გლობალური: საფონდო მახასიათებლები
გაკვეთილის სწავლის მიზნები:
- Understand the different types of stocks such as value და ზრდის აქციები, and how they align with different investment strategies. You will learn which types of companies fall under each category and what they offer to investors.
- Gain clarity on stock size and liquidity, მათ შორის large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks, and how these classifications affect potential risk, return, and ease of trading.
- Explore essential financial metrics მოწონება dividends, earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratioდა beta, and understand how they help assess a company’s financial health and performance.
- Understand penny stocks, including what they are, where they are traded, and the risks and rewards they present to investors seeking high-growth opportunities.
- Learn how to apply this knowledge in real-world investing by selecting stocks that fit your goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
A. Value, Growth, Size, Liquidity, and More
Stocks can be categorized based on a variety of characteristics that help investors determine their potential risk and return. These characteristics include value, growth, sizeდა liquidity. Understanding these traits is essential for developing a well-diversified portfolio.
- Value Stocks: These are stocks that are considered undervalued compared to their fundamentals (such as earnings, revenue, or dividends). Investors in value stocks are looking for companies that may be temporarily underpriced by the market but have strong potential for long-term returns. Value stocks are typically found in mature industries such as energy or banking.
- Growth Stocks: These stocks belong to companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to the market. Growth stocks are often found in fast-growing sectors like technology and healthcare. While these companies may not pay dividends, their stock price is expected to rise significantly over time as the company expands. However, growth stocks tend to be more volatile than value stocks.
- ზომა: Stocks are often categorized by the size of the company, typically measured by market capitalization (market cap), which is the total value of all a company’s outstanding shares.
- Large-cap stocks: Companies with a market cap of $10 billion or more. These are usually well-established, stable companies that provide consistent returns with less volatility.
- Mid-cap stocks: Companies with a market cap between $2 billion and $10 billion. These stocks often provide a balance between stability and growth potential.
- Small-cap stocks: Companies with a market cap of less than $2 billion. Small-cap stocks often offer higher growth potential but come with higher risk due to their size and potential market fluctuations.
- ლიკვიდურობა: Liquidity refers to how easily a stock can be bought or sold in the market without affecting its price. Highly liquid stocks are easier to trade and usually have lower transaction costs. Large-cap stocks tend to be more liquid due to their high trading volumes, while small-cap stocks can be less liquid, making them harder to sell at the desired price.
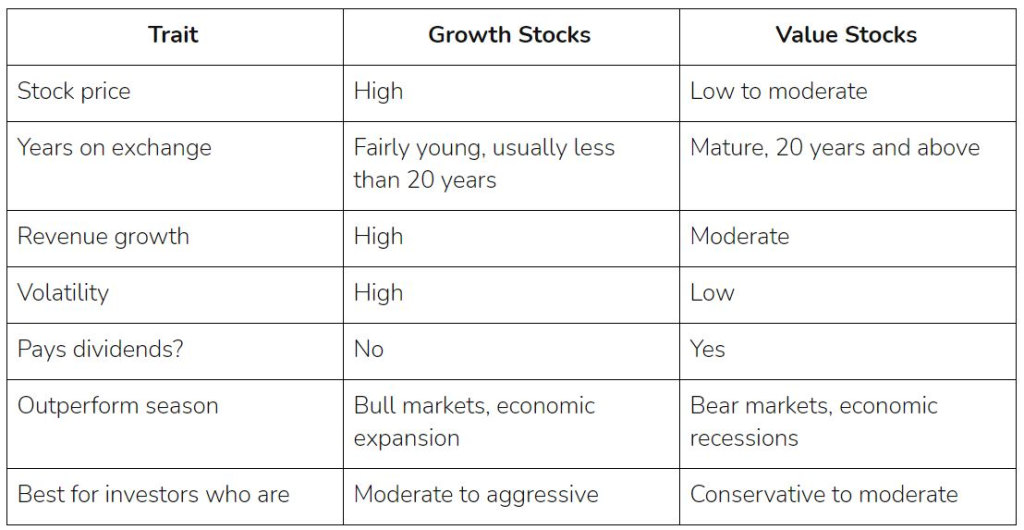
ფიგურა: Growth Stocks vs. Value Stocks
აღწერა:
This table compares ზრდის აქციები და ღირებულების აქციები across various traits like stock price, years on exchange, revenue growth, volatility, dividends, seasons of outperformance, and investor suitability. Growth stocks typically have high stock prices, younger age on the exchangeდა high revenue growth but are also more volatile and usually do not pay dividends. Value stocks, in contrast, have lower stock prices, are more mature, exhibit moderate revenue growth, and offer დივიდენდები with lower volatility.
ძირითადი დასკვნები:
- ზრდის აქციები are characterized by high revenue growth, higher volatility, and better performance during bull markets.
- ღირებულების აქციები are typically mature, have moderate revenue growth, and tend to perform well during bear markets ან economic recessions.
- დივიდენდები are more common with value stocks, making them suitable for conservative investors, whereas growth stocks attract more aggressive investors.
- ზრდის აქციები are often newer to the exchange, whereas ღირებულების აქციები have a longer history.
ინფორმაციის გამოყენება:
Understanding the differences between growth and value stocks can help investors tailor their portfolios to match their risk tolerance and investment strategy. Growth stocks may appeal to investors looking for კაპიტალის ზრდა during economic expansion, while value stocks might suit those seeking income და stability during downturns. This distinction is useful for building a diversified investment strategy that adapts to varying market conditions.
B. Other Stock Information
Aside from the traditional characteristics like size and growth potential, there are other stock features and metrics that investors may consider:
- დივიდენდები: Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash or additional stock. Stocks that pay dividends can provide a steady income stream, making them appealing to income-focused investors. Companies in sectors like utilities, consumer goods, and financial services often offer higher dividends.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS is a company’s profit divided by the number of outstanding shares. It is a key metric used to assess a company’s profitability and is often used by investors to compare profitability across companies in the same industry.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: The P/E ratio measures a company’s stock price relative to its earnings. A high P/E ratio indicates that investors expect higher future growth, while a low P/E ratio may indicate that the stock is undervalued.
- ბეტა: Beta measures a stock’s volatility compared to the overall market. A beta of 1 means the stock moves in line with the market, while a beta higher than 1 indicates the stock is more volatile. A beta lower than 1 indicates less volatility compared to the market.
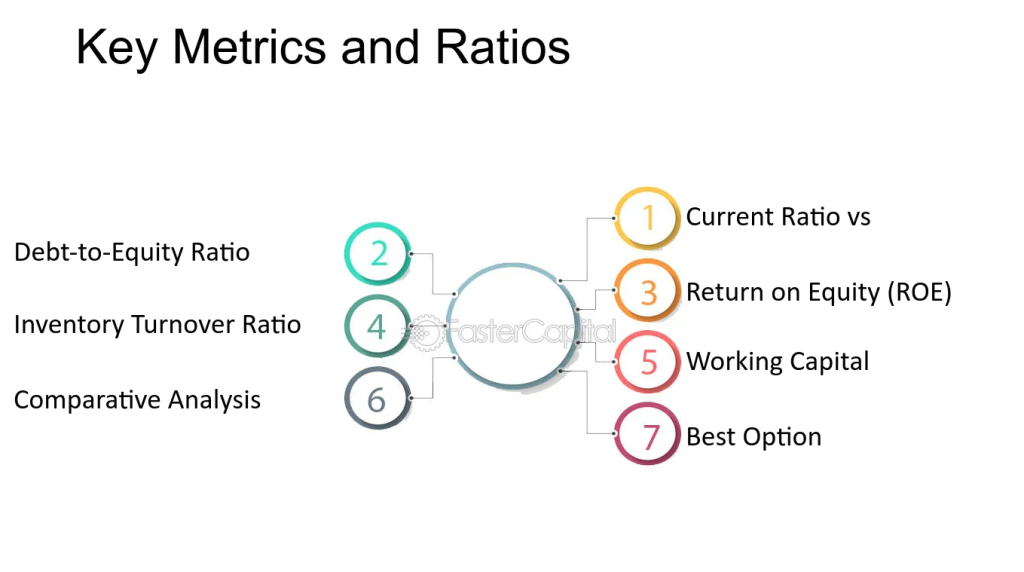
ფიგურა: Key Metrics and Ratios
აღწერა:
This graphic outlines seven critical financial metrics and ratios used to evaluate a company’s financial health and performance. The metrics include the Current Ratio, which measures liquidity; the Debt-to-Equity Ratio, indicating leverage; Return on Equity (ROE), showing profitability; Inventory Turnover Ratio, assessing inventory efficiency; Working Capital, representing operational liquidity; Comparative Analysis, used to compare performance with peers; and Best Option, which suggests the most suitable metric for a specific analysis.
ძირითადი დასკვნები:
- Current Ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations with its short-term assets.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio assesses financial leverage, showing the proportion of debt used relative to equity.
- Return on Equity (ROE) indicates how efficiently a company is using shareholder funds to generate profit.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio helps determine how quickly inventory is sold, reflecting operational efficiency.
- Working Capital gauges a company’s short-term liquidity and overall financial health.
ინფორმაციის გამოყენება:
ამის გაგება key financial metrics and ratios can help investors and analysts assess a company’s financial performance, make informed საინვესტიციო გადაწყვეტილებები, and identify potential strengths or weaknesses. Each metric provides insights into different aspects of a business, such as profitability, efficiency, ან liquidity, making them essential tools in financial analysis.
C. Investing in Penny Stocks
Penny stocks are low-priced stocks, typically trading for less than $5 per share, and are often associated with small-cap companies. While penny stocks offer the potential for significant gains, they also come with high risk due to their volatility, low liquidity, and the fact that these companies often operate in less-established markets or industries.

Figure: Understanding Penny Stocks and Their Dynamics
აღწერა:
This image represents penny stocks, which are low-priced stocks typically traded for less than $5 per share. They are often associated with small companies and are traded over-the-counter (OTC) rather than on major stock exchanges. The image depicts a single coin symbolizing the low value of penny stocks, set against a financial graph background, indicating their potential for growth and volatility.
ძირითადი დასკვნები:
- Penny stocks are low-priced shares of small companies, often trading below $5.
- They are generally high-risk investments due to their price volatility and lack of liquidity.
- These stocks are more likely to be found on over-the-counter markets than on major exchanges.
- Investors may be drawn to penny stocks for their potential high returns, though they require thorough research and caution.
ინფორმაციის გამოყენება:
Investors should approach penny stocks with caution, as they can be highly speculative and are often prone to sharp price swings. However, understanding the dynamics of penny stocks can help investors diversify their portfolios, especially when pursuing high-risk, high-reward strategies. It’s crucial to conduct comprehensive research and understand the associated risks before investing in penny stocks.
- High Risk: Penny stocks are highly speculative, as the companies behind them may have limited financial history, less stringent reporting requirements, and may be more prone to market manipulation. Investors can lose significant amounts of money if the stock price collapses.
- Low Liquidity: Penny stocks often have low trading volumes, which means it can be difficult to buy or sell shares without affecting the stock price. This lack of liquidity can lead to larger bid-ask spreads, increasing the cost of buying or selling the stock.
- მაღალი შემოსავლის პოტენციალი: Despite the risks, penny stocks can provide high returns, as even small price movements can result in significant percentage gains. Some investors seek out penny stocks with the hope that the company will grow rapidly, leading to large profits.
- მარეგულირებელი რისკები: Penny stocks are often traded on over-the-counter (OTC) markets, which have less regulatory oversight than major exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) ან NASDAQ. This makes them more susceptible to fraud and manipulation, adding an additional layer of risk.
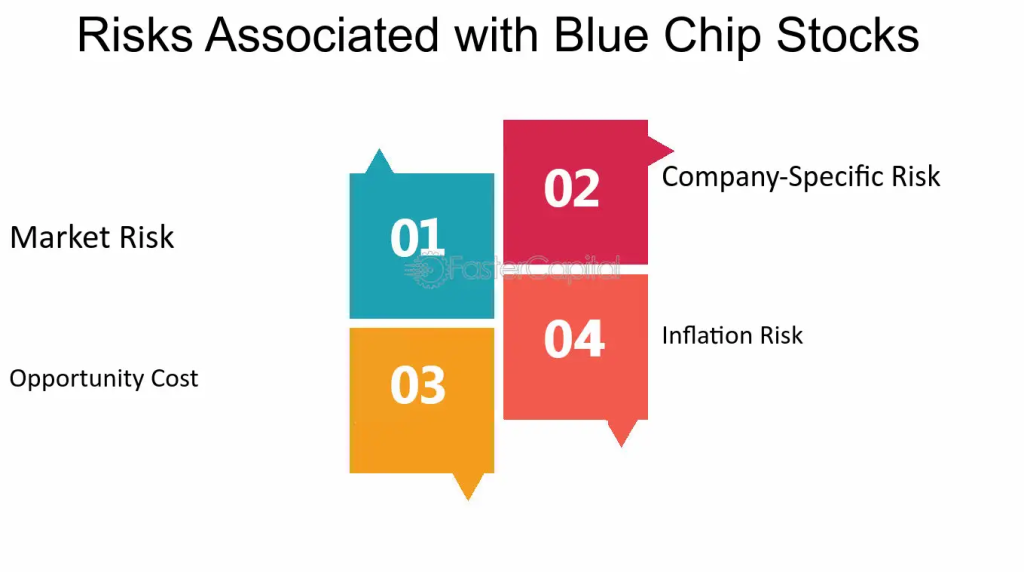
ფიგურა: Risks Associated with Blue Chip Stocks
აღწერა:
This image outlines the primary risks that come with investing in blue-chip stocks. The four main risks highlighted are: Market Risk, Company-Specific Risk, Opportunity Costდა Inflation Risk. Each of these risks can affect the performance of blue-chip stocks, despite their reputation for being stable and established investments.
ძირითადი დასკვნები:
- Market Risk: Blue-chip stocks are not immune to broader market downturns, which can lead to significant losses.
- Company-Specific Risk: Even well-established companies can face internal challenges like management changes or declining sales.
- Opportunity Cost: By investing in blue-chip stocks, investors might miss out on potentially higher returns from riskier or emerging investments.
- Inflation Risk: Blue-chip stocks may not always keep pace with inflation, which can erode real returns over time.
ინფორმაციის გამოყენება:
Investors should be aware that blue-chip stocks, while typically more stable, still carry various risks that can impact returns. Understanding these risks can help investors make informed decisions, particularly when it comes to პორტფელის დივერსიფიკაცია და რისკების მართვა. Proper analysis and a balanced approach can help mitigate these risks while still allowing for potential long-term gains from blue-chip investments.

ფიგურა: Risks and Rewards of Penny Stocks
აღწერა:
This image outlines the main risks and rewards associated with investing in penny stocks. The key aspects include high volatility, lack of liquidity, lack of information, potential for high returnsდა დივერსიფიკაცია. While penny stocks offer potential high returns, they are also prone to significant risks, making them suitable only for investors willing to accept the associated uncertainties.
ძირითადი დასკვნები:
- High Volatility: Prices of penny stocks can fluctuate rapidly, which can lead to both large gains and losses in short periods.
- Lack of Liquidity: Penny stocks often have low trading volumes, making it harder to buy or sell shares at desired prices.
- Lack of Information: Limited financial information and analysis are available for penny stocks, making research more challenging.
- მაღალი შემოსავლის პოტენციალი: Despite the risks, penny stocks can offer significant returns, especially if the company experiences growth.
- დივერსიფიკაცია: Adding penny stocks to a portfolio can provide diversification, but the investor must balance the high risk.
ინფორმაციის გამოყენება:
Investors interested in penny stocks should carefully consider both the risks and rewards. These stocks can be part of a high-risk, high-reward strategy, but due diligence is essential to minimize losses. It is crucial to have a risk management strategy in place and not allocate a large percentage of the portfolio to such stocks, given their speculative nature.
დასკვნა
Understanding the different characteristics of stocks—such as value, growth, size, liquidity, dividends, and risk metrics—is essential for making informed investment decisions. While value and growth stocks offer different opportunities, investors must also consider other factors like dividends, EPS, and beta when evaluating stocks. For risk-tolerant investors, penny stocks may offer high returns, but they also come with increased risks due to low liquidity and regulatory issues. Diversifying across various stock types and characteristics can help balance potential rewards and risks in a portfolio.
გაკვეთილის ძირითადი ინფორმაცია:
- ღირებულების აქციები are typically undervalued companies in mature industries like energy or banking. They may offer დივიდენდები and perform better in bear markets, making them attractive to conservative investors.
- ზრდის აქციები are usually found in sectors like technology and healthcare. These companies often reinvest profits and may not offer dividends, but they present high long-term growth potential—though with more volatility.
- Stock size matters. Large-cap stocks are more stable and liquid, mid-caps offer a balance of stability and growth, and small-cap stocks carry more რისკი but may deliver higher returns if they grow successfully.
- ლიკვიდურობა refers to how easily a stock can be bought or sold. Highly liquid stocks, often from large companies, are easier to trade, while low-liquidity stocks can be harder to sell and may carry higher transaction costs.
- Financial metrics such as EPS და P/E ratio help investors understand profitability and how the market values a company. A high P/E often signals growth expectations, while a low P/E might indicate undervaluation.
- ბეტა measures a stock’s volatility compared to the market. A higher beta means more price swings and risk, while a lower beta indicates steadier performance.
დასკვნითი განცხადება
By understanding stock types, financial metrics, and risk levels—from large-cap stability to penny stock speculation—you can build a smarter investment strategy. This knowledge helps you match investments to your goals, manage risk more effectively, and grow your financial confidence in both local and global markets.