Global: Investment Strategy
Lesson Learning Objectives:
- Understand Value Investing: Learn how to identify undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, including low P/E ratios, dividend stability, and companies in mature industries that offer steady returns.
- Recognize Growth Investing Characteristics: Gain insight into growth investing, which focuses on high-growth stocks with higher P/E ratios and reinvested profits, targeting industries like technology and healthcare for long-term expansion.
- Explore Dividend Investing: Understand the importance of dividend-paying stocks that provide steady income and capital appreciation, and how dividend reinvestment can boost returns over time through compounding.
- Evaluate Key Factors in Dividend Stocks: Learn how to assess dividend yield, payout ratio, and dividend growth to ensure sustainable and reliable income from your investments.
- Identify Industries for Growth and Value: Discover which industries—such as technology, healthcare, financial services, and consumer goods—offer attractive opportunities for both growth and value investors based on market conditions.
Introduction to Investment Strategy
Investment strategies help guide your approach to building a portfolio, based on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and market outlook. Whether you focus on value investing, growth investing, or dividend investing, each strategy offers unique benefits and aligns with different investor objectives. Understanding these strategies allows you to tailor your investments to fit both your short-term and long-term goals.
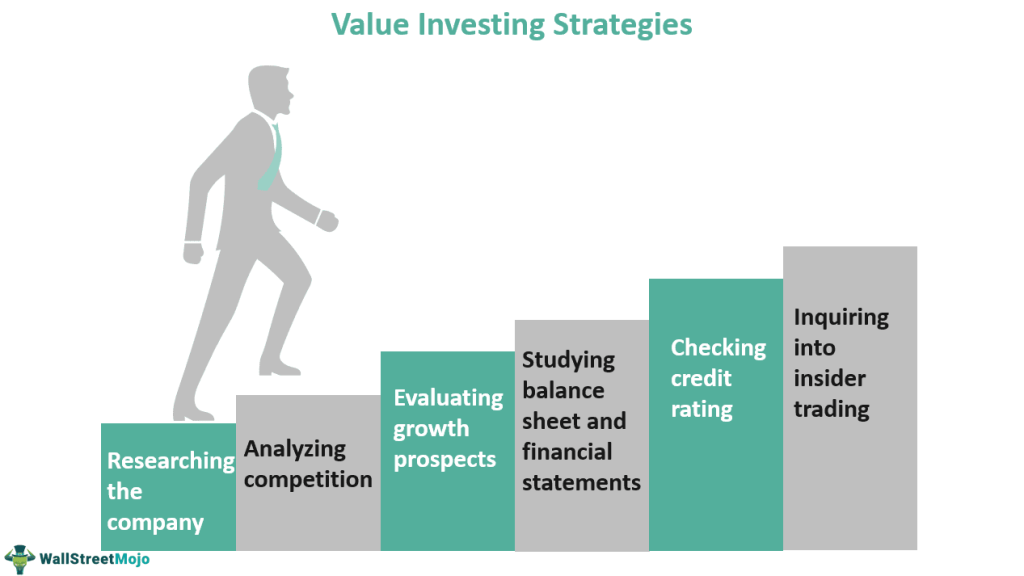
Figure: Steps in Value Investing Process
Description:
The image illustrates key value investing strategies as a step-by-step approach to assessing potential investments. The strategies are presented as steps that investors can take to thoroughly evaluate a company before making an investment decision. These steps include: Researching the company, Analyzing competition, Evaluating growth prospects, Studying balance sheets and financial statements, Checking credit ratings, and Inquiring into insider trading. This structure represents a comprehensive framework for identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals.
Key Takeaways:
- Researching the company is the foundational step, providing insight into the company’s operations and history.
- Analyzing competition helps investors understand the company’s market position and competitive advantages.
- Evaluating growth prospects involves assessing potential for future expansion, revenue, and earnings growth.
- Studying balance sheets and financial statements is crucial for assessing the company’s financial health and sustainability.
- Checking credit ratings offers insights into the company’s creditworthiness and financial risk.
- Inquiring into insider trading can indicate potential signals about the company’s future prospects based on insider behavior.
Application of Information:
Investors can apply these strategies to make informed decisions when selecting undervalued stocks. By thoroughly analyzing these factors, investors can identify companies with strong fundamentals, better manage investment risks, and aim for long-term returns. This framework emphasizes the importance of comprehensive due diligence in value investing.
A. Value Investing
Value investing focuses on finding stocks that are trading for less than their intrinsic value. Investors look for companies that may be undervalued by the market but possess strong fundamentals, such as stable earnings, a healthy balance sheet, and a competitive advantage.
Key characteristics of value stocks include:
- Low price-to-earnings (P/E) and price-to-book (P/B) ratios.
- Strong dividend yields.
- Companies in mature industries that may not be experiencing rapid growth but provide stable returns.
Famous value investors, such as Warren Buffett, have used this strategy to build wealth by purchasing undervalued stocks and holding them long-term as they appreciate in value.
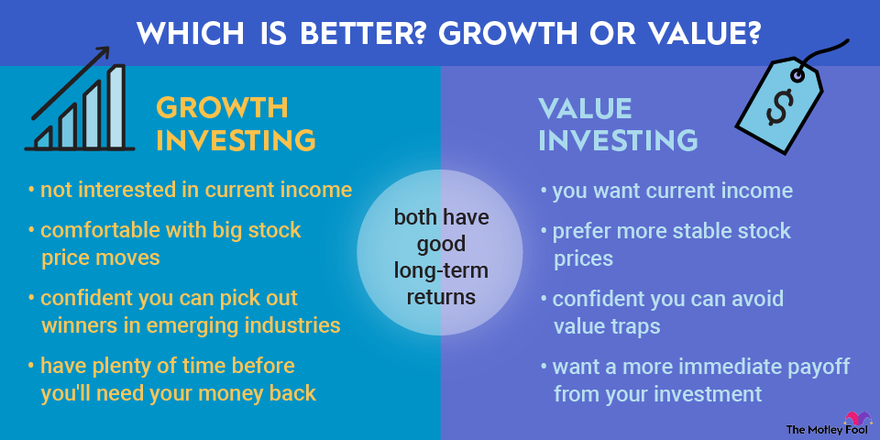
Figure: Which is Better? Growth or Value?
Description:
The image compares growth investing and value investing strategies, detailing their characteristics and goals. Growth investing focuses on stocks with high potential for price increases, often in emerging industries. It involves accepting high volatility and forgoing immediate income, suitable for those with longer investment horizons. In contrast, value investing targets stocks that offer current income, stable prices, and are considered undervalued. This strategy seeks to avoid value traps and prefers more immediate returns. Both approaches aim for good long-term returns but differ in terms of risk tolerance and income expectations.
Key Takeaways:
- Growth investing suits investors comfortable with price volatility, who are focused on high-potential stocks in emerging sectors.
- Value investing attracts those seeking current income, lower volatility, and undervalued stocks with potential for steady returns.
- Both strategies offer long-term return potential, but their success depends on market conditions and investor goals.
- Investors need to choose based on their income needs, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
Application of Information:
Understanding the differences between growth and value investing helps investors align their investment strategy with their personal financial goals. By selecting the right approach, investors can manage risk and achieve desired returns over time. These insights are crucial for building a diversified portfolio that matches both short-term and long-term objectives.
B. Growth Investing
Growth investing targets companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies or the overall market. These stocks are often found in emerging sectors like technology and healthcare, where innovation drives rapid expansion. Growth investors prioritize future potential over current profitability, often accepting higher volatility for the possibility of outsized returns.
Key characteristics of growth stocks include:
- High earnings growth potential.
- Higher P/E ratios than the market average.
- Companies reinvesting profits for expansion rather than paying dividends.
Growth investors aim to capitalize on the increasing revenues and profits of companies in fast-growing industries, though these stocks may experience greater price fluctuations compared to value stocks.
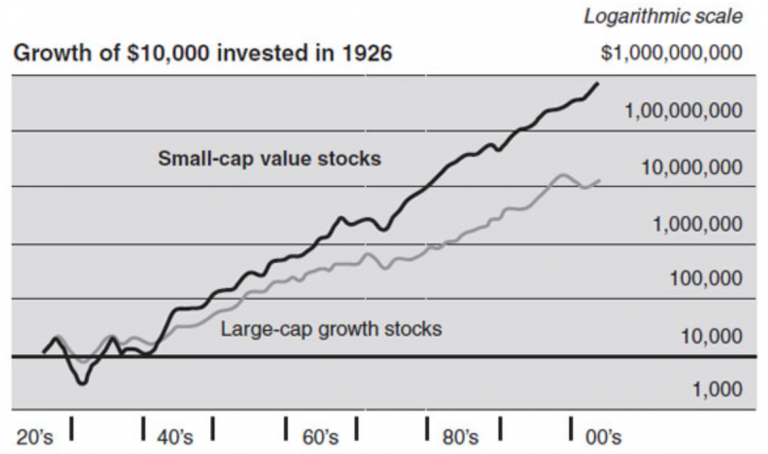
Figure: Growth of $10,000 Invested in 1926
Description:
The graph shows the growth of a $10,000 investment in 1926 over time, comparing the performance of small-cap value stocks and large-cap growth stocks. It uses a logarithmic scale to represent growth, making it easier to visualize significant differences over time. The chart illustrates how small-cap value stocks have outperformed large-cap growth stocks in the long run, growing at a faster rate and reaching a much higher value by the 2000s.
Key Takeaways:
- Small-cap value stocks have historically outperformed large-cap growth stocks over the long term.
- The logarithmic scale highlights exponential growth differences, with small-cap stocks showing higher returns.
- Long-term investment horizons benefit from small-cap value stocks due to their higher compounding growth.
- Growth of $10,000 invested in 1926 illustrates the potential wealth accumulation from different investment strategies.
Application of Information:
This data emphasizes the importance of considering investment type and time horizon when developing a portfolio. Investors seeking higher returns over longer periods may find small-cap value stocks appealing, as they can potentially offer greater compounding. Understanding these historical trends can guide investors in making informed decisions about asset allocation and risk tolerance based on desired returns.
C. Dividend Investing
Dividend investing involves purchasing stocks that regularly pay out a portion of their earnings as dividends. Investors who follow this strategy often seek a combination of steady income and capital appreciation. Dividend stocks are typically associated with stable, established companies that generate consistent cash flows.
Key characteristics of dividend stocks include:
- Regular dividend payouts, often quarterly or annually.
- Lower volatility compared to growth stocks.
- Commonly found in industries like utilities, consumer goods, and financial services.
Dividend investing is popular among investors looking for passive income and those who prioritize cash flow, such as retirees. By reinvesting dividends, investors can also take advantage of compound growth over time.
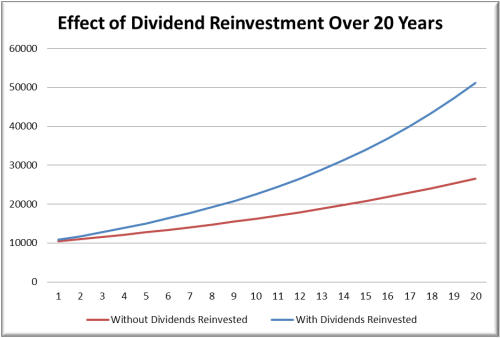
Figure: Effect of Dividend Reinvestment Over 20 Years
Description:
The graph illustrates the impact of dividend reinvestment on investment growth over a 20-year period. It compares the performance of a portfolio where dividends are reinvested (blue line) versus one without reinvestment (red line). The reinvestment strategy shows a significantly higher growth trajectory, highlighting the compounding effect of reinvested dividends, leading to a final value much higher than that of the non-reinvestment strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Dividend reinvestment accelerates portfolio growth over time due to the compounding effect.
- Over 20 years, the strategy of reinvesting dividends leads to a substantially higher final investment value compared to not reinvesting.
- The longer the investment period, the greater the gap in returns between the two strategies.
Application of Information:
Understanding the benefits of dividend reinvestment is crucial for long-term investors aiming to maximize their returns. By reinvesting dividends, investors can take advantage of compounding, potentially leading to greater wealth accumulation over time. This strategy is particularly effective for income-generating stocks and aligns well with a buy-and-hold investment approach.
D. Factors to Consider When Investing in Dividend Stocks
When selecting dividend stocks, investors should consider several factors to ensure a reliable income stream and potential for capital appreciation:
- Dividend Yield: The dividend yield is the annual dividend payment divided by the stock price. A higher yield may be attractive, but it’s important to ensure the dividend is sustainable.
- Payout Ratio: This ratio indicates the percentage of earnings a company uses to pay dividends. A lower payout ratio suggests the company has room to grow its dividend, while a higher ratio might signal that the dividend is at risk of being cut.
- Dividend Growth: Look for companies with a history of regularly increasing their dividend payments. This signals financial strength and a commitment to rewarding shareholders.
- Financial Health: Companies with strong balance sheets and stable cash flow are more likely to maintain or increase dividend payments. Check for metrics like debt levels, profit margins, and earnings consistency.
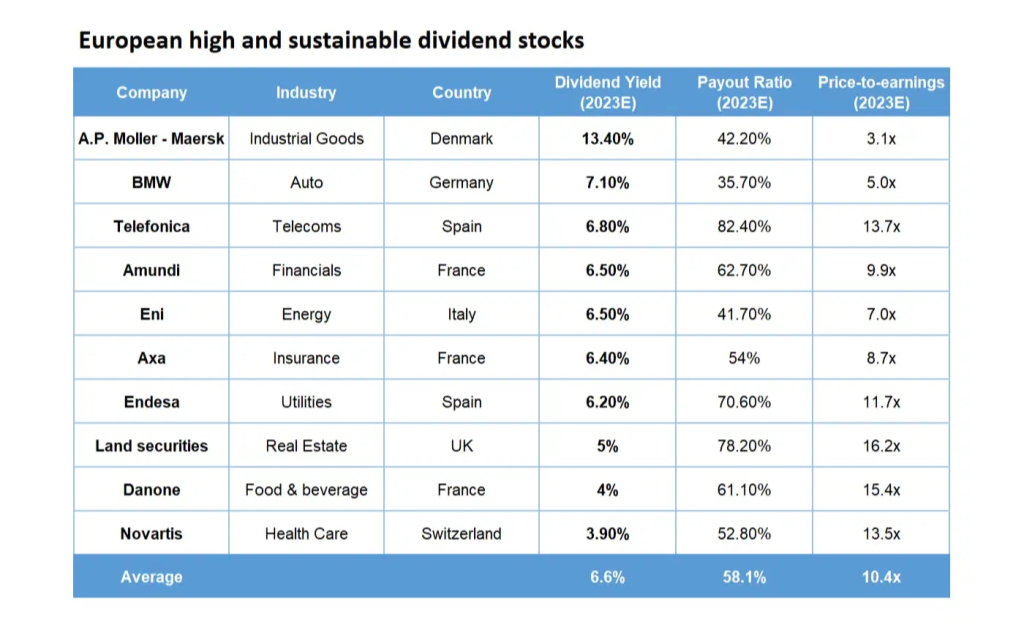
Figure: European High and Sustainable Dividend Stocks
Description:
The table presents a list of European stocks with high and sustainable dividends for 2023. It provides information on each company’s industry, country of origin, dividend yield, payout ratio, and price-to-earnings ratio (P/E). The average dividend yield across these stocks is 6.6%, with a payout ratio of 58.1%, indicating the portion of earnings paid as dividends. The P/E ratio averages 10.4x, reflecting the valuation relative to earnings.
Key Takeaways:
- A.P. Moller – Maersk offers the highest dividend yield at 13.4% among the listed companies.
- The payout ratios vary, indicating different levels of dividend sustainability.
- The P/E ratio provides insight into how each company’s valuation compares to its earnings.
- The average dividend yield of 6.6% suggests these stocks have the potential to generate stable income for investors.
- The industries represented are diverse, including industrial goods, auto, telecoms, financials, energy, insurance, utilities, real estate, food & beverage, and healthcare.
Application of Information:
This table is useful for income-focused investors seeking high dividend yields while ensuring some level of sustainability. It aids in identifying diversified investment opportunities across various industries and countries, potentially enhancing portfolio income and reducing risk.
E. Popular Industries for Growth and Value Investing
Certain industries are particularly attractive for growth and value investors, offering different opportunities based on the strategy:
- Technology: A popular choice for growth investors, the technology sector is known for its innovation and rapid expansion. Companies like Apple, Amazon, and Alphabet consistently deliver strong revenue growth and are key components of growth portfolios.
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector, especially biotech and pharmaceutical companies, offers significant growth potential due to ongoing research and development, aging populations, and rising global healthcare demand. Firms like Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson provide both growth and stability.
- Financial Services: Value investors often turn to financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase and Wells Fargo due to their consistent earnings, attractive valuations, and strong dividend yields.
- Consumer Goods: Companies like Procter & Gamble and Coca-Cola are often favored by value investors due to their market dominance, steady cash flows, and reliable dividends. These companies operate in essential industries with predictable demand.
Conclusion
Investing strategies like value investing, growth investing, and dividend investing offer different approaches to building a portfolio depending on your financial goals and risk tolerance. Value investors seek to buy undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, while growth investors focus on companies with high potential for expansion. Dividend investors prioritize income generation through regular payouts. Understanding the nuances of each strategy and the industries they best apply to can help investors make informed decisions and build a diversified portfolio tailored to their objectives.
Key Lesson Information:
- Value investing targets undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, offering a lower-risk approach for long-term returns. These stocks often come with stable earnings, strong dividends, and low P/E ratios, making them suitable for investors seeking consistent returns over time.
- Growth investing focuses on high-growth stocks with higher P/E ratios. These stocks are expected to grow faster than the market, often found in sectors like technology and healthcare, and are ideal for investors who are willing to accept higher volatility in exchange for higher potential returns.
- Dividend investing offers steady income by investing in companies that regularly pay dividends. This strategy appeals to those seeking passive income, such as retirees, and can benefit from reinvesting dividends to take advantage of compounding growth over time.
- When selecting dividend stocks, investors should consider the dividend yield, payout ratio, and dividend growth to ensure that the dividend payments are sustainable and can grow over time. A low payout ratio suggests room for future dividend increases, while a high payout ratio may signal potential risk.
- Industries like technology, healthcare, financial services, and consumer goods offer excellent opportunities for both growth and value investors. For growth investors, technology and healthcare provide high growth potential, while consumer goods and financial services offer stable earnings and reliable dividends for value investors.
Closing Statement:
Choosing the right investment strategy depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the time horizon for your investments. By understanding value, growth, and dividend investing, you can craft a well-rounded portfolio that suits your needs for income, growth, or stability.


