Local: IPOs in the European Union
पाठ सीखने के उद्देश्य:
- को समझें IPO process in the European Union, including the necessary steps such as prospectus filing, underwriting, and stock exchange listing, guided by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and national regulators.
- के बारे में जानें regulatory framework governing public companies in the EU, including compliance with the EU Prospectus Directive, MiFID II, and the Market Abuse Regulation (MAR), which ensure that companies maintain high standards of transparency and corporate governance.
- Explore the role of key stakeholders in the IPO process, such as investment banks, legal advisors, and regulatory bodies, and their impact on the structure and success of the offering.
- Gain insights into the ongoing obligations of public companies in the EU, including quarterly and annual reporting under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and corporate governance requirements.
27.1 Local:: IPO vs Public Companies
In the European Union, Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) and the regulations governing public companies are influenced by EU-specific laws, ensuring transparency, investor protection, and market stability. The IPO process and the requirements for public companies vary across member states but are largely shaped by EU-wide regulations enforced by bodies like ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority).
27.2 IPOs in the European Union
एक Initial Public Offering (IPO) in the EU allows companies to raise capital by offering shares to the public for the first time. This process is highly regulated to protect investors and ensure transparency in the market.
IPO Process in the EU
In the European Union, companies must follow a structured process to go public, adhering to the rules set by ESMA and other national regulators.
- Prospectus Filing: The company must submit a detailed prospectus, outlining its financials, risks, and business model. This document must be approved by a national regulator, such as the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) in the UK or AMF (Autorité des marchés financiers) in France.
- Underwriting: Major European investment banks such as Deutsche Bank और BNP Paribas underwrite the IPO, determining the initial share price and facilitating the sale of shares.
- Stock Exchange Listing: The company is then listed on one of Europe’s major stock exchanges, such as the London Stock Exchange (LSE), Euronext, or Deutsche Börse.
- उदाहरण: The IPO of Spotify on the New York Stock Exchange in 2018 after extensive regulatory processes in Sweden illustrates the complex nature of cross-border IPOs involving European companies.
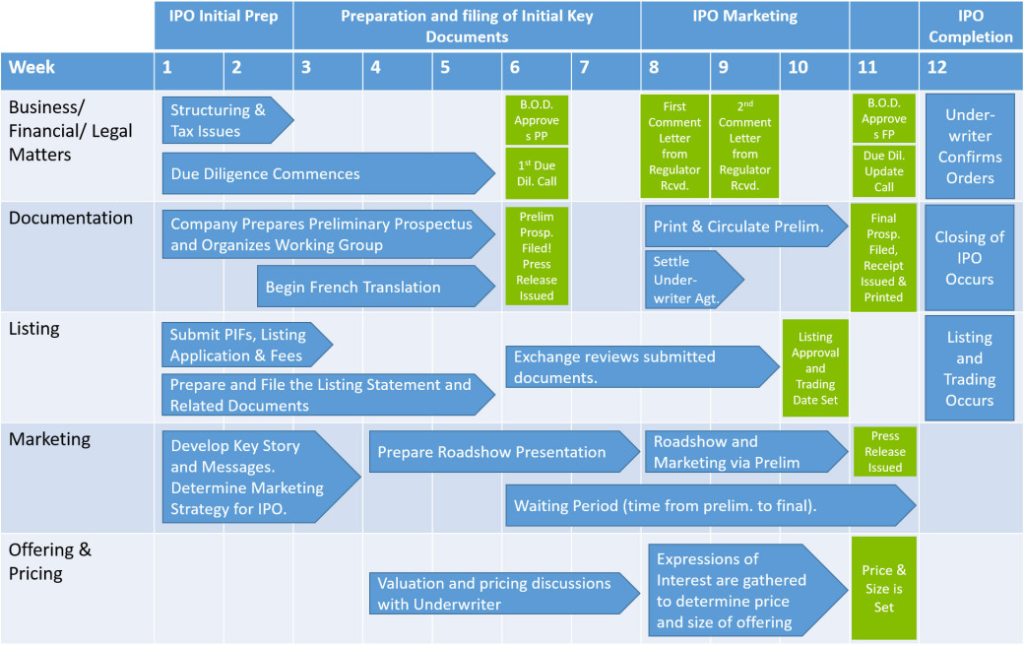
आकृति: IPO Process Timeline
विवरण:
The figure illustrates a 12-week Initial Public Offering (IPO) process, broken down into five key areas: Business/Financial/Legal Matters, Documentation, Listing, Marketing, और Offering & Pricing. Each area has a series of steps spread across four main phases: IPO Initial Prep, Preparation and Filing of Initial Key Documents, IPO Marketing, और IPO Completion. This structured process involves tasks like structuring & tax issues, यथोचित परिश्रम, preparing key documents, roadshow presentations, and final steps such as pricing discussions और listing approval. The timeline includes key milestones like regulatory comments, board approvals, और underwriter confirmation to ensure the successful completion of the IPO.
चाबी छीनना:
- The IPO process is segmented into four main phases: initial preparation, document preparation, marketing, and completion.
- The process involves multiple stakeholders such as legal advisors, underwriters, and regulatory authorities.
- The steps are designed to ensure thorough due diligence, compliance, और effective marketing.
- Roadshows play a crucial role in marketing the IPO to potential investors.
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
समझना IPO process is essential for companies considering going public, as well as for investors evaluating IPO opportunities. By following this structured approach, companies can ensure compliance, manage stakeholder expectations, और optimize pricing. For learners, this timeline offers insights into the strategic planning और execution required to navigate the complexities of going public.
Regulatory Considerations for IPOs in the EU

European IPOs are subject to stringent regulations aimed at maintaining market stability and investor confidence.
- Prospectus Regulation: The EU Prospectus Directive ensures that companies provide detailed and transparent information to investors. All IPO filings must meet these strict requirements before approval.
- MiFID II: The Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) strengthens investor protection and market transparency. It governs how IPOs are marketed to retail investors and the disclosure of risks.
लोरेम इप्सम डोलर सिट अमेट, कंसेक्टेचर एडिपिसिंग एलीट। यूट एलीट टेलस, ल्यूक्टस नेक उल्लमकॉर्पर मैटिस, पुल्विनर डैपिबस लियो।
27.3 Public Companies in the European Union
Once a company completes its IPO, it becomes a public company and must adhere to the EU’s extensive regulatory framework. These regulations ensure ongoing transparency, corporate governance, and investor protection.
Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
Public companies in the EU are required to meet high standards for financial transparency and corporate governance.
- Quarterly and Annual Reports: Public companies must submit detailed financial reports every quarter and year. These reports must comply with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), providing consistency across EU markets.
- Corporate Governance: Public companies must adhere to strict corporate governance rules, including maintaining a board of directors and holding annual general meetings for shareholders. These standards are designed to protect shareholder interests.
27. 4 Regulatory Bodies and Oversight
Public companies in Europe are regulated by ESMA and national financial authorities, such as BaFin in Germany and AMF in France. These bodies enforce compliance with reporting, corporate governance, and trading rules.
- Market Abuse Regulation (MAR): This regulation ensures that public companies disclose important information to the market in a timely manner, particularly when it comes to insider trading or corporate events like mergers and acquisitions.
- MiFID II: MiFID II continues to play a crucial role in ensuring fair market practices by public companies. It requires firms to provide transparent information to investors, particularly in the context of complex financial products and services.
निष्कर्ष
In the European Union, the processes for IPOs and the ongoing regulations governing public companies are designed to ensure transparency, protect investors, and maintain the integrity of financial markets. Companies going public through IPOs must comply with strict EU regulations and guidelines set by national and EU-wide bodies such as ESMA. Once a company becomes public, it is subject to rigorous reporting and governance standards, ensuring that shareholders and the public have access to accurate and timely information. Understanding these EU-specific regulations is essential for investors and companies operating within Europe’s complex financial markets.
मुख्य पाठ जानकारी:
- The IPO Process involves critical steps such as prospectus approval by a national regulator, collaboration with underwriters for pricing and sale, and ultimately, listing on a European stock exchange, each governed by stringent EU regulations to protect investors and ensure market stability.
- Regulatory Considerations, such as the EU Prospectus Directive and MiFID II, play pivotal roles in enhancing transparency and protecting investors by ensuring that all market participants have access to the same comprehensive information about IPOs and public companies.
- Post-IPO Requirements for public companies include rigorous financial reporting and adherence to corporate governance standards, which are vital for maintaining investor trust and ensuring a fair trading environment.
- Regulatory Bodies, including ESMA and national authorities like BaFin and AMF, enforce compliance and oversee the activities of public companies to prevent market abuse and enhance the integrity of European financial markets.
बंद बयान:
Navigating the IPO process and understanding the regulatory environment for public companies in the European Union are crucial for companies aiming to go public and for investors looking to engage with these entities. This knowledge is essential for ensuring compliance with EU regulations and making informed investment decisions.

