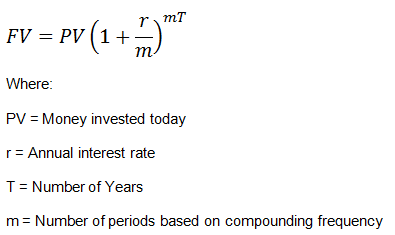第7章 貯蓄と緊急資金
レッスンの学習目標:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet、consectetur adipiscing elit。ウト・エリート・テルス、ルクトゥス・ネク・ウラムコーペル・マティス、プルヴィナー・ダピブス・レオ。

7.1 Types of Accounts and Financial Services
金融機関は、それぞれ特定の金融ニーズに合わせて設計されたさまざまな口座とサービスを提供しています。
当座預金口座:
日常の取引に使用されます。 通常はデビットカードが付属しており、 無制限の入金と出金を提供します。
- 利点: 資金への簡単なアクセス、デビット カード アクセス、オンラインでの請求書支払い。
- デメリット: 通常は利息が低いか、利息がまったく発生しません。
普通預金口座:
Aimed at short-term savings over time. Offer interest on the stored funds.
- 利点: 利息が付き、リスクが低い。
- デメリット: 引き出しが制限されており、他の貯蓄商品に比べて金利が低くなる可能性があります。
マネーマーケット口座(MMA):
当座預金口座と普通預金口座を組み合わせたもので、通常は金利が高く、最低残高要件も高くなります。
- 利点: より高い金利、小切手発行特権。
- デメリット: 最低残高要件が高く、取引が制限されている。
預金証書(CD):
Fixed-term savings account with a guaranteed interest rate.
- 利点: 普通預金口座に比べて金利が高く、利回りが固定されています。
- デメリット: 早期解約にはペナルティがあり、期間が終了するまでお金を引き出すことができません。

Figure: What is a Checking Account?
説明:
This image visually defines a checking account, which is a primary tool for managing day-to-day finances. It highlights the main features of the account, such as a debit card and paper checks, which are used to make purchases and pay bills. The graphic serves as a simple introduction to one of the most basic and essential products in personal finance.
重要なポイント:
- あ checking account is a type of bank account that provides easy access to your money for daily transactions.
- It is designed for high liquidity, meaning you can withdraw or spend your money quickly using tools like a debit card, ATM, or online transfers.
- The main purpose of this account is for spending and bill payments, not for earning interest; most checking accounts offer little to no interest on your balance.
- Keeping track of your transactions through a bank statement or online portal is crucial for 予算編成 and avoiding overdrafts.
情報の応用:
- あ checking account is the foundation of personal financial management, acting as the operational center for your income and expenses.
- Learning to manage a checking account is a critical first step in creating a 予算, tracking your spending, and building good financial habits.
- For anyone new to finance, this account is an essential tool for safely storing money, paying bills efficiently, and participating in the modern economy.
アカウントの開設と管理:
銀行口座を開設するには、通常、個人識別情報、社会保障番号、および最初の預金を提供する必要があります。口座の管理には、残高の監視、入金と引き出し、最低残高要件や当座貸越手数料などの手数料の理解が含まれます。
アカウントのコンポーネント:
口座番号は口座を一意に識別し、ルーティング番号は銀行を識別します。これは直接入金や自動支払いの設定に不可欠です。
信用組合と商業銀行:
Credit unions typically offer lower fees and better interest rates but might have fewer branches and services. Commercial banks offer a broader range of services but may charge higher fees.
学生のための金融商品の評価
学生は考慮すべき 当座預金口座と普通預金口座 手数料が低く、資金へのアクセスが容易で、財務管理に役立つ教育リソースも利用できます。 利点 お金の管理を学び、貯蓄で利息を稼ぐことが含まれます。 デメリット 最低残高要件の管理や、潜在的な手数料の処理が必要になる場合があります。
7.2 Online Banking and Account Management
オンライン バンキングでは、口座開設、残高確認、資金振替などの金融サービスに簡単にアクセスできます。重要な要素には、最低残高要件、月額手数料、当座貸越ペナルティ、金利の理解が含まれます。口座が取引をカバーし、手数料を回避するために、定期的に資金を追跡および管理することが重要です。
形: Key Benefits of Online Banking
説明:
This graphic illustrates the main advantages of using online banking for managing personal or business finances. It visually highlights key features such as 24/7 account access from any device, the ease of making digital payments, and real-time transaction monitoring. The overall message is that online banking offers a more convenient, efficient, and powerful way to handle financial tasks.
重要なポイント:
- Constant Accessibility: A major benefit of online banking is 24/7 access to your accounts from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need to visit a physical bank.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: It saves significant time by allowing you to automate bill payments and transfer funds instantly, and it often comes with lower fees than traditional banking services.
- Enhanced Financial Control: Online banking provides real-time visibility into your transactions and account balances, which is crucial for accurate budgeting and managing cash flow.
- Simplified Record-Keeping: Many platforms can integrate with accounting software, which automates bookkeeping and makes financial reporting much easier for individuals and businesses.
情報の応用:
- Adopting online banking is a foundational step for modern and efficient money management.
- It provides the tools to actively track your spending, automate your savings contributions, and maintain a clear, up-to-the-minute picture of your financial health.
- By leveraging these digital tools, you can reduce time spent on financial administration and focus more energy on achieving your primary goals, like investing for the future or growing a business.
金利と貯蓄
融資の需要が増加すると、銀行はより多くの預金者を引き付け、貸し出し資金を提供するために預金金利を高く設定することがあります。逆に、融資市場が飽和状態になったり景気が低迷したりすると、借入需要が減少し、銀行は貯蓄口座の金利を下げることがあります。
モバイル決済口座と従来の銀行
モバイル決済口座は便利で使いやすいが、通常は利息収入がなく、従来の口座に比べて貯蓄増加の可能性は低い。 普通預金口座、利息を支払います。 暗号通貨アカウント 高いボラティリティと潜在的リターンを提供しますが、連邦政府の保証がなく、連邦政府が保証する貯蓄口座の安全性と安定した成長の可能性とは対照的です。
7.3 Comparing Mobile Payment Accounts, Cryptocurrency Accounts, and Traditional Bank Accounts
While mobile payment platforms like Venmo or Cash App and cryptocurrency wallets offer convenience and fast transactions, they typically do not provide interest earnings or federal insurance protections (like FDIC or NCUA insurance). Traditional savings and checking accounts offer lower risk, provide interest (even if modest), and are protected against institutional failures up to certain limits.
Feature | Mobile Payments | 暗号通貨アカウント | Traditional Bank Accounts |
保険 | No federal insurance | No federal insurance | FDIC/NCUA insured |
Interest Earnings | None | Very rare | Common (low to moderate) |
Accessibility | High (instant transfer) | High (global access) | High (ATM, online banking) |
リスクレベル | Medium to high | High (market volatility) | 低い |
7.4 Why Certificates of Deposit (CDs) Typically Pay Higher Interest Rates
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) generally offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts or interest-bearing checking accounts because they require depositors to commit their money for a specific period. This commitment gives banks more certainty about the availability of funds for lending and investments. In exchange for giving up liquidity (easy access to their funds), depositors are rewarded with higher rates. Early withdrawal often results in penalties, reinforcing the importance of keeping funds deposited for the full term.
例:
A savings account might offer a 1% interest rate, while a 12-month CD could offer 4% during the same period.
長所:
- Higher guaranteed returns over the term.
- Safe and predictable growth.
短所:
- Funds are locked until maturity.
- Penalties for early withdrawal.
7.5 Impact of Loan Demand on Deposit Interest Rates
When the demand for loans rises, banks often need additional funds to meet the demand. To attract more deposits (which they use to fund new loans), they may offer higher interest rates on savings accounts, CDs, and other deposit products. Essentially, banks are willing to pay more to bring in money they can lend out profitably.
例:
If mortgage applications rise sharply, banks may raise deposit rates from 1.5% to 2% to attract savers and balance their funding needs.
7.6 Market Conditions Leading to Lower Savings Rates
In times of economic slowdown or when consumers and businesses are not borrowing as much, banks don’t need as many deposits. As a result, they may lower the interest rates paid on savings accounts. This often occurs during recessions or when central banks lower benchmark interest rates to stimulate the economy.
例:
During a recession, banks may drop savings account interest rates from 2% down to 0.5%, reflecting lower loan demand and economic conditions.
7.7 Impact of Spending vs. Saving
今すぐにお金を使うか、将来のために貯蓄するかの選択は、よくあるジレンマです。すぐに満足すると、家の購入や快適な老後の生活の確保など、より重要な経済的目標の達成が妨げられ、後悔につながる可能性があります。
シナリオ 1:
エミリーは、その高度な機能に惹かれて、衝動的に高性能のノートパソコンを購入することにしました。数か月後、彼女は、キャリアアップにつながるはずだった専門資格のためにお金を貯めていなかったことを後悔し、目先の満足よりも長期的な経済的目標を優先することの重要性を痛感しました。
シナリオ2:
ボーナスを受け取ったジェイクは、すぐに高価な休暇を予約しました。楽しかったものの、車の修理が必要になったときのためにお金の一部を貯めておけばよかったと後悔し、現在を楽しむことと将来に備えることのバランスの重要性を強調しました。
形: Pay Off Debt vs. Save Money: Which Comes First?
説明:
This image tackles the common financial dilemma of whether to focus on paying off debt または building savings. It presents a clear, step-by-step guide to help you decide where to direct your money first. The framework helps you create a balanced strategy that allows you to build a financial safety net while efficiently eliminating debt.
重要なポイント:
- The first priority for almost everyone should be to build a starter 緊急資金 of at least $500 to $1,000. This prevents small emergencies from forcing you into more debt.
- After establishing a small emergency fund, you should aggressively pay down any 高利子債務, like credit card balances, as the interest charged is often very high.
- If your employer offers a retirement plan with a company match, contribute enough to get the full match, as this is essentially a 100% return on your investment and a top priority.
- Once high-interest debt is gone, you can adopt a balanced approach by simultaneously building your full 3-6 month emergency fund and saving for other long-term goals.
情報の応用:
- This model provides a clear roadmap to help you make smart decisions and reduce financial stress when you have competing financial priorities.
- You can use this framework to create an effective cash flow plan, ensuring your money is allocated in the most impactful way.
- By following these steps—starter 緊急資金, attacking 高利子債務, and securing an employer match—you can build a strong financial foundation for future wealth creation.
7.8 Inflation and Interest Rates
インフレは時間の経過とともにお金の価値を下げ、貯蓄の購買力を低下させます。名目金利はインフレを考慮しませんが、実質金利(名目金利からインフレ率を引いたもの)は貯蓄の実際の増加を示します。貯蓄者は貯蓄の価値を維持するために、インフレを上回る名目金利を求めるべきです。
金利=名目金利-インフレ率
例:
普通預金口座の名目金利が 3% で、インフレ率が 2% の場合、実質金利は実質的に 1% になります。1 年間で、この口座のお金の購買力はインフレ調整後 1% しか増加しません。これは、時間の経過とともに資産を本当に増やすには、インフレを上回る貯蓄または投資オプションを探すことの重要性を強調しています。
7.9 Inflation Protection and I Bonds
債券はインフレに対抗する目的で設計されており、その金利はインフレに応じて調整されます。インフレが上昇すると、債券の金利も上昇し、高インフレ環境では固定金利により実質リターンがマイナスになる可能性がある従来の CD とは異なり、貯蓄の購買力が長期にわたって維持されます。
将来価値と割引
形: Calculating the Future Value of a Single Cash Flow
説明:
The infographic likely demonstrates the formula for calculating the future value of a single cash flow, which is a fundamental concept in finance. This formula helps in understanding how much an investment made today will grow to at a future date, considering a specific rate of interest. The formula is typically represented as FV = PV(1 + r)^n, where FV is the future value, PV is the present value, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
重要なポイント:
- 将来価値 (FV) の計算式は、投資が時間の経過とともにどのように成長するかを計算する上で非常に重要です。
- この式を理解することで、投資家は将来の投資価値を見積もることができます。
- 式の変数には、現在価値 (PV)、金利 (r)、期間数 (n) が含まれ、それぞれが計算において重要な役割を果たします。
情報の応用:
This concept is essential for anyone involved in financial planning, investment analysis, or saving for future goals. By applying this formula, individuals can make informed decisions about their investments, understanding how different rates of interest and time periods affect the growth of their money. It encourages strategic investment and helps in setting realistic expectations for investment returns, which is fundamental for long-term financial planning and wealth accumulation.
スプレッドシートを使用して計算すると、10 歳の子供が 8 年後の 1 年間の大学授業料 (推定 $20,000) を賄うには、年間利率 5% で毎月 $200 を貯蓄する必要があることがわかります。この例は、将来の財務目標を達成するために今日いくら貯蓄する必要があるかを判断するために、金利を考慮に入れたお金の将来価値の割り引きを示しています。
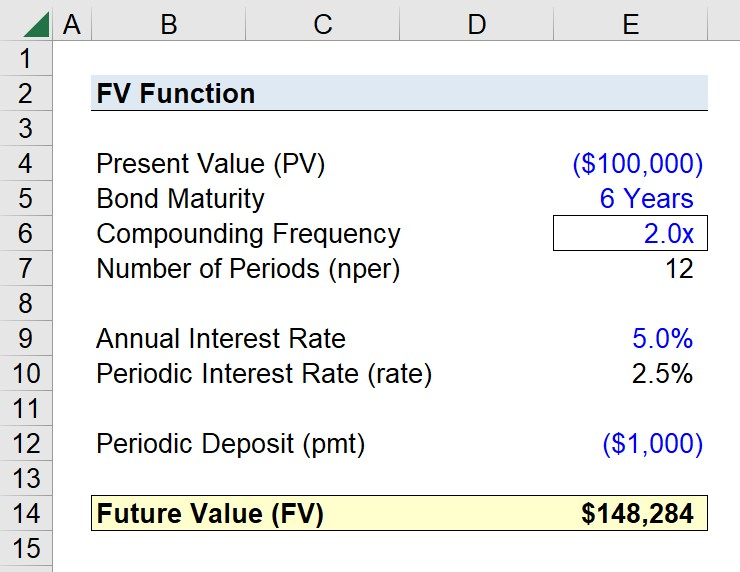
形: Using the FV Function in Excel to Calculate Future Value
説明:
The infographic likely demonstrates how to use the FV function in Excel to calculate the future value of an investment, considering a constant interest rate over a number of periods. The FV function is a powerful tool in Excel for financial analysis, allowing users to input variables such as rate, number of periods, payments, present value, and type (whether payments are made at the beginning or end of periods) to compute the future value of an investment.
重要なポイント:
- Excel の FV 関数は、投資の将来価値を計算するために不可欠です。
- FV 関数の主な入力には、金利、期間数、定期的な支払い、現在価値、支払い時期などがあります。
- FV 関数の使い方を理解すると、財務モデリングと投資分析のスキルが大幅に向上します。
情報の応用:
This knowledge is crucial for finance students, financial analysts, and anyone involved in investment planning or analysis. By mastering the FV function, users can quickly assess the potential future value of investments, aiding in decision-making processes. It’s particularly useful for evaluating the growth of savings accounts, retirement funds, or any investment over time, providing a clear picture of financial futures.
7.10 Down Payments and Loans
住宅ローンの 20% 頭金のように、ローンの頭金を支払うと、借入総額が減り、月々の支払額が減り、金利も下がることがよくあります。これにより、借り手は貸し手にとってより魅力的になり、長期的にはローンのコストを大幅に削減できます。
7.11 Emergency Funds and Financial Planning
緊急資金は、予期せぬ出費に対するセーフティネットを提供し、経済的な安定に不可欠です。短期および長期の貯蓄への割り当てを含む予算を作成し、維持することで、人生の不確実性に備え、経済的な目標に向かって前進することができます。
例:
マリアの車が故障し、高額な修理が必要になりました。彼女は予算を修正して裁量支出を減らし、娯楽や外食の予算から修理費を補うための資金を再配分し、貯蓄口座への積み立てを一時的に減らしました。

形:個人財務計画の6ステッププロセス
説明:
この画像は、個人の財務計画の 6 段階のプロセスを紹介しています。資産と負債を含む現在の財務状況の評価から始まり、財務目標の設定、行動計画の作成、投資オプションの評価、計画の実施、戦略の定期的な見直しと修正へと進みます。
重要なポイント:
- 現在の財務状況の評価 is crucial as a starting point for planning.
- 目標設定 involves assigning value and timelines to short, medium, and long-term financial aspirations.
- アン 行動計画 must consider one’s risk tolerance and align investment choices accordingly.
- 投資オプション 特定の目標に結び付け、税務効率と適合性に基づいて選択する必要があります。
- 定期投資 習慣の形成と財務目標のスムーズな達成に貢献します。
- 定期的なレビュー 投資が順調に進んでいることを確認し、必要に応じて調整できるようにします。
情報の応用:
現在の財務状況の評価から始めることは、個人の財務計画の基本です。財務状況を把握することで、現実的な目標を設定し、改善すべき領域を特定し、財務の安定と成長を達成するためのロードマップを作成できます。このステップにより、その後の計画が現実に即したものとなり、個人の固有の財務状況に合わせて調整されます。
Contingency Planning for Financial Emergencies
Contingency planning involves preparing for unexpected financial shocks by having backup savings or insurance. A good contingency plan can help cover emergency expenses such as car repairs, medical bills, sudden unemployment, or major household repairs without derailing long-term financial goals.
例:
- Backup Fund: Besides an emergency fund, maintain a small “contingency fund” specifically for very short-term needs.
- Insurance: Maintain adequate health, auto, and renters/homeowners insurance to mitigate major risks.
- Backup Budget: Create a reduced-spending version of your budget to activate if income drops suddenly.
給与と控除について理解する
総支給額 控除前の従業員の総収入です。 純支払額、つまり手取り収入は、税金、医療費、その他の控除を差し引いた後の残りです。正確な予算を立てるには、その差を理解することが不可欠です。
7.12 Financial Institutions and Services
銀行、信用組合、オンライン プラットフォームなどの金融機関は、当座預金口座や普通預金口座、財務計画サービスなどのさまざまな商品を提供しています。適切な機関とサービスを選択することは、効果的な資金管理と財務目標の達成に不可欠です。
アカウント管理の例:
当座預金口座を効果的に管理するには、定期的に取引を確認し、個人の記録と照合して正確性を確保する必要があります。モバイル バンキング アプリを利用すると、追跡が簡単になり、当座貸越手数料を回避できます。
7.13 The Role of FDIC and NCUA Insurance
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insures deposits at banks, while the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) insures deposits at credit unions. Both agencies guarantee deposit accounts (up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank or credit union) in case the financial institution fails. This insurance provides consumers with peace of mind that their money is protected against institutional collapse.
例:
If your bank closes unexpectedly, the FDIC will reimburse your insured deposits up to the coverage limit.
結論
Saving, managing financial products, preparing for inflation, and understanding the broader banking environment are essential skills for long-term financial success. By supplementing your knowledge with insights about CDs, market influences on interest rates, the differences between mobile/crypto accounts and traditional banks, federal insurance protections, and emergency contingency planning, you’ll be even better equipped to protect and grow your financial future.
主なレッスン情報:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet、consectetur adipiscing elit。ウト・エリート・テルス、ルクトゥス・ネク・ウラムコーペル・マティス、プルヴィナー・ダピブス・レオ。