Local: Estándares crediticios y endeudamiento responsable
Objetivos de aprendizaje de la lección:
Introducción:
This section focuses on understanding the standards of credit and borrowing responsibly. It emphasizes the role of credit in financial planning and highlights strategies to manage borrowing effectively while avoiding over-indebtedness.
- Understand credit and its implications. Learn how credit works, including the impact of interest rates and loan terms, so you can make informed decisions before borrowing.
- Assess the cost of credit. Know how to evaluate the total cost of borrowing by considering factors such as fees, repayment terms, and how borrowing affects your budget.
- Identify alternatives to borrowing. Explore other ways to meet financial needs without immediately turning to credit, helping you save on interest and reduce financial risk.
- Develop confidence in managing credit. Learn how to handle credit responsibly, avoid debt traps, and make informed decisions about when and how to borrow.
- Improve your credit score awareness. Understand how credit scores work, the factors that affect them, and how to maintain or improve your score for better borrowing options.
Introducción
Consumer decision-making plays a crucial role in managing personal finances, especially when it comes to understanding credit and borrowing responsibly. This chapter explores the importance of credit, how to assess its costs, and the potential risks associated with borrowing. It also covers alternatives to borrowing and offers strategies to avoid over-indebtedness. By understanding the different types of credit available and how to manage them effectively, individuals can make informed financial decisions that promote long-term financial health. Confidence in declining unnecessary credit and understanding the impact of credit scores are also key factors in responsible borrowing.
Understanding Credit and its Implications
Credit is a powerful financial tool that, when used responsibly, can help achieve significant goals, such as purchasing a home, funding education, or starting a business. However, it’s essential to understand the long-term implications of taking on credit commitments, particularly how they affect future disposable income. Borrowing money means committing future income to repay the loan, which can limit financial flexibility.
Before taking on any credit, individuals should thoroughly assess their ability to repay. This includes understanding the impact of interés compuesto on the total amount repaid and considering how long the repayment period will be. Knowing whether the interest rate is fixed or variable is crucial, as it affects the overall cost of credit, especially in the face of fluctuating interest rates or inflation.
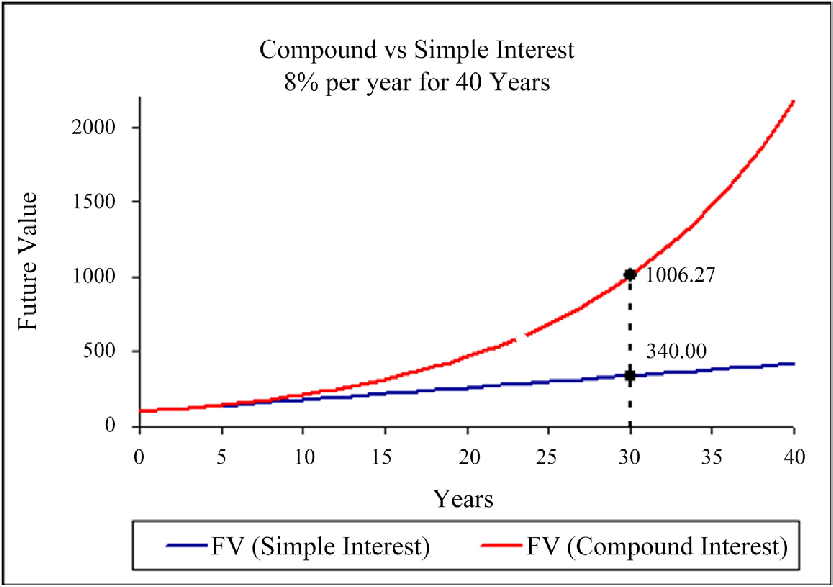
Cifra: Compound vs Simple Interest
Descripción:
The graph compares the future value of investments under compound interest and simple interest over a period of 40 years, with an interest rate of 8% per year. The blue line shows the growth using simple interest, where the value increases linearly, while the red line represents compound interest, which shows exponential growth. After 30 years, the future value with compound interest is significantly higher ($1006.27) compared to simple interest ($340.00).
Conclusiones clave:
- Compound interest results in exponential growth, significantly increasing future value over time compared to simple interest.
- Simple interest grows linearly, accumulating a lesser amount over the same period.
- Over a long period (e.g., 30+ years), the difference between compound and simple interest becomes more pronounced, highlighting the power of compounding.
- Starting early and allowing interest to compound over time can lead to substantial financial growth.
Solicitud de información:
Understanding the benefits of interés compuesto is essential for investors, as it shows the value of reinvesting earnings over time. This concept encourages people to start investing early to take full advantage of compounding, leading to higher returns and financial growth over the long term.
Assessing the Cost of Credit and Borrowing Decisions
When deciding whether to borrow money, it’s important to consider the total cost of credit, not just the interest rate. Additional factors like loan fees, repayment terms, and potential penalties for early or late payments can significantly affect the cost. Moreover, individuals should differentiate between using credit to generate or increase future income or wealth (e.g., investing in education or property) versus using credit for consumption (e.g., purchasing non-essential goods).
Before making a borrowing decision, individuals must assess the likelihood of being able to repay the loan within their current budget and future financial situation. This involves taking into account both the cost of credit y el cost of the item being purchased.
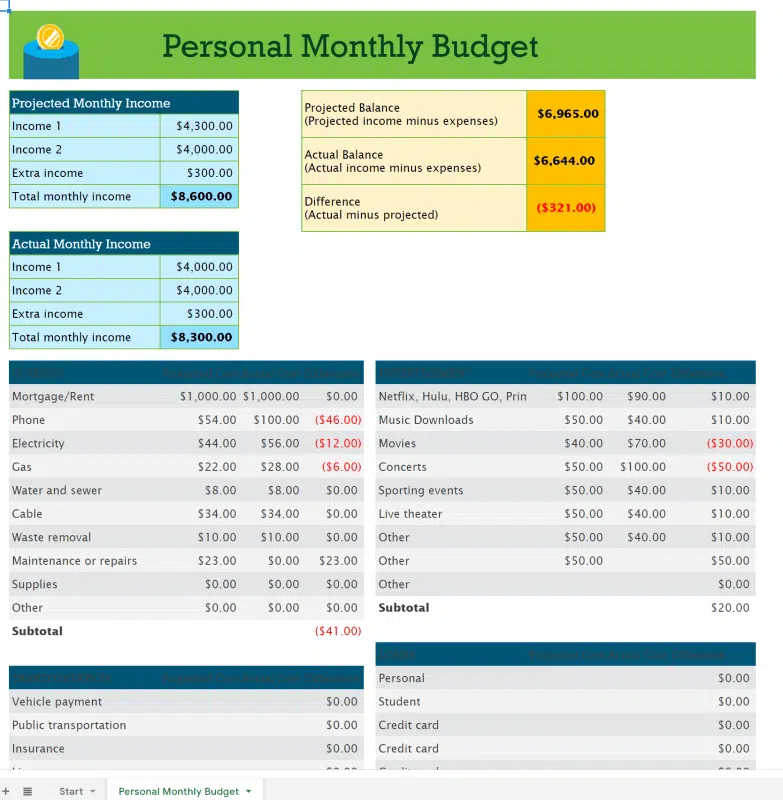
Figure: Personal Monthly Budget
Descripción:
The figure displays a monthly budget that compares projected income and expenses to actual figures. It breaks down different categories such as essential expenses (e.g., rent, utilities) and discretionary spending (e.g., entertainment, phone). It shows a comparison between planned and actual expenses, highlighting variances that may require attention to manage personal finances effectively.
Conclusiones clave:
- Projected vs. Actual Income: The figure highlights the differences between expected and actual monthly incomes, showing a lower actual income than projected.
- Expense Tracking: Detailed comparisons between planned and actual spending help identify where expenses exceeded expectations, such as phone and concert costs.
- Financial Variances: The budget includes calculations for over or under-spending, showing where adjustments might be needed for better financial control.
- Overall Balance: The actual balance is lower than the projected balance, leading to a net difference of -$321.
Solicitud de información:
This budget layout helps users monitor their spending habits, identify overspending, y make necessary adjustments to meet financial goals. It emphasizes the importance of comparing projected and actual figures to maintain control over one’s budget, which is useful for individuals learning to manage their personal finances effectively.
Alternatives to Borrowing
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Rather than immediately turning to credit, individuals should explore alternative options such as saving, leasing, o joint ownership. In many cases, saving up for a purchase can reduce or eliminate the need to borrow, avoiding interest costs and minimizing financial risk. For smaller, short-term needs, other support systems, such as community assistance o social safety nets, can also be valuable alternatives to borrowing.
Being motivated to consider the consequences of accessing credit before making a decision can prevent impulsive borrowing and help maintain financial stability in the long term.
Using Credit with Caution and Avoiding Over-Indebtedness
In today’s digital age, easy-access credit, such as online loans or “buy now, pay later” offers, has become increasingly common. However, such credit products often come with high interest rates y hidden fees that can quickly lead to over-indebtedness.
To avoid falling into debt, individuals must:
- Carefully evaluate the full cost of high-interest, easily accessible credit before committing.
- Be aware that interest-free offers can turn into costly credit if the full balance is not repaid by the end of the promotional period. Consumers must ensure they can repay the loan in full before interest kicks in or be prepared for the financial consequences.
- Decline unwanted credit that is offered with purchases, especially if the credit is not necessary or financially wise. For example, retailers may offer store credit cards or financing options at checkout to incentivize larger purchases, but these often come with higher-than-average interest rates.
Entendiendo el potential risks of online credit offers and being confident in rejecting such credit products when unnecessary helps prevent individuals from accumulating debt.
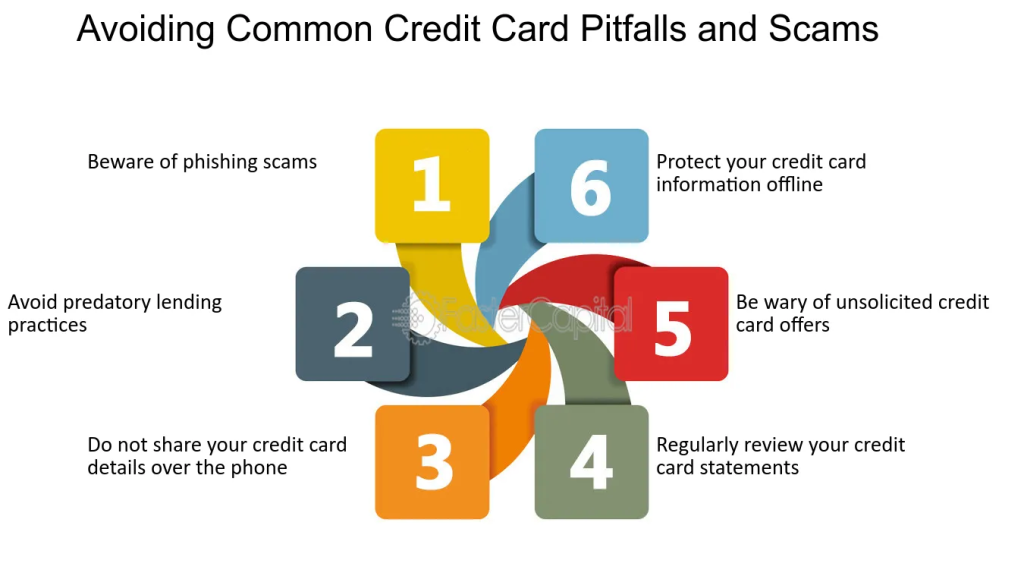
Figure: Avoiding Common Credit Card Pitfalls and Scams
Descripción:
The figure highlights six key strategies to protect oneself from common credit card scams and pitfalls. These include avoiding phishing scams, not sharing credit card details over the phone, and being cautious of unsolicited offers. It also emphasizes regularly reviewing statements, avoiding predatory lending practices, and protecting credit card information both online and offline. These tips aim to safeguard users from fraud and financial risks.
Conclusiones clave:
- Avoid phishing scams to prevent unauthorized access to your credit card information.
- Do not share sensitive details over the phone, especially if the call was unsolicited.
- Be cautious of unsolicited credit card offers that may lead to scams or unfavorable terms.
- Regularly review credit card statements to catch any suspicious activities early.
- Protect your credit card information offline and online to prevent theft and misuse.
- Avoid predatory lending practices by understanding the terms and conditions of credit card offers.
Solicitud de información:
Users can apply these strategies by monitoring their credit card usage, being aware of common fraud tactics, y maintaining security protocols for their personal information. This information is useful to reduce financial risks y build better credit management habits.
Understanding Different Types of Credit
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
There are various types of credit available, each with different purposes, advantages, and risks. Common credit products include:
- Tarjetas de crédito: Convenient but often have high interest rates if balances are not paid in full each month.
- Mortgages: Used for purchasing property, typically secured by the asset being purchased, and can offer lower interest rates over a long term.
- Personal loans: Unsecured loans that may have higher interest rates but are useful for larger purchases or consolidating debt.
- Rotating credit facilities: Allow ongoing access to credit up to a set limit, but can be costly if used frequently or for extended periods.
It’s important to choose credit products carefully, considering factors such as the interest rate, inflation rate, total cost of credit, and the flexibility of the repayment terms. Using comparison tools to evaluate the different features of credit products ensures that individuals make informed decisions.
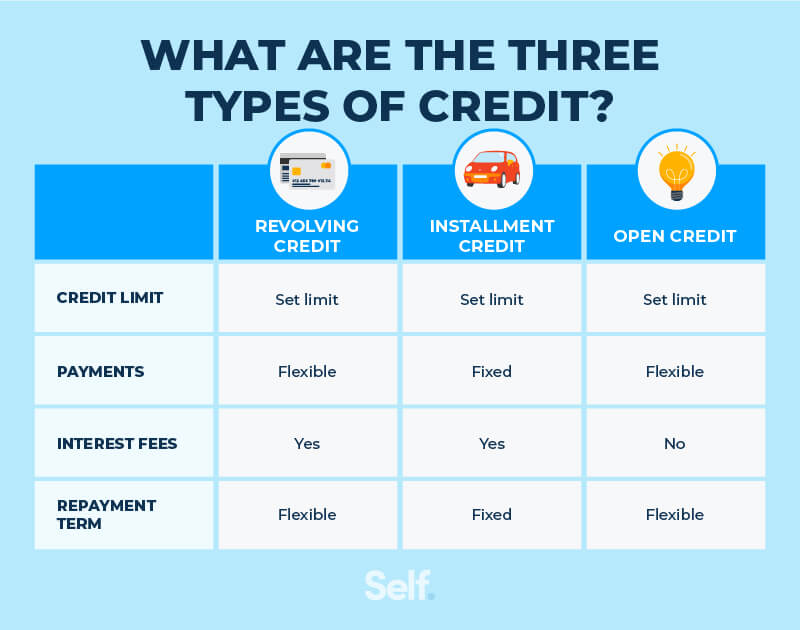
Cifra: What Are the Three Types of Credit?
Descripción:
The figure explains the three types of credit: revolving credit, installment credit, and open credit. It details each type by highlighting key features such as credit limit, payment flexibility, interest fees, and repayment terms. Revolving credit (like credit cards) has flexible payments and a set limit, while installment credit (like loans) involves fixed payments. Open credit allows borrowing up to a set limit but does not charge interest.
Conclusiones clave:
- Revolving credit offers flexibility in payments but usually comes with interest fees.
- Installment credit requires fixed payments over a set term, typically used for loans.
- Open credit does not charge interest and is flexible but still has a limit.
- Understanding repayment terms helps users choose the right type of credit for their needs.
Solicitud de información:
Knowing the differences between credit types helps users manage borrowing y make informed financial decisions. For example, understanding interest fees y repayment terms can guide someone when deciding between using a credit card or taking out a loan.
Credit Providers and the Role of Guarantors
Credit providers may sometimes require a guarantor—a person who agrees to cover the loan payments if the borrower defaults. While this can be a way to secure credit, it carries social and financial implications for both parties. It’s important to carefully consider the responsibilities of becoming a guarantor or asking someone to be one, as it can impact personal relationships and financial well-being.
Some credit providers may also require collateral to secure a loan, such as a house or car, which can be repossessed if payments are not made. Understanding the risks associated with secured loans is crucial for managing credit responsibly.
Credit Scoring and Access to Credit
Credit scores play a key role in determining an individual’s eligibility for credit y el cost of borrowing. A higher credit score can result in lower interest rates and more favorable loan terms, while a low credit score can lead to higher costs or even credit denial. Credit scores are calculated based on factors such as payment history, outstanding debt, y length of credit history.
It’s important for individuals to know how to access their credit score y credit report, and to regularly check for discrepancies that could negatively affect their creditworthiness. Additionally, understanding how certain behaviors, such as late payments o maxing out credit cards, can impact credit scores allows individuals to take steps to improve their credit score over time.
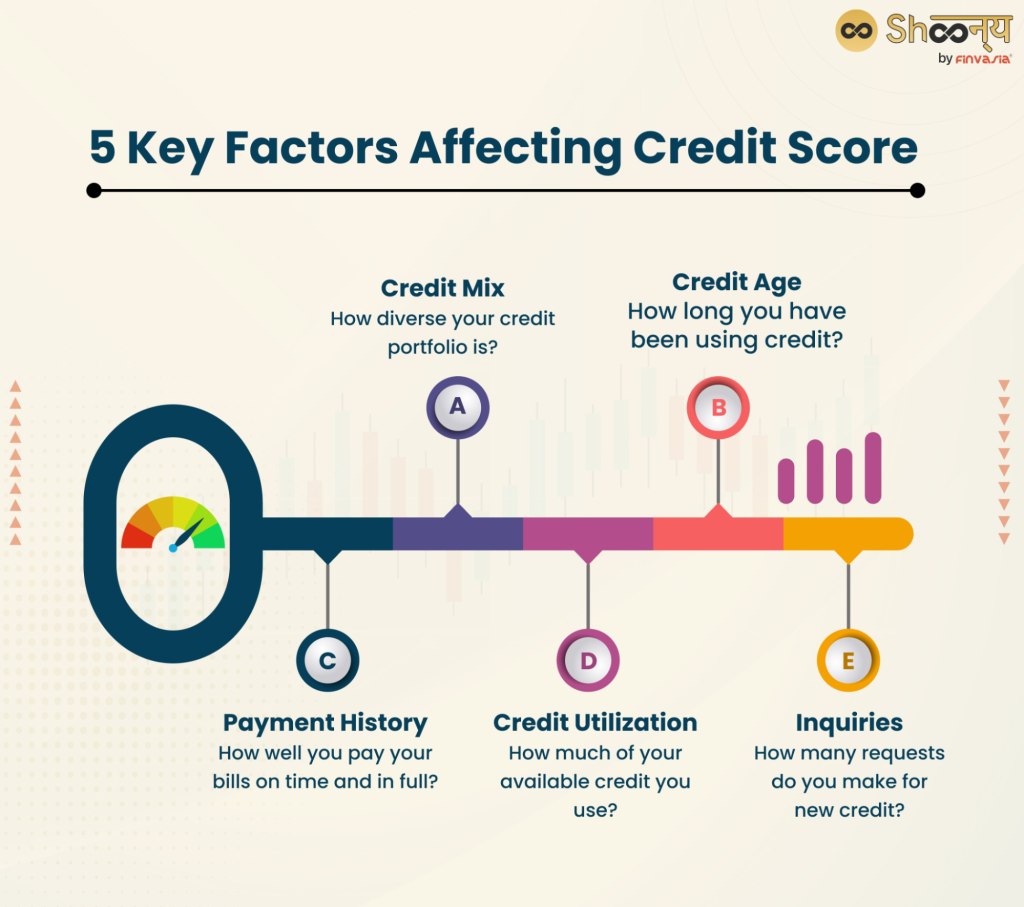
Cifra: 5 Key Factors Affecting Credit Score
Descripción:
The figure highlights five important factors that influence an individual’s credit score. These factors include credit mix (diversity of credit types), credit age (length of credit history), payment history (track record of timely payments), credit utilization (how much of the available credit is used), and inquiries (number of new credit requests). Understanding these elements helps individuals manage their credit more effectively.
Conclusiones clave:
- Credit mix ensures a balanced credit portfolio, showing lenders you can manage different credit types.
- Credit age emphasizes the benefits of a longer credit history.
- Payment history is crucial; consistent on-time payments significantly boost your credit score.
- Credit utilization should be kept low to maintain a healthy score.
- Inquiries can affect your score; too many requests for new credit might lower it.
Solicitud de información:
Knowing these key factors helps users improve and maintain their credit scores. By focusing on making timely payments, maintaining a low credit utilization ratio, and diversifying their credit portfolio, users can manage their credit more effectively.
Managing Credit Commitments
Once credit has been obtained, it’s essential to manage the repayment process carefully. This includes:
- Making timely payments on all credit commitments to avoid late fees and damage to credit scores.
- Paying more than the minimum on flexible credit commitments, such as credit cards, to reduce overall interest costs.
- Considering early repayment of loans if financially possible, as this can save money in the long term by reducing interest payments.
In case of financial difficulty, individuals should be aware that it may be possible to renegotiate credit agreements with lenders to obtain more favorable terms or reduce monthly payments.
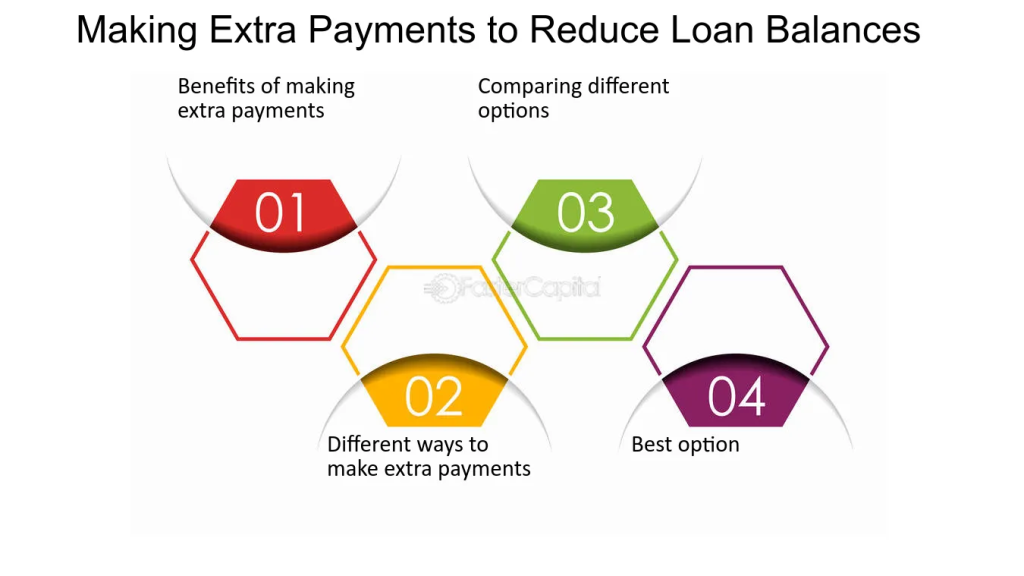
Figure: Making Extra Payments to Reduce Loan Balances
Descripción:
The image illustrates four key aspects of making extra payments on loans to effectively reduce loan balances. It covers the benefits of extra payments, various methods to make them, options for comparing the best payment strategies, and identifying the optimal approach. These steps help borrowers manage their loans more efficiently by reducing the overall debt quicker.
Conclusiones clave:
- Benefits of extra payments include faster loan payoff and reduced interest costs.
- Different payment methods can help in finding a strategy that fits individual financial situations.
- Comparing payment options allows borrowers to understand which methods save the most money.
- Identifying the best approach helps in making informed decisions on managing debt efficiently.
Solicitud de información:
Entendiendo el importance of extra payments helps borrowers reduce overall debt faster and save money on interest. By exploring different payment methods and comparing them, users can find the best strategy to achieve financial freedom more efficiently.
Confidence in Declining Unnecessary Credit
Many retailers and online platforms offer credit options at the point of sale, such as store credit cards o “buy now, pay later” schemes. These offers can be tempting, especially when they are presented as easy, low-cost financing options. However, it’s important to carefully assess whether this credit is truly necessary and if the repayment terms are favorable.
Being confident in declining unwanted credit offers is an essential part of managing finances responsibly. By avoiding unnecessary credit, individuals reduce the risk of over-indebtedness and maintain better control over their financial situation.
Información clave de la lección:
- Credit can be a useful tool when managed carefully. It allows for significant purchases like homes or education but requires thoughtful planning to avoid financial strain.
- Assessing the total cost of credit is crucial. Beyond the interest rate, you need to consider fees, repayment terms, and any penalties. This helps you make informed borrowing decisions and prevents unexpected financial stress.
- Alternatives to borrowing, such as saving, leasing, or community resources, can often meet financial needs without the risks associated with debt. Using alternatives can help maintain financial stability and reduce interest costs.
- Avoiding over-indebtedness involves cautious use of easily accessible credit, like “buy now, pay later” offers or high-interest loans. It is important to understand the terms and only accept credit that fits your financial plan.
- Understanding different credit types, from credit cards to personal loans, is vital. Each has its advantages, risks, and repayment conditions. Knowing the differences helps you choose the right credit product for your needs.
- Monitoring your credit score is essential for better borrowing options. Keeping your credit score high by making timely payments, maintaining low credit utilization, and checking for errors can improve your chances of securing favorable credit terms.
Frase de cierre: Responsible borrowing and effective credit management are key components of financial well-being. By understanding credit, evaluating borrowing costs, and exploring alternatives, you can make informed decisions that promote financial stability.