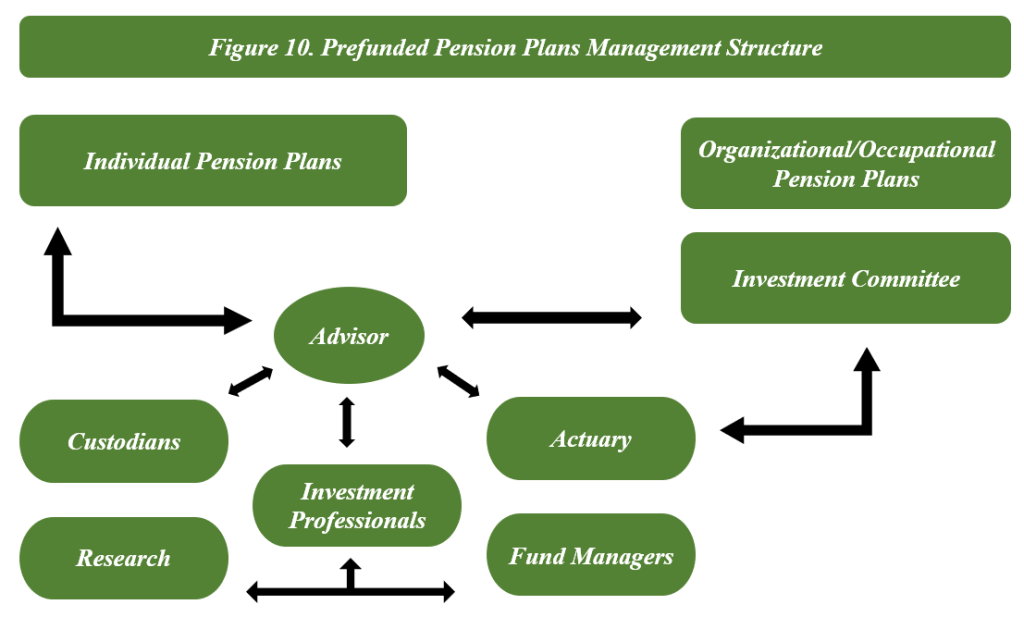
Figure: Prefunded Pension Plans Management Structure
Περιγραφή:
This figure illustrates the structure of prefunded pension plans, showing how different entities and professionals interact within the management of both individual and organizational pension plans. The central role is held by an Advisor, who collaborates with entities such as Custodians, Investment Professionals, Actuaries, και Fund Managers. Το Investment Committee plays a crucial role in guiding investment decisions, while other stakeholders, such as Research teams, provide necessary data and insights.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Advisors are central to the coordination of pension management, ensuring alignment among various stakeholders.
- Investment Professionals and Fund Managers are critical for executing investment strategies and managing funds.
- Custodians ensure the safekeeping of assets, while Actuaries assess financial stability and future obligations.
- Research provides necessary data to inform investment decisions, supporting overall pension management.
- Investment Committees set policies and guide long-term strategies to optimize pension funds.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
This structure helps investors understand how pension funds are managed and the roles of different entities in ensuring the funds’ success. Recognizing these roles can assist individuals in choosing effective pension plans and highlight the importance of comprehensive management for long-term financial security.
Key Considerations for Retirement Planning
- Compulsory Schemes provide a foundation for retirement but may not be sufficient to maintain the desired standard of living. Individuals should assess whether additional optional savings are needed.
- Occupational Pensions: If available through an employer, these pensions often come with significant benefits, including employer matching contributions and automatic enrollment. However, it’s important to understand the specific terms and investment choices associated with these plans.
- Individual Pensions: For those seeking more control over their investments, individual pension schemes offer flexibility and customization. These plans allow individuals to tailor their retirement savings to their personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and preferences for sustainable investments (ESG-focused funds).
By understanding the differences between compulsory and optional schemes and between occupational and individual plans, individuals can make informed decisions about how to structure their retirement savings in line with their long-term financial goals.
Choosing Pension Products and Understanding Risks
When planning for retirement, individuals must choose between various pension products and strategies, taking into account their ανοχή ρίσκου, financial goals, and sustainability preferences. Some may prefer to combine different pension schemes, such as state pensions, employer-provided pensions, and individual retirement savings accounts, to diversify their income sources.
It is also essential to understand the risks associated with withdrawing funds from retirement accounts before reaching retirement age. Borrowing against retirement savings or withdrawing funds early can lead to tax penalties and reduce the overall value of retirement savings.
- Withdrawal Options: Upon retirement, individuals must decide how to draw an income from their pension. Common options include annuities, which provide regular payments, and lump sum withdrawals, which offer more flexibility but come with the risk of running out of savings too quickly.
Example: A person in Spain might choose to withdraw a portion of their pension as a lump sum while leaving the rest in an annuity to ensure a steady income during retirement.
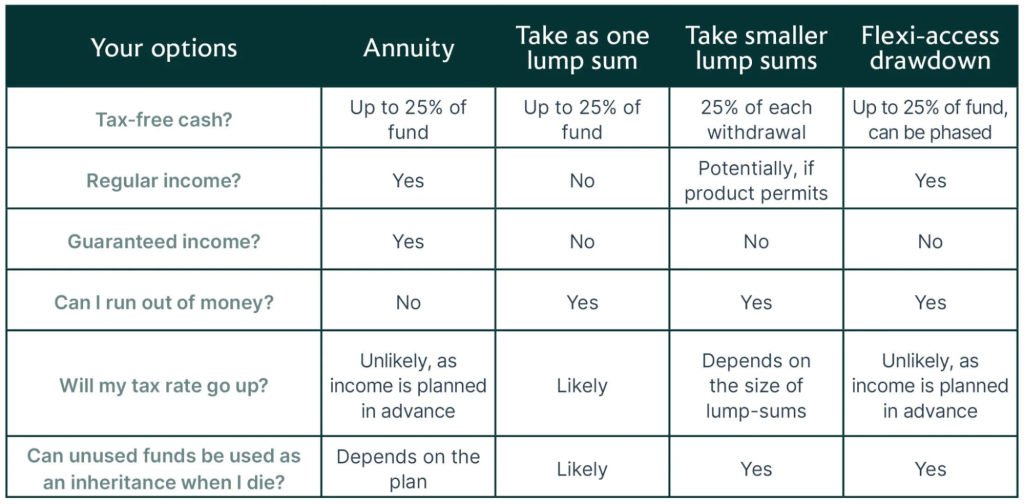
Figure: Your options for accessing pension funds
Περιγραφή:
This table outlines various options for withdrawing pension funds, comparing features such as tax-free cash, regular income, guaranteed income, and the potential risk of running out of money. The options include Annuity, One lump sum, Smaller lump sums, και Flexi-access drawdown, with each method offering different benefits, risks, and tax implications. It helps users understand how each option can affect their retirement planning and income management.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Annuities provide guaranteed income but may limit flexibility.
- Lump sum withdrawals offer quick access to cash but could lead to a higher tax rate and deplete funds faster.
- Flexi-access drawdown allows for phased withdrawals, offering more flexibility in managing income.
- Smaller lump sums can provide periodic access, though may not guarantee regular income.
- Φορολογικές επιπτώσεις vary significantly between these methods, with some increasing the likelihood of running out of funds.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Κατανόηση αυτών pension withdrawal options helps individuals plan their retirement by choosing the method that aligns with their needs, risk tolerance, and tax considerations. Knowing the pros and cons of each option can help retirees balance σταθερότητα εισοδήματος και financial flexibility during their retirement years.
Using Digital Tools for Retirement Planning
Many ψηφιακά εργαλεία are available to help individuals calculate their retirement needs and manage their pension contributions. These tools allow individuals to simulate different retirement scenarios based on their expected income, savings, and lifestyle preferences. Using these tools can help individuals stay on track with their retirement goals and make adjustments as necessary.
For example, an individual in France might use a retirement planning calculator to assess whether their current pension contributions will provide enough income to maintain their desired standard of living after retirement.
Managing Pension Savings and Adjusting Plans
Once a retirement plan is in place, individuals must regularly review and adjust their savings strategies. Factors such as inflation, changes in income, or shifts in financial goals may require adjustments to ensure that enough income will be available in retirement.
In the EU, many countries offer incentives to encourage retirement savings, such as employer matching contributions ή tax advantages. For example, some countries provide tax deductions for pension contributions, which can help reduce taxable income and increase retirement savings.
Additionally, sustainability criteria have become important in the context of pension planning. Many individuals now choose pension products based on Περιβαλλοντικά, Κοινωνικά και Εταιρικά (ESG) factors, ensuring that their savings align with their ethical and sustainability preferences.
- ESG and Sustainability Preferences: It’s essential to assess whether pension products meet personal sustainability criteria. Many pension funds now incorporate βιώσιμες επενδύσεις options, allowing individuals to invest in companies that prioritize environmental and social responsibility. When choosing a pension product, individuals can align their retirement savings with their values by selecting funds that meet Περιβαλλοντικά, Κοινωνικά και Εταιρικά (ESG) standards.
- Making Demands for Sustainability: Consumers should feel confident asking pension providers for more sustainable investment options. If a pension product does not meet personal sustainability criteria, individuals can request better options that align with their ethical standards, such as avoiding funds that invest in fossil fuels or unethical industries.
- Risks of Greenwashing: Individuals must be aware of greenwashing, where pension products or investments falsely claim to be environmentally friendly or socially responsible. Conducting research and asking for transparency from pension providers can help avoid such pitfalls.
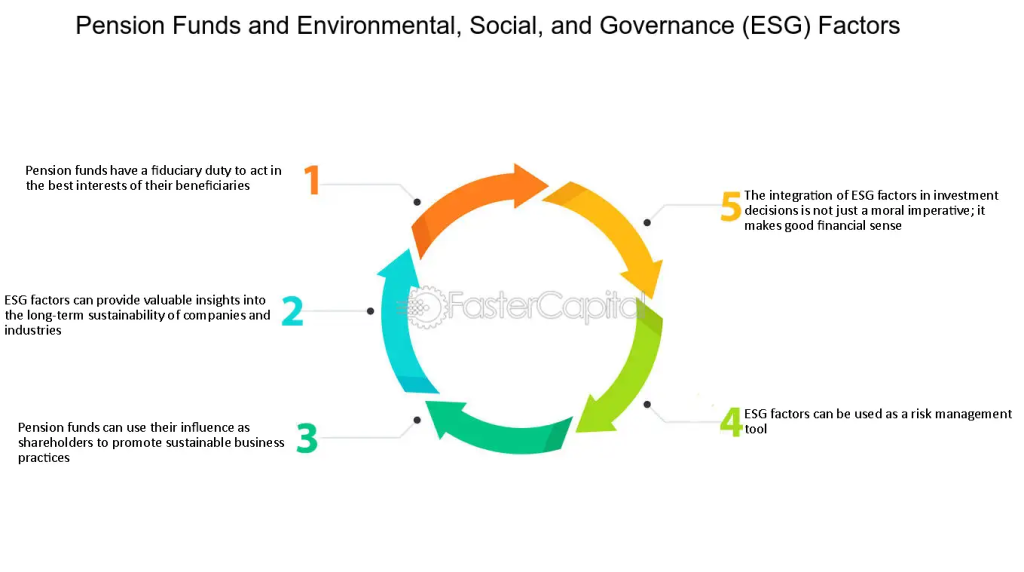
Figure: Pension Funds and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors
Περιγραφή:
This image illustrates the relationship between pension funds and ESG factors. It emphasizes how pension funds have a fiduciary duty to act in their beneficiaries’ best interests, and integrating ESG factors can provide insights into sustainability, promote responsible business practices, and serve as a risk management tool. Additionally, the integration of ESG factors is portrayed as beneficial not just from a moral perspective, but also as a sound financial strategy.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Pension funds have a responsibility to prioritize beneficiaries’ interests, which can be aligned with sustainable investing through ESG.
- ESG factors help identify the long-term viability and sustainability of companies and industries.
- Shareholder influence allows pension funds to encourage sustainable practices.
- ESG considerations serve as a tool for mitigating risks in investment portfolios.
- Integrating ESG factors can make investments both ethically responsible and financially beneficial.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Investors can use the integration of ESG factors to ensure that their portfolios are not only aligned with sustainable and ethical practices but also protected against potential long-term risks. Understanding how pension funds leverage ESG can guide individuals in adopting similar strategies for their own investments, emphasizing both responsible investing και οικονομική σταθερότητα.
Planning for the Pay-Out Phase of Retirement
While much of retirement planning focuses on accumulating savings, it’s equally important to plan for the pay-out phase—the period during which savings are used to fund retirement. Understanding how to structure withdrawals, manage taxes, and balance income streams is crucial to ensuring financial security throughout retirement.
Example: A retiree in the Netherlands may opt to receive a portion of their pension as a fixed monthly payment while keeping some funds in an investment account to continue growing their assets during retirement.
Figure: Understanding Retirement Income Sources
Περιγραφή:
The figure outlines six main sources of retirement income: pensions and annuities, investment income, business ventures and entrepreneurship, social security benefits, employment and part-time work, and rental properties. It highlights how retirees can diversify their income streams by leveraging these different options, thus ensuring financial stability during retirement.
Βασικά συμπεράσματα:
- Pensions and annuities provide a stable income stream that can be planned in advance.
- Investment income allows retirees to earn returns from savings, stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
- Business ventures και επιχειρηματικότητα offer opportunities for continued income and engagement.
- Social security benefits are a key component of retirement income, especially for those without other investments.
- Part-time work can supplement income and keep retirees active and engaged.
- Rental properties can generate passive income and be a valuable asset.
Εφαρμογή πληροφοριών:
Understanding these diverse sources of retirement income can help individuals plan for a more secure and well-rounded retirement. By identifying and combining different income streams, people can reduce their financial risk and create a more sustainable retirement plan, thus making informed decisions about long-term financial security.
Βασικές πληροφορίες μαθήματος:
- Starting early with retirement planning allows you to benefit from compound interest, which grows your savings faster over time. The longer the investment period, the greater the impact of compounding, making it crucial to begin saving as soon as possible.
- State pensions provide a foundation for retirement income, but they may not be enough to sustain your desired standard of living. Supplementing state pensions with occupational or individual schemes helps create a more secure financial future.
- Compulsory savings are often mandated by law, ensuring a basic retirement income. Optional savings allow for additional flexibility, enabling you to contribute more and have greater control over investment choices.
- Understanding different withdrawal options, such as annuities and lump sums, helps manage retirement income efficiently. Planning withdrawals carefully is essential to ensure that you do not deplete funds too quickly and maintain a stable income.
- Incorporating ESG factors in your pension investments can align financial growth with ethical values, promoting sustainability. However, be cautious of greenwashing, where funds may falsely claim to be environmentally friendly.
Τελική δήλωση: By understanding different pension schemes, managing contributions effectively, and considering sustainable investment options, individuals can build a well-rounded retirement plan that ensures financial stability and aligns with personal goals.