Veicoli di investimento: padroneggiare l’arte della diversificazione
Obiettivi chiave di apprendimento:
Introduzione: This section introduces various investment vehicles and underscores the importance of diversification in managing risks and enhancing returns. You’ll learn practical ways to diversify your investments and navigate associated costs effectively.
- Understand Investment Options: Gain a clear understanding of the variety of investment vehicles available for diversification.
- Practical Application: Learn how to practically diversify your investments in real-life situations, ensuring a balanced approach to risk and reward.
- Navigate Investment Costs: Acquire the knowledge to identify and minimize unnecessary costs, maximizing your investment returns.

Figura: This infographic showcases a detailed flow or process, possibly related to a financial or investment strategy. The intricate design suggests a step-by-step guide or a roadmap. It would be beneficial for users to closely follow the sequence or steps presented to gain a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
9.1. Individual Stocks: Picking the Winners and Losers

Figura: The infographic outlines the steps to picking a stock. It emphasizes that stock picking is the selection of equities based on specific criteria and highlights the challenges of analyzing vast amounts of information for investment decisions. The infographic suggests creating a screening process to sift through numerous ideas, resulting in a manageable number of stocks that warrant further investigation.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
Individual stocks represent shares of ownership in a company. They can be bought and sold on stock exchanges, and their prices fluctuate based on market demand and a company’s financial performance. Investing in individual stocks can be exciting, but it also comes with certain risks.
Professionisti:
- High potential returns: Picking the right stock can yield significant returns.
- Control: You decide which companies to invest in and when to buy or sell.
Contro:
- Higher risk: Individual stocks are subject to company-specific risks, like poor management or market disruptions.
- Requires research: Selecting the right c statements, industry trends, and market conditions.
Esempio: If you had invested $1,000 in Apple Inc. (AAPL) in 2000, your investment would be worth over $200,000 today, assuming dividends were reinvested. This demonstrates the high potential returns of individual stocks.
9.2. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Harnessing the Power of Diversification
Figura: The infographic provides an overview of a specific type of investment known as Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). It highlights that ETFs are a type of index fund that tracks a benchmark index and aims to mirror that index’s performance. Additionally, the infographic emphasizes that ETFs trade on an exchange similar to stocks, allowing investors to buy and sell them throughout the day, leading to price fluctuations.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
An ETF is a type of investment fund that holds a basket of assets, like stocks, bonds, or commodities and is traded on stock exchanges just like individual stocks. ETFs offer a convenient way to diversify your portfolio while retaining the flexibility to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day.
Professionisti:
- Diversificazione: An ETF can provide exposure to various sectors, industries, or asset classes, reducing risk.
- Lower costs: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios than mutual funds.
- Liquidità: ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day, offering flexibility.
Contro:
- Trading costs: Buying and selling ETFs can incur transaction fees, especially for frequent traders.
- Potential tracking errors: ETFs aim to replicate the performance of an index, but discrepancies can occur due to fees or management decisions.
Important terms to know:
- Expense ratio: The annual fee charged by the ETF issuer as a percentage of your investment.
- Tracking error: The difference between the ETF’s performance and that of its underlying index.
Before investing in an ETF, check the expense ratio, tracking error, and the fund’s underlying assets to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives.
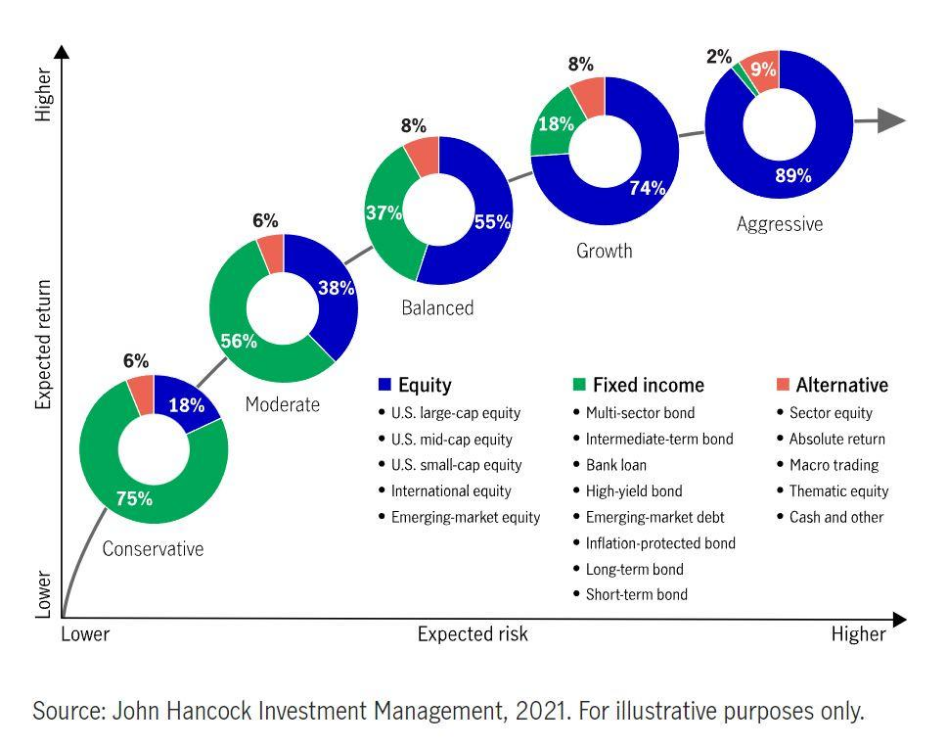
Titolo della figura: Portfolio Allocation: Balancing Risk and Reward
Fonte: John Hancock Investments
Descrizione: The visual depicts the relationship between portfolio allocation and its corresponding expected risk and reward. It demonstrates that by adjusting the balance of equities, fixed income (bonds), and alternative investments in a portfolio, an investor can influence the potential risk (represented on the x-axis) and the anticipated reward (y-axis).
Punti chiave:
- Equity Exposure: An increase in equity allocation generally leads to higher expected returns, but it also brings higher risks.
- Reddito fisso: Bonds and other fixed income instruments can provide stability, potentially reducing the risk but might offer lower returns compared to equities.
- Investimenti alternativi: These can diversify the portfolio further, offering varied risk and reward dynamics.
- Diversificazione: The mix and balance of these asset classes determine the overall portfolio characteristics, helping in striking a balance between risk and reward.
Applicazione: A well-diversified portfolio can be a key tool for investors aiming to achieve specific financial goals while managing potential risks. By understanding the risk-reward dynamics of different asset allocations, investors can tailor their portfolios to align with their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
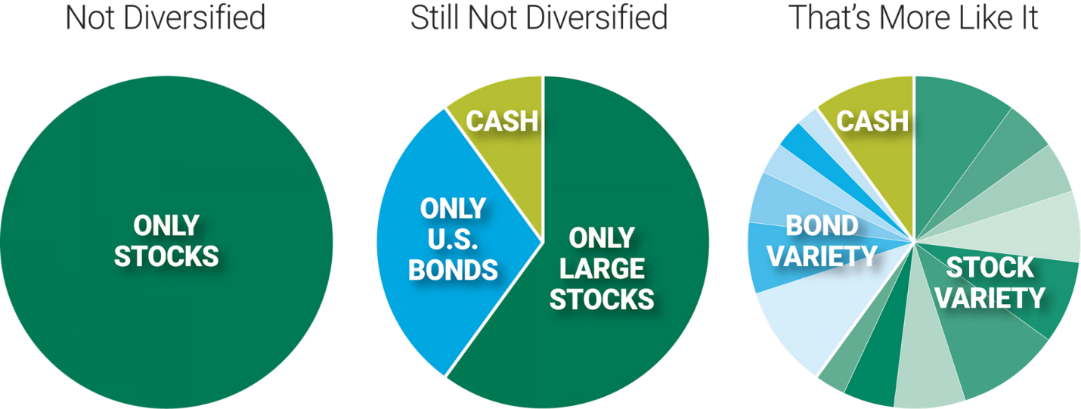
Titolo della figura: Understanding Diversification in Investments
Fonte: American Century Investments
Descrizione: The graphic emphasizes the essence of diversification in investments. It illustrates that holding merely a single asset or stock leads to a lack of diversification. To truly spread risk and potentially enhance returns, an investor should distribute their investments across various assets.
Punti chiave:
- Single Asset: Holding just one stock or asset can expose the investor to high risks specific to that particular asset.
- Diversificazione: This involves spreading investments across different assets, which can reduce risks associated with any single asset’s poor performance.
- Gestione del rischio: Diversification can be a method to mitigate potential losses while possibly enjoying gains from various investments.
Applicazione: Diversification is a foundational principle in investing, aiming to optimize returns while managing risks. By understanding and implementing diversification, investors can potentially shield their portfolios from isolated downturns and achieve a more balanced performance.
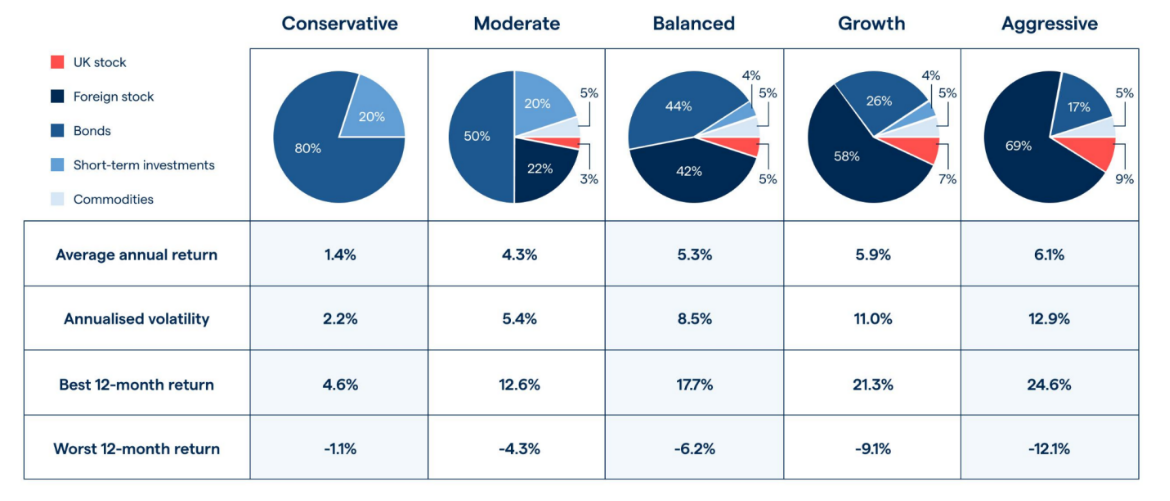
Titolo della figura: Risk and Return Metrics of Different Portfolio Types
Fonte: IG International
Descrizione: The image displays a range of portfolios categorized from conservative to aggressive on the X-axis. The Y-axis exhibits several key metrics: average annual return, annualized volatility, best 12-month return, and worst 12-month return. A clear pattern emerges: as portfolios transition from conservative to aggressive, there’s a rise in annualized volatility, symbolizing an increase in risk. Alongside this, the average annual return also increases, indicating a direct correlation between risk and potential returns.
Punti chiave:
- Portfolio Types: Portfolios are categorized as conservative, moderate, balanced, growth, and aggressive.
- Risk and Return: There’s a direct relationship between risk (annualized volatility) and expected returns. As one rises, so does the other.
- High Reward, High Risk: The more aggressive the portfolio, the higher its potential returns, but also the greater its potential volatility.
Applicazione: Investors should comprehend the risk-reward trade-off when determining which portfolio type aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance. Grasping this concept can aid in making informed decisions about the right balance of risk and potential returns in one’s investment strategy.
9.3. Mutual Funds: Letting the Pros Manage Your Money
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle where a pool of money from multiple investors is used to buy a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks and bonds. Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.

Figura: The infographic provides an overview of mutual funds. It highlights that mutual funds allow investors to buy a diverse range of investments in one transaction. The funds gather money from numerous investors and employ a professional manager to invest that capital in stocks, bonds, or other assets.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
Consiglio: Mutual funds offer a convenient way for investors to diversify their portfolio without the need to individually select and manage multiple assets. By pooling resources, investors can access a broader range of investments and benefit from professional management. However, it’s essential to research and understand the fund’s objectives, fees, and past performance before investing.

Figura: The image illustrates the concept of investment in mutual funds. It depicts coins placed inside a jar filled with soil, and a plant sprouting from the soil, symbolizing growth. This visual metaphor emphasizes the idea of nurturing investments, much like how one would nurture a plant, to achieve financial growth and prosperity.
Fonte: iStockFoto
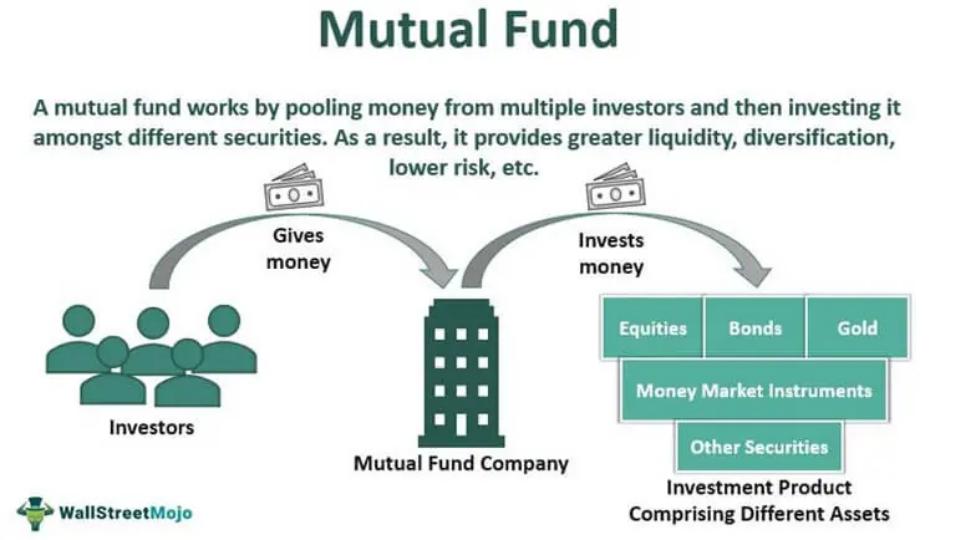
Figure title: Mechanism of Mutual Funds
Fonte: Mojo di Wall Street
Descrizione: The image delineates the fundamental workings of a mutual fund. In essence, a mutual fund involves pooling funds from numerous investors, which are then entrusted to a mutual fund company. This company subsequently employs professional fund managers, compensating them with a fee, to judiciously allocate and manage these pooled funds. Depending on the mutual fund’s defined objectives and strategies, the capital gets diversified across a myriad of assets, leading to varied levels of exposure and associated risks.
Punti chiave:
- Pooling of Funds: Mutual funds gather money from a multitude of investors, providing a collective investment platform.
- Gestione professionale: The pooled capital is overseen by expert fund managers who strategize and allocate funds to achieve optimal returns.
- Diverse Investment Styles: Each mutual fund boasts a unique investment strategy, which dictates its risk level and asset allocation.
Applicazione: For potential investors, understanding the mutual fund mechanism is pivotal. Mutual funds offer an avenue for diversification and professional management, which can be beneficial for those who might not possess the time or expertise to manage their investments individually. By selecting a mutual fund that aligns with one’s risk appetite and financial goals, one can tailor their investment approach accordingly.
Professionisti:
- Diversificazione: Mutual funds provide instant diversification by investing in multiple assets.
- Professional management: Fund managers have the expertise and access to research that individual investors may not have.
- Simplified investing: Investors don’t need to worry about researching and selecting individual assets.
Contro:
- Commissioni più alte: Mutual funds typically have higher expense ratios than ETFs due to management and operational costs.
- Limited liquidity: Mutual funds are bought and sold at the end of the trading day, unlike ETFs, which trade throughout the day.
Important terms to know:
- Net asset value (NAV): The price per share of a mutual fund, calculated by dividing the total value of the fund’s assets by the number of shares outstanding.
- Load: A sales charge or commission that may be applied when you buy or sell shares of a mutual fund.
Before investing in a mutual fund, check the expense ratio, load fees, and the fund’s historical performance to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives.
Difference between a mutual fund and ETF:

Figura: The image portrays the concept of choosing between ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) and mutual funds as investment alternatives. It features a businessman or investor holding a balance scale, with one side representing ETFs and the other side representing mutual funds. This highlights the decision-making process investors undergo when weighing the pros and cons of these two popular investment vehicles.
Fonte: iStockFoto
- Mutual funds are actively managed by professional fund managers, while most ETFs are passively managed, tracking an index.
- Mutual funds are bought and sold at the end of the trading day, while ETFs can be traded throughout the day.
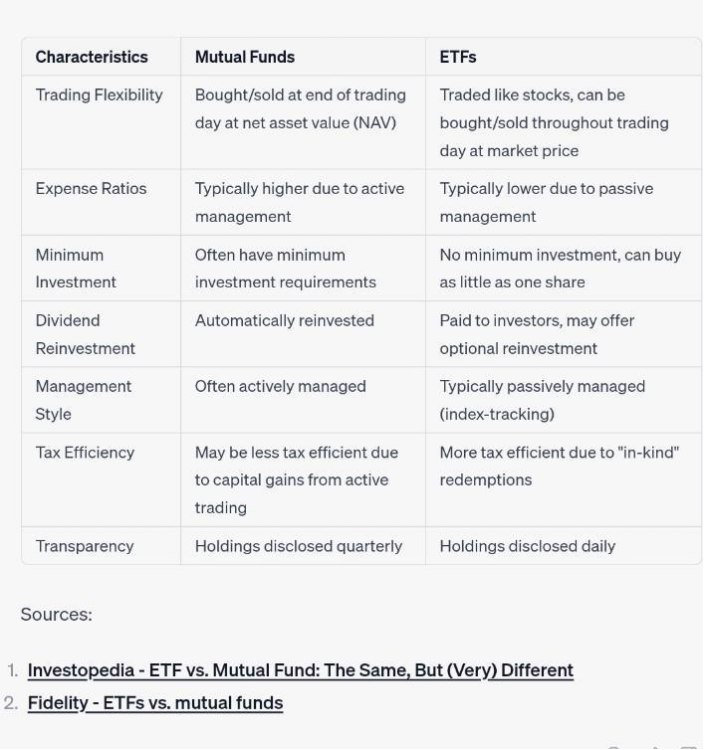
Figura: This infographic provides a comparative analysis between Mutual Funds and ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds). It highlights key characteristics such as trading flexibility, expense ratios, minimum investment requirements, dividend reinvestment, management style, tax efficiency, and transparency. The infographic clearly distinguishes the features of both investment vehicles, making it easier for investors to understand their differences and make informed decisions.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
Descrizione:
The infographic contrasts Mutual Funds and ETFs based on several parameters:
- Trading Flexibility: Mutual Funds are bought/sold at the end of the trading day at their net asset value (NAV), while ETFs can be traded like stocks throughout the trading day at market price.
- Expense Ratios: Mutual Funds typically have higher expense ratios due to active management, whereas ETFs generally have lower expense ratios because of passive management.
- Minimum Investment: Mutual Funds often have minimum investment requirements, while ETFs do not have such requirements and allow investors to buy as little as one share.
- Dividend Reinvestment: For Mutual Funds, dividends are automatically reinvested. In contrast, ETFs pay dividends to investors, with some offering optional reinvestment.
- Management Style: Mutual Funds are often actively managed, while ETFs are typically passively managed, tracking an index.
- Efficienza fiscale: Mutual Funds may be less taxefficient due to capital gains from active trading. ETFs are more taxefficient because of “inkind” redemptions.
- Transparency: Mutual Funds disclose their holdings quarterly, while ETFs disclose their holdings daily.
Punti chiave:
- Mutual Funds and ETFs offer different trading flexibilities.
- ETFs generally have lower expense ratios due to passive management.
- Mutual Funds often come with minimum investment requirements, unlike ETFs.
- ETFs are typically more taxefficient than Mutual Funds.
- Transparency differs, with ETFs providing daily disclosures and Mutual Funds providing quarterly disclosures.
Applicazione:
For investors looking for flexibility in trading and lower expense ratios, ETFs might be a more suitable option. However, those who prefer active management and are okay with a minimum investment requirement might lean towards Mutual Funds. It’s essential to understand the differences and choose the investment vehicle that aligns with one’s financial goals and strategies.

Titolo della figura: Differences Between ETFs and Mutual Funds
Fonte: ODS on Finance
Descrizione: The image elucidates the primary distinctions between Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) and mutual funds. It highlights how each investment vehicle approaches trading, emphasizing the continuous intraday trading flexibility of ETFs versus the end-of-day or other specific trading limitations of mutual funds. Additionally, the depiction underscores the differing tax implications associated with both ETFs and mutual funds.
Punti chiave:
Trading Mechanism: ETFs offer the ability to be traded throughout the day, much like individual stocks, while mutual funds generally trade only at the close of the market or under specific conditions.
Tax Treatment: The tax structures and implications for ETFs and mutual funds differ, influencing their attractiveness based on individual tax considerations.
Applicazione: For prospective investors, grasping the disparities between ETFs and mutual funds is essential. These distinctions can have implications on liquidity, flexibility, and tax efficiency. Recognizing these differences assists investors in making informed decisions tailored to their individual investment strategy and financial goals.
9.4. The Power of Index Investing: Steady Growth and Peace of Mind
Index investing involves buying and holding a portfolio that replicates the performance of a market index, such as the S&P 500 or the FTSE 100. This strategy provides broad market exposure, and studies have shown that most investors don’t beat the index over the long term.
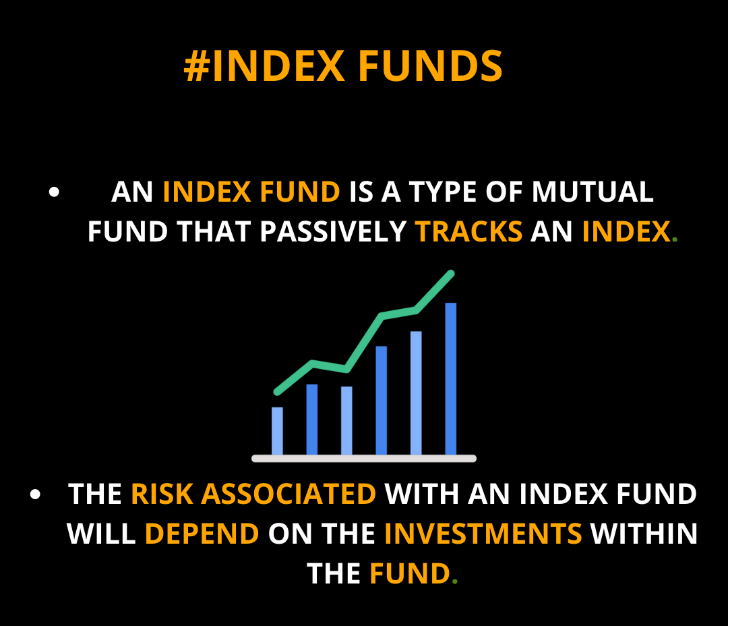
Figura: The infographic provides an overview of index funds. It defines an index fund as a type of mutual fund that passively tracks an index. The visual emphasizes that the risk associated with an index fund will depend on the investments within the fund. For those considering investment options, understanding the nature of index funds and their associated risks is crucial.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
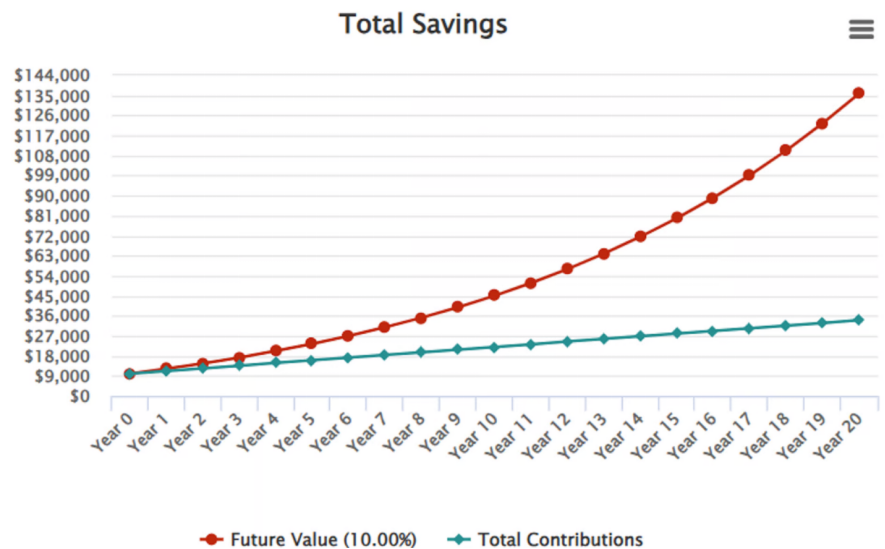
Titolo della figura: Compound Growth of $10,000 Investment in S&P 500 Over 20 Years
Fonte: Il pazzo eterogeneo
Descrizione: The visual representation illustrates the transformative power of compound growth over 20 years for a $10,000 investment in the S&P 500 with a $100 monthly contribution. While the blue line captures the incremental increase due to the monthly $100 addition without any appreciation, the red line vividly demonstrates the amplified growth when a 10% annual return is integrated, showcasing the exponential rise in value.
Punti chiave:
- Power of Compounding: Over the long-term, consistent contributions combined with a consistent return can result in exponential growth.
- Monthly Contributions: The consistent addition of $100 monthly provides a steady base growth.
- Impact of Appreciation: Even a 10% annual appreciation can lead to dramatic increases in investment value over two decades.
Applicazione: Understanding the profound impact of compound interest is critical for investors. The difference between just saving money and investing it with a consistent return is vast. For those looking to maximize their financial growth over time, the power of compound interest, as displayed by the 10% appreciation, shouldn’t be underestimated.
Professionisti:
- Diversificazione: Index funds provide exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing risk.
- Lower costs: Index funds have lower fees compared to actively managed funds.
- Less stress: Index investing doesn’t require constant monitoring of individual stocks or market trends.
Media del costo in dollari (DCA) is a popular strategy used in conjunction with index investing. DCA involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach helps mitigate the impact of market volatility and eliminates the need to time the market.
Esempio: If you invested $500 every month into an S&P 500 index fund over the past 20 years, your investment would have grown significantly, even during periods of market downturns.
9.5. ETFs for Portfolio Investing: Accessing Multiple Indexes with Ease
Figura: The infographic provides a clear understanding of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). It emphasizes that ETFs are a type of index fund that tracks a benchmark index, aiming to mirror that index’s performance. Unlike traditional mutual funds, ETFs trade on an exchange similar to stocks, allowing for buying and selling throughout the day with fluctuating prices. For anyone considering diversifying their investment portfolio, understanding the nature of ETFs is crucial.
Fonte: infografica personalizzata
Some ETFs are designed to replicate the exposure to multiple indexes, providing a convenient way for investors to access a diversified portfolio of assets across various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
Professionisti:
- Diversificazione: Multi-index ETFs offer an easy way to diversify risk across various asset classes.
- Commissioni più basse: Investing in a single ETF can be more cost-effective than buying individual assets or multiple funds.
- Simplified investing: Investors don’t need to research and manage a complex portfolio of assets.
Contro:
- Limited customization: Investors cannot adjust the specific allocation of assets within a multi-index ETF.
- Potential tracking errors: As with any ETF, discrepancies may occur between the ETF’s performance and that of its underlying indexes.
Examples of popular index funds from around the world include the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI), iShares MSCI EAFE ETF (EFA), and the iShares Core MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (IEMG).
Now that you’ve learned about various investment vehicles, you’re ready to apply this knowledge to your personal financial journey. In the next chapter, we’ll discuss the importance of risk management and asset allocation to help you optimize your portfolio for long-term success.

Figure title: Diverse Range of ETF Offerings
Fonte: Baldwin Financial Services
Descrizione: The image delineates various types of Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) available for investors. It exemplifies how ETFs serve as a versatile investment vehicle, granting exposure to a multitude of asset classes, strategies, and regions, from traditional index tracking to more specialized options like inverse ETFs and sector-focused funds.
Punti chiave:
- Versatility: ETFs cover a wide spectrum of investment avenues, from broad market indexes to niche sectors.
- Inverse ETFs: These unique ETFs offer potential profit during market downturns by betting against certain indexes or sectors.
- Specialized Exposure: ETFs grant access to specific industries, commodities, or even active management strategies.
- Global Reach: Investors can gain exposure to international markets and assets using certain ETFs.
Applicazione: For investors looking to diversify their portfolio or target specific investment themes, ETFs offer a pragmatic solution. With the plethora of ETF options available, it’s essential for investors to research and understand each type’s objectives, risks, and benefits.
Figure title: Importance of Index Funds in a Portfolio
Fonte: Motley Fool
Descrizione: The image highlights the significance of index funds within an investment portfolio. Index funds mirror the performance of a particular market index, thus providing broad market exposure and eliminating the risks associated with individual stock selections or sector biases.
Punti chiave:
- Broad Market Exposure: Index funds offer a snapshot of the market’s overall health and trends.
- Minimized Risk: By investing in the entire index, one dilutes the negative impact of any single underperforming stock or sector.
- Avoid Active Management Pitfalls: Index funds sidestep potential errors in stock picking or sector overexposure that can be common in active fund management.
Applicazione: For investors looking for a stable foundation in their portfolio, index funds offer a less volatile, diversified option. They serve as a reliable base, reducing the chances of significant losses due to individual stock or sector downturns.
Informazioni chiave sulla lezione:
Dichiarazione di chiusura: Mastering the art of diversification through different investment vehicles is integral to a balanced and risk-managed investment approach. This section arms you with the knowledge to explore various investment options, apply diversification in practice, and navigate investment costs for better financial outcomes.
-
- Investment Variety: There’s a plethora of investment options – from stocks to bonds, to mutual funds, each with its specific characteristics allowing for informed decision-making.
- ETFs Are Key: ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) allow for diversificazione within a single investment, representing sectors, commodities, or indexes, providing flexibility and broad exposure.
- Cost Awareness: Keeping an eye on associated fees is paramount; lower costs often translate to better net returns over the long term, making it essential to understand and reduce these costs wherever possible.
