Global: Acciones individuales: ¿Quiénes son los ganadores y los perdedores?
Objetivos de aprendizaje de la lección:
- Learn the benefits and risks of investing in individual stocks. You’ll understand how stock-picking gives you control and the potential for higher rewards, but also comes with more risk and the need for careful research.
- Understand what ETFs are and how they offer easy diversification. You’ll see how ETFs give access to many assets in one investment and why they’re a low-cost, flexible option for many investors.
- Explore mutual funds and how professional management can help or hurt performance. You’ll learn how mutual funds work, their advantages in access and management, and their drawbacks like higher fees and limited trading flexibility.
- Gain insights into index investing as a long-term strategy. You’ll understand why tracking a whole market index can provide steady growth, low fees, and lower risk over time.
- See how ETFs can be used for building a full portfolio. You’ll discover how ETFs allow easy access to different sectors and asset classes, helping you customize a low-cost, diversified investment strategy.
A. Individual Stocks: Picking the Winners and Losers
Acciones individuales allow investors to own a share of a single company. This approach can be highly rewarding but also carries significant risks, as the performance of a single stock can be volatile and unpredictable.
Ventajas:
- High growth potential: Individual stocks can provide significant returns if a company performs well.
- Control over investments: Investors can choose specific companies they believe will outperform the market.
- Dividendos: Many companies pay dividends, offering a steady income stream to shareholders.
Contras:
- High risk: Stock prices can be highly volatile, and poor company performance can lead to significant losses.
- Requires research: Successful stock picking requires extensive research and knowledge of the company, industry, and market conditions.
- Lack of diversification: Investing in individual stocks means you’re putting all your eggs in one basket, increasing the risk if the stock underperforms.
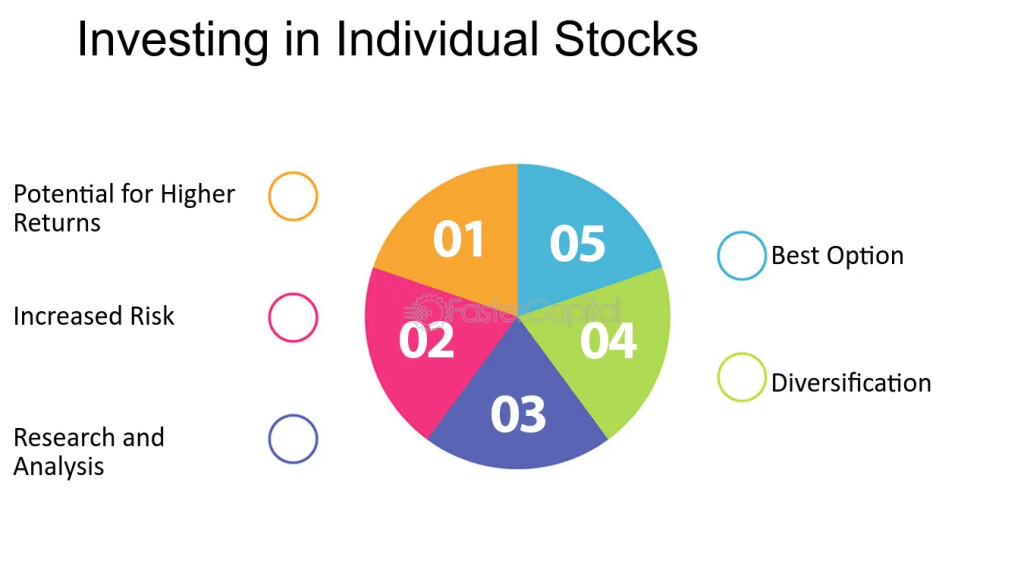
Cifra: Investing in Individual Stocks
Descripción:
This pie chart highlights the five key factors associated with investing in individual stocks: potential for higher returns, increased risk, research and analysis, diversificación, y choosing the best option. Each section represents an essential aspect investors should consider when making decisions about individual stocks.
Conclusiones clave:
- Potential for higher returns is a significant advantage of investing in individual stocks.
- Increased risk is inherent in individual stock investments, requiring careful management.
- Research and analysis are crucial to understanding individual stock performance and market conditions.
- Diversificación helps reduce risk by balancing investments across different stocks.
- Selecting the best option involves evaluating stocks based on performance, risk, and market trends.
Application of Information:
Investors can use this information to understand the benefits and challenges of investing in individual stocks. By focusing on research and diversification, they can manage risks while aiming for higher returns. This framework aids in creating a balanced stock portfolio tailored to an investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
B. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Harnessing the Power of Diversification
ETF are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges, offering exposure to a basket of securities. They can include stocks, bonds, commodities, or a combination of assets, making them a popular choice for diversification.
Ventajas:
- Diversificación: ETFs allow investors to own a broad range of assets, reducing risk by spreading exposure across multiple companies or sectors.
- Liquidez: ETFs are traded throughout the day on exchanges, making them highly liquid and easy to buy or sell.
- Low costs: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them cost-efficient.
- Transparency: ETFs usually track a specific index or asset, making it easy for investors to understand what they’re investing in.
Contras:
- Market risk: While ETFs are diversified, they still reflect the overall market movements, so they can lose value if the entire market declines.
- Lower growth potential: Because ETFs are diversified, they may not offer the same growth potential as high-performing individual stocks.
- Trading fees: Frequent buying and selling of ETFs can incur trading fees, reducing overall returns.
Important Terms to Know:
- Expense Ratio: The annual fee charged by an ETF to cover management and operational costs.
- Tracking Error: The difference between the performance of the ETF and the index it tracks.
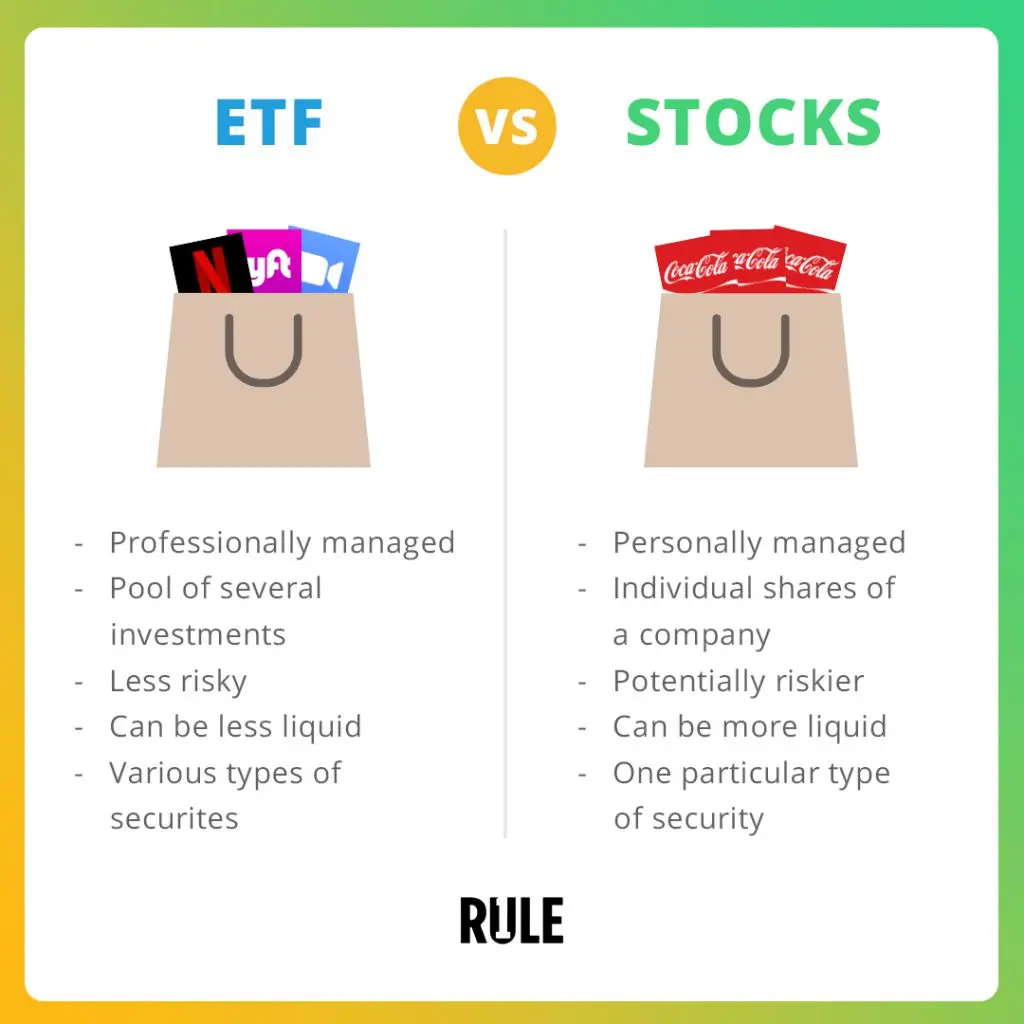
Cifra: ETF vs. Stocks
Descripción:
This image compares ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) y cepo. ETFs represent a professionally managed pool of various investments, making them less risky and more diversified, although they can be less liquid. In contrast, stocks are personally managed investments in individual companies, offering potential for higher gains but with greater risks and better liquidity.
Conclusiones clave:
- ETF are diversified, professionally managed, and generally less risky, but they may offer lower liquidity compared to stocks.
- Cepo involve investing in specific companies, offering potentially higher returns with higher risks y better liquidity.
- ETFs contain various securities, while stocks focus on one company at a time.
Application of Information:
Understanding the differences between ETF y cepo helps investors make informed decisions based on their risk tolerance and investment goals. Those seeking diversification and lower risks may prefer ETFs, while investors aiming for potentially higher returns might focus on individual stocks.
C. Mutual Funds: Letting the Pros Manage Your Money
Los fondos de inversión pool money from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They are actively managed by professional fund managers who aim to outperform the market.
Ventajas:
- Gestión profesional: Mutual funds are managed by experienced professionals who make investment decisions on behalf of investors.
- Diversificación: Like ETFs, mutual funds invest in a variety of assets, reducing risk through diversification.
- Access to a wide range of assets: Mutual funds provide exposure to a wide range of securities, including stocks, bonds, and other assets that may be difficult for individual investors to access.
Contras:
- Higher fees: Mutual funds typically have higher expense ratios due to active management, which can reduce overall returns.
- Less flexibility: Mutual funds are bought and sold at the end of the trading day, so investors cannot take advantage of intraday price movements.
- Underperformance risk: Actively managed funds do not always outperform the market, and in some cases, they can underperform passive investments like ETFs.
Important Terms to Know:
- Net Asset Value (NAV): The per-share value of the mutual fund, calculated at the end of each trading day.
- Load Fees: A commission or sales charge applied when buying or selling mutual fund shares.
Difference Between a Mutual Fund and ETF:
- Trading Flexibility: ETFs trade throughout the day like stocks, while mutual funds are only traded once per day at the closing NAV.
- Cost: ETFs generally have lower fees and are passively managed, while mutual funds often have higher fees due to active management.
- Management Style: ETFs are typically passively managed, tracking an index, while mutual funds are usually actively managed by professionals.


Cifra: ETF Index Funds vs. Mutual Index Funds
Descripción:
This image compares ETF (Exchange-Traded Funds) and Mutual Index Funds. ETFs can be traded at any time during the trading day, while Mutual Index Funds only allow transactions at the end of the day. Regarding taxes, selling an ETF incurs a capital gains tax for the seller, whereas net gains in Mutual Funds are distributed among all investors, leading to a small fraction of capital gains tax even without selling.
Conclusiones clave:
- ETF offer flexibility in trading, while Los fondos de inversión restrict transactions to the end of the day.
- Capital gains tax on ETFs is only applicable to the seller, whereas Mutual Fund investors might incur taxes without selling.
- Both have index fund equivalents offering similar exposure.
Application of Information:
Understanding the differences between ETF y Mutual Index Funds helps investors choose based on trading flexibility, tax implications, y investment goals. Those seeking active trading opportunities might prefer ETFs, while investors who are less concerned with daily trading might opt for Mutual Funds.
D. The Power of Index Investing: Steady Growth and Peace of Mind
Index investing involves investing in a portfolio that tracks a specific index, such as the S&P 500 or the FTSE 100. This strategy allows investors to match the performance of the broader market, providing steady growth over time without the need for active management.
Ventajas:
- Low fees: Index funds and ETFs typically have very low fees compared to actively managed funds, as they simply replicate an index.
- Steady growth: Index investing offers long-term growth by tracking the overall market, which tends to increase in value over time.
- Riesgo reducido: By investing in a wide array of companies, index investing reduces the risk associated with individual stock performance.
E. ETFs for Portfolio Investing: Accessing Multiple Indexes with Ease
ETF designed for portfolio investing provide easy access to multiple indexes, sectors, or asset classes. This allows investors to build a diversified portfolio with minimal effort, using ETFs that target specific markets or strategies.
Ventajas:
- Portfolio diversification: Investors can gain exposure to multiple asset classes and sectors using different ETFs, creating a balanced portfolio.
- Customizable strategy: ETFs provide the flexibility to invest in specific sectors, geographies, or asset classes based on the investor’s goals.
- Cost-efficient: ETFs typically have lower fees than mutual funds, making them an attractive option for building a diversified portfolio.
Contras:
- Market volatility: While ETFs offer diversification, they are still subject to overall market fluctuations, meaning they can lose value during downturns.
- Tracking error: Some ETFs may not perfectly match the performance of the index they are designed to replicate, which could impact returns.
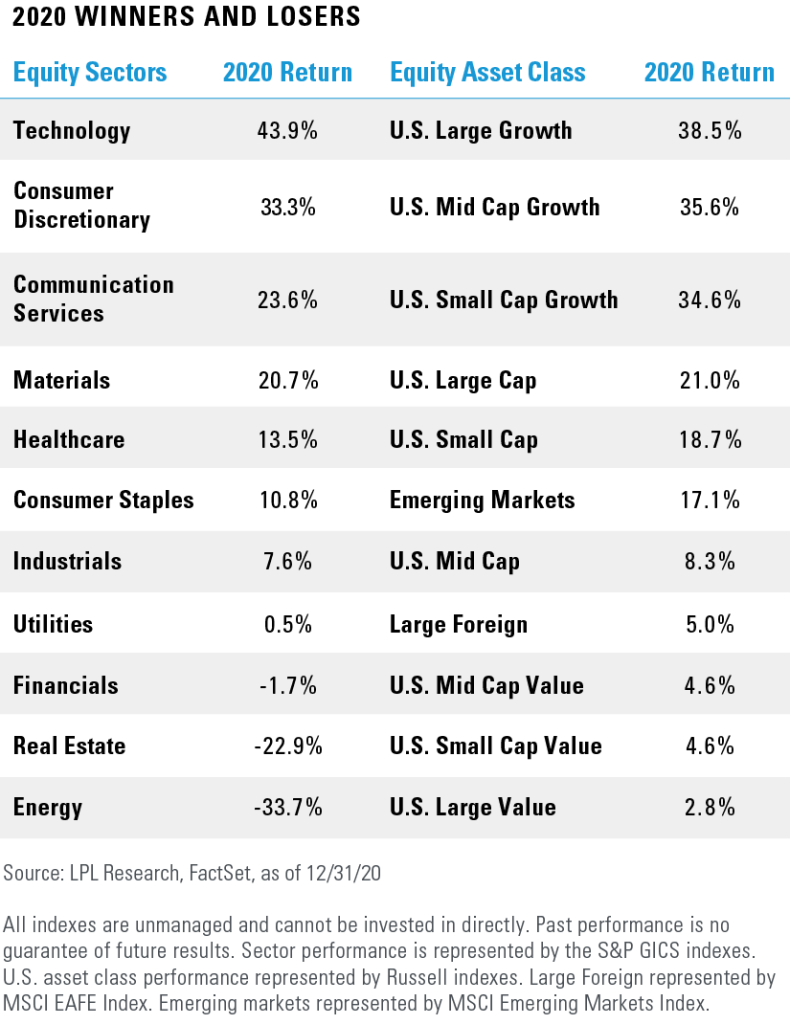
Cifra: 2020 Winners and Losers
Descripción:
This table shows the 2020 performance of various equity sectors and corresponding asset classes. It ranks the sectors based on their returns, with Tecnología leading at 43.9%, followed by Consumer Discretionary at 33.3%. The table also highlights the U.S. Large Growth asset class as a top performer with 38.5% return. At the bottom, Bienes raíces y Energy posted significant negative returns of -22.9% y -33.7%, respectively.
Conclusiones clave:
- Tecnología y Consumer Discretionary were the top-performing sectors in 2020.
- U.S. Large Growth y U.S. Mid Cap Growth were the strongest asset classes.
- Bienes raíces y Energy faced the largest declines among sectors.
- The best returns were generally in growth-oriented sectors and asset classes.
Application of Information:
This data helps investors understand which sectors and asset classes performed well or poorly during 2020, potentially guiding future investment strategies. It can also assist in analyzing market trends during economic downturns or recoveries. Understanding these trends allows investors to make more informed asset allocation decisions based on sector performance y growth potential.
Conclusión
Mastering the art of diversification involves understanding various investment vehicles like acciones individuales, ETF, mutual funds, y index investing. Each vehicle has its own pros and cons, and the best choice depends on the investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. Acciones individuales offer high growth potential but come with greater risk, while ETF y mutual funds provide diversification at a lower cost. Index investing offers steady, long-term growth, while portfolio investing with ETFs provides the flexibility to customize and balance investments across various sectors and asset classes.
Información clave de la lección:
- Acciones individuales offer the chance for high returns y dividends, but come with high risk, especially if the company performs poorly. Picking the right stocks takes time, research, and understanding of the market.
- ETF provide diversificación, liquidity, y low costs. They allow you to invest in many companies or sectors at once, reducing your risk. However, market risk still applies, and frequent trading may lead to extra fees.
- Los fondos de inversión are managed by professionals and give you access to a wide range of assets. But they often come with higher fees, less trading flexibility, and don’t always perform better than simpler investments like ETFs.
- Index investing helps you follow the performance of a market over time. It offers steady growth, low fees, y less risk by investing in many companies at once instead of trying to pick winners.
- ETFs for portfolio investing allow you to build a diversified investment plan using different types of ETFs for specific goals, like investing in sectors, countries, or asset types. They are cost-effective and customizable but can still face market ups and downs.
- Past performance data, like the 2020 sector results, can help investors understand which areas of the market perform well during certain times. For example, Tecnología y Consumer Discretionary led in growth, while Energy y Bienes raíces saw losses. These trends help with future investment planning.
Frase de cierre:
Knowing the differences between stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, and index investing allows you to build a smart and personalized investment plan. These tools can help you balance riesgo, growth, y costs based on your goals and comfort level.

