Fideicomisos de inversión inmobiliaria (REIT)
Objetivos clave de aprendizaje:
Introducción: This section introduces Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) as an innovative mechanism to invest in the real estate sector. By exploring the different types of REITs and their operational intricacies, you will gain insights into how REITs offer both liquidity and exposure to real estate assets.
- Obtain a comprehensive understanding of the foundation of REITs, their regulatory requirements, and the diverse landscape encompassing equity, mortgage, and hybrid REITs.
- Distinguish between public and private REITs, appreciating the trade-offs in terms of liquidity, potential returns, and accessibility criteria.
- Differentiate between equity and mortgage REITs, noting how each generates income – through property ownership and rental for the former and through mortgages and interest for the latter.
- Equip yourself with the knowledge of the advantages, such as portfolio diversification and dividend income, and challenges, including market volatility and unique tax considerations, of investing in REITs.

Título de la figura: Understanding REITs: A 3D Conceptualization
Fuente: iStock:
Investing in real estate can be done through various methods, including direct property ownership, debt financing, and public markets using investment vehicles such as Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). This section will provide an overview of REITs, their types, and the benefits and drawbacks of investing in them.
A. Introduction to REITs
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own or finance income-producing real estate properties. They offer investors the opportunity to invest in real estate without directly owning or managing the properties themselves. REITs are traded on major stock exchanges and are regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
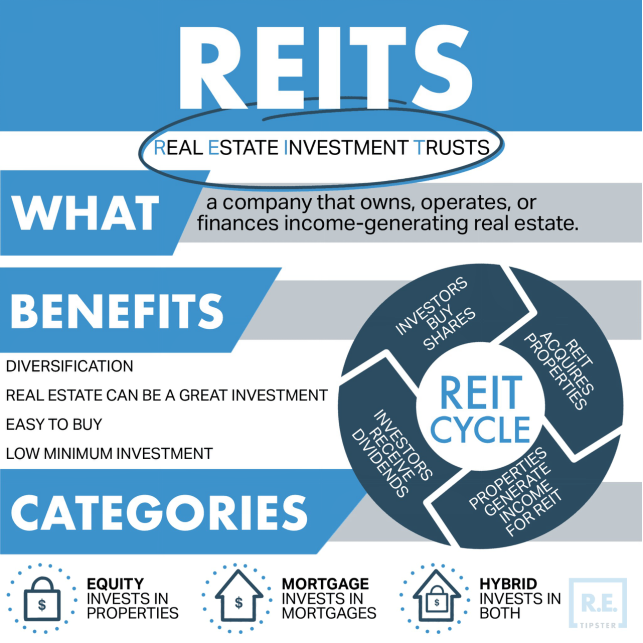
Título de la figura: Unraveling REITs: A Comprehensive Guide
Fuente: REtipster
Descripción: This infographic serves as an educational tool, explaining the structure, types, and benefits of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), making it accessible for beginners in real estate investment.
Conclusiones clave:
- REIT Essentials: The infographic might begin by defining REITs, explaining their primary function of owning, operating, or financing income-producing real estate.
- Diverse Types: It could categorize different types of REITs, such as equity, mortgage, and hybrid, illustrating their distinct characteristics and functions.
- Benefits & Returns: The visual likely underscores the advantages of investing in REITs, touching upon aspects like diversification, liquidity, and dividend income.
Solicitud: As REITs gain popularity among investors for their unique benefits, it’s crucial to have resources that explain their intricacies. This infographic serves as an invaluable tool for real estate professionals, financial advisors, and educators to introduce and explain REITs to their audience. It underscores the value of REITs in building diversified portfolios and generating consistent income, making it a must-have for anyone keen on exploring real estate investments beyond traditional property ownership.
B. Public vs. Private REITs
Public REITs: These are listed on major stock exchanges and are available for anyone to purchase. Public REITs offer higher liquidity, as they can be easily bought and sold on the stock market.
Private REITs: These are not publicly traded and are only available to accredited investors. Private REITs may offer higher potential returns but come with lower liquidity and higher minimum investment requirements.
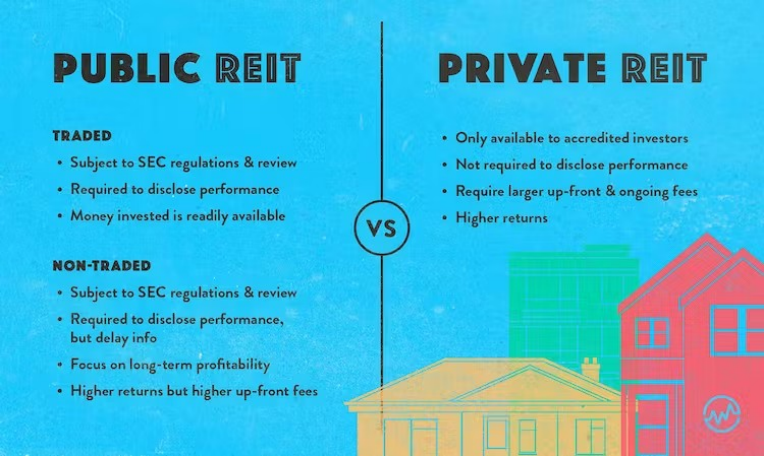
Título de la figura: The REIT Landscape: An Introduction
Fuente: Wealthfit
Descripción: This infographic provides a beginner-friendly overview of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), highlighting their purpose, types, and the advantages they offer to investors.
Conclusiones clave:
- REIT Purpose: Learn how REITs allow individuals to invest in large-scale real estate operations, which were previously accessible only to wealthy investors.
- REIT Varieties: Get to know the different kinds of REITs, including those that invest in properties (equity REITs) and those that invest in mortgages (mortgage REITs).
- Investor Advantages: REITs are known for providing regular income streams, tax advantages, and a way to invest in real estate without owning physical property.
Solicitud: An understanding of REITs is invaluable for those looking to diversify their investment portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. The visual serves as an entry point, piquing interest and inviting further exploration. Financial educators, real estate experts, or investment platforms can leverage such an image to demystify REITs, laying the groundwork for deeper discussions or analyses. Whether it’s for educational webinars, articles, or presentations, the image offers a concise yet comprehensive overview of the REIT landscape.
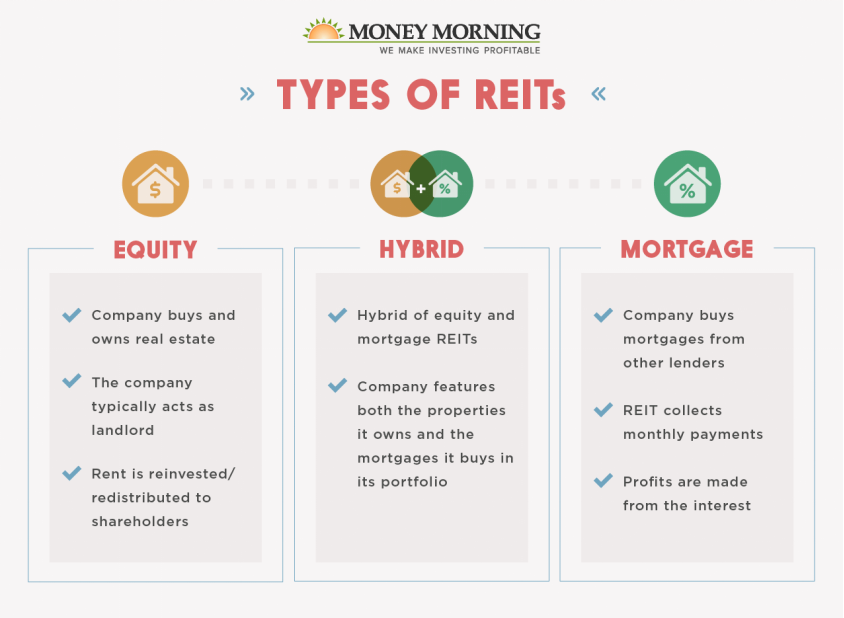
C. Equity vs. Mortgage REITs
Equity REITs: These REITs invest in and own physical properties such as apartment buildings, shopping centers, and office buildings. They generate income by renting out space and collecting rent from tenants.
Mortgage REITs: These REITs invest in and own mortgages on real estate properties. They generate income by collecting interest on these mortgages. Mortgage REITs are more sensitive to interest rate fluctuations and may carry higher risks compared to equity REITs.
Título de la figura: Single Taxation: A Unique REIT Benefit
Fuente: Arrived
Descripción: This image likely sheds light on the taxation benefits associated with Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). The visual may feature graphical representations like a dollar sign, percentage icons, or even a REIT-specific illustration, all focusing on the concept of taxation. The image might be designed to convey how REITs, unlike traditional corporations, avoid double taxation, with tax implications primarily falling on the shareholders.
Conclusiones clave:
- Tax Efficiency: REITs offer a unique advantage by being taxed only at the shareholder level, avoiding the double taxation typically seen in corporations.
- Higher Dividends: Due to the single taxation system, REITs can distribute a larger portion of profits as dividends to investors.
- Accessible Real Estate Investment: Investors can gain exposure to real estate with potentially lower tax liabilities compared to direct property ownership.
Solicitud: Taxation is a crucial consideration for any investor. By highlighting the single taxation benefit of REITs, this visual serves as a compelling tool for financial educators, tax consultants, and investment advisors. It succinctly communicates the potential tax advantages of REITs, enabling investors to make informed decisions. Such visuals can be instrumental in articles, presentations, or webinars targeting potential REIT investors or anyone interested in expanding their knowledge of the financial landscape.
D. Benefits and Drawbacks of Investing in REITs
Benefits:
a. Diversification: Investing in REITs allows investors to diversify their portfolio and gain exposure to the real estate market
b. Regular Income: REITs provide investors with the potential for regular income in the form of dividends, as they are required to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders.
c. Professional Management: Investors in REITs benefit from the expertise of professional management teams that oversee the properties and make decisions on their behalf.
Drawbacks:
a. Market Volatility: REITs are subject to market volatility and can be influenced by factors such as interest rates and economic conditions.
b. Lack of Direct Control: Investors in REITs do not have direct control over the properties owned by the REIT and are reliant on the management to make decisions on their behalf.
c. Tax Implications: Dividends from REITs are often taxed as ordinary income, which may result in higher taxes for some investors compared to the long-term capital gains tax rate applied to other investments.
By understanding the different types of REITs and their benefits and drawbacks, investors can make informed decisions about whether investing in REITs is suitable for their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusiones clave:
Frase de cierre: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) present an unparalleled gateway to the realm of real estate investments. Through this section, you are acquainted with the core attributes, benefits, and challenges of REITs, paving the way for informed investment decisions.
- REITs offer a streamlined approach to delve into real estate, allowing investors the privilege of real estate exposure without the intricacies of direct property management or substantial capital outlays.
- The distinction between public and private REITs is pivotal. Public REITs provide enhanced liquidity, whereas private REITs might cater to a niche audience with potentially higher returns but less liquidity.
- The income generation avenues differ between equity and mortgage REITs – with equity REITs capitalizing on rental income from owned properties and mortgage REITs benefiting from interest on the mortgages they hold.
- While REITs proffer several advantages, including potential for consistent dividends and portfolio diversification, it’s imperative to remain aware of the inherent risks such as market fluctuations and distinct tax implications.

