Local: analyzing European companies
수업 학습 목표:
- Learn about the income statement under IFRS. You will understand how revenues, 경비, 그리고 net income are reported, along with the inclusion of other comprehensive income (OCI). This helps investors assess a company’s profitability and financial performance.
- Understand the balance sheet under IFRS. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, 그리고 형평성, offering insights into the company’s financial position. Learn about the distinctions between current and non-current items and how they reflect a company’s liquidity and solvency.
- Explore the cash flow statement under IFRS. The cash flow statement outlines how cash is generated and used across operating, investing, 그리고 financing activities. You will learn how this statement helps assess a company’s liquidity and its ability to generate cash to fund operations and investments.
- Gain insights into the overall structure and application of IFRS in European financial reporting. Understanding IFRS helps ensure transparency and comparability, making it easier to analyze financial statements and make informed investment decisions across borders.
소개
Understanding the core financial concepts is essential for any investor. Financial statements provide critical insights into a company’s financial health and performance, helping investors evaluate profitability, liquidity, and growth potential. This section will introduce the fundamental financial statements—손익계산서, 대차대조표, 그리고 cash flow statement—and explain how to analyze these documents. We will also discuss key financial data points that investors use to assess a company’s performance.
22.1 Financial Statements
When analyzing European companies, it’s essential to understand that their financial statements are typically prepared according to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), a global accounting framework that ensures transparency and comparability across borders. In Europe, IFRS is mandatory for all publicly listed companies, providing investors with consistent and clear financial information. This section introduces how financial statements in Europe adhere to IFRS, ensuring high-quality reporting.
IFRS and Income Statement
Under IFRS, the 손익계산서 (also called the statement of comprehensive income) follows a structured approach, similar to financial statements globally, but with some unique European nuances. The income statement provides detailed insight into a company’s revenues, costs, and overall profitability.
- Revenue Recognition: Under IFRS, revenue is recognized when control of a product or service is transferred to the customer. European companies must adhere to these rules, ensuring that revenues are reported accurately based on performance obligations, not just when payments are received.
- 운영 비용: Expenses are classified by either their nature (e.g., wages, materials) or their function (e.g., cost of sales, administrative expenses). This flexibility allows European companies to present their income statements in a way that best reflects their operational structure.
- Other Comprehensive Income: IFRS emphasizes the importance of other comprehensive income (OCI), which includes gains or losses not reflected in the net income, such as foreign exchange differences or revaluation of financial instruments. This is particularly relevant for European companies operating in multiple currencies.
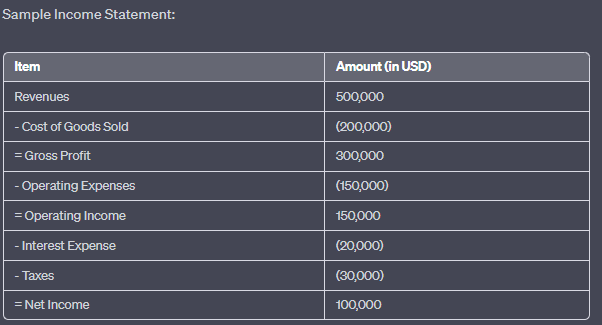
수치: 샘플 손익계산서
설명:
The image presents a sample income statement, breaking down the financial performance of a company over a specific period. It starts with the total revenues and subtracts various expenses to arrive at the net income. The statement showcases the following items:
수익: $500,000
매출원가: $(200,000)
매출 총이익: $300,000
운영 비용: $(450,000)
영업수익: $150,000
이자비용: $(20,000)
세금: $(30,000)
순이익: $100,000
주요 시사점:
- 수익: 비용을 들이기 전 회사가 벌어들인 총 금액.
- 매출원가(COGS): 판매된 상품의 생산에 기인하는 직접 비용.
- 매출 총이익: 총 수익에서 매출원가(COGS)를 공제한 후 회사가 얻는 이익.
- 운영 비용: 기업의 일상 운영과 관련된 비용입니다.
- 영업이익: 사업 운영으로 인한 이익(이자 및 세금 공제 전).
- 이자 비용: 자금을 빌리는 데 드는 비용.
- 구실: 회사의 과세소득을 기준으로 정부에 지불하는 금액.
- 당기순이익: 수익에서 모든 비용을 공제한 후 회사의 총 이익.
정보의 응용:
손익계산서는 투자자와 이해관계자에게 특정 기간 동안 기업의 수익성에 대한 통찰력을 제공하는 기본적인 재무 문서입니다. 손익계산서를 분석하면 기업의 매출 흐름, 비용 구조, 그리고 전반적인 재무 건전성을 파악할 수 있습니다. 이러한 데이터는 정보에 기반한 투자 결정을 내리고 기업의 운영 효율성을 평가하는 데 매우 중요합니다.
22.2 IFRS and Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
그만큼 대차대조표, known under IFRS as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. IFRS requires companies to clearly differentiate between current and non-current items to offer a transparent view of a company’s financial health.
- Asset Classification: European companies report assets as either current or non-current. Current assets include items like cash, receivables, and inventory, while non-current assets encompass long-term investments such as property, plant, and equipment (PPE), as well as intangible assets like goodwill.
- 부채: Under IFRS, liabilities are also divided into 현재의 (due within a year) and non-current. European companies must report their obligations, including debt, leases, and pensions, in this format, providing clear insights into their short-term and long-term obligations.
- Shareholders’ Equity: The shareholders’ equity section under IFRS is structured to show both contributed capital (from shareholders) and retained earnings (profits that have been reinvested into the business). European firms must also disclose other reserves, including revaluation reserves and foreign currency translation adjustments.
- Asset Classification: European companies report assets as either current or non-current. Current assets include items like cash, receivables, and inventory, while non-current assets encompass long-term investments such as property, plant, and equipment (PPE), as well as intangible assets like goodwill.
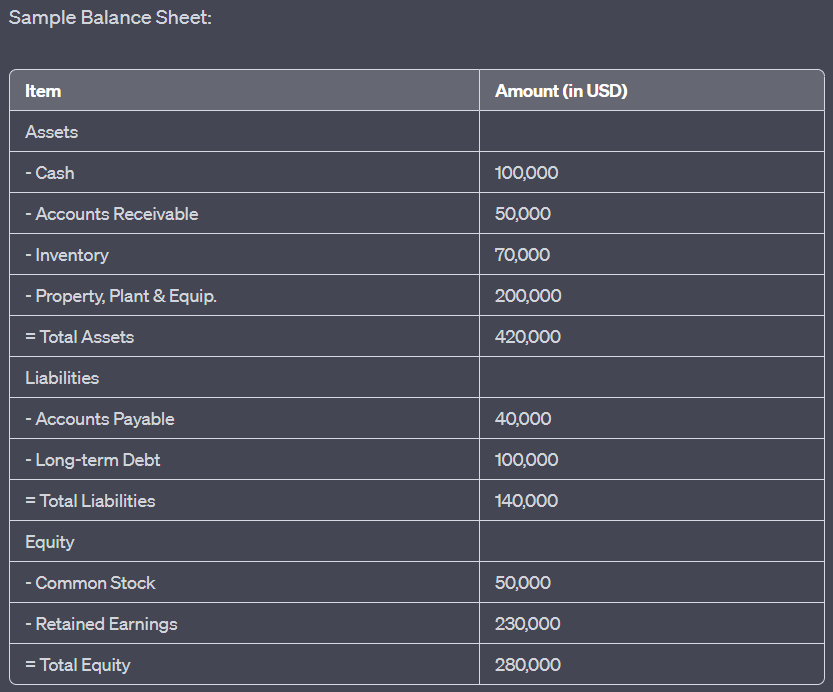
수치: Sample Balance Sheet
설명:
The image displays a sample balance sheet, which provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It categorizes the company’s resources (assets) and the claims against those resources (liabilities and equity). The balance sheet showcases the following items:
- 자산: 현금($400,000), 매출채권($50,000), 재고($70,000), 부동산, 플랜트 및 장비($200,000)를 포함하여 총 $420,000입니다.
- 부채: 총 $140,000이며, 여기에는 미지급금($40,000)과 장기 부채($400,000)가 포함됩니다.
- 형평성: 보통주($50,000)와 이익잉여금($230,000)을 합해 총 $280,000입니다.
주요 시사점:
- 자산: 회사가 소유한 경제적 가치가 있는 자원.
- 부채: 회사가 외부 기관에 지고 있는 의무.
- 형평성: 주주가 투자한 자금과 누적 이익을 포함하여 회사의 소유권 지분을 나타냅니다.
- The fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
\(\textbf{회계 방정식:}\)
\[ \displaystyle \text{자산} = \text{부채} + \text{자본} \]
\(\textbf{범례:}\)
\(\text{자산}\) = 총 자산
\(\text{부채}\) = 총 부채
\(\text{자본}\) = 총 자본
정보의 응용:
A balance sheet is a foundational financial statement that offers insights into a company’s financial health. By analyzing the balance sheet, stakeholders can assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. This information is vital for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions related to the company’s financial position
22.3 IFRS and Cash Flow Statement
그만큼 cash flow statement under IFRS follows a similar structure to other global standards but places particular emphasis on transparency in how cash is generated and used by the company. European companies use this statement to report cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities.
- 운영 활동: IFRS allows for flexibility in reporting cash flows from operating activities, either through the direct method (showing cash receipts and payments) or the indirect method (starting with net income and adjusting for non-cash items). Most European companies opt for the indirect method.
- Investing and Financing Activities: Cash flows related to investments in assets or securities and activities such as issuing shares or repaying debt are reported here. European companies must clearly distinguish these transactions to show how they are funding their growth and managing their financial obligations.
- Foreign Exchange Impacts: Given that many European companies operate across multiple countries and currencies, IFRS requires the inclusion of cash flow impacts due to changes in foreign exchange rates, providing investors with a clearer understanding of how currency movements affect a company’s cash position.
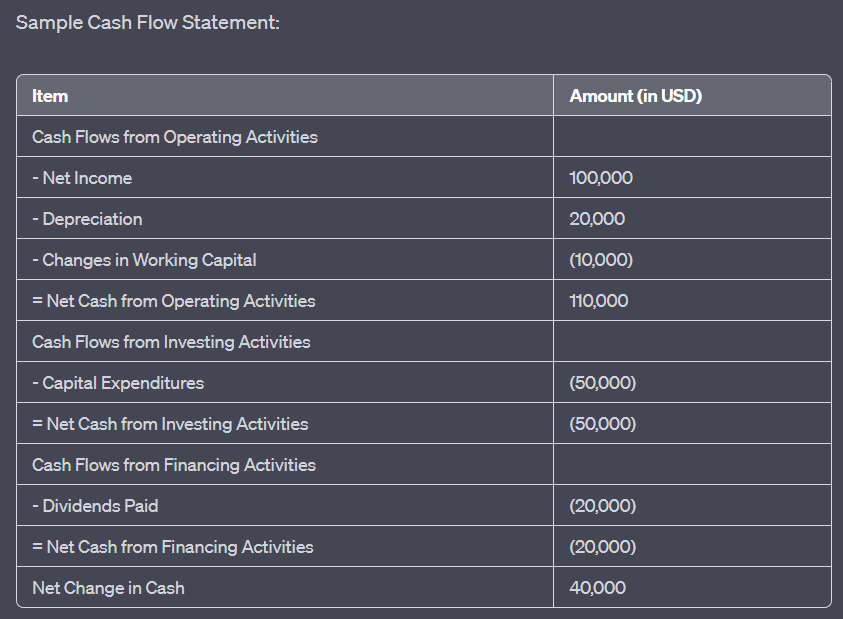
수치: Sample Cash Flow Statement
설명:
The image illustrates a sample cash flow statement, which provides a detailed account of the cash inflows and outflows for a company over a specific period. The statement is segmented into three main categories: Operating Activities, Investing Activities, and Financing Activities. The key items include:
영업 활동으로 인한 현금 흐름: 순수익($100,000), 감가상각비($20,000), 유동자산 변동(-$10,000)으로 인해 영업 활동으로 인한 순 현금은 $110,000입니다.
투자 활동으로 인한 현금 흐름: 자본 지출(-$50,000)로 인해 투자 활동으로부터 순 현금이 -$50,000이 됩니다.
재무 활동으로 인한 현금 흐름: 지급된 배당금(-$20,000)으로 인해 재무 활동으로 인한 순 현금은 -$20,000입니다.
현금의 전체 순변화는 $40,000입니다.
주요 시사점:
- 운영 활동: 핵심 사업 운영에서 창출되거나 사용된 현금을 반영합니다.
- 투자 활동: 자산 투자에 사용된 현금이나 자산 매각으로 인해 발생한 현금을 나타냅니다.
- 재무 활동: 대출자, 주주 등 외부 자금 조달원으로부터의 현금 흐름을 보여줍니다.
- 현금 순변화는 기간 동안 회사의 현금 보유액의 전반적인 증가 또는 감소를 보여줍니다.
정보의 응용:
The cash flow statement is an essential financial tool that offers insights into a company’s liquidity and its ability to generate and use cash effectively. By analyzing the cash flow statement, stakeholders can understand how a company manages its cash resources, which is crucial for assessing its financial health and making informed investment decisions.
결론
In Europe, financial statements are prepared according to IFRS, ensuring a high level of consistency, transparency, and comparability across countries and industries. The 손익계산서, 대차대조표, 그리고 cash flow statement under IFRS provide investors with the detailed information needed to assess the financial health of European companies. IFRS’s global standards ensure that European companies’ financial reports meet international expectations, making it easier for investors to analyze and compare firms operating in different regions.
주요 수업 정보:
- The income statement shows a company’s profitability. The income statement provides a breakdown of a company’s revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, 그리고 net income. By analyzing this statement, investors can evaluate how efficiently a company is generating profits and managing costs. Revenue recognition under IFRS ensures accurate reporting based on performance obligations.
- The balance sheet offers a snapshot of a company’s financial position. It categorizes a company’s assets, liabilities, 그리고 형평성. By examining these elements, investors can assess a company’s liquidity (ability to meet short-term obligations), solvency (ability to meet long-term obligations), and financial health. The fundamental accounting equation ~의 assets = liabilities + equity is key to understanding this statement.
- The cash flow statement tracks how cash is used. The statement divides cash flows into operating, investing, 그리고 financing activities. By analyzing this statement, investors can understand how the company generates cash from its operations, how it funds investments, and how it manages external financing. Positive cash flow from operating activities signals a strong cash position.
마무리 진술:
Financial statements under IFRS provide essential insights into a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing the 손익계산서, 대차대조표, 그리고 cash flow statement, investors can make well-informed decisions based on transparency, consistency, and detailed reporting, helping them assess the company’s profitability, liquidity, and long-term sustainability.

