अध्याय 5: बजट और व्यय प्रबंधन
पाठ सीखने के उद्देश्य:
लोरेम इप्सुम डोलर सिट अमेट, कॉन्सेक्टूर एडिपिसिंग एलिट। उत एलीट टेलुस, लक्टस नेक उल्लमकोर्पर मैटिस, पुल्विनार डेपिबस लियो।
बजट और व्यय प्रबंधन का परिचय
बजट बनाना और व्यय प्रबंधन व्यक्तिगत वित्त के मूलभूत पहलू हैं। यह अध्याय बताता है कि आपातकालीन निधि के लिए आवंटन सहित अल्पकालिक और दीर्घकालिक वित्तीय लक्ष्यों के साथ संरेखित बजट कैसे बनाया जाए, और उपभोक्ता निर्णयों की गतिशीलता और उनके व्यापक प्रभावों को संबोधित करता है। इसके अतिरिक्त, हम बचत बनाम निवेश के सार, जीवन में बदलावों को समायोजित करने के लिए बजट में संशोधन, और नकदी प्रवाह और वित्तीय शुल्कों को समझने के महत्व पर गहराई से चर्चा करेंगे।
5.1 Developing a Budget
चुनने के लिए कई तरह के बजट बनाने के तरीके हैं, जिनमें से हर एक के अपने फायदे और नुकसान हैं। अपनी ज़रूरतों और प्राथमिकताओं के हिसाब से सबसे बेहतर तरीका चुनना ज़रूरी है। यहाँ तीन लोकप्रिय बजट बनाने के तरीके दिए गए हैं:
बजट बनाने में आय पर नज़र रखना, विभिन्न खर्चों के लिए धन आवंटित करना और वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने के लिए बचत अलग रखना शामिल है। एक अच्छी तरह से तैयार किए गए बजट में शामिल हैं:
- निश्चित व्ययआवर्ती लागतें जैसे कि किराया या बंधक, ऋण भुगतान और बीमा।
- परिवर्तनशील खर्च: ऐसे खर्चे जिनमें उतार-चढ़ाव रहता है, जैसे कि किराने का सामान, उपयोगिताएँ और मनोरंजन।
- बचत: भविष्य में उपयोग के लिए निर्धारित निधि, जिसमें आपातकालीन निधि और दीर्घकालिक बचत लक्ष्य शामिल हैं।
- आपातकालीन निधि: वित्तीय नियोजन का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा, जो अप्रत्याशित खर्चों को कवर करने के लिए बनाया गया है, जैसे चिकित्सा आपातस्थितियां या कार की मरम्मत।
Example Scenario: Jamie earns $3,000 monthly and wants to save for a vacation while covering living expenses. A budget might allocate $1,000 to rent, $300 to groceries, $200 to utilities, $400 to loan payments, $100 to entertainment, and $600 to an emergency fund, illustrating a balanced approach to managing fixed and variable costs and prioritizing savings.
आकृति: बजट बनाने की विधियों के प्रकार
विवरण:
छवि विभिन्न बजट विधियों को दर्शाती है जो विभिन्न प्राथमिकताओं और वित्तीय स्थितियों को पूरा करती हैं। यह बजट की अवधारणा को सरल बनाता है, इसे अधिक सुलभ बनाता है, और 50/30/20 बजट, लिफाफा बजट, शून्य-आधारित बजट और नो-बजट बजट जैसी विधियों की व्याख्या करता है, जिनमें से प्रत्येक को व्यक्तियों को अपने वित्त को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने में मदद करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
चाबी छीनना:
- 50/30/20 बजट: एक सरल दृष्टिकोण, जिसमें 50% आय को आवश्यकताओं के लिए, 30% इच्छाओं के लिए, तथा 20% बचत या ऋण भुगतान के लिए आवंटित किया जाता है।
- लिफाफा बजट: एक विधि जिसमें नकदी को विशिष्ट श्रेणियों के लिए भौतिक लिफाफों में आवंटित किया जाता है। खर्च प्रत्येक लिफाफे में उपलब्ध नकदी तक सीमित होता है।
- शून्य-आधारित बजट: अर्जित प्रत्येक डॉलर को एक विशिष्ट उद्देश्य दिया जाता है, जिससे यह सुनिश्चित होता है कि महीने के अंत में बजट शून्य हो जाए।
- नो-बजट बजट: अच्छी वित्तीय आदतों वाले उच्च आय वाले लोगों के लिए उपयुक्त। इसमें खर्च करने और अंतर को निवेश करने से ज़्यादा कमाने पर ध्यान दिया जाता है।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
अलग-अलग बजट बनाने के तरीके अलग-अलग व्यक्तित्व प्रकारों और वित्तीय स्थितियों को पूरा करते हैं। सही दृष्टिकोण को समझना और चुनना व्यक्तियों को अपने वित्त को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने में सक्षम बना सकता है, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि वे अपने साधनों के भीतर रहते हैं और अपने वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करते हैं। चाहे कोई व्यक्ति अधिक खर्च को रोकना चाहता हो, कुशलतापूर्वक धन आवंटित करना चाहता हो, या बस अपने वित्त पर बेहतर नियंत्रण प्राप्त करना चाहता हो, ये तरीके उन उद्देश्यों को प्राप्त करने के लिए संरचित तरीके प्रदान करते हैं।

5.2 Making Informed Consumer Decisions
उपभोक्ता के निर्णय मूल्य, उत्पाद विकल्प, बजट बाधाओं और संभावित सामाजिक और पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव जैसे कारकों से प्रभावित होते हैं।
सूचित निर्णय लेने की प्रक्रिया:
- अनुसंधान: उत्पाद और विकल्पों के बारे में जानकारी इकट्ठा करें।
- बजट: इस बात पर विचार करें कि खरीदारी आपके बजट में कितनी फिट बैठती है।
- प्रभाव: पर्यावरण और समाज पर संभावित प्रभावों का मूल्यांकन करें।
उदाहरण: पेट्रोल कार की तुलना में इलेक्ट्रिक वाहन का चयन, उच्च प्रारंभिक लागत के बावजूद, ईंधन पर दीर्घकालिक बचत, पर्यावरणीय लाभ और उपलब्ध कर प्रोत्साहन से प्रभावित हो सकता है।
5.3 Consumer Decision Factors
चयनित उत्पाद: इलेक्ट्रिक वाहन (ईवी)
खरीद निर्णय को प्रभावित करने वाले कारक:
- उत्पाद की कीमत: इलेक्ट्रिक वाहन की शुरुआती लागत पेट्रोल से चलने वाले वाहन की तुलना में ज़्यादा हो सकती है। हालाँकि, कर प्रोत्साहन और कम परिचालन लागत शुरुआती खर्च की भरपाई कर सकती है।
- विकल्प की कीमत: पारंपरिक गैसोलीन वाहन आम तौर पर शुरू में सस्ते होते हैं, लेकिन समय के साथ ईंधन और रखरखाव की लागत बढ़ जाती है।
- उपभोक्ता का बजट और प्राथमिकताएं: उपभोक्ता की ईवी खरीदने की क्षमता और पर्यावरण के अनुकूल विकल्पों के प्रति उनकी प्राथमिकता महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती है। कुछ लोग लागत से ज़्यादा पर्यावरण-मित्रता को प्राथमिकता देते हैं, जबकि अन्य लंबी अवधि की बचत पर ध्यान केंद्रित कर सकते हैं।
- पर्यावरण, समाज और अर्थव्यवस्था पर प्रभाव: इलेक्ट्रिक वाहन खरीदने से पर्यावरण पर कम असर पड़ता है क्योंकि इससे उत्सर्जन कम होता है। यह विकल्प अक्षय ऊर्जा क्षेत्र के विकास में भी सहायक हो सकता है, जिससे सामाजिक और आर्थिक बदलाव स्थिरता की ओर बढ़ सकते हैं।
सूचित उपभोक्ता निर्णय लेने की प्रक्रिया:
- अनुसंधान: विभिन्न मॉडलों के बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करें, जिसमें उनकी विशेषताएं, लागत और समीक्षाएं शामिल हों।
- तुलना: लागत, प्रदर्शन और आवश्यकताओं के लिए उपयुक्तता के संदर्भ में ई.वी. की तुलना पारंपरिक वाहनों से करें।
- बजट मूल्यांकन: सामर्थ्य का निर्धारण करने के लिए व्यक्तिगत वित्त का मूल्यांकन करें और दीर्घकालिक बचत पर विचार करें।
- पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव: ई.वी. के पारिस्थितिक लाभों पर विचार करें।
- अंतिम निर्णय: उपरोक्त कारकों पर संतुलित विचार के आधार पर चयन करें।
इलेक्ट्रिक वाहन खरीदने के प्रभाव:
- सकारात्मक: कार्बन उत्सर्जन कम होता है, परिचालन लागत कम होती है, नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा उद्योगों को बढ़ावा मिलता है।
- नकारात्मक: उच्च प्रारंभिक लागत से बजट पर दबाव पड़ सकता है; ईवी बैटरियों के उत्पादन और निपटान का पर्यावरण पर प्रभाव पड़ता है।
5.4 Managing Expenses and Budgeting
खर्च:
- Fixed Expenses: Rent, mortgage, car payments – costs that remain constant each month.
- परिवर्तनशील खर्च: Groceries, utilities, entertainment – costs that can fluctuate.
- Irregular Expenses: Annual insurance premiums, holiday gifts – costs that occur occasionally and can disrupt a regular budget.
मेरा मासिक बजट उदाहरण:
- निश्चित व्यय: $1,200 किराया, $300 कार भुगतान, $100 बीमा।
- परिवर्तनीय व्यय: $400 किराने का सामान, $150 उपयोगिताएँ, $100 मनोरंजन।
- अनियमित व्यय: सदस्यता या सदस्यता जैसी वार्षिक लागतों के लिए मासिक $50 अलग रखें।
- बचत: आपातकालीन निधि और भविष्य के निवेश के लिए मासिक $500 की बचत करने का लक्ष्य रखें।
- अधिशेष या घाटा: आय में से कुल व्यय (बचत सहित) घटाकर यह निर्धारित करें कि आप अपनी क्षमता के अनुसार जीवनयापन कर रहे हैं या अधिक व्यय कर रहे हैं।
बजट रणनीतियाँ:
- लिफाफा प्रणाली: हर महीने अलग-अलग खर्चों के लिए नकदी को वर्गीकृत लिफाफों में आवंटित करें। एक बार लिफाफे में रखी नकदी खत्म हो जाने के बाद, अगले महीने तक उस श्रेणी में कोई और खर्च करने की अनुमति नहीं है।
- बजट को जीवित रखना: अपने बजट की नियमित समीक्षा करें और उसे समायोजित करें। खर्च पर नज़र रखें, पैटर्न पहचानें और लक्ष्य पूरे करने के लिए बदलाव करें। रीयल-टाइम ट्रैकिंग और समायोजन के लिए बजटिंग ऐप या स्प्रेडशीट का उपयोग करें।
व्यय प्रबंधन
खर्च को नियंत्रित करने के लिए, आवश्यक और विवेकाधीन खर्चों के बीच अंतर करना आवश्यक है। अनावश्यक खर्च को कम करने की रणनीतियों में आवेगपूर्ण खरीद की पहचान करना, नकद व्यय के प्रबंधन के लिए लिफाफा प्रणाली का उपयोग करना और नियमित रूप से खर्च करने की आदतों की समीक्षा करना शामिल है।
आवश्यक (अनिवार्य) व्यय दैनिक जीवन में बुनियादी जीवनयापन और कामकाज के लिए आवश्यक लागतें हैं। ये खर्च किसी व्यक्ति या परिवार के लिए स्वस्थ और सुरक्षित जीवनशैली बनाए रखने के लिए न्यूनतम आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करते हैं। आवश्यक खर्चों में आम तौर पर ये शामिल हैं:
- आवास: किराया या बंधक भुगतान।
- उपयोगिताएँ: पानी, बिजली, गैस और कभी-कभी इंटरनेट सेवा, जो दूरस्थ कार्य या शिक्षा की आवश्यकता पर निर्भर करती है।
- भोजन: घर पर तैयार भोजन के लिए आवश्यक किराने का सामान।
- स्वास्थ्य देखभाल: बीमा प्रीमियम, चिकित्सा बिल, नुस्खे, और कोई भी चल रहा चिकित्सा उपचार।
- परिवहन: काम या स्कूल जाने के लिए यात्रा से जुड़ी लागतें, जिनमें कार भुगतान, सार्वजनिक परिवहन किराया, गैस और आवश्यक वाहन रखरखाव शामिल हैं।
- बीमा: आवश्यक बीमा पॉलिसियाँ, जिनमें स्वास्थ्य, वाहन, तथा मकान मालिक या किरायेदार बीमा शामिल हैं।
आवश्यक व्यय का उदाहरण: सारा किराए के लिए हर महीने $1,000, उपयोगिताओं के लिए $200, किराने के सामान के लिए $300, कार के बिल और गैस के लिए $250 और स्वास्थ्य बीमा के लिए $150 का बजट बनाती है। सुरक्षित और आराम से रहने के लिए ये लागतें गैर-परक्राम्य हैं।
विवेकाधीन (गैर-आवश्यक) व्यय वे लागतें हैं जो लोगों को उन चीज़ों से जुड़ी हैं जो वे चाहते हैं लेकिन बुनियादी जीवनशैली जीने के लिए उनकी ज़रूरत नहीं होती। ये खर्च अक्सर जीवन की गुणवत्ता को बढ़ाते हैं लेकिन ज़रूरत पड़ने पर इन्हें कम किया जा सकता है या खत्म किया जा सकता है। विवेकाधीन खर्चों में शामिल हैं:
- मनोरंजन: फिल्मों, संगीत समारोहों, स्ट्रीमिंग सेवाओं या अन्य मनोरंजक गतिविधियों पर खर्च किया गया धन।
- बाहर भोजन करना: पोषण के लिए आवश्यक राशि से अधिक रेस्तरां में खाने पर होने वाला व्यय।
- शौक: शौक या अवकाश गतिविधियों से संबंधित लागतें, जैसे शिल्प सामग्री, खेल उपकरण, या पुस्तक खरीद।
- यात्रा: छुट्टियों और गैर-आवश्यक यात्रा की लागत।
- विलासिता: उच्च श्रेणी के इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स, डिजाइनर कपड़े और अन्य विलासिता की वस्तुएं जो बुनियादी जरूरतों से परे हैं।
विवेकाधीन व्यय का उदाहरण: एलेक्स को बाहर खाना पसंद है, वह रेस्तराँ में हर महीने औसतन $300 खर्च करता है, कई स्ट्रीमिंग सेवाओं की सदस्यता लेता है जिसकी मासिक लागत $50 है, और शौक और मनोरंजन के लिए $200 आवंटित करता है। हालाँकि ये उसके जीवन को बेहतर बनाते हैं, लेकिन उन्हें उसके वित्तीय लक्ष्यों या स्थिति के आधार पर समायोजित किया जा सकता है।
आवश्यक एवं विवेकाधीन व्यय का प्रबंधनप्रभावी वित्तीय नियोजन में सबसे पहले यह सुनिश्चित करना शामिल है कि आवश्यक व्यय व्यक्ति के बजट में शामिल हैं। उसके बाद बची हुई आय को विवेकाधीन व्यय, बचत और निवेश के लिए आवंटित किया जा सकता है। विवेकाधीन व्यय पर बचत और ऋण चुकौती को प्राथमिकता देना दीर्घकालिक वित्तीय स्वास्थ्य के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है। व्यक्तियों को आय या वित्तीय लक्ष्यों में परिवर्तन के जवाब में अपने बजट को समायोजित करने के लिए समय-समय पर अपनी खर्च करने की आदतों, विशेष रूप से विवेकाधीन व्यय की समीक्षा करने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
आवश्यक और विवेकाधीन व्ययों के बीच अंतर करके और समग्र वित्तीय नियोजन पर उनके प्रभाव को समझकर, व्यक्ति अपनी प्राथमिकताओं और वित्तीय उद्देश्यों के अनुरूप सूचित निर्णय ले सकते हैं, जिससे उनके लक्ष्यों के प्रति स्थिरता और प्रगति सुनिश्चित होगी।
5.5 Creating and Revising Budgets
आय, जीवन परिस्थितियों और वित्तीय लक्ष्यों में परिवर्तन को प्रतिबिंबित करने के लिए बजट को लचीला होना चाहिए।
- अल्पावधि बचत: आपातकालीन और अप्रत्याशित खर्चों को कवर करना चाहिए।
- दीर्घकालिक बचत: भविष्य की आकांक्षाओं, जैसे घर का स्वामित्व या सेवानिवृत्ति, पर लक्षित।
बजट अनुकूलन: जीवन की घटनाएं, जैसे नौकरी में बदलाव या अप्रत्याशित बिल, वित्तीय रूप से पटरी पर बने रहने के लिए बजट समायोजन को आवश्यक बनाती हैं।
Example: If Alex experiences a job loss, the budget must be revised to reduce variable expenses and prioritize essential costs and minimal savings until income stabilizes.
- बचत का अर्थ है भविष्य में उपयोग के लिए धन अलग रखना, आमतौर पर कम जोखिम वाले, आसानी से उपलब्ध साधनों में। बचत बनाम निवेश हिसाब किताब।
- निवेश में ऐसी परिसंपत्तियों को खरीदना शामिल है जिनमें समय के साथ अधिक रिटर्न की संभावना होती है, लेकिन इसमें अधिक जोखिम भी शामिल होता है।
इस अंतर को समझने से वित्तीय रणनीतियों को लक्ष्यों के साथ संरेखित करने, बचत की सुरक्षा और निवेश की वृद्धि क्षमता के बीच संतुलन बनाने में मदद मिलती है।
5.6 Designing a Personal Budget
एक व्यक्तिगत बजट में व्यक्ति की विशिष्ट वित्तीय स्थिति, लक्ष्य और प्राथमिकताएँ प्रतिबिंबित होनी चाहिए। इसमें शामिल हैं:
- लक्ष्यों का समायोजन: स्पष्ट एवं प्राप्त करने योग्य उद्देश्य निर्धारित करें।
- आय का आवंटन: आय को व्यय, बचत और निवेश में वितरित करें।
- निगरानी एवं संशोधन: परिस्थितियों के अनुसार बजट की नियमित समीक्षा करें और उसे समायोजित करें।
5.7 Impact of External Factors:
कर, मुद्रास्फीति और व्यक्तिगत परिवर्तन (जैसे, विवाह, बच्चे) बजटीय आवश्यकताओं और वित्तीय नियोजन को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित करते हैं।
यथार्थवादी व्यक्तिगत या पारिवारिक बजट तैयार करना:
- आय के स्रोतों की पहचान करें: सभी स्रोतों से कुल मासिक आय की गणना करें।
- व्ययों की सूची बनाएं और उन्हें वर्गीकृत करेंव्यय को निश्चित, परिवर्तनीय और अनियमित श्रेणियों में अलग करें।
- बचत के लिए धन आवंटित करेंबचत और आपातकालीन निधि के लिए आय का एक हिस्सा अलग रखने को प्राथमिकता दें।
- अधिशेष या घाटे के लिए समायोजन: अगर खर्चे आय से ज़्यादा हैं, तो कटौती के लिए जगह तलाशें। अगर बचत ज़्यादा है, तो बचत या कर्ज चुकाने के लिए अतिरिक्त पैसे आवंटित करें।
- निगरानी एवं समीक्षा: अपने बजट को वास्तविक खर्च के साथ नियमित रूप से जांचें और ट्रैक पर बने रहने के लिए आवश्यकतानुसार समायोजन करें।
5.8 Interest and Fees in Money Management
खर्च, उधार और बचत से जुड़ी ब्याज दरों और शुल्कों को समझना महत्वपूर्ण है। बचत पर ब्याज जमा हो सकता है, जिससे धन में वृद्धि हो सकती है, या ऋण पर, जिससे उधार ली गई धनराशि की लागत बढ़ सकती है।
ब्याज की गणना:
उदाहरण के लिए, 1.5% वार्षिक ब्याज दर वाले बचत खाते से एक वर्ष में $10,000 शेष राशि पर $150 प्राप्त होगा, जबकि 20% ब्याज दर वाले क्रेडिट कार्ड से उसी अवधि में $1,000 बकाया राशि पर $200 ब्याज प्राप्त हो सकता है।
बजट और व्यय प्रबंधन के सिद्धांतों में निपुणता प्राप्त करके, व्यक्ति आत्मविश्वास के साथ अपनी वित्तीय यात्रा को आगे बढ़ा सकते हैं, तथा सूचित निर्णय ले सकते हैं, जो स्थिरता, विकास और संतुष्टि को बढ़ावा देते हैं।
करों में परिवर्तन
प्रभाव: करों में वृद्धि, चाहे वह आयकर हो, संपत्ति कर हो या बिक्री कर हो, सीधे तौर पर किसी व्यक्ति या परिवार की प्रयोज्य आय की मात्रा को कम कर देती है। उदाहरण के लिए, यदि आयकर बढ़ता है, तो करों के बाद शुद्ध आय घट जाती है, जिससे खर्च और बचत के लिए कम पैसे बचते हैं। इसके विपरीत, कर में कमी से प्रयोज्य आय बढ़ सकती है, जिससे बजट में अन्य खर्चों या बचत के लिए अधिक जगह मिल सकती है।
उदाहरण: मान लीजिए कि टैक्स कानून में बदलाव के कारण एलेक्स की प्रभावी आयकर दर बढ़ जाती है। परिणामस्वरूप, उसका मासिक टेक-होम वेतन घट जाता है। समायोजन के लिए, एलेक्स को अपनी वित्तीय स्थिरता बनाए रखने के लिए अपने विवेकाधीन खर्च को कम करने या अपने बचत योगदान का पुनर्मूल्यांकन करने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
मुद्रा स्फ़ीति
प्रभाव: मुद्रास्फीति समय के साथ क्रय शक्ति को कम करती है, जिसका अर्थ है कि एक ही राशि से कम सामान और सेवाएँ खरीदी जा सकती हैं। भोजन, आवास और स्वास्थ्य सेवा जैसी आवश्यक वस्तुओं की कीमतें बढ़ने पर, व्यक्तियों को लग सकता है कि उनका मौजूदा बजट अब उनकी ज़रूरतों को पूरा नहीं कर पा रहा है। इसके लिए या तो आय बढ़ाने के तरीके खोजने होंगे या जीवन की बढ़ती लागत को समायोजित करने के लिए खर्च करने की आदतों को समायोजित करना होगा।
उदाहरण: यदि वार्षिक मुद्रास्फीति दर 3% है, और एमिली का वेतन नहीं बढ़ता है, तो उसके जीवन-यापन के खर्च बढ़ जाएँगे, जिससे उसकी डिस्पोजेबल आय प्रभावी रूप से कम हो जाएगी। एमिली को गैर-ज़रूरी खर्चों में कटौती करनी पड़ सकती है, आय के अतिरिक्त स्रोतों की तलाश करनी पड़ सकती है, या जीवन-यापन की बढ़ी हुई लागत को प्रबंधित करने के लिए अपने खर्चों को अलग तरह से प्राथमिकता देनी पड़ सकती है।
व्यक्तिगत परिस्थितियाँप्रभाव: जीवन की घटनाएँ जैसे कि विवाह, तलाक, बच्चे का जन्म, नौकरी छूटना या विरासत प्राप्त करना किसी व्यक्ति की वित्तीय स्थिति और बजट को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित कर सकता है। सकारात्मक परिवर्तनों के परिणामस्वरूप वित्तीय स्थिरता बढ़ सकती है, जबकि चुनौतीपूर्ण घटनाओं के लिए बजट को कड़ा करना या नई मांगों को पूरा करने के लिए धन का पुनर्वितरण करना पड़ सकता है।
उदाहरण 1: अपने बच्चे के जन्म के बाद, जॉर्डन और टेलर को एहसास होता है कि उनका मौजूदा अपार्टमेंट बहुत छोटा है। बड़े घर में जाने से उनका किराया बढ़ जाता है, जिससे इस ज़रूरी खर्च को पूरा करने के लिए उन्हें अपने बजट में बदलाव करने पड़ते हैं।
उदाहरण 2: सारा को पर्याप्त वेतन वृद्धि के साथ पदोन्नति मिलती है। वह अपनी सेवानिवृत्ति बचत योगदान को बढ़ाने और अपने बच्चों के लिए कॉलेज फंड शुरू करने का फैसला करती है, जो उसकी बेहतर वित्तीय स्थिति को दर्शाता है।
परिवर्तनों के साथ समायोजनकरों, मुद्रास्फीति और व्यक्तिगत परिस्थितियों में होने वाले परिवर्तनों के अनुकूल ढलने के लिए, व्यक्तियों को निम्न की आवश्यकता हो सकती है:
- नियमित रूप से बजट की समीक्षा करें और उसे समायोजित करें: आय और व्यय में परिवर्तन के अनुरूप बजट को लचीला बनाए रखें।
- खर्च को प्राथमिकता दें: इच्छाओं की अपेक्षा आवश्यकताओं पर ध्यान दें, विशेषकर वित्तीय कठिनाई के समय।
- आय बढ़ाने के अवसर तलाशें: अतिरिक्त काम तलाशें, वेतन वृद्धि की मांग करें, या बेहतर वेतन वाली नौकरियों के लिए नए कौशल हासिल करें।
- आपातकालीन निधि बनाएं: अप्रत्याशित परिवर्तनों या चुनौतियों का प्रबंधन करने में सहायता के लिए वित्तीय बफर उपलब्ध कराना।
प्रभावी बजट और व्यय प्रबंधन वित्तीय स्थिरता प्राप्त करने और दीर्घकालिक लक्ष्यों को पूरा करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं। इन सिद्धांतों को समझना और लागू करना व्यक्तियों को सूचित उपभोक्ता निर्णय लेने और एक स्वस्थ वित्तीय जीवन शैली बनाए रखने की अनुमति देता है।
आकृति: 10 आवश्यक बजट श्रेणियाँ
विवरण:
छवि दस आवश्यक बजट श्रेणियों की सूची प्रस्तुत करती है, जिन पर व्यक्तियों को अपने वित्त की योजना बनाते समय विचार करना चाहिए। ये श्रेणियाँ व्यय और बचत क्षेत्रों की एक श्रृंखला को कवर करती हैं, जिससे व्यक्तियों को अपने धन को प्रभावी ढंग से आवंटित करने में मदद मिलती है।
चाबी छीनना:
- बंधक या किराया: आवास व्यय के लिए धन आवंटित करें।
- बचत और निवेश: भविष्य के वित्तीय लक्ष्यों और धन संचय के लिए धन अलग रखें।
- ऋण या छात्र ऋण: ऋण और शैक्षिक ऋण के पुनर्भुगतान की योजना बनाएं।
- परिवहन: आवागमन, वाहन रखरखाव और अन्य परिवहन-संबंधी लागतों के लिए बजट बनाएं।
- विविध व्यय: अप्रत्याशित या विविध व्ययों के लिए धन आवंटित करें।
- सदस्यताएँ: मासिक या वार्षिक सदस्यता सेवाओं के लिए बजट।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
प्रभावी वित्तीय नियोजन के लिए बजट क्षेत्रों का स्पष्ट वर्गीकरण होना महत्वपूर्ण है। व्यय और बचत को विशिष्ट श्रेणियों में विभाजित करके, व्यक्ति अपनी वित्तीय आदतों की बेहतर समझ प्राप्त कर सकते हैं, सुधार के क्षेत्रों की पहचान कर सकते हैं और सूचित निर्णय ले सकते हैं। यह वर्गीकरण किसी भी व्यक्ति के लिए एक व्यापक बजट बनाने के लिए एक आधारभूत मार्गदर्शिका के रूप में कार्य करता है, यह सुनिश्चित करता है कि सभी आवश्यक क्षेत्रों को कवर किया गया है और वित्तीय लक्ष्य पूरे किए गए हैं।
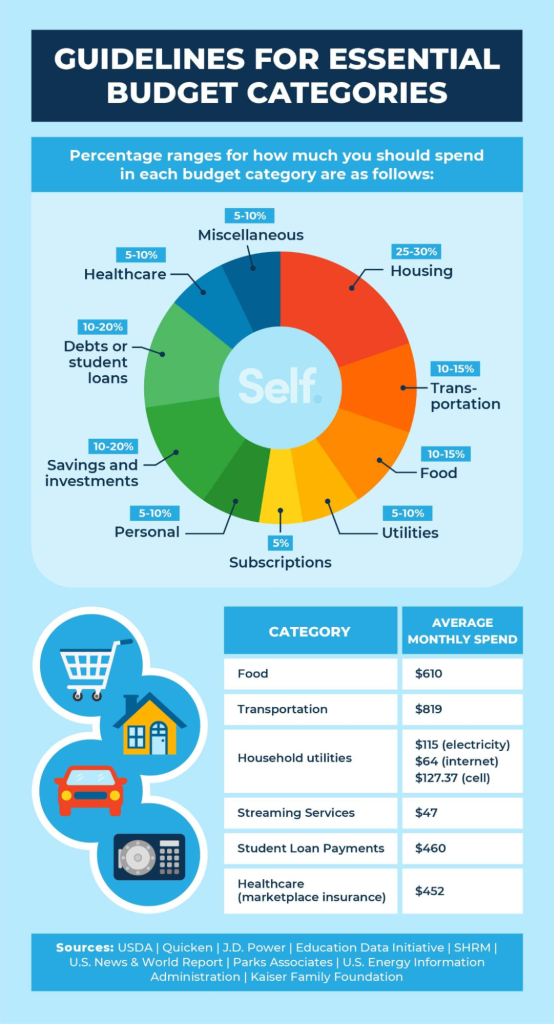
Figure: Essential Budget Categories for Financial Planning
विवरण:
The image from Self.inc outlines ten essential budget categories that are critical for effective financial planning. These categories help individuals understand their spending patterns and manage their finances by allocating funds appropriately to areas such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare.
चाबी छीनना:
- आवास पर आम तौर पर लगभग 30% आय खर्च होनी चाहिए, जिसमें बीमा और कर जैसी संबद्ध लागतें भी शामिल हैं।
- भोजन संबंधी व्यय आय के 10% से 16% तक हो सकता है, जिसमें परिवार के आकार और आहार विकल्पों के आधार पर भिन्नता हो सकती है।
- परिवहन लागत, जिसमें वाहन भुगतान और सार्वजनिक परिवहन शामिल हैं, आदर्श रूप से मासिक आय के 15% से अधिक नहीं होनी चाहिए।
- ऊर्जा-बचत उपायों और सेवा योजना तुलनाओं के माध्यम से उपयोगिता बिलों को आय के 5% से 10% के भीतर रखा जा सकता है।
- नियमित और संभावित अप्रत्याशित चिकित्सा व्यय को ध्यान में रखते हुए, स्वास्थ्य देखभाल लागत को 5% से 10% के बीच बजट में रखने की सिफारिश की जाती है।
सूचना का अनुप्रयोग:
By categorizing expenses, individuals can create a structured budget that aligns with their income and financial goals. This approach allows for a clear understanding of where money is being spent and where adjustments can be made to save more or pay off debt. It’s particularly useful for those looking to gain control over their finances and work towards financial stability and independence.
5.9 Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Price and Product Comparison
When making a purchase, price is often one of the primary deciding factors. Consumers frequently compare prices for similar products before settling on a purchase. For example, when buying a new smartphone, a consumer may compare prices across various retailers or online platforms to ensure they’re getting the best deal.
- पेशेवर:
- Helps the consumer save money by identifying the most affordable option.
- Encourages consumers to seek the best value for their purchase.
- Helps the consumer save money by identifying the most affordable option.
- दोष:
- Price comparisons can be time-consuming, especially when there are many options available.
- Focusing too heavily on price may result in overlooking product quality and features.
- Price comparisons can be time-consuming, especially when there are many options available.
Brand and Reputation
Some consumers may have a preference for certain brands due to reputation, previous experiences, or trust in the brand’s quality. For example, someone may opt for an Apple iPhone over other phones due to its known brand reliability, even if it costs more than other smartphones.
- पेशेवर:
- Offers peace of mind knowing that the product is from a trusted brand.
- Ensures a certain level of quality and performance based on brand reputation.
- Offers peace of mind knowing that the product is from a trusted brand.
- दोष:
- Higher brand premiums may result in paying more than necessary for a product that may not offer significant added value.
- Brand loyalty may limit exploration of more affordable alternatives.
- Higher brand premiums may result in paying more than necessary for a product that may not offer significant added value.
Functionality and Features
The functionality and features of a product greatly influence consumer decisions. For example, when purchasing a laptop, a consumer may prioritize factors like screen size, battery life, or processing speed, depending on their needs (e.g., work or entertainment).
- पेशेवर:
- Allows consumers to select products tailored to their needs.
- Increases satisfaction with the purchase when the product meets specific requirements.
- Allows consumers to select products tailored to their needs.
- दोष:
- A focus on functionality may result in higher costs if consumers opt for more feature-packed versions.
- Sometimes, additional features may be unnecessary for the consumer’s intended use, leading to overpaying.
- A focus on functionality may result in higher costs if consumers opt for more feature-packed versions.
Process for Making Informed Consumer Decisions
Step 1: Identifying Needs vs. Wants
The first step in making an informed purchase is distinguishing between needs and wants. A need could be a basic necessity, such as a phone that can make calls and send messages, while a want could be a high-end model with additional features that aren’t necessary.
- पेशेवर:
- Helps prevent unnecessary purchases and ensures that essential needs are met.
- Promotes smarter financial decisions by focusing on what’s truly needed.
- Helps prevent unnecessary purchases and ensures that essential needs are met.
- दोष:
- The line between needs and wants can sometimes be subjective, leading to confusion or indecision.
- Restricting spending on wants may reduce immediate satisfaction.
- The line between needs and wants can sometimes be subjective, leading to confusion or indecision.
Step 2: Researching Options
Once needs are determined, consumers should research their options. This involves reading customer reviews, checking product comparisons, and looking into expert opinions.
- पेशेवर:
- Ensures that consumers make an informed and educated decision.
- Provides insight into potential product flaws or advantages that may not be obvious at first glance.
- Ensures that consumers make an informed and educated decision.
- दोष:
- Researching multiple products can be time-consuming and may cause decision fatigue.
- The abundance of information available can sometimes overwhelm the consumer, making it harder to make a decision.
- Researching multiple products can be time-consuming and may cause decision fatigue.
Step 3: Evaluating Price vs. Value
Before making a final decision, consumers should assess whether the price aligns with the value they are getting. This means considering factors like product quality, longevity, and after-sales service in addition to the initial price tag.
- पेशेवर:
- Helps consumers balance cost with the quality and benefits of the product, ensuring better value for money.
- Encourages more thoughtful and deliberate purchasing, reducing impulse buying.
- Helps consumers balance cost with the quality and benefits of the product, ensuring better value for money.
- दोष:
- Some products might appear overpriced based on initial cost but offer long-term value through durability or lower maintenance.
- Finding the right balance between price and value can be subjective and vary from person to person.
- Some products might appear overpriced based on initial cost but offer long-term value through durability or lower maintenance.
Positive and Negative Effects of Consumer Decisions
Example: Purchasing an Electric Vehicle (EV)
- Positive Environmental Impact:
- EVs contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, helping reduce pollution and combating climate change.
- EVs contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, helping reduce pollution and combating climate change.
- Positive Societal Impact:
- Purchasing an EV supports the growth of the green energy sector, promoting sustainable transportation options and supporting eco-friendly innovations.
- Purchasing an EV supports the growth of the green energy sector, promoting sustainable transportation options and supporting eco-friendly innovations.
- Negative Environmental Impact:
- The production of EV batteries requires mining materials like lithium, which can lead to environmental degradation and significant resource extraction.
- The production of EV batteries requires mining materials like lithium, which can lead to environmental degradation and significant resource extraction.
- Negative Economic Impact:
- EVs often come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional vehicles, which may be a financial burden for some consumers, especially those on tighter budgets.
- EVs often come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional vehicles, which may be a financial burden for some consumers, especially those on tighter budgets.
- पेशेवर:
- Encourages sustainable choices and supports global initiatives for environmental protection.
- Helps consumers align their financial decisions with their personal values, like environmental consciousness.
- Encourages sustainable choices and supports global initiatives for environmental protection.
- दोष:
- The upfront cost may not be accessible for all consumers, which can limit adoption.
- The environmental impact of battery production is a downside that many consumers may overlook.
- The upfront cost may not be accessible for all consumers, which can limit adoption.
Financial Responsibility and Budget Planning
Preparing for Life Events and Changing Budgets
Unexpected life changes, such as job loss, having a child, or a medical emergency, can significantly impact an individual’s budget. For example, after a job loss, a consumer may need to adjust their budget by cutting back on discretionary spending and prioritizing essential expenses.
- पेशेवर:
- Having a flexible budget ensures financial stability during uncertain times.
- Helps individuals stay on track with financial goals even when life events cause disruptions.
- Having a flexible budget ensures financial stability during uncertain times.
- दोष:
- Regularly revising budgets due to unexpected events can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
- It may require sacrifices in other areas, such as entertainment or personal spending.
- Regularly revising budgets due to unexpected events can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
Factors Affecting Financial Goals
External factors such as location, culture, और peer influences can significantly impact one’s financial goals. For example, someone living in a high-cost area may need a larger budget for housing and transportation compared to someone living in a lower-cost area.
- पेशेवर:
- Understanding these external influences helps individuals recognize patterns in their financial behavior and spending.
- Encourages self-awareness, enabling consumers to make more informed financial decisions.
- Understanding these external influences helps individuals recognize patterns in their financial behavior and spending.
- दोष:
- Overcoming the influence of peer pressure or cultural expectations can be challenging.
- These external factors may lead to unsustainable financial choices if not carefully managed.
- Overcoming the influence of peer pressure or cultural expectations can be challenging.
Techniques to Decrease Expenses
Comparison Shopping
Comparison shopping helps consumers find the best prices for products by comparing different stores and online retailers. For example, when buying a laptop, a consumer might use comparison websites to see if the item is cheaper elsewhere.
- पेशेवर:
- Can lead to substantial savings by identifying the best prices.
- Provides a broader view of available options, ensuring that the consumer gets the best deal.
- Can lead to substantial savings by identifying the best prices.
- दोष:
- Time-consuming, especially when comparing many different options.
- The lowest price may not always correspond with the best quality or service.
- Time-consuming, especially when comparing many different options.
Negotiating Prices
Negotiating the price of large purchases (e.g., cars, furniture) or even monthly bills (e.g., cable, insurance) can lead to significant savings. For instance, a consumer might negotiate a lower rate on their cable bill by threatening to cancel the service.
- पेशेवर:
- Provides an opportunity to lower the overall cost of big-ticket items or services.
- Can build confidence in consumers when dealing with sales representatives.
- Provides an opportunity to lower the overall cost of big-ticket items or services.
- दोष:
- Not all merchants are open to negotiation, and it may feel uncomfortable for some consumers.
- It can be difficult to know when negotiation is appropriate, and sometimes it may not be effective.
- Not all merchants are open to negotiation, and it may feel uncomfortable for some consumers.
Using Technology for Financial Management
Financial Management Tools
There are various digital tools and apps that help track and manage spending, such as Mint, वाईएनएबी, और mobile banking apps. These tools can automatically categorize expenses, track income, and help users stick to their budget.
- पेशेवर:
- Real-time tracking and budgeting make it easier to stay on top of finances.
- Automates savings and bill payments, making it easier for consumers to manage their money.
- Real-time tracking and budgeting make it easier to stay on top of finances.
- दोष:
- Some apps or tools may require subscriptions or fees, which may eat into savings.
- Technical issues or security concerns with apps could compromise financial data
Conclusion: Mastering Budgeting and Expense Management
Budgeting and managing expenses are the foundations of personal financial success. Throughout this chapter, we explored how creating and maintaining a thoughtful budget empowers individuals to take control of their money, plan for both expected and unexpected life events, and align their spending habits with their long-term goals. Whether choosing a structured method like the 50/30/20 rule, tracking expenses through modern apps, or adapting to life’s inevitable changes, the tools and strategies discussed offer a path toward financial stability and growth.
Effective budgeting is not just about restriction; it’s about making intentional choices that reflect your values and aspirations. Understanding the difference between needs and wants, making informed consumer decisions, adjusting to economic shifts like inflation or tax changes, and regularly revisiting your budget ensures that your financial plan remains a living, flexible guide.
By practicing disciplined budgeting, making mindful purchasing decisions, and proactively managing necessary and discretionary expenses, individuals can not only meet their financial obligations but also build security, achieve personal goals, and enjoy greater peace of mind. Ultimately, mastering budgeting and expense management is not just a financial skill—it’s a key to building a life of opportunity, resilience, and freedom.
मुख्य पाठ जानकारी:
लोरेम इप्सुम डोलर सिट अमेट, कॉन्सेक्टूर एडिपिसिंग एलिट। उत एलीट टेलुस, लक्टस नेक उल्लमकोर्पर मैटिस, पुल्विनार डेपिबस लियो।