株式市場を理解する
主な学習目標:
導入: This section dives into the world of stock markets, unraveling its functionality and introducing you to the benefits, risks, and various types of investors involved. It’s crucial for developing a solid understanding to navigate through your investment journey.
- Decipher the Functionality of Stock Markets: Understand what the 株式市場 is, its significance, and its role in the 経済.
- Distinguish the Benefits and Risks: 理解する リスク そして benefits associated with stock investments and learn strategies to manage these risks effectively.
- Identify Various Types of Investors: Recognize the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of retail, institutional, そして high-frequency traders.
導入: This section dives into the world of stock markets, unraveling its functionality and introducing you to the benefits, risks, and various types of investors involved. It’s crucial for developing a solid understanding to navigate through your investment journey.
2.1 What is the Stock Market?
The stock market is a platform where buyers and sellers come together to trade shares of publicly traded companies. These shares, also known as stocks, represent a portion of ownership in a company. When you buy stocks, you essentially become a shareholder and gain a stake in the company’s assets and future earnings.
Stock markets serve several key functions in the economy. They provide a venue for companies to raise capital, allowing them to grow and create jobs. At the same time, they enable investors to generate wealth through capital appreciation and dividends.

形: The infographic offers a concise guide on “How to Invest in Stocks.” It outlines a series of steps for beginners, starting with deciding the method of investment. The visual then suggests opening an investing account and understanding the distinction between individual stocks and stock mutual funds. It also emphasizes the importance of setting a budget for stock investments and taking the initial steps to start the investment journey.
出典: カスタム インフォグラフィック
The stock market is a platform where buyers and sellers come together to trade shares of publicly traded companies. These shares, also known as stocks, represent a portion of ownership in a company. When you buy stocks, you essentially become a shareholder and gain a stake in the company’s assets and future earnings.
Stock markets serve several key functions in the economy. They provide a venue for companies to raise capital, allowing them to grow and create jobs. At the same time, they enable investors to generate wealth through capital appreciation and dividends.
形: The infographic presents the “Top 5 Golden Rules of Stock Investing.” It emphasizes a long-term investment mindset, advising individuals to think of stock investments as a marathon, not a sprint. The visual also stresses the importance of investing in good companies, ensuring safety before investing, conducting thorough research, and understanding one’s investments. Lastly, it advises against blindly following the masses and underscores the significance of staying calm and rational in the face of market volatility.
出典: カスタム インフォグラフィック

2.2 Why Do People Invest in Stocks? Benefits, Risks, and Risk Management

形: The infographic emphasizes the importance of long-term investment with a prominent quote: “Only buy something that you’d be perfectly happy to hold if the market shut down for 10 years.” This advice underscores the significance of patience and a long-term perspective when it comes to stock investing.
出典: カスタム インフォグラフィック

形: The infographic introduces the concept of “Stocks” as a type of investment. It defines a stock as an investment in a specific company, emphasizing that when an individual purchases a stock, they are essentially buying a share or a small piece of that company’s earnings and assets.
出典: カスタム インフォグラフィック
People invest in stocks for a variety of reasons, including:
- 資本の評価増: Over the long term, stocks have historically offered higher returns than other investment options, such as bonds or cash. As the value of a company grows, so does the value of its stock, providing potential gains for investors.
- 配当金: Some companies pay regular dividends to shareholders, providing a steady income stream.
- 多様化: Investing in a diverse portfolio of stocks can help spread risk across different sectors, reducing the impact of any single stock’s poor performance.
However, investing in stocks also comes with risks, such as market volatility and the potential for loss. To decrease these risks, investors should:
- Diversify their portfolio by investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets.
- Focus on long-term investing strategies rather than attempting to time the market.
- Conduct thorough research and analysis before making investment decisions.
2.3 Types of Investors:
There are various types of investors in the stock market, each with its objectives and strategies.
a) Retail investors:
These are individual investors who buy and sell stocks for their accounts. They typically invest for long-term growth, income generation, or to save for future goals, such as retirement or education expenses.
利点:
- 柔軟性: Retail investors can make their own investment decisions based on personal preferences and risk tolerance.
デメリット:
- Limited resources: Retail investors may have less access to information, research, and tools compared to institutional investors.
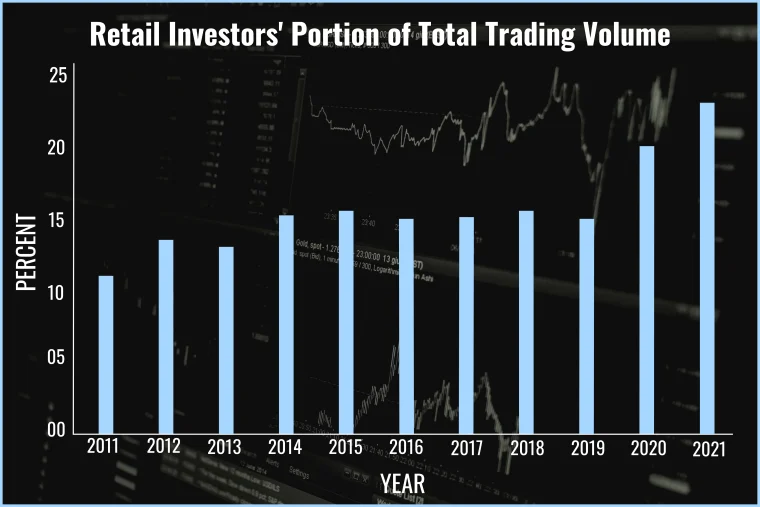
Figure Title: Retail Investors’ Portion of Total Trading Volume ; Source: TheStreet.com
説明: The graph depicts the rise of retail trading as a portion of the total trading volume over the years. It shows the percentage of trading volume attributed to retail investors in different years, starting from 2011 to the present. The data highlights the increasing involvement of individual retail investors in the financial markets compared to institutional investors.
重要なポイント:
- Retail Trading Growth: The graph demonstrates the significant growth of retail trading participation in the stock market over time. The increasing percentage of retail investors’ contribution to the total trading volume suggests a rise in individual investors’ interest in actively managing their investments.
- Factors Driving Retail Trading: Several factors contribute to the surge in retail trading. Increased access to online trading platforms, lower trading fees, and advancements in technology have democratized investment opportunities for retail investors. Moreover, the ease of accessing information, social media platforms, and online investing communities has facilitated the dissemination of investment ideas and strategies, attracting more retail traders to the market.
- Market Impact: The increasing presence of retail investors can influence market dynamics. Retail investors’ collective actions, influenced by social media trends or speculative fervor, have led to notable price movements and heightened market volatility in certain stocks.
- Investor Empowerment: The data showcases how technological advancements and reduced barriers to entry have empowered retail investors, providing them with opportunities to participate actively in the stock market. This trend encourages individuals to take charge of their financial futures and make informed investment decisions.
Application of Information: Understanding the growing significance of retail investors in the market can help users, especially new investors, recognize the changing landscape of investing. It emphasizes the importance of staying informed and educated to make sound investment decisions. For learners of finance and stock investing, this data highlights the relevance of considering retail investor behavior and the potential impact it can have on individual stock movements and market trends. As retail trading continues to play a significant role in the financial markets, investors can apply this knowledge to adapt their strategies and stay aligned with evolving market dynamics.
b) Institutional investors:

形: The infographic provides a detailed overview of an “Institutional Investor.” It lists various entities that fall under this category, including pension plans that make investments on behalf of employees, businesses that invest either directly or through a captive fund, mutual funds, hedge funds, and other funds (which may or may not be publicly traded), large money managers, and sovereign wealth funds.
出典: カスタム インフォグラフィック
Institutional investors include pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds. They manage large pools of money on behalf of their clients or beneficiaries.
利点:
- Access to resources: Institutional investors have access to in-depth research, sophisticated tools, and professional expertise.
- Economies of scale: They can negotiate better fees and trading costs due to the large volume of assets they manage.
デメリット:
- Constraints: Institutional investors may be subject to investment guidelines, limiting their flexibility in making investment decisions.
c) High-frequency traders (HFTs):
HFTs use advanced algorithms and technology to execute trades at extremely high speeds, often profiting from minuscule price differences or market inefficiencies.
利点:
- Speed and efficiency: HFTs can capitalize on short-term opportunities that other investors may miss.
デメリット:
- Short-term focus: HFTs may not contribute to long-term price discovery or the efficient allocation of capital.
Each type of investor contributes to the overall liquidity and functioning of the stock market, creating a dynamic ecosystem where various investment strategies coexist.
重要なポイント:
閉会の辞: The understanding of stock market functionality and the types of investors involved is pivotal for making informed investment decisions. This section offers the knowledge required to differentiate between various investment scenarios and manage associated risks.
- Stock markets are platforms for trading shares representing ownership in companies, crucial for companies to raise capital.
- 株式 offer potential for capital appreciation そして dividends, yet come with リスク which can be mitigated through strategies like 多様化 そして research.
- The stock market ecosystem comprises different types of investors including retail investors, institutional investors, そして HFTs, each bringing unique dynamics to the market.

