지역(유럽 특정) 콘텐츠: 유럽의 REITs
수업 학습 목표:
- Understand what REITs are and how they allow individuals to invest in real estate without owning property, especially through stock exchanges like Euronext Paris and London Stock Exchange.
- Learn about REIT regulations in Europe, including country-specific rules like required income distribution in France and the U.K., which make REITs tax-efficient investment options.
- Distinguish between public and private REITs, understanding their accessibility, liquidity, and risk levels, and how they cater to different types of investors.
- Compare Equity REITs and Mortgage REITs, identifying how each earns income—whether through rent or interest—and what types of properties or loans they are involved in.
- Explore the benefits and drawbacks of investing in REITs in Europe, evaluating factors like income, liquidity, tax treatment, and sensitivity to market changes to determine if REITs align with your investment goals.
9.1 Introduction to REITs in Europe
ㅏ Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is a company that invests in income-producing real estate, such as residential, commercial, and industrial properties. In Europe, REITs offer investors the opportunity to invest in real estate without directly owning physical properties. REITs are traded on major European stock exchanges, such as Euronext Paris 그리고 London Stock Exchange, providing liquidity similar to stocks.
REIT Regulations in Europe
In Europe, REITs are governed by specific country regulations that define how they must operate. For example, in France, REITs are known as Sociétés d’Investissement Immobilier Cotée (SIIC), and they must distribute at least 85% of their rental income to shareholders. In the U.K., REITs are required to distribute 90% of their rental income. These regulations make REITs a tax-efficient investment option for those seeking exposure to the real estate market.
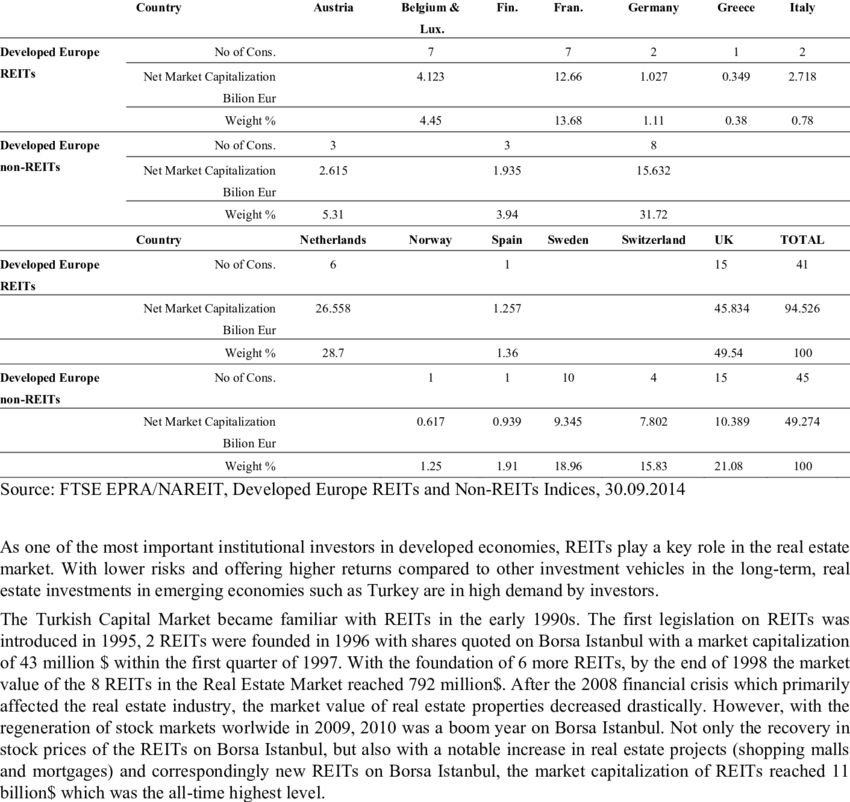
수치: Country Breakdown of REITs in Europe
설명:
This figure provides an analysis of the 부동산 투자 신탁(REIT) 그리고 non-REITs in developed European countries. It shows the number of companies in each category, their net market capitalization in billion Euros, and their percentage weight within the total market. Countries like the United Kingdom 그리고 Netherlands dominate the REIT market, while countries such as Spain 그리고 Switzerland hold significant portions of the non-REIT sector. It also highlights the growing importance of REITs in real estate investments due to their higher returns and lower risks compared to non-REIT alternatives.
주요 시사점:
- United Kingdom leads the REIT market with 15 REITs, representing 49.54% of the total REIT market capitalization in Europe.
- Netherlands follows with only 6 REITs but contributes 28.7% to the REIT market due to the large size of its real estate investments.
- Spain and Switzerland dominate the non-REIT sector, holding 18.96% 그리고 15.83% of the non-REIT market, respectively.
- REITs were introduced in the 1990s across Europe and have shown consistent growth, particularly after the 2008 financial crisis, when real estate markets began recovering.
- Countries like Austria 그리고 Greece have minimal REIT market presence, indicating room for development and investment growth.
정보의 응용:
This data is highly useful for 투자자들 as it highlights the regions and countries with the most active REIT markets, providing insights into where to focus investments for higher returns and stability. It also helps policymakers 그리고 market analysts identify potential growth areas in the REIT and non-REIT sectors. Understanding the breakdown between REITs and non-REITs can guide learners in analyzing real estate market dynamics and diversifying their portfolios effectively. Real estate developers can use this data to target lucrative markets for expansion or collaborations.
9.2 Public vs. Private REITs in Europe
공공 REIT
Public REITs in Europe are listed on major stock exchanges and are accessible to the general public. Investors can buy and sell shares in European REITs like British Land 또는 Unibail-Rodamco-Westfield on exchanges like London Stock Exchange 또는 Euronext Paris. Public REITs offer transparency, liquidity, and ease of access to real estate investments.
사모 REIT
Private REITs in Europe are not publicly traded and are typically available to accredited or institutional investors. These REITs often focus on niche markets or specific real estate sectors, such as luxury residential properties ~에 France 또는 commercial properties ~에 Germany. Private REITs can offer higher returns but come with higher risk and lower liquidity.
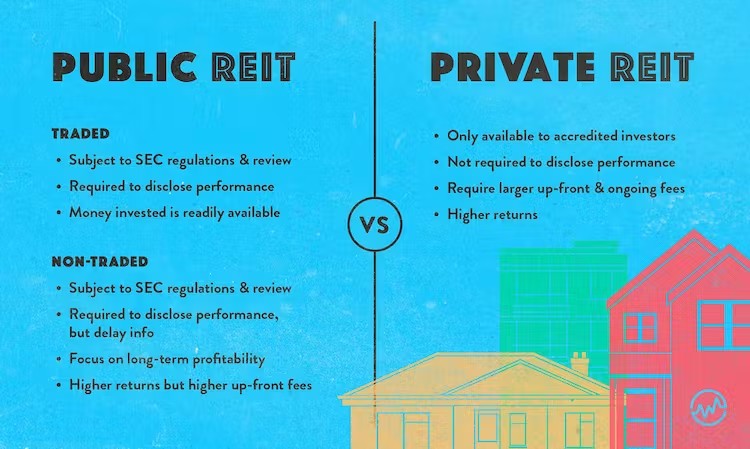
수치: The REIT Landscape: An Introduction
설명:
This infographic provides a beginner-friendly overview of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), highlighting their purpose, types, and the advantages they offer to investors.
주요 시사점:
- REIT 목적: REIT를 통해 이전에는 부유한 투자자들만 접근할 수 있었던 대규모 부동산 운영에 개인이 투자할 수 있는 방법을 알아보세요.
- REIT 종류: REIT의 종류에 대해 알아보세요. 부동산에 투자하는 자산(주식 REIT)과 모기지(모기지 REIT)에 투자합니다.
- 투자자 이점: REIT는 정기적인 수입원, 세금 혜택, 물리적 재산을 소유하지 않고도 부동산에 투자할 수 있는 방법을 제공하는 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
정보의 응용:
An understanding of REITs is invaluable for those looking to diversify their investment portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. The visual serves as an entry point, piquing interest and inviting further exploration. Financial educators, real estate experts, or investment platforms can leverage such an image to demystify REITs, laying the groundwork for deeper discussions or analyses. Whether it’s for educational webinars, articles, or presentations, the image offers a concise yet comprehensive overview of the REIT landscape.
9.3 Equity vs. Mortgage REITs in Europe
지분 REIT
Equity REITs are the most common type of REIT in Europe. These REITs own and operate income-generating properties such as shopping centers, office buildings, and apartments. In cities like Paris 그리고 Amsterdam, equity REITs invest in high-demand commercial and residential properties. Investors earn income through rent collection and property value appreciation.
모기지 REIT
Mortgage REITs (mREITs) invest in property debt rather than directly owning properties. In Europe, mortgage REITs are less common but still present in countries like Ireland 그리고 Spain, where they provide financing for property owners. These REITs generate income from the interest on mortgages and mortgage-backed securities.
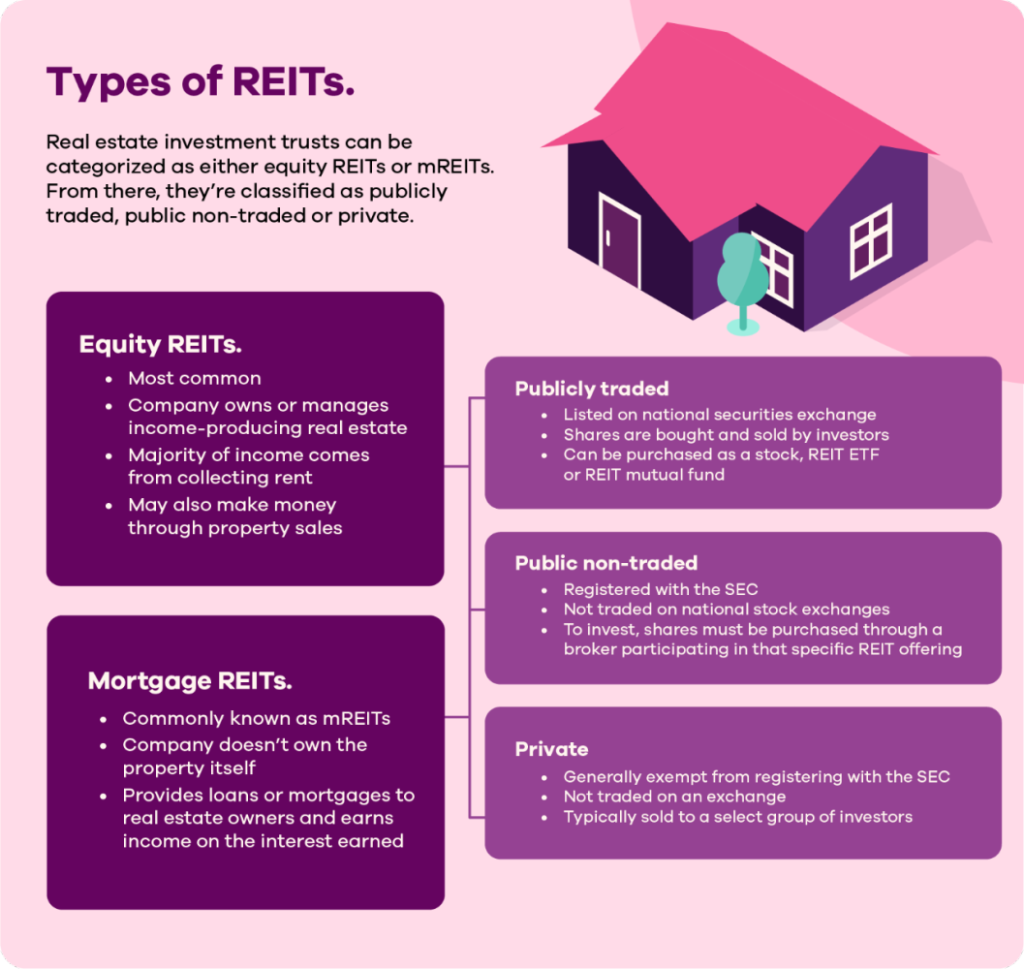
수치: Types of REITs
설명:
This figure categorizes 부동산 투자 신탁(REIT) into 지분 REIT 그리고 Mortgage REITs (mREITs), based on their operations and income sources. 지분 REIT focus on owning or managing income-generating properties and derive their income from rent and property sales. On the other hand, 모기지 REIT provide loans or mortgages and earn interest income. Additionally, REITs are divided into publicly traded, public non-traded, 그리고 private categories based on their trading mechanisms and accessibility, with publicly traded REITs being the most accessible through stock exchanges and private REITs reserved for select investors.
주요 시사점:
- 지분 REIT are the most common type, focusing on properties and earning income from rent and sales.
- 모기지 REIT provide loans or mortgages and generate income through 관심, without owning the properties themselves.
- Publicly traded REITs are listed on stock exchanges and easily bought and sold like stocks or ETFs.
- Public non-traded REITs are not listed on exchanges and require purchases via brokers, offering limited liquidity.
- 사모 REIT are not publicly available and are generally restricted to 기관 투자자 or specific high-net-worth groups.
정보의 응용:
Understanding these REIT categories allows investors to tailor their portfolios to their investment goals and risk tolerance. 지분 REIT may be ideal for those seeking steady rental income, while 모기지 REIT are suitable for income from interest. Differentiating between publicly traded, non-traded, and private REITs helps investors assess liquidity 그리고 accessibility, enabling informed decisions about their investments. This information is especially helpful for learning about real estate investments and diversifying portfolios.
9.4 Benefits and Drawbacks of Investing in REITs in Europe
이익:
- 유동성: Public REITs in Europe offer high liquidity, allowing investors to buy and sell shares on stock exchanges, providing more flexibility compared to direct property ownership.
- 정기소득: European REITs must distribute a significant portion of their income to shareholders, offering consistent dividends, which can be higher than those from regular stocks.
- 세금 효율성: REITs in Europe benefit from favorable tax treatment, making them a tax-efficient way to invest in real estate. In France 그리고 Germany, REIT dividends are often taxed at lower rates.
- 다각화: REITs allow investors to gain exposure to a variety of real estate sectors, such as retail, office, residential, and industrial properties, which helps diversify their portfolio.
단점:
- Market Volatility: REITs traded on European exchanges are subject to stock market fluctuations, making them more volatile than direct real estate investments.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: REITs are sensitive to changes in interest rates. Rising interest rates in countries like the U.K. 또는 Italy can increase borrowing costs, affecting REIT profitability.
- Limited Control: Investors in REITs have no direct control over the properties or the decisions made by the REIT managers, which can impact returns.
- Dividend Taxation: In some European countries, REIT dividends may be taxed at higher rates compared to other investment income, reducing the overall return on investment.
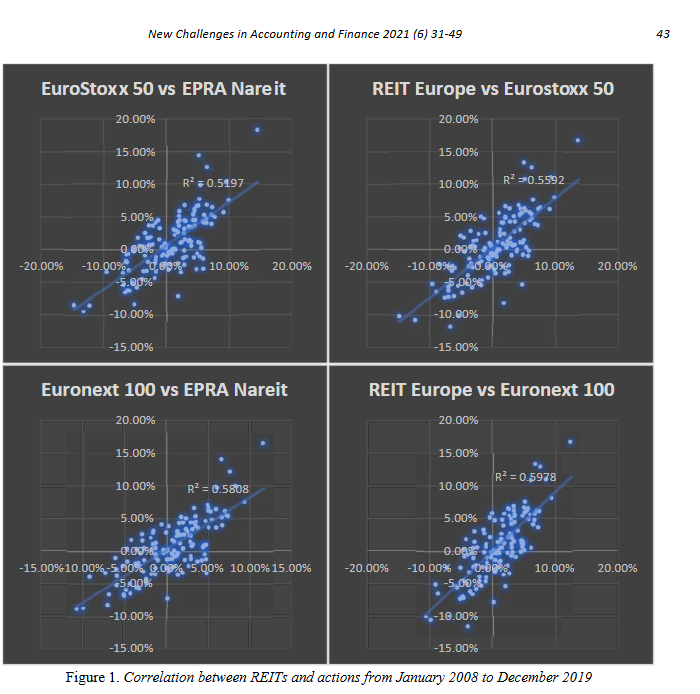
수치: Correlation between REITs and indices (January 2008–December 2019)
설명:
This figure shows the correlation between European Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and key financial indices over the period from January 2008 to December 2019. The scatterplots compare the returns of the EuroStoxx 50, Euronext 100, and their respective REIT counterparts such as EPRA Nareit Europe. Each chart includes an R² value indicating the strength of the correlation. Higher R² values suggest a stronger linear relationship between REIT performance and general market indices, reflecting the degree of movement REITs share with these indices.
주요 시사점:
- Positive correlations: REITs show a positive relationship with general market indices, but the correlation is not perfect, highlighting partial diversification benefits.
- R² values indicate that around 50–59% of REIT movements are explained by the indices, suggesting REITs partially track broader market trends while retaining unique characteristics.
- Market-specific performance: Different indices (e.g., EuroStoxx 50 and Euronext 100) exhibit similar levels of correlation with REITs, indicating consistent behavior across major European markets.
- Diversification potential: The scatterplots confirm that REITs do not fully mirror equity markets, providing an opportunity for portfolio diversification.
- Stability across time: Correlations remained consistent during the analyzed period, including the 2008 financial crisis recovery phase, showing REITs’ resilience.
정보의 응용:
The data highlights the importance of incorporating REITs into diversified portfolios, especially for investors seeking exposure to real estate markets while balancing broader equity market risks. The R² values help assess how much REIT performance depends on the broader market, enabling investors to estimate potential risks and returns. These insights are valuable for those constructing portfolios with a mix of equity and real estate investments to optimize risk-adjusted returns.
주요 수업 정보:
- REITs in Europe are companies that invest in real estate and are traded on stock exchanges, offering liquidity and ease of access similar to stocks. This allows individuals to invest in real estate markets without owning or managing properties directly.
- REIT regulations vary by country, with France (SIIC) and the U.K. requiring REITs to distribute a large portion of rental income to shareholders, creating a tax-efficient income stream for investors.
- 공공 REIT are listed on major exchanges and offer transparency and liquidity, while 사모 REIT cater to accredited investors, often offering higher potential returns but with lower liquidity and greater risk.
- 지분 REIT are the most common and generate income from rent and property appreciation, while 모기지 REIT earn income from interest on loans and are more common in countries like Ireland and Spain.
- REITs offer benefits such as regular income, diversification, 그리고 favorable tax treatment, but they also come with risks like market volatility, interest rate sensitivity, 그리고 limited investor control over property decisions.
마무리 진술
REITs provide a unique gateway into real estate investing without the need to manage physical property. Understanding the different types, markets, and risk factors associated with REITs in Europe empowers investors to diversify their portfolios and pursue reliable income opportunities.