第14B章: 自動車の購入と資金調達
レッスンの学習目標:
導入: Understanding the intricacies of buying a car is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This section will guide you through the entire process, from assessing your needs to financing options and managing ongoing costs.
- Assessing Your Needs: Learn to evaluate your requirements based on the purpose, size, and features of the car, ensuring you choose a vehicle that suits your lifestyle.
- Setting a Budget: Understand how to determine a budget for your car purchase, including down payment, monthly payments, insurance, maintenance, and fuel costs.
- Financing Options: Gain knowledge about different financing methods, such as traditional bank loans, dealer financing, and leasing, to select the best option for your financial situation.
- New vs. Used Cars: Compare the pros and cons of buying new versus used cars, including considerations for depreciation, cost, and maintenance.
- Negotiation and Legal Considerations: Learn best practices for negotiating at the dealership and understanding loan agreements and warranty coverage to ensure you get the best deal.
Introduction to Automobile Purchases
Buying a car is a significant financial decision that requires careful planning and consideration. This chapter will guide you through the process of purchasing a car, understanding financing options, and managing the associated costs. We will also cover best practices for buying new and used cars, and provide tips for negotiating at the dealership.
Section 1: Understanding the Car Buying Process
Assessing Your Needs
Before purchasing a car, it’s essential to assess your needs and determine the type of vehicle that best suits your lifestyle. Consider factors such as:
- Purpose: Commuting, family use, recreational activities, etc.
- サイズ: Compact, sedan, SUV, truck, etc.
- Features: Safety features, fuel efficiency, technology, and comfort.

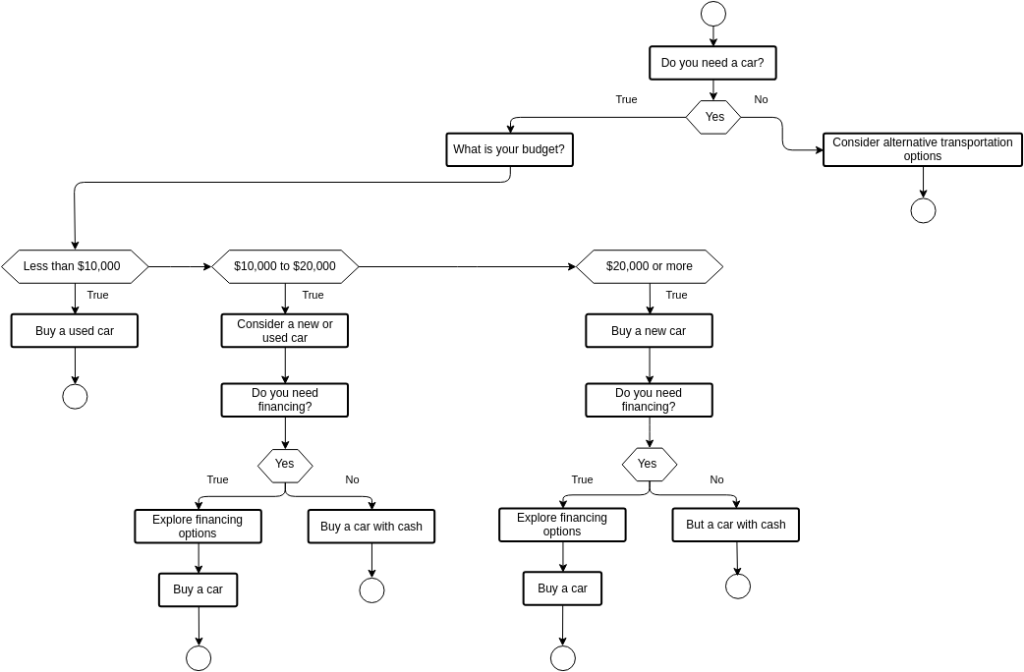
形: Decision-Making Flowchart for Buying a Car
ソース: Visual Paradigm
説明:
The flowchart provides a step-by-step guide to help individuals make informed decisions when buying a car. It starts with the initial decision to buy a car and leads through various considerations such as budget, new vs. used cars, financing options, and additional costs like insurance and maintenance. The flowchart uses a series of questions and decision points to guide users through the car-buying process, ensuring they evaluate all critical factors before making a purchase.
重要なポイント:
- Initial Decision: Start by determining the need for a new car.
- Budget Consideration: Establish a budget to understand how much you can afford.
- New vs. Used: Decide between buying a new or used car based on budget and preferences.
- 資金調達オプション: Explore different financing options, including loans and leasing.
- 追加費用: Consider ongoing costs such as insurance, maintenance, and fuel.
- Final Decision: Make an informed decision after evaluating all factors.
Application of Information:
使用して decision-making flowchart helps prospective car buyers navigate the complex process of purchasing a vehicle. By following this structured approach, individuals can ensure they consider all necessary factors, from budgeting に financing options そして additional costs, leading to a well-informed purchase. For those learning about 個人融資 そして consumer decision-making, this flowchart provides a practical example of how to make significant financial decisions systematically, promoting better financial planning そして decision-making skills.
Setting a Budget
Determine how much you can afford to spend on a car, including the down payment, monthly payments, insurance, maintenance, and fuel costs. A common guideline is to spend no more than 15% of your monthly income on car expenses.
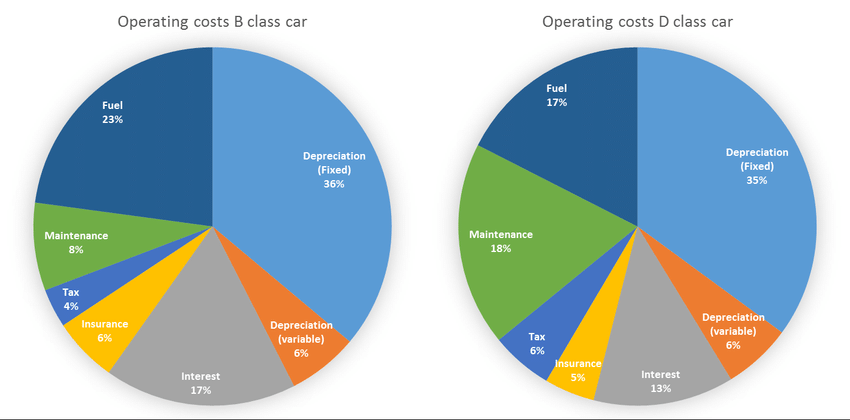
形: Car Cost Breakdown for Leisure and Business Cars
ソース: リサーチゲート
説明:
The figure presents a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with owning and operating cars for leisure and business purposes. It categorizes expenses into various components such as purchase price, fuel, maintenance, insurance, taxes, and depreciation. The breakdown highlights the differences in cost allocation between leisure and business cars, providing insights into how each type of use impacts overall vehicle expenses. This comparison helps in understanding the financial implications of car ownership for different purposes.
重要なポイント:
- 購入価格: Initial cost of acquiring the vehicle, which can vary significantly between leisure and business cars.
- Fuel Costs: Ongoing expense for fuel, typically higher for business cars due to more frequent use.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and repairs, necessary to keep the car in good working condition.
- 保険: Cost of insuring the vehicle, which may differ based on usage type and coverage requirements.
- 税金: Government taxes and fees associated with vehicle ownership.
- 減価償却費: The reduction in the car’s value over time, an important factor in overall cost considerations.
Application of Information:
理解する car cost breakdown for leisure and business cars is essential for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about vehicle purchases and usage. For businesses, this information aids in budgeting and expense management, ensuring cost-efficiency in fleet operations. For individuals, it highlights the financial impact of different car uses, helping in planning and budgeting for vehicle ownership. This knowledge is beneficial for those studying 個人融資 そして business management, providing a clear example of cost analysis and financial planning related to vehicle ownership.
Section 2: New vs. Used Cars
New Cars
長所:
- Latest Technology: New cars come with the latest features and safety technology.
- Warranty: Most new cars come with comprehensive warranties.
- Reliability: Lower risk of mechanical issues and repairs in the first few years.
短所:
- 減価償却費: New cars lose value quickly, with the most significant depreciation occurring in the first few years.
- Higher Cost: New cars are more expensive upfront compared to used cars.
Things to Look Out For:
- Research Models: Compare different models and their features.
- Manufacturer Incentives: Look for promotions, rebates, and special financing offers.
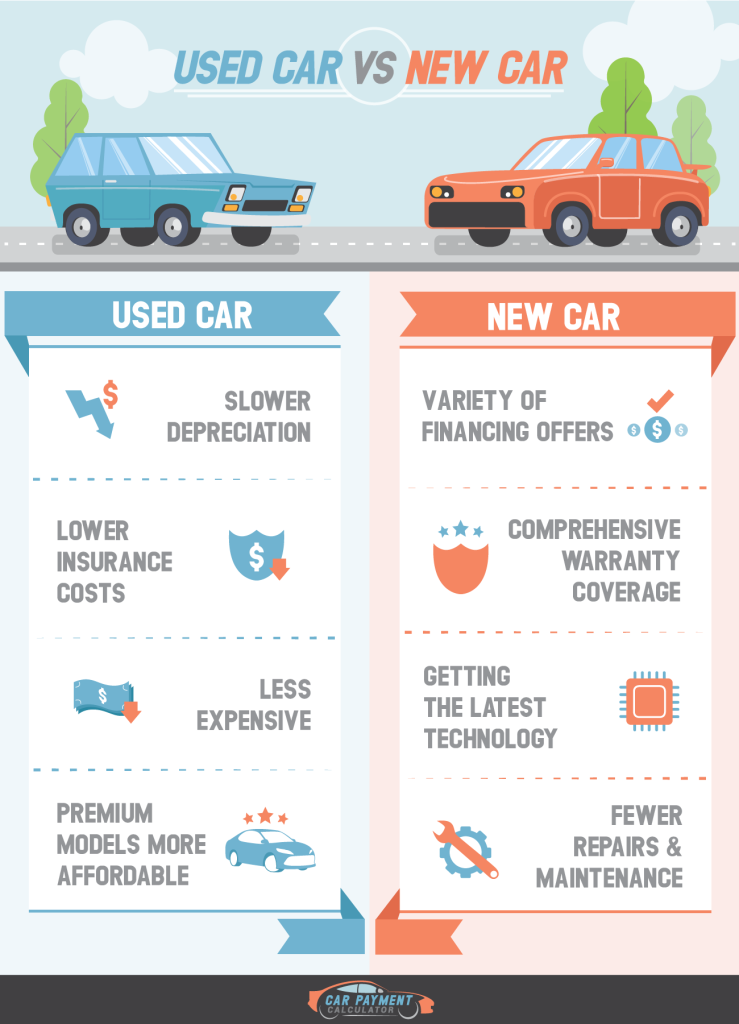
形: Pros and Cons of Buying a New Car
ソース: Evans Auto Brokerage
説明:
The infographic compares the pros and cons of buying a new car. It outlines advantages such as having the latest technology, warranty coverage, and lower maintenance costs initially. Conversely, it also highlights the downsides, including higher purchase prices, rapid depreciation, and higher insurance costs. This comparison helps potential buyers weigh the benefits and drawbacks of purchasing a new vehicle, aiding in making a well-informed decision.
重要なポイント:
- 長所:
- Latest Technology: New cars come equipped with the most recent technological advancements and features.
- Warranty Coverage: New cars typically include comprehensive warranty plans, reducing out-of-pocket repair costs.
- Lower Initial Maintenance Costs: New cars usually require less maintenance and repairs initially.
- 短所:
- Higher Purchase Price: New cars have a higher upfront cost compared to used vehicles.
- Rapid Depreciation: New cars lose value quickly, especially within the first few years.
- Higher Insurance Costs: Insurance premiums for new cars are generally higher due to their greater value.
Application of Information:
理解する pros and cons of buying a new car helps potential buyers make informed decisions about their vehicle purchase. For those learning about 個人融資, this comparison underscores the importance of considering both short-term and long-term costs associated with new car ownership. It aids in evaluating whether the benefits, such as latest technology そして warranty coverage, outweigh the higher costs and rapid depreciation. This knowledge is crucial for making strategic financial decisions and planning for significant purchases.
Used Cars
長所:
- Lower Cost: Used cars are generally more affordable than new cars.
- Less Depreciation: Used cars have already undergone significant depreciation.
短所:
- Higher Maintenance: Older cars may require more frequent repairs and maintenance.
- Limited Warranty: Used cars may not have a warranty, or it may be limited.
Things to Look Out For:
- Vehicle History Report: Obtain a report to check for accidents, title status, and service history.
- Inspection: Have the car inspected by a trusted mechanic before purchasing.
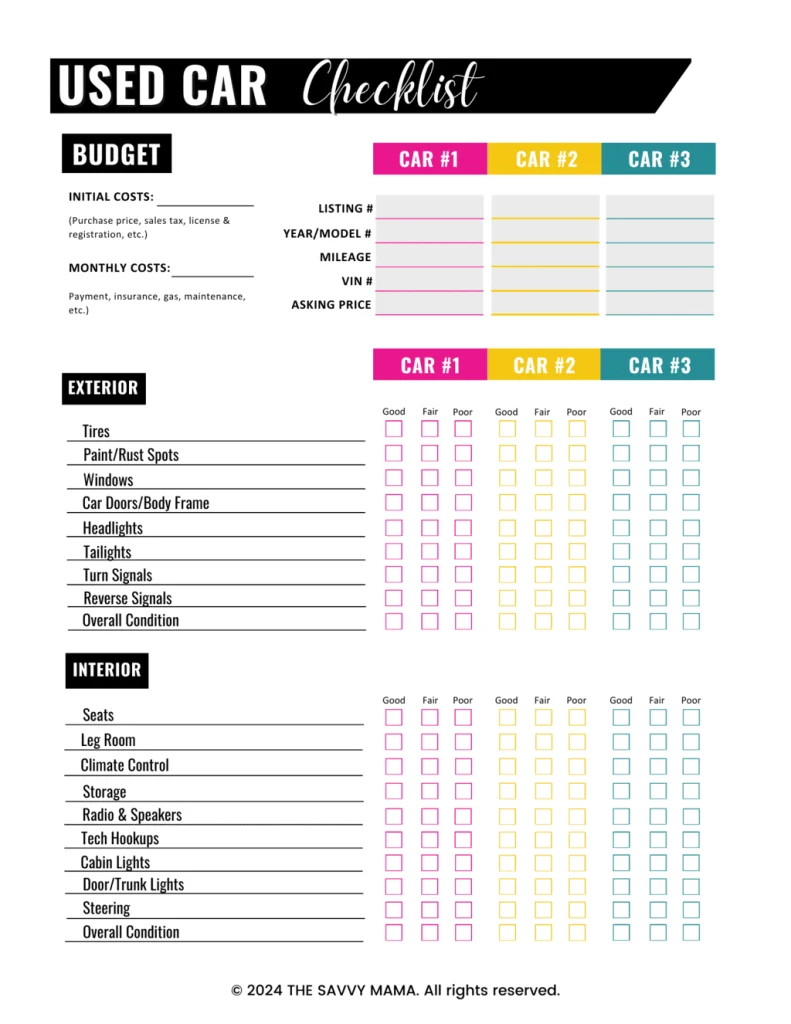
Figure: Used Car Purchase Checklist
ソース: The Savvy Mama
説明:
The infographic provides a comprehensive checklist for purchasing a used car. It includes essential steps and considerations such as researching the car’s history, inspecting the vehicle, taking it for a test drive, and evaluating the price. Additional tips cover checking the vehicle identification number (VIN), verifying ownership, and reviewing maintenance records. This guide ensures buyers are well-prepared to make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls when buying a used car.
重要なポイント:
- Research Car History: Check the vehicle’s history report for any accidents, repairs, or previous ownership issues.
- Vehicle Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the car for any signs of wear, damage, or mechanical issues.
- Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to assess its performance, handling, and comfort.
- Evaluate Price: Compare the car’s price with market value to ensure a fair deal.
- Check VIN: Verify the vehicle identification number to confirm its authenticity and history.
- Review Maintenance Records: Look at the car’s maintenance history to ensure it has been properly cared for.
Application of Information:
使用して used car purchase checklist helps potential buyers systematically evaluate a vehicle, ensuring they make a well-informed purchase decision. For those learning about 個人融資 そして consumer decision-making, this checklist highlights the importance of due diligence そして thorough evaluation before making significant purchases. It aids buyers in identifying potential issues and negotiating better deals, ultimately leading to more satisfactory and financially sound decisions. This approach is essential for avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring a successful used car purchase.
Section 3: Financing a Car
Types of Car Loans
- Traditional Bank Loans: Obtained from a bank or credit union, often with competitive interest rates.
- Dealer Financing: Financing provided directly through the dealership, which can be convenient but may have higher interest rates.
- リース契約: An alternative to buying, where you make monthly payments to use the car for a specific period.
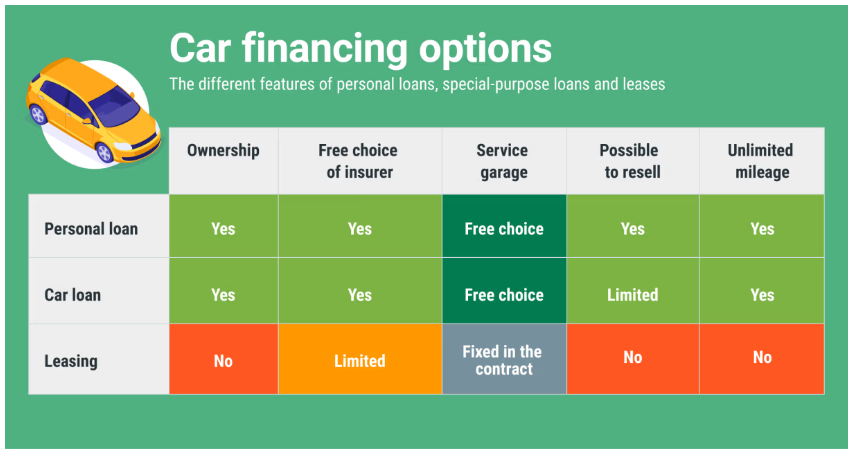
形: Options for Car Financing
ソース: Comparis
説明:
The infographic outlines various options for car financing. It covers methods such as paying with savings, taking out a personal loan, using dealership financing, leasing, and exploring credit options. Each financing method is explained with its benefits and drawbacks, helping potential car buyers understand the different ways to finance their vehicle purchase. The infographic also provides a comparative analysis of the costs and commitments associated with each option.
重要なポイント:
- Paying with Savings: No interest payments, but depletes personal savings.
- Personal Loan: Fixed monthly payments and interest rates, may require a good credit score.
- Dealership Financing: Convenient but may come with higher interest rates compared to personal loans.
- Leasing: Lower monthly payments but no ownership at the end of the lease term.
- Credit Options: Various credit options are available depending on the borrower’s financial situation and preferences.
Application of Information:
Understanding the different car financing options helps buyers make informed decisions based on their financial situation and preferences. For those learning about 個人融資 そして consumer credit, this infographic provides a clear comparison of financing methods, highlighting the benefits and drawbacks of each. This knowledge aids in selecting the most suitable financing option, ensuring better financial planning and management. It emphasizes the importance of comparing costs and commitments to avoid potential financial strain and make the best choice for car financing.
Understanding Interest Rates
The interest rate on a car loan affects the total cost of the loan. Rates can vary based on your credit score, loan term, and the lender. It’s essential to shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders.
Loan Terms
Car loans typically range from 36 to 72 months. Longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs.
形: Choosing the Right Loan Term: Impact on Interest Rates and Monthly Payments
ソース: ファスターキャピタル
説明:
The infographic illustrates the relationship between loan terms, interest rates, and monthly payments. It shows how choosing a shorter loan term results in higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid over the life of the loan. Conversely, longer loan terms reduce monthly payments but increase the overall interest paid. The visual highlights the importance of balancing monthly affordability with the total cost of borrowing when selecting a loan term.
重要なポイント:
- Shorter Loan Terms: Higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid, leading to quicker loan payoff.
- Longer Loan Terms: Lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid, extending the loan payoff period.
- 関心度: Shorter terms typically come with lower interest rates, while longer terms may have higher rates.
- Total Cost of Borrowing: Understanding the trade-off between monthly affordability and the total cost of borrowing is crucial.
Application of Information:
Selecting the right loan term is vital for balancing monthly affordability そしてその total cost of borrowing. For borrowers, understanding these trade-offs helps in making informed decisions that align with their financial goals and capabilities. For those studying 個人融資 そして loan management, this infographic emphasizes the importance of evaluating both short-term and long-term financial impacts when choosing a loan term. It aids in advising clients or making personal decisions that optimize financial health and minimize borrowing costs.
Section 4: Best Practices for Car Financing
Improving Your Credit Score
A higher credit score can help you secure a lower interest rate. Pay your bills on time, reduce debt, and check your credit report for errors.
頭金
A larger down payment reduces the loan amount and can lower your monthly payments and overall interest costs.
Loan Pre-Approval
Get pre-approved for a loan before visiting the dealership. This gives you a clear budget and strengthens your negotiating position.

形: Steps to Improve Your Credit Score
ソース: ファスターキャピタル
説明:
The infographic provides a comprehensive guide on steps to improve your credit score. It includes actionable tips such as paying bills on time, reducing debt levels, checking credit reports for errors, and maintaining a low credit utilization ratio. The visual aids in understanding how these factors influence credit scores and offers practical advice for making positive changes to financial behavior.
重要なポイント:
- Pay Bills on Time: Consistently paying bills by their due dates significantly impacts credit scores.
- Reduce Debt Levels: Lowering overall debt helps improve the debt-to-income ratio and boosts credit scores.
- Check Credit Reports: Regularly reviewing credit reports for errors and disputing inaccuracies ensures accurate credit history.
- Low Credit Utilization: Keeping credit card balances low relative to credit limits maintains a healthy credit utilization ratio.
- Diversify Credit Types: Having a mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards and installment loans, positively affects credit scores.
Application of Information:
Improving a credit score is crucial for securing better loan terms そして 関心度. By following these steps, individuals can enhance their financial health and access more favorable credit opportunities. For those learning about 個人融資, this guide provides essential strategies for maintaining and improving creditworthiness, highlighting the importance of responsible financial behavior そして regular credit monitoring. This knowledge is vital for advising clients or managing personal finances to achieve better credit outcomes and overall financial stability.
Section 5: Tips for Negotiating at the Dealership
Do Your Research
- 市場価格: Know the market value of the car you want to buy.
- Trade-In Value: If trading in a car, research its value to ensure you get a fair deal.
Be Prepared to Walk Away
Don’t feel pressured to make a deal immediately. If the terms aren’t favorable, be prepared to walk away and explore other options.
Focus on the Total Price
Negotiate the total price of the car rather than the monthly payment. Dealers may adjust the loan term to offer a lower monthly payment, which could result in higher overall costs.

形: Seven Tips to Negotiate Your Way to a More Challenging and Satisfying Role
ソース: Catalyst
説明:
The infographic provides seven actionable tips for negotiating a more challenging and satisfying role at work. It includes strategies such as understanding your value, preparing thoroughly, practicing negotiation skills, setting clear goals, building alliances, staying flexible, and following up after negotiations. Each tip is designed to help individuals effectively communicate their career aspirations and secure roles that align with their professional growth and satisfaction.
重要なポイント:
- Understand Your Value: Recognize and articulate your skills, achievements, and contributions.
- Prepare Thoroughly: Research the role, company needs, and industry standards to build a strong case.
- Practice Negotiation Skills: Rehearse discussions and anticipate possible responses and objections.
- 明確な目標を設定する: Define what you want to achieve from the negotiation and prioritize your objectives.
- Build Alliances: Seek support from colleagues, mentors, or allies within the organization.
- 柔軟性を保つ: Be open to alternative solutions and compromises that can still meet your goals.
- Follow Up: Ensure commitments made during negotiations are documented and followed through.
Application of Information:
Using these negotiation tips helps individuals advocate for their career advancement and achieve more fulfilling roles. For those learning about career development そして workplace dynamics, this guide offers practical strategies to enhance negotiation skills and effectively navigate career growth discussions. Understanding and applying these tips can lead to greater job satisfaction, better alignment with personal and professional goals, and a more proactive approach to career management.
Section 6: Legal Considerations
Contract Review
Carefully review all terms and conditions of the loan agreement. Ensure there are no hidden fees or unexpected charges.
Warranty and Insurance
Understand the warranty coverage and consider purchasing additional insurance if necessary. Extended warranties and gap insurance can provide extra protection.

Figure: Auto Loan Agreement Template
ソース: eSign
説明:
The image showcases a template for an auto loan agreement. This document outlines the terms and conditions under which a lender provides a loan to a borrower for the purchase of a vehicle. Key components typically include the loan amount, interest rate, repayment schedule, and both parties’ obligations. It also covers details such as the vehicle’s description, insurance requirements, late payment penalties, and the consequences of default.
重要なポイント:
- Loan Amount and Interest Rate: Specifies the amount borrowed and the interest rate applied to the loan.
- Repayment Schedule: Details the repayment terms, including the frequency and amount of payments.
- Borrower and Lender Obligations: Outlines the responsibilities and commitments of both parties.
- Vehicle Description: Provides specific details about the vehicle being financed.
- Insurance Requirements: States the insurance coverage the borrower must maintain for the vehicle.
- Penalties and Default Terms: Defines the penalties for late payments and the actions taken in case of default.
Application of Information:
Understanding an auto loan agreement is essential for both borrowers そして lenders to ensure clarity and mutual agreement on the loan’s terms. For borrowers, it helps in comprehending their financial obligations and the costs associated with the loan. For those learning about 個人融資 そして auto financing, this template provides a clear example of how auto loans are structured, emphasizing the importance of reading and understanding loan agreements thoroughly before committing to a loan. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions and managing auto loans effectively.
Section 7: Maintenance and Ongoing Costs
Regular Maintenance
Budget for regular maintenance, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections. Keeping up with maintenance can prevent costly repairs in the future.
Fuel Costs
Consider the fuel efficiency of the car and estimate your monthly fuel costs. More fuel-efficient cars can save money in the long run.
保険
Car insurance is a mandatory expense. Compare insurance quotes to find the best coverage at the most affordable rate.
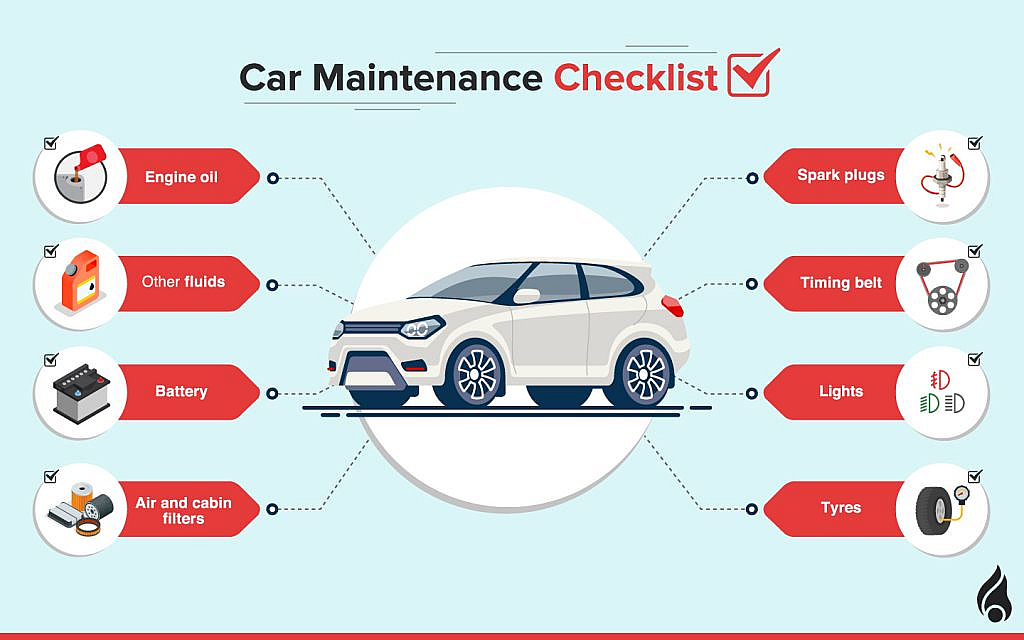
Figure: Car Maintenance Checklist
ソース: dubizzle
説明: The infographic provides a comprehensive car maintenance checklist, highlighting essential tasks to keep a vehicle in optimal condition. It includes routine checks such as oil changes, tire inspections, brake checks, fluid level monitoring, battery maintenance, and inspection of belts and hoses. The checklist emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance to ensure vehicle safety, reliability, and longevity, and offers guidelines on how frequently each task should be performed.
重要なポイント:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes keep the engine lubricated and running smoothly.
- Tire Inspections: Checking tire pressure and tread depth ensures safe driving and prolongs tire life.
- Brake Checks: Regularly inspecting brake pads and discs to maintain braking efficiency and safety.
- Fluid Levels: Monitoring and topping off fluids such as coolant, brake fluid, and windshield washer fluid.
- Battery Maintenance: Ensuring the battery is clean and terminals are corrosion-free for reliable starts.
- Belts and Hoses: Inspecting for wear and tear to prevent breakdowns and maintain engine performance.
Application of Information:
Following a car maintenance checklist helps vehicle owners ensure their cars remain in good working order, reducing the risk of breakdowns and expensive repairs. For those learning about automotive maintenance そして vehicle ownership, this guide highlights the essential tasks and their importance in proactive car care. Regular maintenance enhances vehicle safety, パフォーマンス、 そして longevity, making it crucial for maintaining the overall value and reliability of the car. Understanding and adhering to these maintenance tasks can lead to a better driving experience and lower long-term ownership costs.
Section 8: Real-World Examples
Example 1: Calculating Monthly Payments
Suppose you are purchasing a car for $20,000 with a 10% down payment and a loan term of 60 months at an interest rate of 5%. Using a car loan calculator, you can determine that your monthly payment would be approximately $340.
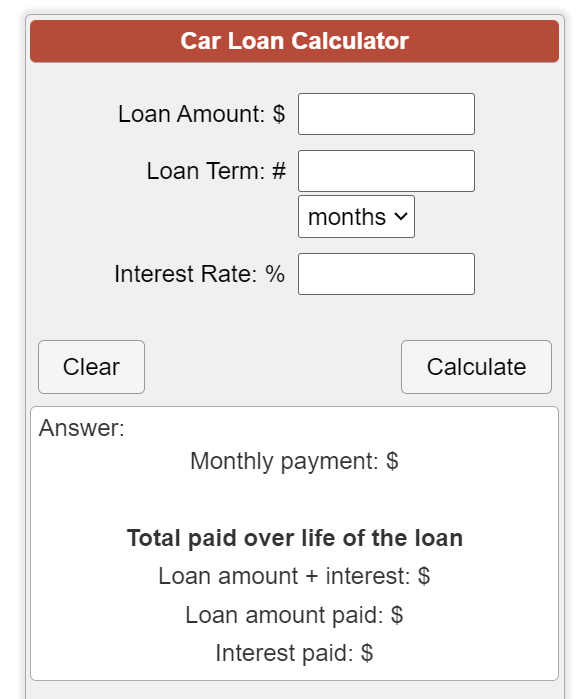
Figure: Car Loan Calculator
ソース: CalculatorSoup
説明:
The web page features a car loan calculator, a tool designed to help users estimate their monthly car loan payments. By inputting details such as the loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and down payment, users can calculate the monthly payment amount. The calculator also provides a breakdown of the total interest paid over the life of the loan and the overall cost of the car. This tool assists potential car buyers in understanding their financial commitments and planning their budgets accordingly.
重要なポイント:
- Loan Amount: The total amount borrowed for purchasing the car.
- Interest Rate: The annual percentage rate (APR) applied to the loan.
- ローン期間: The duration of the loan repayment period, usually in months or years.
- 頭金: The initial payment made towards the car, which reduces the loan amount.
- Monthly Payment Calculation: The tool calculates the monthly payments based on the input values.
- Total Interest Paid: Provides a summary of the total interest costs over the loan term.
- Overall Loan Cost: Offers insights into the total cost of the car, including principal and interest.
Application of Information:
使用して car loan calculator helps potential car buyers plan their finances by estimating monthly payments and the total cost of the loan. For those learning about 個人融資 そして auto financing, this tool demonstrates the impact of different variables such as interest rates, loan terms, and down payments on the cost of borrowing. It aids in making informed decisions about car purchases, ensuring that buyers understand their financial obligations and can budget accordingly. This knowledge is essential for effective financial planning and managing debt responsibly.
Example 2: Evaluating Affordability
If your gross monthly income is $3,500, applying the 15% rule means your car expenses should not exceed $525 per month. This includes the loan payment, insurance, maintenance, and fuel.

形: How Much Should I Spend on a Car?
ソース: 投資ペディア
説明:
The infographic provides guidelines on how to determine the amount to spend on purchasing a car. It recommends using the 20/4/10 rule, which suggests putting down at least 20% as a down payment, financing the car for no more than 4 years, and ensuring that total monthly car expenses do not exceed 10% of your gross monthly income. The infographic emphasizes the importance of budgeting and financial planning to avoid overextending oneself financially.
重要なポイント:
- 20% Down Payment: Putting down at least 20% of the car’s price helps reduce the loan amount and monthly payments.
- 4-Year Loan Term: Financing the car for no more than 4 years minimizes interest costs and the risk of being upside-down on the loan.
- 10% Monthly Income: Keeping total car expenses (including payments, insurance, and maintenance) within 10% of gross monthly income ensures affordability.
- 予算編成: Following these guidelines helps buyers avoid financial strain and maintain overall financial health.
Application of Information:
Understanding how much to spend on a car helps individuals make informed decisions that align with their financial situation and goals. For those learning about 個人融資, this guide emphasizes the importance of budgeting そして financial planning when making significant purchases. By adhering to the 20/4/10 rule, buyers can ensure they do not overextend themselves financially, maintaining affordability and avoiding debt-related stress. This approach promotes responsible spending and long-term financial stability.
結論
Purchasing a car is a significant financial decision that requires careful planning and consideration. By understanding the car buying process, exploring financing options, and following best practices, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals. Remember to budget for ongoing costs and consider both new and used cars to find the best fit for your needs.
主なレッスン情報:
閉会の辞: Purchasing a car is a substantial financial commitment. By following the structured approach outlined in this chapter, you can make an informed and financially sound decision. Understanding your needs, setting a budget, exploring financing options, and considering ongoing costs are essential steps towards successful car ownership. This knowledge empowers you to navigate the car buying process confidently and ensures long-term satisfaction with your purchase.
- Assessing Your Needs: Identifying your car needs based on its purpose, size, and features helps in making an informed decision. For example, a compact car might be ideal for city commuting, while an SUV could be better for a family with children.
- Setting a Budget: Establishing a budget that includes the down payment, monthly payments, insurance, maintenance, and fuel costs ensures you do not overspend. A common guideline is to spend no more than 15% of your monthly income on car expenses.
- Financing Options: Exploring different financing options such as traditional bank loans, dealer financing, and lease agreements allows you to choose the one that best fits your financial needs. Understanding interest rates and loan terms is crucial for making cost-effective decisions.
- New vs. Used Cars: Evaluating the pros and cons of new and used cars helps you decide based on cost, depreciation, and maintenance needs. New cars offer the latest technology and warranty coverage, but used cars are more affordable and have less depreciation.

