Global: Cómo tomar decisiones financieras informadas
Objetivos de aprendizaje de la lección:
Introducción:
This section explains how to make informed financial decisions, emphasizing the importance of gathering relevant information and understanding the consequences of each choice. This knowledge can help you manage your finances effectively, whether buying products, investing, or borrowing.
- Understand how to make informed financial decisions by gathering information and analyzing options. This skill is useful for daily purchases, investments, or loans, ensuring that choices are based on facts rather than emotions.
- Learn the steps involved in responsible financial decision-making, from comparing prices and understanding costs to avoiding impulsive decisions. This process helps users manage finances better and achieve long-term goals.
- Gain insights into managing debt effectively, focusing on avoiding high-interest debt, creating a repayment plan, and balancing loans with other financial needs. Understanding debt management is crucial for maintaining financial stability.
- Develop the ability to set and achieve financial goals, both short-term and long-term. Knowing how to categorize goals and create plans for savings and investments is essential for financial success.
A. Making Informed Financial Decisions
Making informed financial decisions involves understanding the risks, rewards, y long-term consequences of various choices. Whether you’re purchasing a product, investing in a stock, or taking out a loan, it’s crucial to gather all relevant information and compare options. This ensures that decisions are based on facts and analysis rather than emotions or external pressures.
For example, when considering whether to buy a car, factors like purchase price, maintenance costs, fuel efficiency, insurance, and financing options should all be evaluated to determine the true cost of ownership. It’s also essential to avoid impulsive purchases and resist the pressure of marketing campaigns that push for immediate decisions without careful thought.
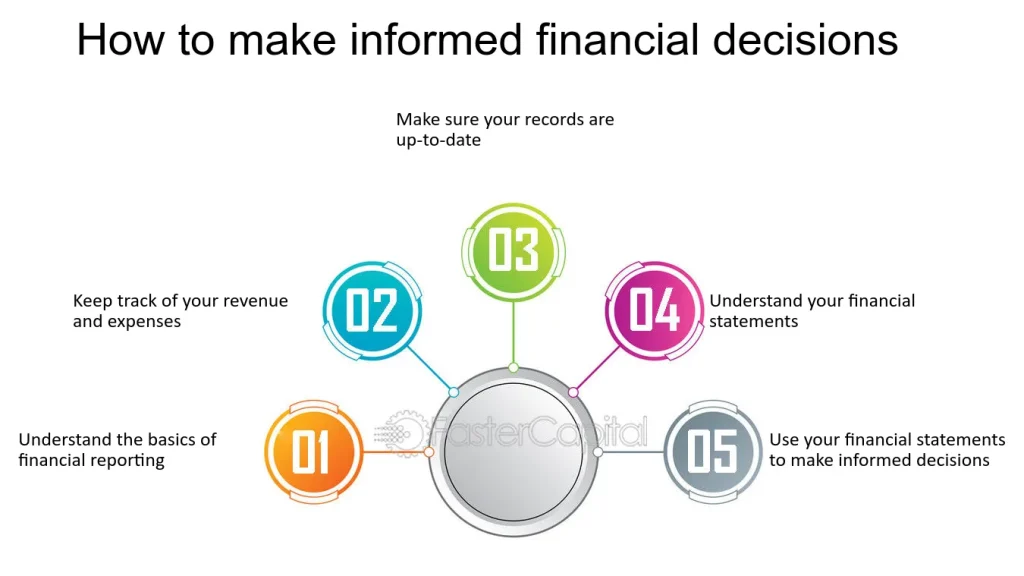
Cifra: How to Make Informed Financial Decisions
Descripción:
This figure outlines the five key steps necessary for making informed financial decisions. It starts with understanding the basics of financial reporting and progresses to keeping track of revenue and expenses, ensuring records are up-to-date, and comprehending financial statements. The final step encourages using the gathered financial information to make decisiones informadas. Each step builds on the previous one, helping individuals improve their financial understanding and decision-making.
Conclusiones clave:
- Entendiendo el basics of financial reporting is the foundation for sound financial decisions.
- Keeping accurate records of revenue and expenses is crucial for financial tracking.
- Ensuring up-to-date records helps individuals and businesses monitor their financial health.
- Interpreting financial statements allows for better analysis of financial performance.
- Using financial data to make decisiones informadas enhances personal and business success.
Solicitud de información:
Applying these steps can help individuals and businesses improve their financial management and make better choices based on accurate data. Whether for budgeting, investing, o strategic planning, understanding and using financial statements is key to maximizing financial outcomes and minimizing risks.
B. Financial Responsibility and Decision-Making
Financial responsibility is about understanding how each financial choice affects both current and future financial health. Being financially responsible means:
- Setting financial priorities: Allocating funds first to essential needs (housing, food, healthcare) before discretionary spending.
- Avoiding unnecessary debt: Only taking on loans or credit when absolutely necessary, and understanding the full cost of borrowing, including interest rates y fees.
- Practicing disciplined saving: Regularly setting aside money for future needs, such as emergencies, education, or retirement.
Financially responsible individuals take the time to analyze their decisions and consider the potential risks, such as job loss o market downturns, that may affect their ability to meet their financial obligations.
C. Managing Debt and Protecting Your Financial Well-being
Debt can be a useful financial tool, but it must be managed carefully to avoid jeopardizing financial well-being. There are several key strategies to manage debt effectively:
- Avoid high-interest debt: Credit card debt, payday loans, or any other form of high-interest borrowing should be avoided as much as possible.
- Pay off high-interest debt first: When dealing with multiple loans, focus on paying off those with the highest interest rates to reduce the total cost of borrowing.
- Create a repayment plan: Having a structured plan for repaying debt, whether it’s through debt consolidation or a simple snowball method, can help keep finances on track.
- Managing debt also means understanding the different types of loans and their impact on personal cash flow. For example, a mortgage is often considered “good debt” because it can build equity, whereas credit card debt is “bad debt” due to its high-interest rates and lack of long-term benefits.
By carefully managing debt, individuals protect their financial well-being and ensure they have resources available for other important life goals, such as saving for retirement or paying for education.
D. Achieving Short- and Long-Term Financial Goals
Setting both short-term and long-term financial goals is a key part of personal finance. Short-term goals may include saving for a vacation, paying off a small loan, o building an emergency fund. Long-term goals often include buying a home, retirement savings, o funding education.
To achieve these goals, it’s important to:
- Set clear, measurable goals: Clearly define what you want to achieve, how much it will cost, and the timeline for achieving it.
- Develop a savings plan: Automate savings if possible, allocating a portion of each paycheck to different goals (e.g., 10% for retirement, 5% for an emergency fund).
- Review progress regularly: Periodically check how well you’re meeting your goals and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Short-term goals require more liquidity (easily accessible cash), while long-term goals can involve investments that grow over time, such as stocks or retirement accounts. Regularly reviewing and updating these goals helps ensure financial success over both the short and long term.
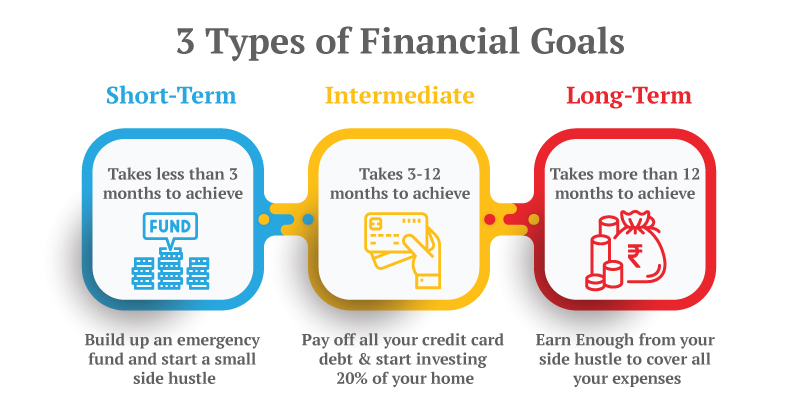
Cifra: 3 Types of Financial Goals
Descripción:
This figure illustrates three types of financial goals: Short-Term, Intermediate, y Long-Term. It highlights the different time frames needed to achieve each goal: less than 3 months for short-term goals, 3-12 months for intermediate goals, and more than 12 months for long-term goals. The image provides examples for each, such as building an emergency fund (short-term), paying off credit card debt (intermediate), and earning enough to cover all expenses through a side hustle (long-term). Each section explains the duration and importance of these financial objectives.
Conclusiones clave:
- Short-term financial goals are achievable in under 3 months, such as saving for an emergency fund.
- Intermediate goals take between 3-12 months, like paying off debts and starting to invest.
- Long-term goals take more than 12 months and include large financial milestones, like ensuring your side hustle covers all expenses.
- Timeframes for financial goals help in setting clear, actionable steps toward financial success.
Solicitud de información:
By categorizing financial goals into short-term, intermediate, and long-term, users can break down their financial planning into manageable segments. This helps prioritize goals based on urgency and timeframe, making it easier to focus on immediate actions while also preparing for future financial needs. Understanding these distinctions is vital for investors and learners in setting realistic goals and achieving financial stability.
Información clave de la lección:
- Making informed financial decisions requires understanding the costs, benefits, and long-term consequences of each choice. Whether buying a product or investing, it’s crucial to gather all relevant information to avoid costly mistakes.
- Financial responsibility involves prioritizing essential needs, avoiding unnecessary debt, and saving regularly. By making careful decisions and considering potential risks, individuals can maintain a healthy financial status and prepare for unexpected changes.
- Effective debt management focuses on minimizing high-interest debt, paying off loans with the highest rates first, and planning repayment. This approach helps individuals reduce borrowing costs and protect their financial health.
- Achieving financial goals involves clear planning and regular progress checks. Short-term goals, like building an emergency fund, need quick access to cash, while long-term goals, like retirement, benefit from investments that grow over time.
- Reviewing financial goals regularly ensures that your plans align with changing circumstances, allowing for adjustments to stay on track. Whether it’s saving for education or buying a home, adapting strategies helps achieve financial stability.
Frase de cierre: Understanding how to make informed financial decisions and manage debt effectively is vital for achieving both short-term and long-term financial goals. By being responsible with your finances, you can ensure a secure and successful financial future.

