5장: 예산 및 비용 관리
수업 학습 목표:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elittellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
예산 및 비용 관리 소개
예산 책정과 지출 관리가 개인 재정의 기본 측면입니다. 이 장에서는 비상 기금 할당을 포함하여 단기 및 장기 재정 목표에 부합하는 예산을 만드는 방법을 살펴보고 소비자 결정의 역학과 더 광범위한 영향을 다룹니다. 또한 저축 대 투자의 본질, 삶의 변화에 맞게 예산을 수정하는 방법, 현금 흐름과 재정 비용을 이해하는 것의 중요성에 대해 자세히 알아봅니다.
5.1 Developing a Budget
선택할 수 있는 다양한 예산 책정 방법이 있으며 각각 고유한 장점과 단점이 있습니다. 귀하의 필요와 선호도에 가장 적합한 방법을 찾는 것이 중요합니다. 다음은 널리 사용되는 세 가지 예산 책정 방법입니다.
예산 책정에는 수입 추적, 다양한 비용에 자금 할당, 재정적 목표를 달성하기 위한 저축이 포함됩니다. 잘 만들어진 예산에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 고정 비용: 임대료나 주택담보대출, 대출금 상환, 보험 등과 같은 반복적인 비용입니다.
- 가변 비용: 식료품, 공공 서비스, 오락비 등 변동이 심한 비용.
- 저금: 비상 자금과 장기 저축 목표를 포함하여 미래에 사용하기 위해 마련된 자금입니다.
- 비상 자금: 예상치 못한 의료비나 자동차 수리비 등 예상치 못한 비용을 충당하기 위해 고안된 금융 계획의 중요한 부분입니다.
Example Scenario: Jamie earns $3,000 monthly and wants to save for a vacation while covering living expenses. A budget might allocate $1,000 to rent, $300 to groceries, $200 to utilities, $400 to loan payments, $100 to entertainment, and $600 to an emergency fund, illustrating a balanced approach to managing fixed and variable costs and prioritizing savings.
수치: 예산 방법의 유형
설명:
이미지는 다양한 선호도와 재정 상황에 맞는 다양한 예산 책정 방법을 보여줍니다. 예산의 개념을 단순화하여 더욱 접근하기 쉽게 만들고, 개인이 재정을 효과적으로 관리할 수 있도록 고안된 50/30/20 예산, 봉투 예산, 제로 기반 예산, 예산 없음 예산과 같은 방법을 설명합니다.
주요 시사점:
- 2020년 50월 30일 예산: 50%의 소득을 필요에 할당하고, 30%를 원하는 데, 20%를 저축이나 부채 상환에 할당하는 간단한 접근 방식입니다.
- 봉투 예산 편성: 특정 항목에 대한 물리적 봉투에 현금을 배분하는 방식입니다. 지출은 각 봉투에 들어 있는 현금으로 제한됩니다.
- 제로 기반 예산: 벌어들인 모든 달러에는 특정 목적이 할당되어 월말에 예산 균형이 0이 되도록 합니다.
- 예산이 없는 예산: 좋은 재정 습관을 가진 고소득자에게 적합합니다. 지출보다 더 많은 돈을 벌고 차액을 투자하는 데 초점이 맞춰져 있습니다.
정보의 응용:
다양한 예산 책정 방법은 다양한 성격 유형과 재정 상황에 맞춰 제공됩니다. 올바른 접근 방식을 이해하고 선택하면 개인이 자신의 재정을 효과적으로 관리하여 자신의 수입 내에서 생활하고 재정적 목표를 달성할 수 있도록 할 수 있습니다. 과도한 지출을 억제하거나, 자금을 효율적으로 할당하거나, 단순히 재정에 대한 더 나은 통제권을 얻으려는 경우 이러한 방법은 이러한 목표를 달성하기 위한 구조화된 방법을 제공합니다.

5.2 Making Informed Consumer Decisions
소비자의 결정은 가격, 제품 대안, 예산 제약, 잠재적인 사회적 및 환경적 영향과 같은 요소에 의해 형성됩니다.
정보에 입각한 결정을 내리는 과정:
- 연구: 제품과 대안에 대한 정보를 수집하세요.
- 예산: 구매가 예산에 얼마나 들어맞는지 고려하세요.
- 영향: 환경과 사회에 미치는 잠재적 영향을 평가합니다.
예: 가솔린 차량 대신 전기 자동차를 선택하면 초기 비용이 더 많이 들더라도 장기적으로 연료비를 절감할 수 있고, 환경적 이점이 있으며, 세금 혜택도 받을 수 있습니다.
5.3 Consumer Decision Factors
선택된 제품: 전기 자동차(EV)
구매 결정에 영향을 미치는 요소:
- 제품 가격: EV의 초기 비용은 가솔린 차량보다 높을 수 있습니다. 그러나 세금 인센티브와 낮은 운영 비용이 초기 비용을 상쇄할 수 있습니다.
- 대안의 가격: 전통적인 가솔린 차량은 일반적으로 초기 비용은 저렴하지만 시간이 지남에 따라 연료 및 유지 관리 비용이 높아집니다.
- 소비자의 예산 및 선호도: 소비자의 EV 구매 능력과 환경 친화적 옵션에 대한 선호도는 중요한 역할을 합니다. 어떤 사람들은 비용보다 환경 친화성을 우선시하는 반면, 다른 사람들은 장기적인 절감에 집중할 수 있습니다.
- 환경, 사회 및 경제에 미치는 영향: EV를 구매하면 배출량이 감소하여 환경에 미치는 영향이 줄어듭니다. 이러한 선택은 또한 재생 에너지 부문의 성장을 지원하여 지속 가능성을 향한 사회적, 경제적 변화에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
정보에 입각한 소비자 결정을 내리는 프로세스:
- 연구: 다양한 모델에 대한 기능, 비용, 리뷰 등 정보를 수집하세요.
- 비교: 비용, 성능, 요구 사항 적합성 측면에서 전기 자동차를 기존 차량과 비교해보세요.
- 예산 평가: 개인 재정을 평가하여 지불 가능 여부를 파악하고 장기적인 저축을 고려하세요.
- 환경 영향: 전기 자동차의 생태적 이점을 생각해 보세요.
- 최종 결정: 위의 요소들을 균형 있게 고려하여 선택하세요.
EV 구매의 효과:
- 긍정적 측면: 탄소발자국이 줄어들고, 운영 비용이 낮아지며, 재생 에너지 산업이 촉진됩니다.
- 부정적 측면: 초기 비용이 높아 예산에 부담을 줄 수 있음; EV 배터리 생산과 폐기는 환경에 영향을 미침.
5.4 Managing Expenses and Budgeting
경비:
- Fixed Expenses: Rent, mortgage, car payments – costs that remain constant each month.
- 가변 비용: Groceries, utilities, entertainment – costs that can fluctuate.
- Irregular Expenses: Annual insurance premiums, holiday gifts – costs that occur occasionally and can disrupt a regular budget.
내 월 예산 예시:
- 고정 비용: 임대료 $1,200, 자동차 대출금 $300, 보험 $100.
- 변동 비용: 식료품 $400, 공공 서비스 비용 $150, 오락비 $100.
- 불규칙적인 비용: 구독료나 멤버십과 같은 연간 비용으로 매달 $50을 따로 마련하세요.
- 저축: 비상금과 미래 투자를 위해 매달 $500을 저축하는 것을 목표로 하세요.
- 잉여 또는 적자: 수입에서 총 지출(저축 포함)을 뺀 값을 계산하여 소비 수준에 맞게 생활하고 있는지, 아니면 지출이 너무 많은지 확인하세요.
예산 전략:
- 봉투 시스템: 매달 가변 비용에 대한 현금을 분류된 봉투에 할당합니다. 봉투에 있는 현금이 없어지면 다음 달까지 해당 범주에서 더 이상 지출할 수 없습니다.
- 예산 유지: 예산을 정기적으로 검토하고 조정하세요. 지출을 추적하고, 패턴을 인식하고, 목표를 달성하기 위해 변경하세요. 실시간 추적 및 조정을 위해 예산 앱이나 스프레드시트를 활용하세요.
비용 관리
지출을 통제하려면 필수 지출과 재량 지출을 구별하는 것이 필수적입니다. 불필요한 지출을 줄이는 전략에는 충동 구매를 파악하고, 현금 지출을 관리하기 위해 봉투 시스템을 활용하고, 지출 습관을 정기적으로 검토하는 것이 포함됩니다.
필수(필수) 비용 기본적인 생활과 일상생활에 필요한 비용입니다. 이러한 비용은 개인이나 가족이 건강하고 안전한 생활 방식을 유지하는 데 필요한 최소한의 필요를 충당합니다. 필요한 비용은 일반적으로 다음과 같습니다.
- 주택: 임대료 또는 주택담보대출금.
- 공공 서비스: 물, 전기, 가스, 그리고 때로는 원격 작업이나 교육의 필요에 따라 인터넷 서비스가 제공됩니다.
- 식량: 집에서 요리하는 데 필요한 식료품.
- 의료: 보험료, 의료비, 처방전, 진행 중인 치료비.
- 교통: 직장이나 학교로 출퇴근하는 데 드는 비용으로, 자동차 대출금, 대중교통 요금, 주유비, 필수적인 차량 유지관리 비용이 포함됩니다.
- 보험: 건강, 자동차, 주택 소유자 또는 임차인 보험을 포함한 필수 보험 정책입니다.
필수 비용의 예: Sarah는 임대료로 매달 $1,000, 공공 서비스 비용으로 $200, 식료품 비용으로 $300, 자동차 대출금과 주유비로 $250, 건강 보험 비용으로 $150을 예산으로 책정했습니다. 이러한 비용은 그녀가 안전하고 편안하게 살기 위해 협상할 수 없는 비용입니다.
임의적(비필수적) 비용 사람들이 원하지만 기본적인 생활 방식을 사는 데 필요하지 않은 것과 관련된 비용입니다. 이러한 비용은 종종 삶의 질을 향상시키지만 필요한 경우 줄이거나 없앨 수 있습니다. 임의 비용에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 오락: 영화, 콘서트, 스트리밍 서비스 또는 기타 여가 활동에 쓰이는 돈.
- 외식: 영양 섭취에 필요한 것 이상으로 레스토랑에서 식사하는 데 드는 비용.
- 취미: 공예 재료, 스포츠 장비, 도서 구입 등 취미나 여가 활동과 관련된 비용입니다.
- 여행: 휴가 및 필수적이지 않은 여행에 드는 비용.
- 사치품: 고급 전자제품, 디자이너 의류, 기본적인 필요 이상의 기타 사치품.
재량적 지출의 예: 알렉스는 외식을 좋아하고, 레스토랑에서 한 달에 평균 $300을 지출하고, 한 달에 $50이 드는 여러 스트리밍 서비스를 구독하고, 취미와 오락에 $200을 할당합니다. 이것들은 그의 삶을 향상시키지만, 그의 재정적 목표나 상황에 따라 조정할 수 있습니다.
필수 및 재량 비용 관리: 효과적인 재정 계획은 먼저 예산 내에서 필요한 비용을 충당하는 것을 포함합니다. 남은 소득은 재량 지출, 저축 및 투자에 할당할 수 있습니다. 재량 지출보다 저축과 부채 상환을 우선시하는 것은 장기적인 재정 건강에 중요합니다. 개인은 소득이나 재정 목표의 변화에 대응하여 예산을 조정하기 위해 지출 습관, 특히 재량 지출을 주기적으로 검토해야 할 수도 있습니다.
필수 지출과 재량 지출을 구별하고 전반적인 재정 계획에 미치는 영향을 이해함으로써 개인은 우선순위와 재정 목표에 맞춰 정보에 입각한 결정을 내릴 수 있으며, 이를 통해 안정성과 목표 달성을 보장할 수 있습니다.
5.5 Creating and Revising Budgets
예산은 소득, 삶의 환경, 재정 목표의 변화를 반영하기 위해 유연해야 합니다.
- 단기 저축: 긴급 상황과 예상치 못한 비용을 충당해야 합니다.
- 장기적 저축: 주택 소유나 은퇴와 같은 미래의 포부를 목표로 합니다.
예산 조정: 직장 변경이나 예상치 못한 청구서와 같은 생활 속의 사건으로 인해 재정적으로 안정을 유지하기 위해 예산을 조정해야 할 때가 있습니다.
Example: If Alex experiences a job loss, the budget must be revised to reduce variable expenses and prioritize essential costs and minimal savings until income stabilizes.
- 저축은 일반적으로 위험이 적고 쉽게 접근할 수 있는 미래 사용을 위해 돈을 따로 모으는 것입니다. 저축 vs. 투자 계정.
- 투자는 시간이 지남에 따라 더 높은 수익률이 가능한 자산을 매수하는 것이지만, 더 큰 위험을 수반합니다.
이러한 차이점을 이해하면 재정 전략을 목표에 맞게 조정하고, 저축의 안전성과 투자의 성장 잠재력 간의 균형을 맞추는 데 도움이 됩니다.
5.6 Designing a Personal Budget
개인 예산은 개인의 고유한 재정 상황, 목표 및 우선순위를 반영해야 합니다. 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 목표 설정: 명확하고 달성 가능한 목표를 정의하세요.
- 소득 배분: 수입을 지출, 저축, 투자에 분배하세요.
- 모니터링 및 수정: 상황에 따라 예산을 정기적으로 검토하고 조정하세요.
5.7 Impact of External Factors:
세금, 인플레이션, 개인적 변화(예: 결혼, 자녀)는 예산 요구와 재정 계획에 상당한 영향을 미칩니다.
현실적인 개인 또는 가족 예산 준비:
- 소득원 파악: 모든 소득원으로부터 총 월수입을 계산합니다.
- 비용 목록 및 분류: 비용을 고정, 변동, 불규칙 범주로 구분합니다.
- 저축을 위한 자금 할당: 소득의 일부를 저축과 비상금을 위해 따로 마련하는 것을 우선시하세요.
- 잉여 또는 적자에 대한 조정: 지출이 수입을 초과하면 줄일 부분을 찾으세요. 잉여금이 있으면 여분의 자금을 저축이나 부채 상환에 할당하세요.
- 모니터링 및 검토: 정기적으로 예산과 실제 지출을 비교 검토하고, 계획에 맞게 필요한 대로 조정하세요.
5.8 Interest and Fees in Money Management
지출, 차용, 저축과 관련된 이자율과 수수료를 이해하는 것은 매우 중요합니다. 이자는 저축에 누적되어 부를 늘리거나 부채에 누적되어 빌린 자금의 비용을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
이자 계산:
예를 들어, 연 이자율이 1.5%인 저축 계좌는 1년 동안 잔액 $10,000에 대해 $150의 이자가 발생하지만, 연 이자율이 20%인 신용카드는 같은 기간 동안 잔액 $1,000을 갚지 않고 사용할 경우 $200의 이자가 발생합니다.
예산 책정과 지출 관리의 원칙을 숙지함으로써 개인은 자신감을 가지고 재정 여정을 헤쳐나가며 안정성, 성장, 성취를 촉진하는 정보에 입각한 결정을 내릴 수 있습니다.
세금 변경
영향: 소득세, 재산세 또는 매출세 등 세금 인상은 개인이나 가구의 가처분 소득을 직접적으로 감소시킵니다. 예를 들어, 소득세가 상승하면 세금 공제 후 순이익이 감소하여 지출과 저축을 위한 돈이 줄어듭니다. 반대로 세금이 감소하면 가처분 소득이 증가하여 예산에 다른 지출이나 저축을 위한 여유가 더 많아집니다.
예: 세법의 변화로 인해 알렉스의 실질 소득세율이 증가한다고 가정합니다. 그 결과, 그의 월 실수령액이 감소합니다. 알렉스는 조정하기 위해 재량 지출을 줄이거나 저축 기여금을 재평가하여 재정적 안정을 유지해야 할 수도 있습니다.
인플레이션
영향: 인플레이션은 시간이 지남에 따라 구매력을 침식하여 같은 금액으로 더 적은 상품과 서비스를 살 수 있음을 의미합니다. 음식, 주택, 의료와 같은 필수품의 가격이 오르면 개인은 기존 예산으로는 더 이상 필요를 충족할 수 없다는 것을 알게 될 수 있습니다. 이는 소득을 늘리거나 생활비 상승에 맞춰 지출 습관을 조정하는 방법을 찾아야 합니다.
예: 연간 인플레이션율이 3%이고 에밀리의 급여가 증가하지 않으면 그녀의 생활비는 증가하여 실질적으로 그녀의 가처분 소득이 감소합니다. 에밀리는 생활비 증가를 관리하기 위해 불필요한 지출을 줄이거나 추가 소득원을 찾거나 지출을 다르게 우선시해야 할 수도 있습니다.
개인적 상황영향: 결혼, 이혼, 자녀 출산, 실직, 상속과 같은 삶의 사건은 개인의 재정 상황과 예산에 상당한 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 변화는 재정적 안정성을 증가시킬 수 있는 반면, 도전적인 사건은 예산을 삭감하거나 새로운 수요를 충족하기 위해 자금을 재분배해야 할 수 있습니다.
예시 1: 조던과 테일러는 아이를 낳은 후, 현재 아파트가 너무 작다는 것을 깨달았습니다. 더 큰 집으로 이사하면서 임대료가 올라가고, 이 필수적인 비용을 충당하기 위해 예산을 조정해야 했습니다.
예시 2: Sarah는 상당한 급여 인상과 함께 승진을 합니다. 그녀는 은퇴 저축 기여금을 늘리고 자녀들을 위한 대학 기금을 마련하기로 결정하여 재정 상황이 개선되었음을 보여줍니다.
변화에 적응하다세금, 인플레이션 및 개인 상황의 변화에 적응하기 위해 개인은 다음을 수행해야 할 수도 있습니다.
- 정기적으로 예산을 검토하고 조정하세요: 수입과 지출의 변화에 맞춰 예산을 유연하게 유지하세요.
- 지출 우선 순위 정하기: 특히 재정적으로 어려운 시기에는 원하는 것보다 필요한 것에 집중하세요.
- 소득을 늘릴 수 있는 기회를 찾으세요: 부업을 모색하고, 급여 인상을 요청하고, 급여가 더 나은 직업을 위해 새로운 기술을 습득하세요.
- 비상 자금 구축: 예상치 못한 변화나 어려움을 관리하는 데 도움이 되는 재정적 여유를 제공합니다.
효과적인 예산 책정과 지출 관리가 재정적 안정을 이루고 장기적 목표를 달성하는 데 중요합니다. 이러한 원칙을 이해하고 적용하면 개인이 정보에 입각한 소비자 결정을 내리고 건강한 재정적 라이프스타일을 유지할 수 있습니다.
주요 시사점:
- 모기지 또는 임대료: 주거비를 위한 자금을 할당합니다.
- 저축과 투자: 미래의 재정적 목표와 부의 축적을 위해 돈을 따로 저축해 두십시오.
- 부채 또는 학자금 대출: 부채 상환 및 학자금 대출 계획.
- 운송: 통근, 차량 유지 관리, 기타 교통 관련 비용에 대한 예산을 책정합니다.
- 기타 비용: 예상치 못한 비용이나 다양한 비용에 대비해 자금을 할당하세요.
- 구독: 월간 또는 연간 구독 서비스에 대한 예산을 세우세요.
정보의 응용:
효과적인 재정 계획을 위해서는 예산 영역을 명확하게 분류하는 것이 중요합니다. 비용과 저축을 특정 범주로 분류함으로써 개인은 자신의 재정 습관을 더 잘 이해하고 개선할 영역을 식별하며 정보에 입각한 결정을 내릴 수 있습니다. 이 분류는 포괄적인 예산을 수립하려는 모든 사람에게 기본 가이드 역할을 하며 모든 필수 영역이 포함되고 재정적 목표가 충족되도록 보장합니다.
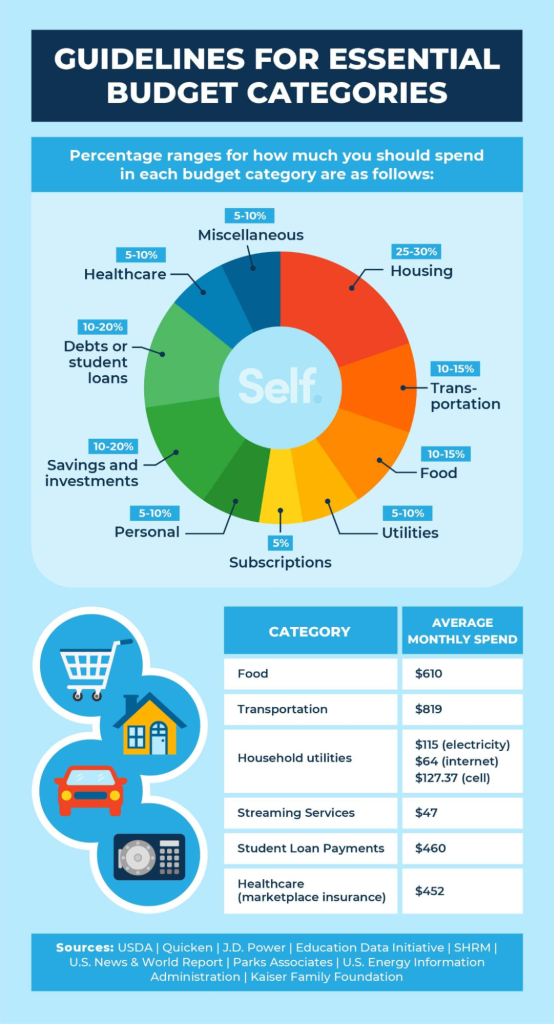
Figure: Essential Budget Categories for Financial Planning
설명:
The image from Self.inc outlines ten essential budget categories that are critical for effective financial planning. These categories help individuals understand their spending patterns and manage their finances by allocating funds appropriately to areas such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare.
주요 시사점:
- 주택은 일반적으로 보험 및 세금과 같은 관련 비용을 포함하여 약 30%의 소득을 소비해야 합니다.
- 식비는 소득의 10%에서 16%까지 다양하며 가구 규모와 식단 선택에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
- 차량 대금과 대중교통을 포함한 교통비는 이상적으로 월 소득의 15%를 초과하지 않아야 합니다.
- 에너지 절약 조치와 서비스 요금제 비교를 통해 공과금을 소득의 5%~10% 범위 내에서 유지할 수 있습니다.
- 의료비는 정기적인 의료비와 예상하지 못한 의료비를 모두 고려하여 5%에서 10% 사이로 예산을 책정하는 것이 좋습니다.
정보의 응용:
By categorizing expenses, individuals can create a structured budget that aligns with their income and financial goals. This approach allows for a clear understanding of where money is being spent and where adjustments can be made to save more or pay off debt. It’s particularly useful for those looking to gain control over their finances and work towards financial stability and independence.
5.9 Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Price and Product Comparison
When making a purchase, price is often one of the primary deciding factors. Consumers frequently compare prices for similar products before settling on a purchase. For example, when buying a new smartphone, a consumer may compare prices across various retailers or online platforms to ensure they’re getting the best deal.
- 장점:
- Helps the consumer save money by identifying the most affordable option.
- Encourages consumers to seek the best value for their purchase.
- Helps the consumer save money by identifying the most affordable option.
- 단점:
- Price comparisons can be time-consuming, especially when there are many options available.
- Focusing too heavily on price may result in overlooking product quality and features.
- Price comparisons can be time-consuming, especially when there are many options available.
Brand and Reputation
Some consumers may have a preference for certain brands due to reputation, previous experiences, or trust in the brand’s quality. For example, someone may opt for an Apple iPhone over other phones due to its known brand reliability, even if it costs more than other smartphones.
- 장점:
- Offers peace of mind knowing that the product is from a trusted brand.
- Ensures a certain level of quality and performance based on brand reputation.
- Offers peace of mind knowing that the product is from a trusted brand.
- 단점:
- Higher brand premiums may result in paying more than necessary for a product that may not offer significant added value.
- Brand loyalty may limit exploration of more affordable alternatives.
- Higher brand premiums may result in paying more than necessary for a product that may not offer significant added value.
Functionality and Features
The functionality and features of a product greatly influence consumer decisions. For example, when purchasing a laptop, a consumer may prioritize factors like screen size, battery life, or processing speed, depending on their needs (e.g., work or entertainment).
- 장점:
- Allows consumers to select products tailored to their needs.
- Increases satisfaction with the purchase when the product meets specific requirements.
- Allows consumers to select products tailored to their needs.
- 단점:
- A focus on functionality may result in higher costs if consumers opt for more feature-packed versions.
- Sometimes, additional features may be unnecessary for the consumer’s intended use, leading to overpaying.
- A focus on functionality may result in higher costs if consumers opt for more feature-packed versions.
Process for Making Informed Consumer Decisions
Step 1: Identifying Needs vs. Wants
The first step in making an informed purchase is distinguishing between needs and wants. A need could be a basic necessity, such as a phone that can make calls and send messages, while a 원하다 could be a high-end model with additional features that aren’t necessary.
- 장점:
- Helps prevent unnecessary purchases and ensures that essential needs are met.
- Promotes smarter financial decisions by focusing on what’s truly needed.
- Helps prevent unnecessary purchases and ensures that essential needs are met.
- 단점:
- The line between needs and wants can sometimes be subjective, leading to confusion or indecision.
- Restricting spending on wants may reduce immediate satisfaction.
- The line between needs and wants can sometimes be subjective, leading to confusion or indecision.
Step 2: Researching Options
Once needs are determined, consumers should research their options. This involves reading customer reviews, checking product comparisons, and looking into expert opinions.
- 장점:
- Ensures that consumers make an informed and educated decision.
- Provides insight into potential product flaws or advantages that may not be obvious at first glance.
- Ensures that consumers make an informed and educated decision.
- 단점:
- Researching multiple products can be time-consuming and may cause decision fatigue.
- The abundance of information available can sometimes overwhelm the consumer, making it harder to make a decision.
- Researching multiple products can be time-consuming and may cause decision fatigue.
Step 3: Evaluating Price vs. Value
Before making a final decision, consumers should assess whether the price aligns with the value they are getting. This means considering factors like product quality, longevity, and after-sales service in addition to the initial price tag.
- 장점:
- Helps consumers balance cost with the quality and benefits of the product, ensuring better value for money.
- Encourages more thoughtful and deliberate purchasing, reducing impulse buying.
- Helps consumers balance cost with the quality and benefits of the product, ensuring better value for money.
- 단점:
- Some products might appear overpriced based on initial cost but offer long-term value through durability or lower maintenance.
- Finding the right balance between price and value can be subjective and vary from person to person.
- Some products might appear overpriced based on initial cost but offer long-term value through durability or lower maintenance.
Positive and Negative Effects of Consumer Decisions
Example: Purchasing an Electric Vehicle (EV)
- Positive Environmental Impact:
- EVs contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, helping reduce pollution and combating climate change.
- EVs contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, helping reduce pollution and combating climate change.
- Positive Societal Impact:
- Purchasing an EV supports the growth of the green energy sector, promoting sustainable transportation options and supporting eco-friendly innovations.
- Purchasing an EV supports the growth of the green energy sector, promoting sustainable transportation options and supporting eco-friendly innovations.
- Negative Environmental Impact:
- The production of EV batteries requires mining materials like lithium, which can lead to environmental degradation and significant resource extraction.
- The production of EV batteries requires mining materials like lithium, which can lead to environmental degradation and significant resource extraction.
- Negative Economic Impact:
- EVs often come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional vehicles, which may be a financial burden for some consumers, especially those on tighter budgets.
- EVs often come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional vehicles, which may be a financial burden for some consumers, especially those on tighter budgets.
- 장점:
- Encourages sustainable choices and supports global initiatives for environmental protection.
- Helps consumers align their financial decisions with their personal values, like environmental consciousness.
- Encourages sustainable choices and supports global initiatives for environmental protection.
- 단점:
- The upfront cost may not be accessible for all consumers, which can limit adoption.
- The environmental impact of battery production is a downside that many consumers may overlook.
- The upfront cost may not be accessible for all consumers, which can limit adoption.
Financial Responsibility and Budget Planning
Preparing for Life Events and Changing Budgets
Unexpected life changes, such as job loss, having a child, or a medical emergency, can significantly impact an individual’s budget. For example, after a job loss, a consumer may need to adjust their budget by cutting back on discretionary spending and prioritizing essential expenses.
- 장점:
- Having a flexible budget ensures financial stability during uncertain times.
- Helps individuals stay on track with financial goals even when life events cause disruptions.
- Having a flexible budget ensures financial stability during uncertain times.
- 단점:
- Regularly revising budgets due to unexpected events can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
- It may require sacrifices in other areas, such as entertainment or personal spending.
- Regularly revising budgets due to unexpected events can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
Factors Affecting Financial Goals
External factors such as location, culture, 그리고 peer influences can significantly impact one’s financial goals. For example, someone living in a high-cost area may need a larger budget for housing and transportation compared to someone living in a lower-cost area.
- 장점:
- Understanding these external influences helps individuals recognize patterns in their financial behavior and spending.
- Encourages self-awareness, enabling consumers to make more informed financial decisions.
- Understanding these external influences helps individuals recognize patterns in their financial behavior and spending.
- 단점:
- Overcoming the influence of peer pressure or cultural expectations can be challenging.
- These external factors may lead to unsustainable financial choices if not carefully managed.
- Overcoming the influence of peer pressure or cultural expectations can be challenging.
Techniques to Decrease Expenses
Comparison Shopping
Comparison shopping helps consumers find the best prices for products by comparing different stores and online retailers. For example, when buying a laptop, a consumer might use comparison websites to see if the item is cheaper elsewhere.
- 장점:
- Can lead to substantial savings by identifying the best prices.
- Provides a broader view of available options, ensuring that the consumer gets the best deal.
- Can lead to substantial savings by identifying the best prices.
- 단점:
- Time-consuming, especially when comparing many different options.
- The lowest price may not always correspond with the best quality or service.
- Time-consuming, especially when comparing many different options.
Negotiating Prices
Negotiating the price of large purchases (e.g., cars, furniture) or even monthly bills (e.g., cable, insurance) can lead to significant savings. For instance, a consumer might negotiate a lower rate on their cable bill by threatening to cancel the service.
- 장점:
- Provides an opportunity to lower the overall cost of big-ticket items or services.
- Can build confidence in consumers when dealing with sales representatives.
- Provides an opportunity to lower the overall cost of big-ticket items or services.
- 단점:
- Not all merchants are open to negotiation, and it may feel uncomfortable for some consumers.
- It can be difficult to know when negotiation is appropriate, and sometimes it may not be effective.
- Not all merchants are open to negotiation, and it may feel uncomfortable for some consumers.
Using Technology for Financial Management
Financial Management Tools
There are various digital tools and apps that help track and manage spending, such as Mint, YNAB, 그리고 mobile banking apps. These tools can automatically categorize expenses, track income, and help users stick to their budget.
- 장점:
- Real-time tracking and budgeting make it easier to stay on top of finances.
- Automates savings and bill payments, making it easier for consumers to manage their money.
- Real-time tracking and budgeting make it easier to stay on top of finances.
- 단점:
- Some apps or tools may require subscriptions or fees, which may eat into savings.
- Technical issues or security concerns with apps could compromise financial data
Conclusion: Mastering Budgeting and Expense Management
Budgeting and managing expenses are the foundations of personal financial success. Throughout this chapter, we explored how creating and maintaining a thoughtful budget empowers individuals to take control of their money, plan for both expected and unexpected life events, and align their spending habits with their long-term goals. Whether choosing a structured method like the 50/30/20 rule, tracking expenses through modern apps, or adapting to life’s inevitable changes, the tools and strategies discussed offer a path toward financial stability and growth.
Effective budgeting is not just about restriction; it’s about making intentional choices that reflect your values and aspirations. Understanding the difference between needs and wants, making informed consumer decisions, adjusting to economic shifts like inflation or tax changes, and regularly revisiting your budget ensures that your financial plan remains a living, flexible guide.
By practicing disciplined budgeting, making mindful purchasing decisions, and proactively managing necessary and discretionary expenses, individuals can not only meet their financial obligations but also build security, achieve personal goals, and enjoy greater peace of mind. Ultimately, mastering budgeting and expense management is not just a financial skill—it’s a key to building a life of opportunity, resilience, and freedom.
주요 수업 정보:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elittellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.