Analyzing Companies’ Financial Statements
수업 학습 목표:
Introduction: This section navigates through the landscape of Financial Ratios, their categorization, and
the profound insights they provide into a company’s financial health and performance.
1. Financial Ratios Categorization: Understand the different groups of financial ratios such as
solvency, liquidity, turnover, coverage, and market prospects, each focusing on specific
aspects of a company’s financial standing.
2. In-depth Ratio Analysis: Delve into each ratio, like the debt-to-equity ratio, the current
ratio, or the price-to-earnings ratio, offering unique insights into the financial health and
performance of a company.
3. Combining Ratios: Learn the benefit of examining certain ratios together, like the 현재의
and quick ratios or the price-to-earnings and price-to-sales ratios, for a more
comprehensive analysis.

수치: A consulting auditor meticulously analyzing financial reports, including balance sheets and income statements. The image emphasizes the importance of detailed financial analysis in making informed business decisions.
원천: iStock사진
24.1 Introduction
Welcome to the world of financial statement analysis! In this chapter, we will delve into the key financial ratios that investors use to assess a company’s profitability, solvency, liquidity, turnover, coverage, and market prospects. By understanding and applying these ratios, you can make more informed investment decisions and identify potential red flags or opportunities in a company’s financials.
24.2 Ratio Categories
Financial ratios can be broadly categorized into six main groups: profitability ratios, solvency ratios, liquidity ratios, turnover ratios, coverage ratios, and market prospect ratios. Let’s take a closer look at each of these categories and the logic behind their significance.

수치: The infographic provides a comprehensive breakdown of the four main categories of finance ratios: Profitability, Liquidity, Leverage, and Valuation. Under each category, specific ratios are listed, such as Gross Margin, Return-on-Assets, and Return-on-Equity for Profitability; Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Inventory Turnover for Liquidity; Debt-to-Equity and Debt-to-EBITDA for Leverage; and Price-to-Earnings, Price-to-Book, and Price-to-Sales for Valuation. These ratios are essential tools for analyzing a company’s financial health, performance, and valuation.
출처: 맞춤형 인포그래픽
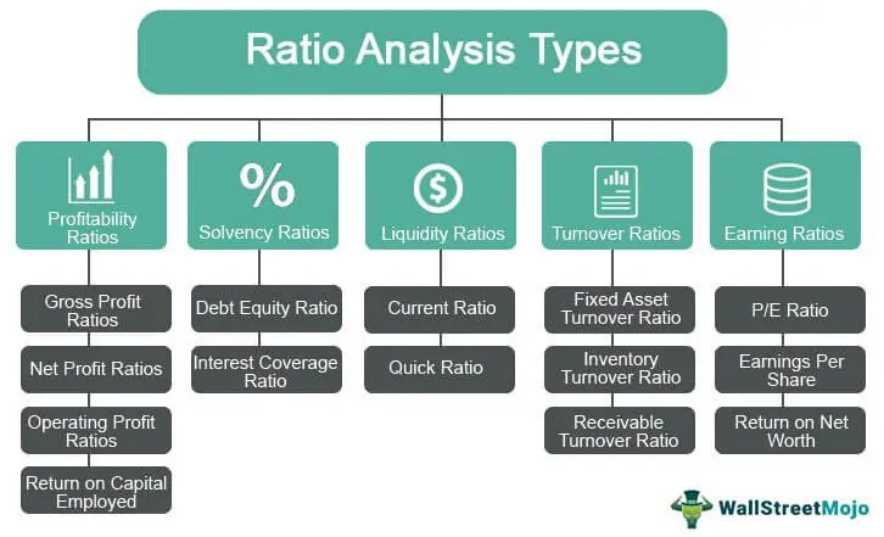
Figure title: Types of Financial Ratios
원천: WallStreetMojo
설명: This figure categorizes various financial ratios into subtypes such as profitability, solvency, liquidity, turnover, and earnings ratios, outlining their importance in financial analysis.
주요 내용:
- Profitability Ratios: These show how efficiently a company generates profit relative to its size, assets, or equity.
- Solvency Ratios: These measure a company’s ability to meet long-term obligations.
- Liquidity Ratios: These ratios indicate how well a company can meet its short-term debts.
- Turnover Ratios: These show how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales.
애플리케이션: Financial ratios are vital tools for investors aiming for thorough due diligence. These ratios simplify complex financial statements, making it easier to compare companies and assess risk and potential.
24.3 Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profit relative to its sales, assets, or equity. They help investors assess the company’s overall financial performance and potential for growth. Some common profitability ratios include:
24.3.1 Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Sales) x 100
The gross profit margin shows the percentage of revenue that remains after accounting for the cost of goods sold (COGS). A higher gross profit margin indicates that the company has more money to cover its operating expenses and generate profit. The gross profit margin is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies have more efficient cost structures.
장점:
- Easy to calculate and understand
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in sales or COGS, which may not always reflect the company’s overall profitability
24.3.2 Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin = (Net Income / Sales) x 100
The net profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that remains after accounting for all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, and taxes. A higher net profit margin indicates a more profitable company. The net profit margin is useful for comparing the overall profitability of different companies or industries.
장점:
- Takes into account all expenses, providing a more comprehensive view of profitability
- Useful for comparing companies across different industries
단점:
- Can be influenced by non-operating items or one-time expenses, which may not reflect the company’s ongoing profitability
24.3.3 Return on Assets (ROA)
ROA = (Net Income / Total Assets)
The return on assets measures how efficiently a company is using its assets to generate profit. A higher ROA indicates a more efficient company. Investors can use the ROA to compare companies within the same industry or across different industries to assess their efficiency in generating profit from their assets.
장점:
- Measures the efficiency of a company’s asset utilization
- Useful for comparing companies within the same industry or across different industries
단점:
- Can be influenced by the company’s asset base, which may not always reflect its profitability
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different capital structures
Combining Ratios for Better Insight: Gross Profit Margin and Net Profit Margin
Using both the gross profit margin and net profit margin together can provide a more complete view of a company’s profitability. While the gross profit margin focuses on the company’s efficiency in managing its production costs, the net profit margin takes into account all expenses. By analyzing both ratios, investors can better understand how a company is managing its overall costs and generating profit.
24.4 Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations. They help investors assess the financial health and stability of a company by determining its ability to pay off long-term debts. Some common solvency ratios include:
24.4.1 Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
The debt-to-equity ratio measures the proportion of a company’s total debt relative to its shareholders’ equity. A higher ratio indicates that the company relies more on borrowed funds to finance its activities, which can be risky. A lower ratio, on the other hand, suggests that the company is less reliant on debt financing. Investors can use this ratio to compare companies within the same industry or across different industries to assess their capital structure and financial stability.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s capital structure
- Useful for comparing companies within the same industry or across different industries
단점:
- Can be influenced by industry norms, which may not reflect the company’s overall financial health
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different financial Strategies t6 or business models
24.4.2 Debt Ratio
Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
The debt ratio measures the proportion of a company’s total assets that are financed by debt. A higher debt ratio indicates that a greater percentage of a company’s assets are financed by debt, which can be risky. A lower debt ratio, on the other hand, suggests that the company has a lower proportion of debt relative to its assets. Investors can use this ratio to compare the financial health of companies within the same industry or across different industries.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s overall debt burden
- Useful for comparing companies within the same industry or across different industries
단점:
- Can be influenced by industry norms, which may not reflect the company’s overall financial health
May not be suitable for comparing companies with different asset bases or capital structures
Combining Ratios for Better Insight: Debt-to-Equity Ratio and Debt Ratio
By analyzing both the debt-to-equity ratio and the debt ratio together, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health and risk profile. While the debt-to-equity ratio focuses on the company’s capital structure, the debt ratio takes into account the proportion of a company’s assets financed by debt. By examining both ratios, investors can assess a company’s overall debt burden and its ability to meet long-term financial obligations.
24.5 Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. They help investors assess the financial health of a company by determining if it can pay off its debts as they come due. Some common liquidity ratios include:
24.5.1 Current Ratio
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
This ratio indicates whether a company has enough current assets to cover its current liabilities. A current ratio above 1 indicates that the company can meet its short-term obligations, while a ratio below 1 suggests potential liquidity issues. The current ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies have more liquid assets to cover their short-term liabilities.
장점:
- Easy to calculate and understand
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in current assets or current liabilities, which may not always reflect the company’s overall liquidity
24.5.2 Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio)
Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities
The quick ratio is similar to the current ratio but excludes inventory from current assets. This is because inventory may not be as easily convertible to cash in the short term. A higher quick ratio indicates better short-term liquidity.
예: Company A has $500,000 in current assets, $100,000 in inventory, and $400,000 in current liabilities. Its quick ratio is 1 ($400,000 / $400,000), which indicates that the company can meet its short-term obligations without relying on inventory sales.
장점:
- Provides a more conservative view of a company’s short-term liquidity
- Useful for comparing companies with varying inventory levels
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in inventory levels, which may not always reflect the company’s overall liquidity
- May not be suitable for comparing companies in industries with different inventory turnover rates
Combining Ratios for Better Insight: Current Ratio and Quick Ratio
By analyzing both the current ratio and the quick ratio together, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s short-term liquidity position. While the current ratio focuses on the overall ability of a company to cover its short-term liabilities, the quick ratio provides a more conservative view by excluding inventory. By examining both ratios, investors can assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations without relying on inventory sales.
24.6 Turnover Ratios
Turnover ratios measure the efficiency with which a company uses its assets or manages its liabilities. They help investors assess the operational efficiency of a company by determining how well it manages its resources. Some common turnover ratios include:
24.6.1 Inventory Turnover
Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
그만큼 inventory turnover ratio measures how quickly a company sells its inventory during a given period. A higher inventory turnover ratio indicates that the company is selling its inventory more quickly, which can be a sign of efficient inventory management. The inventory turnover ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies have more efficient inventory management practices.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s inventory management efficiency
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by seasonal fluctuations or changes in inventory levels, which may not always reflect the company’s overall inventory management efficiency
- May not be suitable for comparing companies in industries with different inventory turnover norms
24.6.2 Accounts Receivable Turnover
Accounts Receivable Turnover = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
그만큼 accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how quickly a company collects payments from its customers. A higher accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that the company is collecting payments more quickly, which can be a sign of efficient credit management. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies have more efficient credit management practices.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s credit management efficiency
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in credit terms or collection practices, which may not always reflect the company’s overall credit management efficiency
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different credit policies or customer bases
Combining Ratios for Better Insight: Inventory Turnover and Accounts Receivable Turnover
By analyzing both the inventory turnover and accounts receivable turnover ratios together, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s operational efficiency. While the inventory turnover ratio focuses on the efficiency of inventory management, the accounts receivable turnover ratio assesses the efficiency of credit management. By examining both ratios, investors can assess a company’s overall ability to manage its resources and generate sales.
24.7 Coverage Ratios
Coverage ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations, such as interest payments or dividends. They help investors assess the financial stability of a company by determining its ability to fulfill its commitments. Some common coverage ratios include:
24.7.1 Times Interest Earned (TIE) Ratio
Times Interest Earned Ratio = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) / Interest Expense
The times’ interest earned ratio measures how many times a company’s earnings can cover its interest expenses. A higher TIE ratio indicates that the company has a greater ability to meet its interest obligations, which can be a sign of financial stability. The TIE ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies have a stronger ability to meet their interest obligations.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s ability to meet its interest obligations
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in interest rates or earnings, which may not always reflect the company’s overall financial stability
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different capital structures or debt levels
24.7.2 Dividend Coverage Ratio
Dividend Coverage Ratio = Net Income / Dividends
The dividend coverage ratio measures how many times a company’s net income can cover its dividend payments to shareholders. A higher dividend coverage ratio indicates that the company has a greater ability to meet its dividend obligations, which can be a sign of financial stability. The dividend coverage ratio is useful for comparing companies with similar dividend policies, as it can reveal which companies have a stronger ability to maintain their dividend payments.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s ability to meet its dividend obligations
- Useful for comparing companies with similar dividend policies
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in net income or dividend policies, which may not always reflect the company’s overall financial stability
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different dividend policies or payout ratios
Combining Ratios for Better Insight:
Times Interest Earned and Dividend Coverage Ratios
By analyzing both the times’ interest earned and dividend coverage ratios together, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations. While the TIE ratio focuses on the company’s ability to meet its interest obligations, the dividend coverage ratio assesses the company’s ability to meet its dividend obligations. By examining both ratios, investors can assess a company’s overall financial stability and ability to fulfill its commitments.
24.8 Market Prospects Ratios
Market prospects ratios measure a company’s financial performance relative to its market valuation. They help investors assess the potential for future growth and profitability of a company by comparing its financial metrics to its market price. Some common market prospects ratios include:
24.8.1 Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
Price-to-Earnings Ratio = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share
The price-to-earnings ratio measures the market price of a company’s shares relative to its earnings per share. A higher P/E ratio indicates that investors are willing to pay more for a company’s earnings, which can be a sign of strong growth prospects. The P/E ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies are valued more highly by the market.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s market valuation relative to its earnings
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in market conditions or earnings, which may not always reflect the company’s overall growth prospects
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different growth rates or business models
24.8.2 Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio
Price-to-Sales Ratio = Market Price per Share / Sales per Share
The price-to-sales ratio measures the market price of a company’s shares relative to its sales per share. A higher P/S ratio indicates that investors are willing to pay more for a company’s sales, which can be a sign of strong growth prospects. The P/S ratio is useful for comparing companies in the same industry, as it can reveal which companies are valued more highly by the market based on their sales.
장점:
- Provides insight into a company’s market valuation relative to its sales
- Useful for comparing companies in the same industry
단점:
- Can be influenced by changes in market conditions or sales, which may not always reflect the company’s overall growth prospects
- May not be suitable for comparing companies with different growth rates or business models
Combining Ratios for Better Insight: Price-to-Earnings and Price-to-Sales Ratios
By analyzing both the price-to-earnings and price-to-sales ratios together, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s market valuation and growth prospects. While the P/E ratio focuses on the company’s earnings, the P/S ratio assesses the company’s sales. By examining both ratios, investors can assess a company’s overall market valuation and determine whether it is overvalued or undervalued based on its financial performance.
Key Takeaway:
마무리 진술: Financial Ratios serve as a compass in your investment journey, providing a clearer picture of a company’s overall health, efficiency, and growth potential. As you delve deeper into ratio analysis and understand their contextual relevance, you become better equipped to make informed, intelligent investment decisions.
- Essential Analytical Tool: Financial ratios are vital tools for investors and financial analysts, providing a clearer picture of a company’s overall health, efficiency, and growth potential.
- Industry Context Matters: Always take into account industry standards and specific company contexts when interpreting these ratios to gain a more accurate perspective.
정보를 바탕으로 결정: By understanding and effectively applying these ratios, stakeholders can make better-informed decisions regarding investments, lending, or company management.

