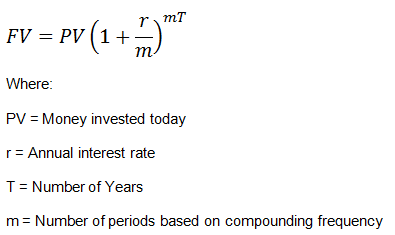अध्याय 7: बचत और आपातकालीन निधि
पाठ सीखने के उद्देश्य:
लोरेम इप्सुम डोलर सिट अमेट, कॉन्सेक्टूर एडिपिसिंग एलिट। उत एलीट टेलुस, लक्टस नेक उल्लमकोर्पर मैटिस, पुल्विनार डेपिबस लियो।
बचत और वित्तीय उत्पादों का परिचय
व्यक्तिगत वित्त प्रबंधन में विभिन्न वित्तीय उत्पादों और बचत के महत्व को समझना महत्वपूर्ण है। यह अध्याय विभिन्न प्रकार के बैंक खातों, आपातकालीन निधियों के महत्व और मुद्रास्फीति और ब्याज दरों के बचत को प्रभावित करने के तरीके पर गहराई से चर्चा करता है। इसके अतिरिक्त, यह वित्तीय संस्थानों की मूल बातें और व्यक्तिगत वित्त को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने और बढ़ाने के तरीके को कवर करता है।

7.1 Types of Accounts and Financial Services
वित्तीय संस्थाएं विभिन्न प्रकार के खाते और सेवाएं प्रदान करती हैं, जिनमें से प्रत्येक विशिष्ट वित्तीय आवश्यकताओं के लिए डिज़ाइन की गई हैं:
चेकिंग खाते:
दैनिक लेनदेन के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। वे आम तौर पर डेबिट कार्ड के साथ आते हैं और असीमित जमा और निकासी की पेशकश।
- लाभ: धन तक आसान पहुंच, डेबिट कार्ड का उपयोग, ऑनलाइन बिल भुगतान।
- नुकसान: आमतौर पर कम ब्याज मिलता है या कोई ब्याज नहीं मिलता।
बचत खाते:
Aimed at short-term savings over time. Offer interest on the stored funds.
- लाभ: ब्याज कमाना, जोखिम कम।
- नुकसान: सीमित निकासी, अन्य बचत उत्पादों की तुलना में संभावित रूप से कम ब्याज दरें।
मनी मार्केट खाते (एमएमए):
चेकिंग और बचत खातों का मिश्रण, जिसमें आमतौर पर उच्च ब्याज दरें और उच्च न्यूनतम शेषराशि की आवश्यकता होती है।
- लाभ: उच्च ब्याज दरें, चेक लिखने की सुविधा।
- नुकसान: उच्च न्यूनतम शेष राशि आवश्यकताएं, सीमित लेनदेन।
जमा प्रमाणपत्र (सीडी):
Fixed-term savings account with a guaranteed interest rate.
- लाभ: बचत खातों की तुलना में उच्च ब्याज दर, निश्चित रिटर्न।
- नुकसान: समय से पहले निकासी पर जुर्माना, अवधि समाप्त होने तक धन प्राप्त नहीं हो पाता।

Figure: What is a Checking Account?
विवरण:
This image visually defines a checking account, which is a primary tool for managing day-to-day finances. It highlights the main features of the account, such as a debit card and paper checks, which are used to make purchases and pay bills. The graphic serves as a simple introduction to one of the most basic and essential products in personal finance.
चाबी छीनना:
- ए checking account is a type of bank account that provides easy access to your money for daily transactions.
- It is designed for high liquidity, meaning you can withdraw or spend your money quickly using tools like a debit card, ATM, or online transfers.
- The main purpose of this account is for spending and bill payments, not for earning interest; most checking accounts offer little to no interest on your balance.
- Keeping track of your transactions through a bank statement or online portal is crucial for बजट and avoiding overdrafts.
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
- ए checking account is the foundation of personal financial management, acting as the operational center for your income and expenses.
- Learning to manage a checking account is a critical first step in creating a budget, tracking your spending, and building good financial habits.
- For anyone new to finance, this account is an essential tool for safely storing money, paying bills efficiently, and participating in the modern economy.
खाता खोलना और प्रबंधित करना:
बैंक खाता खोलने के लिए आम तौर पर व्यक्तिगत पहचान, सामाजिक सुरक्षा संख्या और प्रारंभिक जमा राशि प्रदान करने की आवश्यकता होती है। खाते का प्रबंधन करने में शेष राशि की निगरानी, जमा और निकासी करना और न्यूनतम शेष राशि की आवश्यकताओं और ओवरड्राफ्ट शुल्क जैसी फीस को समझना शामिल है।
खाता घटक:
खाता संख्या आपके खाते की विशिष्ट पहचान करती है, जबकि रूटिंग संख्या आपके बैंक की पहचान करती है - जो प्रत्यक्ष जमा और स्वचालित भुगतान स्थापित करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
क्रेडिट यूनियन बनाम वाणिज्यिक बैंक:
Credit unions typically offer lower fees and better interest rates but might have fewer branches and services. Commercial banks offer a broader range of services but may charge higher fees.
छात्रों के लिए वित्तीय उत्पादों का मूल्यांकन
छात्रों को विचार करना चाहिए चेकिंग और बचत खाते कम फीस, धन तक आसान पहुंच, तथा वित्तीय प्रबंधन में सहायता के लिए शैक्षणिक संसाधन। लाभ इसमें धन प्रबंधन सीखना और बचत पर ब्याज अर्जित करना शामिल है। नुकसान इसमें न्यूनतम शेष राशि की आवश्यकताओं का प्रबंधन या संभावित शुल्कों का प्रबंधन शामिल हो सकता है।
7.2 Online Banking and Account Management
ऑनलाइन बैंकिंग वित्तीय सेवाओं तक सुविधाजनक पहुँच प्रदान करती है, जिसमें खाता खोलना, शेष राशि की जाँच करना और निधि हस्तांतरण शामिल है। मुख्य घटकों में न्यूनतम शेष राशि की आवश्यकताओं, मासिक शुल्क, ओवरड्राफ्ट दंड और ब्याज दरों को समझना शामिल है। खातों में लेन-देन को कवर करने और शुल्क से बचने के लिए नियमित रूप से धन को ट्रैक और प्रबंधित करना आवश्यक है।
आकृति: Key Benefits of Online Banking
विवरण:
This graphic illustrates the main advantages of using online banking for managing personal or business finances. It visually highlights key features such as 24/7 account access from any device, the ease of making digital payments, and real-time transaction monitoring. The overall message is that online banking offers a more convenient, efficient, and powerful way to handle financial tasks.
चाबी छीनना:
- Constant Accessibility: A major benefit of online banking is 24/7 access to your accounts from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need to visit a physical bank.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: It saves significant time by allowing you to automate bill payments and transfer funds instantly, and it often comes with lower fees than traditional banking services.
- Enhanced Financial Control: Online banking provides real-time visibility into your transactions and account balances, which is crucial for accurate budgeting and managing cash flow.
- Simplified Record-Keeping: Many platforms can integrate with accounting software, which automates bookkeeping and makes financial reporting much easier for individuals and businesses.
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
- Adopting online banking is a foundational step for modern and efficient money management.
- It provides the tools to actively track your spending, automate your savings contributions, and maintain a clear, up-to-the-minute picture of your financial health.
- By leveraging these digital tools, you can reduce time spent on financial administration and focus more energy on achieving your primary goals, like investing for the future or growing a business.
ब्याज दरें और बचत
जब ऋण की मांग बढ़ती है, तो बैंक अधिक बचतकर्ताओं को आकर्षित करने के लिए जमाराशियों पर उच्च ब्याज दर की पेशकश कर सकते हैं, जिससे उन्हें उधार देने के लिए धन उपलब्ध हो सके। इसके विपरीत, संतृप्त ऋण बाजार या आर्थिक मंदी में, उधार लेने की मांग कम हो जाती है, और बैंक बचत खातों पर ब्याज दरें कम कर सकते हैं।
मोबाइल भुगतान खाते बनाम पारंपरिक बैंकिंग
मोबाइल भुगतान खाते सुविधा और उपयोग में आसानी प्रदान करते हैं, लेकिन आमतौर पर इनमें ब्याज आय की कमी होती है, जिससे पारंपरिक भुगतान खातों की तुलना में बचत वृद्धि की संभावना कम हो जाती है। बचत खाते, जो ब्याज प्रदान करते हैं। क्रिप्टोकरेंसी खाते इनमें उच्च अस्थिरता और संभावित प्रतिफल की पेशकश की जाती है, लेकिन संघीय बीमा का अभाव होता है, जो कि संघीय बीमा वाले बचत खातों की सुरक्षा और स्थिर वृद्धि क्षमता के विपरीत है।
7.3 Comparing Mobile Payment Accounts, Cryptocurrency Accounts, and Traditional Bank Accounts
While mobile payment platforms like Venmo or Cash App and cryptocurrency wallets offer convenience and fast transactions, they typically do not provide interest earnings or federal insurance protections (like FDIC or NCUA insurance). Traditional savings and checking accounts offer lower risk, provide interest (even if modest), and are protected against institutional failures up to certain limits.
Feature | Mobile Payments | क्रिप्टोकरेंसी खाते | Traditional Bank Accounts |
बीमा | No federal insurance | No federal insurance | FDIC/NCUA insured |
Interest Earnings | None | Very rare | Common (low to moderate) |
सरल उपयोग | High (instant transfer) | High (global access) | High (ATM, online banking) |
Risk Level | Medium to high | High (market volatility) | Low |
7.4 Why Certificates of Deposit (CDs) Typically Pay Higher Interest Rates
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) generally offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts or interest-bearing checking accounts because they require depositors to commit their money for a specific period. This commitment gives banks more certainty about the availability of funds for lending and investments. In exchange for giving up liquidity (easy access to their funds), depositors are rewarded with higher rates. Early withdrawal often results in penalties, reinforcing the importance of keeping funds deposited for the full term.
उदाहरण:
A savings account might offer a 1% interest rate, while a 12-month CD could offer 4% during the same period.
पेशेवर:
- Higher guaranteed returns over the term.
- Safe and predictable growth.
दोष:
- Funds are locked until maturity.
- Penalties for early withdrawal.
7.5 Impact of Loan Demand on Deposit Interest Rates
When the demand for loans rises, banks often need additional funds to meet the demand. To attract more deposits (which they use to fund new loans), they may offer higher interest rates on savings accounts, CDs, and other deposit products. Essentially, banks are willing to pay more to bring in money they can lend out profitably.
उदाहरण:
If mortgage applications rise sharply, banks may raise deposit rates from 1.5% to 2% to attract savers and balance their funding needs.
7.6 Market Conditions Leading to Lower Savings Rates
In times of economic slowdown or when consumers and businesses are not borrowing as much, banks don’t need as many deposits. As a result, they may lower the interest rates paid on savings accounts. This often occurs during recessions or when central banks lower benchmark interest rates to stimulate the economy.
उदाहरण:
During a recession, banks may drop savings account interest rates from 2% down to 0.5%, reflecting lower loan demand and economic conditions.
7.7 Impact of Spending vs. Saving
तत्काल खर्च करने और भविष्य के लिए बचत करने के बीच चयन करना एक आम दुविधा है। तत्काल संतुष्टि से पछतावे की स्थिति पैदा हो सकती है अगर यह अधिक महत्वपूर्ण वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने से रोकता है, जैसे कि घर खरीदना या आरामदायक सेवानिवृत्ति सुनिश्चित करना।
परिद्रश्य 1:
एमिली ने इसके उन्नत फीचर्स से आकर्षित होकर आवेग में आकर एक हाई-एंड लैपटॉप खरीदने का फैसला किया। महीनों बाद, उसे पछतावा हुआ कि उसने उस पैसे को एक पेशेवर प्रमाणन के लिए क्यों नहीं बचाया, जो उसके करियर को आगे बढ़ा सकता था, जिससे उसे तत्काल संतुष्टि पर दीर्घकालिक वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को प्राथमिकता देने के महत्व पर प्रकाश डाला गया।
परिदृश्य 2:
बोनस मिलने के बाद, जेक तुरंत एक महंगी छुट्टी की बुकिंग करता है। मज़ेदार होने के बावजूद, बाद में उसे लगता है कि उसने अपनी कार की अप्रत्याशित मरम्मत के लिए आपातकालीन निधि के लिए कुछ पैसे बचाए होते, जिससे वर्तमान का आनंद लेने और भविष्य की तैयारी के बीच संतुलन पर ज़ोर पड़ता है।
आकृति: Pay Off Debt vs. Save Money: Which Comes First?
विवरण:
This image tackles the common financial dilemma of whether to focus on paying off debt या building savings. It presents a clear, step-by-step guide to help you decide where to direct your money first. The framework helps you create a balanced strategy that allows you to build a financial safety net while efficiently eliminating debt.
चाबी छीनना:
- The first priority for almost everyone should be to build a starter आपातकालीन निधि of at least $500 to $1,000. This prevents small emergencies from forcing you into more debt.
- After establishing a small emergency fund, you should aggressively pay down any high-interest debt, like credit card balances, as the interest charged is often very high.
- If your employer offers a retirement plan with a company match, contribute enough to get the full match, as this is essentially a 100% return on your investment and a top priority.
- Once high-interest debt is gone, you can adopt a balanced approach by simultaneously building your full 3-6 month emergency fund and saving for other long-term goals.
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
- This model provides a clear roadmap to help you make smart decisions and reduce financial stress when you have competing financial priorities.
- You can use this framework to create an effective cash flow plan, ensuring your money is allocated in the most impactful way.
- By following these steps—starter आपातकालीन निधि, attacking high-interest debt, and securing an employer match—you can build a strong financial foundation for future wealth creation.
7.8 Inflation and Interest Rates
मुद्रास्फीति समय के साथ पैसे के मूल्य को कम करती है, जिससे बचत की क्रय शक्ति कम हो जाती है। नाममात्र ब्याज दर मुद्रास्फीति के लिए जिम्मेदार नहीं है, जबकि वास्तविक ब्याज दर (नाममात्र दर घटा मुद्रास्फीति दर) बचत की वास्तविक वृद्धि को दर्शाती है। बचतकर्ताओं को अपनी बचत के मूल्य को बनाए रखने के लिए मुद्रास्फीति से आगे निकलने वाली नाममात्र दर की तलाश करनी चाहिए।
ब्याज दर = नाममात्र ब्याज - मुद्रास्फीति की दर
उदाहरण:
यदि बचत खाते पर नाममात्र ब्याज दर 3% है और मुद्रास्फीति दर 2% है, तो वास्तविक ब्याज दर प्रभावी रूप से 1% है। एक वर्ष में, मुद्रास्फीति के लिए समायोजित करने पर इस खाते में धन की क्रय शक्ति केवल 1% तक बढ़ती है, जो समय के साथ वास्तव में धन बढ़ाने के लिए मुद्रास्फीति को पीछे छोड़ने वाले बचत या निवेश विकल्पों की तलाश करने के महत्व को रेखांकित करता है।
7.9 Inflation Protection and I Bonds
बांड मुद्रास्फीति से सुरक्षा के लिए डिज़ाइन किए गए हैं, क्योंकि उनकी ब्याज दरें मुद्रास्फीति के साथ समायोजित होती हैं। जब मुद्रास्फीति बढ़ती है, तो बांड पर ब्याज दर बढ़ जाती है, जिससे यह सुनिश्चित होता है कि बचत समय के साथ अपनी क्रय शक्ति बनाए रखे, पारंपरिक सीडी के विपरीत, जहां निश्चित ब्याज दरें उच्च मुद्रास्फीति वाले वातावरण में नकारात्मक वास्तविक रिटर्न का कारण बन सकती हैं।
भावी मूल्य और छूट
आकृति: Calculating the Future Value of a Single Cash Flow
विवरण:
The infographic likely demonstrates the formula for calculating the future value of a single cash flow, which is a fundamental concept in finance. This formula helps in understanding how much an investment made today will grow to at a future date, considering a specific rate of interest. The formula is typically represented as FV = PV(1 + r)^n, where FV is the future value, PV is the present value, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
चाबी छीनना:
- भविष्य मूल्य (एफवी) फार्मूला यह गणना करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है कि समय के साथ निवेश कैसे बढ़ता है।
- इस सूत्र को समझने से निवेशकों को भविष्य में निवेश के मूल्य का अनुमान लगाने में मदद मिलती है।
- सूत्र में शामिल चरों में वर्तमान मूल्य (PV), ब्याज दर (r) और अवधियों की संख्या (n) शामिल हैं, जिनमें से प्रत्येक गणना में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
This concept is essential for anyone involved in financial planning, investment analysis, or saving for future goals. By applying this formula, individuals can make informed decisions about their investments, understanding how different rates of interest and time periods affect the growth of their money. It encourages strategic investment and helps in setting realistic expectations for investment returns, which is fundamental for long-term financial planning and wealth accumulation.
स्प्रेडशीट का उपयोग करके, हम गणना करते हैं कि एक 10 वर्षीय बच्चे को कॉलेज की एक वर्ष की ट्यूशन फीस वहन करने के लिए 5% वार्षिक ब्याज दर पर $200 प्रति माह की बचत करने की आवश्यकता है, जिसका अनुमान आज से आठ वर्ष बाद $20,000 है। यह उदाहरण भविष्य के वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को पूरा करने के लिए आज कितनी बचत करने की आवश्यकता है, यह निर्धारित करने के लिए ब्याज के लिए लेखांकन करते हुए, धन के भविष्य के मूल्य को छूट देता है।
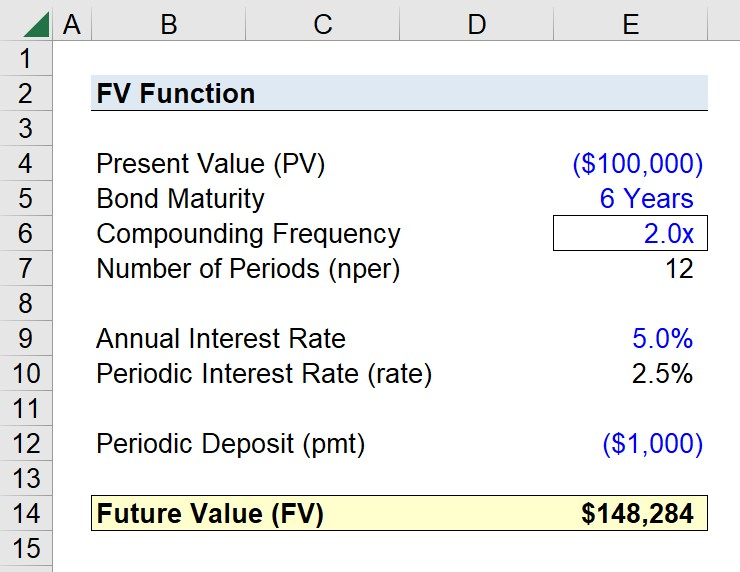
आकृति: Using the FV Function in Excel to Calculate Future Value
विवरण:
The infographic likely demonstrates how to use the FV function in Excel to calculate the future value of an investment, considering a constant interest rate over a number of periods. The FV function is a powerful tool in Excel for financial analysis, allowing users to input variables such as rate, number of periods, payments, present value, and type (whether payments are made at the beginning or end of periods) to compute the future value of an investment.
चाबी छीनना:
- एक्सेल में FV फ़ंक्शन निवेश के भावी मूल्य की गणना के लिए आवश्यक है।
- एफवी फ़ंक्शन के लिए प्रमुख इनपुट में ब्याज दर, अवधियों की संख्या, आवधिक भुगतान, वर्तमान मूल्य और भुगतान समय शामिल हैं।
- एफवी फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग कैसे किया जाए, यह समझने से वित्तीय मॉडलिंग और निवेश विश्लेषण कौशल में महत्वपूर्ण वृद्धि हो सकती है।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
This knowledge is crucial for finance students, financial analysts, and anyone involved in investment planning or analysis. By mastering the FV function, users can quickly assess the potential future value of investments, aiding in decision-making processes. It’s particularly useful for evaluating the growth of savings accounts, retirement funds, or any investment over time, providing a clear picture of financial futures.
7.10 Down Payments and Loans
ऋण पर डाउन पेमेंट करना, जैसे कि घर पर 20% डाउन पेमेंट, उधार ली गई कुल राशि को कम करता है, जिससे मासिक भुगतान कम होता है और अक्सर बेहतर ब्याज दरें मिलती हैं। यह उधारकर्ता को ऋणदाताओं के लिए अधिक आकर्षक बनाता है और समय के साथ ऋण की लागत को काफी कम कर सकता है।
7.11 Emergency Funds and Financial Planning
आपातकालीन निधि वित्तीय स्थिरता के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है, यह अप्रत्याशित खर्चों के लिए सुरक्षा जाल प्रदान करती है। अल्पकालिक और दीर्घकालिक बचत के लिए आवंटन शामिल करने वाला बजट बनाना और बनाए रखना जीवन की अनिश्चितताओं के लिए तैयारी और वित्तीय लक्ष्यों की दिशा में प्रगति सुनिश्चित करता है।
उदाहरण:
मारिया की कार खराब हो जाती है, जिसके लिए उसे महंगी मरम्मत की ज़रूरत होती है। वह विवेकाधीन खर्च को कम करने के लिए अपने बजट में संशोधन करती है और मरम्मत की लागत को पूरा करने के लिए अपने मनोरंजन और बाहर खाने-पीने की श्रेणियों से धन का पुनर्वितरण करती है, जबकि अपने बचत खाते में योगदान को अस्थायी रूप से कम करती है।

आकृति:व्यक्तिगत वित्त नियोजन की छह-चरणीय प्रक्रिया
विवरण:
यह छवि व्यक्तिगत वित्त नियोजन के लिए छह-चरणीय प्रक्रिया का परिचय देती है। इसकी शुरुआत व्यक्ति की वर्तमान वित्तीय स्थिति का आकलन करने से होती है, जिसमें संपत्ति और देनदारियाँ शामिल हैं, और वित्तीय लक्ष्य निर्धारित करने, कार्य योजना बनाने, निवेश विकल्पों का मूल्यांकन करने, योजना को लागू करने और रणनीति की नियमित समीक्षा और संशोधन करने के माध्यम से आगे बढ़ती है।
चाबी छीनना:
- वर्तमान वित्त का आकलन योजना के लिए प्रारंभिक बिंदु के रूप में यह महत्वपूर्ण है।
- लक्ष्य की स्थापना इसमें लघु, मध्यम और दीर्घकालिक वित्तीय आकांक्षाओं के लिए मूल्य और समयसीमा निर्धारित करना शामिल है।
- एक कार्य योजना किसी को अपनी जोखिम सहनशीलता पर विचार करना चाहिए और उसके अनुसार निवेश विकल्पों को संरेखित करना चाहिए।
- निवेश विकल्प इन्हें विशिष्ट लक्ष्यों से जोड़ा जाना चाहिए तथा कर दक्षता और उपयुक्तता के आधार पर चुना जाना चाहिए।
- नियमित निवेश आदत निर्माण और वित्तीय लक्ष्यों की सुचारू प्राप्ति में योगदान देता है।
- आवधिक समीक्षा यह सुनिश्चित करें कि निवेश सही दिशा में हो और आवश्यकतानुसार समायोजन की अनुमति हो।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
व्यक्तिगत वित्त नियोजन में अपनी वर्तमान वित्तीय स्थिति का आकलन करना आधारभूत है। वित्तीय रूप से अपनी स्थिति को समझकर, आप यथार्थवादी लक्ष्य निर्धारित कर सकते हैं, सुधार के क्षेत्रों की पहचान कर सकते हैं, और वित्तीय स्थिरता और विकास प्राप्त करने के लिए एक रोडमैप बना सकते हैं। यह कदम सुनिश्चित करता है कि बाद की योजना वास्तविकता पर आधारित हो और व्यक्ति की विशिष्ट वित्तीय परिस्थितियों के अनुरूप हो।
Contingency Planning for Financial Emergencies
Contingency planning involves preparing for unexpected financial shocks by having backup savings or insurance. A good contingency plan can help cover emergency expenses such as car repairs, medical bills, sudden unemployment, or major household repairs without derailing long-term financial goals.
उदाहरण:
- Backup Fund: Besides an emergency fund, maintain a small “contingency fund” specifically for very short-term needs.
- Insurance: Maintain adequate health, auto, and renters/homeowners insurance to mitigate major risks.
- Backup Budget: Create a reduced-spending version of your budget to activate if income drops suddenly.
वेतन और कटौतियों को समझना
सकल भुगतान किसी भी कटौती से पहले कर्मचारी की कुल कमाई है। कुल भुगतान, या टेक-होम वेतन, वह है जो करों, स्वास्थ्य सेवा और अन्य कटौतियों के बाद बचता है। सटीक बजट बनाने के लिए अंतर को समझना आवश्यक है।
7.12 Financial Institutions and Services
बैंक, क्रेडिट यूनियन और ऑनलाइन प्लेटफ़ॉर्म सहित वित्तीय संस्थान, चेकिंग और बचत खाते और वित्तीय नियोजन सेवाओं जैसे विभिन्न उत्पाद प्रदान करते हैं। प्रभावी धन प्रबंधन और वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने के लिए सही संस्थान और सेवाओं का चयन करना महत्वपूर्ण है।
खाता प्रबंधन का उदाहरण:
चेकिंग अकाउंट को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, नियमित रूप से लेन-देन की समीक्षा करें और सटीकता सुनिश्चित करने के लिए व्यक्तिगत रिकॉर्ड के साथ मिलान करें। मोबाइल बैंकिंग ऐप का उपयोग ट्रैकिंग को सरल बना सकता है और ओवरड्राफ्ट शुल्क से बचने में मदद कर सकता है।
7.13 The Role of FDIC and NCUA Insurance
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insures deposits at banks, while the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) insures deposits at credit unions. Both agencies guarantee deposit accounts (up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank or credit union) in case the financial institution fails. This insurance provides consumers with peace of mind that their money is protected against institutional collapse.
उदाहरण:
If your bank closes unexpectedly, the FDIC will reimburse your insured deposits up to the coverage limit.
निष्कर्ष
Saving, managing financial products, preparing for inflation, and understanding the broader banking environment are essential skills for long-term financial success. By supplementing your knowledge with insights about CDs, market influences on interest rates, the differences between mobile/crypto accounts and traditional banks, federal insurance protections, and emergency contingency planning, you’ll be even better equipped to protect and grow your financial future.
मुख्य पाठ जानकारी:
लोरेम इप्सुम डोलर सिट अमेट, कॉन्सेक्टूर एडिपिसिंग एलिट। उत एलीट टेलुस, लक्टस नेक उल्लमकोर्पर मैटिस, पुल्विनार डेपिबस लियो।