Global : Introduction aux cycles économiques et aux classes d'actifs
Objectifs d'apprentissage de la leçon :
- Understand the global business cycle: Learn how international factors such as trade flows et prix des matières premières influence the global business cycle and its phases.
- Identify impacts on various asset classes: Découvrez comment stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, et matières premières react differently during each phase of the global business cycle.
- Analyze the influence of central banks: Explore how policies from central banks around the world, like the Federal Reserve et le ECB, affect global markets and asset performances.
- Apply global market strategies: Develop strategies to optimize investment portfolios by understanding and leveraging the effects of global economic activities on asset classes.
A. Introduction to Business Cycles and Asset Classes
Globally, the business cycle follows similar stages, but international factors such as global interest rates, trade flows, et prix des matières premières also play a critical role. The performance of asset classes—actions, obligations, cash, immobilier, et matières premières—varies depending on these phases and regional economic conditions. Investors need to consider how global factors like central bank policies and international trade influence these asset classes.
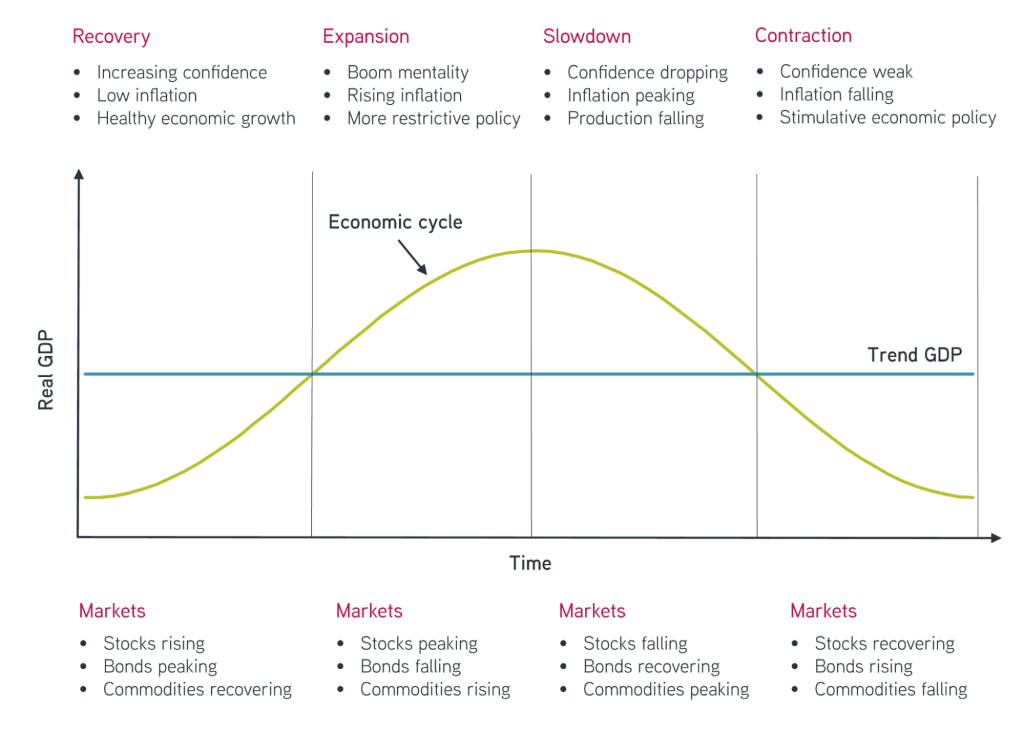
Chiffre: Economic Cycle and Market Performance
Description:
La figure illustre le cycle économique and its four phases: Recovery, Expansion, Slowdown, and Contraction. It highlights how real GDP fluctuates over time, showing the relationship between economic activity and market behavior. During each phase, different asset classes—stocks, bonds, and commodities—react in varying ways, reflecting market trends in response to economic changes.
Points clés à retenir:
- Récupération is characterized by rising confidence, low inflation, and healthy growth, with stocks and bonds generally increasing.
- Expansion indicates a boom mentality, rising inflation, and restrictive policies, often leading to stocks peaking and bonds falling.
- Ralentir shows confidence dropping, inflation peaking, and production falling, causing stocks to fall and bonds to recover.
- Contraction involves weak confidence, falling inflation, and stimulative policies, with stocks declining and bonds rising.
Application des informations :
Comprendre le cycle économique helps investors anticipate market behavior and adjust their strategies accordingly. By knowing which assets perform best during each phase, investors can optimize their portfolios to align with economic conditions, improving potential returns and managing risks.
B. Stocks, Bonds, and Cash: A Primer
Globally, these three asset classes respond differently across business cycles:
- Actions: Stock performance is typically strong during expansion phases, with technologie et consommation discrétionnaire sectors driving growth. However, global stocks are volatile during contractions.
- Obligations: Government bonds, especially U.S. Treasuries, provide safety during recessions, while high-yield corporate bonds perform better during expansions as credit risks decrease.
- Espèces: Cash becomes an attractive asset in global markets during recessions when investors seek safety and liquidity amid uncertainty in stocks and bonds.
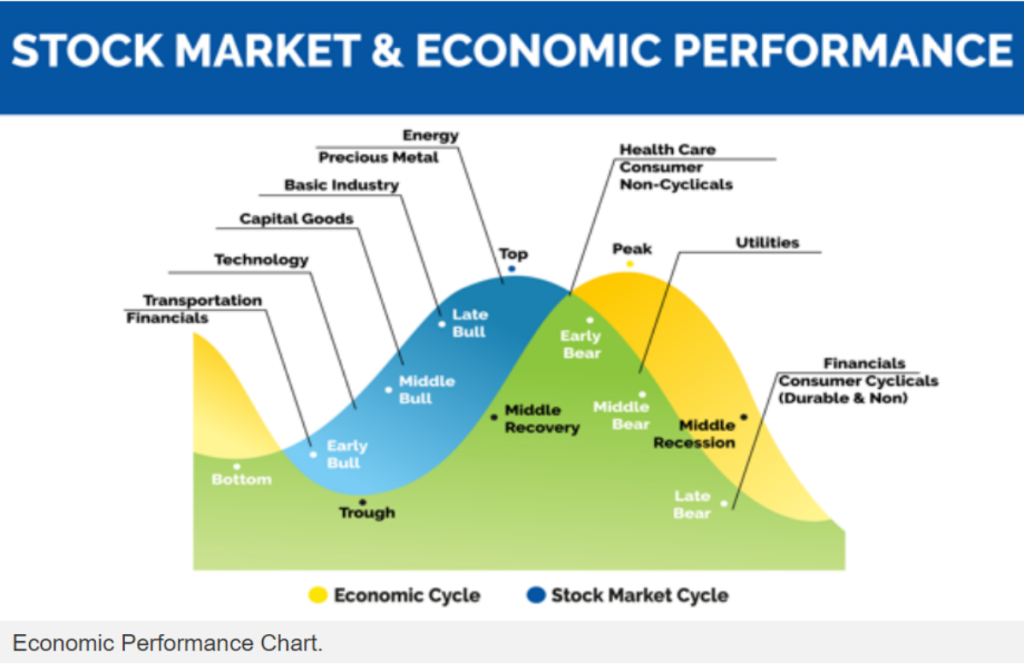
Chiffre: Stock Market & Economic Performance
Description:
La figure illustre la relation entre les cycle économique et le cycle boursier. Il décrit les différentes étapes de chaque cycle, y compris des phases comme Taureau précoce, Taureau du Milieu, Taureau tardif, Early Bear, et Récession du milieu. Des secteurs clés tels que Énergie, Services publics, et Soins de santé sont alignées sur des phases spécifiques, indiquant leur performance lors des transitions économiques.
Points clés à retenir:
- Le cycle économique et cycle boursier comportent des phases distinctes mais interconnectées.
- Des secteurs comme Transport et Données financières performer bien dans le taureau précoce phase, tandis que Services publics exceller dans le culminer.
- industries de base et biens d'équipement obtenir de meilleurs résultats dans le taureau moyen phase, en phase avec la reprise économique.
- Métaux précieux et énergie pic généralement pendant taureau tardif phase.
- Soins de santé et Biens de consommation non cycliques offrir de la stabilité pendant récessions.
Application des informations :
Comprendre la corrélation entre les cycle économique et performance du marché boursier peut aider les investisseurs à prendre des décisions éclairées concernant la répartition sectorielle en fonction des phases économiques. En alignant les investissements sur des phases comme récupération ou récession, les utilisateurs peuvent optimiser leurs rendements et gérer efficacement les risques. Cette approche contribue à diversification stratégique du portefeuille quelles que soient les conditions économiques.
C. Early Expansion Phase
In global markets, the early expansion phase is marked by recovery from recession:
- Actions: Global stocks surge, with companies in emerging markets often leading the way as they experience rapid recovery.
- Obligations: High-yield bonds perform well globally as investors regain confidence and seek higher returns.
- Espèces: Cash positions are reduced as investors move into riskier assets for growth.
D. Mid Expansion Phase
Globally, mid expansion sees more stable but slower growth:
- Actions: Global equity markets continue to perform well, but the focus shifts to industrial et financial sectors as growth moderates.
- Obligations: Bond performance weakens, especially obligations d'État, as interest rates rise globally.
- Espèces: Cash positions remain low as growth expectations persist.
E. Late Expansion Phase
Globally, the late expansion phase is characterized by high volatility:
- Actions: Investors shift to defensive sectors globally, such as consumer staples et soins de santé.
- Obligations: Safe-haven bonds, like U.S. Treasuries, gain popularity as inflation pressures mount.
- Espèces: Cash and equivalents become more desirable as recession fears grow.
F. Recession
Globally, recessions impact all asset classes:
- Actions: Global stock markets decline, with emerging markets often suffering the most severe losses.
- Obligations: obligations d'État provide a safe haven, while obligations d'entreprises face risks of default.
- Espèces: Cash is highly favored as it protects against further losses.
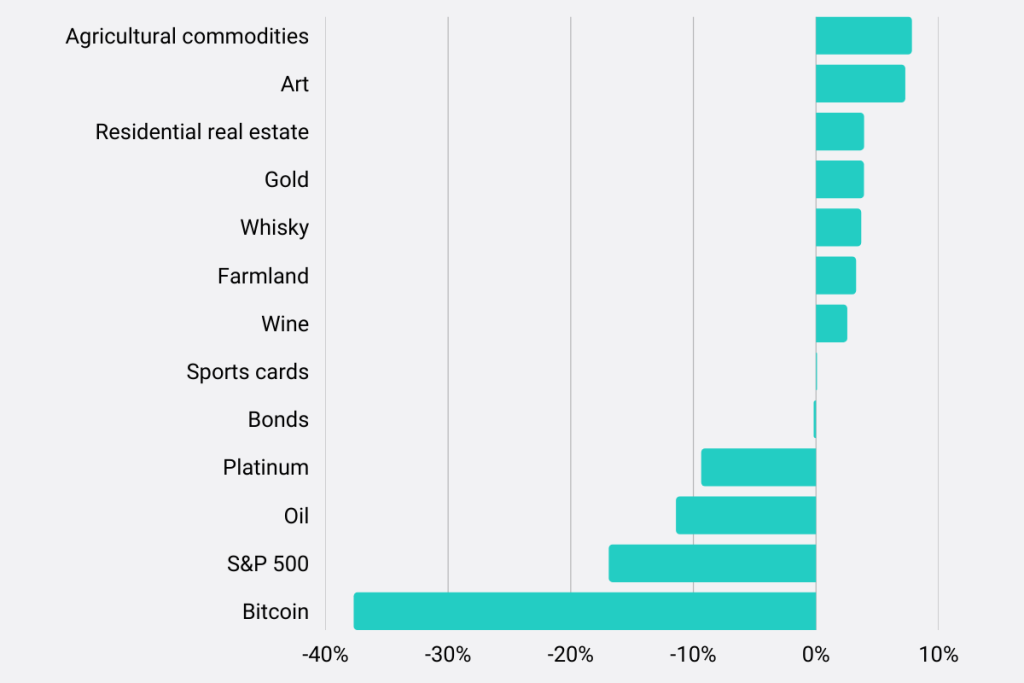
Chiffre: Top Performing Asset Classes During a Recession
Description:
The figure compares the performance of various asset classes during a recession, showing their average return percentages. Asset classes include agricultural commodities, art, immobilier résidentiel, or, whisky, farmland, wine, sports cards, obligations, platinum, huile, S&P 500, et Bitcoin. The chart reveals that while some assets have positive returns during economic downturns, others experience negative returns, with Bitcoin showing the largest decline.
Points clés à retenir:
- Agricultural commodities, art, et immobilier résidentiel have positive returns during recessions.
- Or, whisky, et farmland also maintain a positive return trend, indicating resilience in uncertain times.
- Bitcoin, S&P 500, et huile are among the worst performers, showing negative returns during recessions.
- The data suggests that tangible assets comme farmland et matières premières may offer better stability during economic downturns.
Application des informations :
Understanding which asset classes perform well during recessions can help investors diversify their portfolios. By including more recession-resistant assets, investors can minimize potential losses and enhance portfolio stability in turbulent economic times.
G. Real Estate and Commodities: An Overview
Globally, real estate and commodities follow similar trends, but with additional factors like global demand et geopolitical tensions affecting performance:
- Immobilier: Global real estate markets thrive in early and mid-expansion phases, driven by low interest rates and rising demand.
- Matières premières: Des matières premières comme huile et metals perform well during global expansions, while or is a safe-haven asset during recessions.
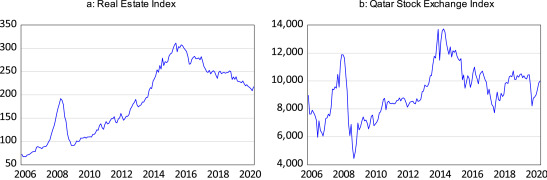
Chiffre: Real Estate Index vs. Qatar Stock Exchange Index
Description:
The figure consists of two line charts that depict the performance of the Real Estate Index (left) and the Qatar Stock Exchange Index (right) from 2006 to 2020. The Real Estate Index shows a steady rise until 2015, after which it experiences a decline. The Qatar Stock Exchange Index demonstrates a more volatile pattern, with significant peaks and troughs over the same period, indicating fluctuations in the stock market.
Points clés à retenir:
- Le Real Estate Index showed consistent growth until 2015 but began declining afterward, reflecting potential changes in the real estate market.
- Le Qatar Stock Exchange Index experienced more volatility, with sharp rises and falls, indicating higher sensitivity to market conditions and economic events.
- Immobilier appears to have had more stable growth compared to the bourse, although both indexes experienced downturns after 2015.
Application des informations :
Investors can use these charts to understand the historical performance of immobilier versus the bourse in Qatar. The data can help inform decisions about diversification du portefeuille, especially in contexts where volatilité des marchés is a concern. It also highlights the potential benefits of including immobilier as a stabilizing asset in a broader investment strategy.
H. Real Estate Across Business Cycle Stages
- Expansion précoce: Global real estate markets recover as economic growth resumes.
- Expansion moyenne: Strong performance, especially in emerging markets, where urbanization drives demand.
- Expansion tardive: Real estate becomes riskier as borrowing costs rise.
- Récession: Property values fall as demand decreases and financing becomes harder to obtain.
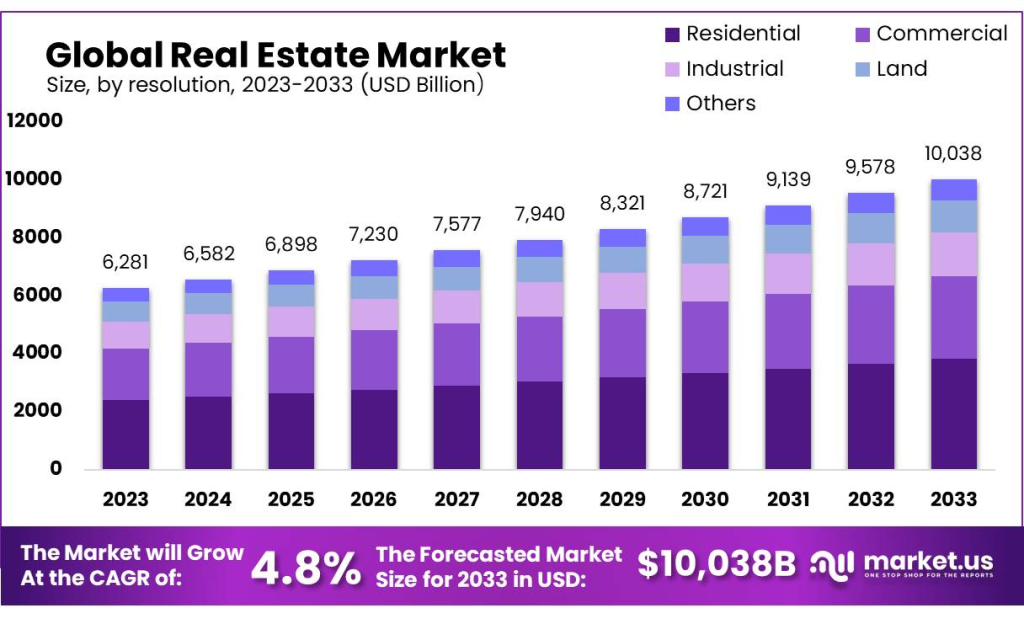
Chiffre: Global Real Estate Market: Size, by Resolution, 2023-2033 (USD Billion)
Description:
The stacked bar chart represents the projected size of the global real estate market from 2023 to 2033, categorized by different sectors: Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Land, and Others. The market shows consistent growth over the years, increasing from $6,281 billion in 2023 to a forecasted size of $10,038 billion in 2033. The chart also highlights a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.8% over the forecast period.
Points clés à retenir:
- Le global real estate market is projected to grow steadily from 2023 to 2033, reaching $10,038 billion.
- Le residential sector consistently holds the largest share, followed by commercial et industrial sectors.
- The market’s CAGR is anticipated to be 4.8% over the forecast period, indicating stable growth.
- The sectoral distribution remains relatively consistent throughout the years, suggesting balanced growth across different real estate sectors.
Application des informations :
This data helps investors understand the growth potential in the global real estate market. It emphasizes the importance of diversifying investments across different real estate sectors, considering the consistent growth forecasted. Real estate investors can use this projection to plan long-term strategies, targeting sectors like residential et commercial, which hold significant shares of the overall market.
I. Commodities Across Business Cycle Stages
- Expansion précoce: Commodities start to recover, driven by rising global demand for raw materials.
- Expansion moyenne: Commodities benefit from increasing industrial and consumer demand.
- Expansion tardive: Des matières premières comme or become attractive due to rising inflation and uncertainty.
- Récession: Commodity prices, except for gold, typically decline as global demand weaken
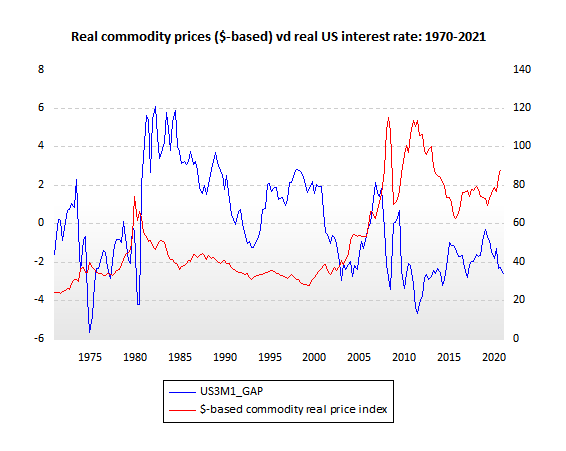
Chiffre: Real Commodity Prices (USD-based) vs. Real US Interest Rate: 1970-2021
Description:
The chart illustrates the relationship between real commodity prices (USD-based, in red) and the real US interest rate (in blue) over the period from 1970 to 2021. The red line represents the commodity real price index, while the blue line shows the US3M1_GAP, which reflects the real US interest rate. The two variables often move in opposite directions, demonstrating an inverse relationship between commodity prices and real interest rates over time.
Points clés à retenir:
- Real commodity prices et real US interest rates tend to move inversely, suggesting that when interest rates increase, commodity prices often decrease, and vice versa.
- Periods of high real interest rates, such as during the early 1980s and early 2000s, correspond with lower prix des matières premières.
- Conversely, lower real interest rates, such as in the mid-1970s and early 2010s, often coincide with higher prix des matières premières.
- This relationship highlights the impact of monetary policy on commodity markets, making it crucial for investors to consider interest rate trends when analyzing commodity prices.
Application des informations :
Comprendre le inverse relationship entre real commodity prices et real interest rates is critical for commodity investors and traders. This chart demonstrates how shifts in politique monétaire can affect commodity prices, enabling investors to anticipate price movements based on changes in interest rates. For example, a declining interest rate environment may signal potential upward movement in prix des matières premières, offering insights for strategic investment decisions in commodity markets.
Conclusion
Understanding how asset classes perform across different stages of the business cycle is essential for investors looking to maximize returns and minimize risks. Whether focusing on local European markets or global trends, aligning investment strategies with the business cycle allows for better portfolio management and informed decision-making. Diversification across actions, obligations, cash, immobilier, et matières premières helps investors manage risk throughout the different phases of the business cycle. By recognizing how each asset class responds to economic conditions, investors can make more informed decisions, positioning themselves to take advantage of opportunities in expansion phases and protecting their portfolios during contractions and recessions.
Informations clés sur la leçon :
- Business cycles are globally interconnected: Recognize how phases like récupération et contraction in the global business cycle affect asset classes differently, influencing investment decisions.
- Central bank policies are pivotal: Policies set by central banks significantly impact global asset classes, highlighting the importance of staying informed on global economic policies.
- Diversification on a global scale is beneficial: Diversifying investments across various global asset classes can help mitigate risks and exploit growth opportunities during different economic phases.
- Strategic asset allocation is key: Aligning investment choices with the stages of the global business cycle can lead to optimized portfolio performance and better risk management.
Déclaration finale :
Understanding the complexities of the global business cycle and its impact on various asset classes is crucial for investors to make informed decisions, enhancing their ability to manage risks and capitalize on opportunities in the international market.

