Taxes and Fees in Stock Trading
주요 학습 목표:
소개: This section navigates the often complex and daunting realm of taxes and fees in stock trading. Acquire practical strategies to manage or reduce the tax implications of your stock investments and learn how to optimize your investment costs.
- Navigate Taxes and Fees in Stock Trading: Understand the various taxes, like capital gains and dividend taxes, and 수수료, including brokerage and management fees, associated with stock trading.
- Implement Strategies to Minimize Taxes: Learn practical methods to manage or reduce the tax implications of your stock investments.
- Optimize Investment Costs: Familiarize yourself with approaches to minimize fees and expenses, ensuring that more of your money remains invested.
소개
In this chapter, we will discuss the importance of managing taxes and fees in stock trading. We will cover strategies to reduce or manage tax and explore other fees and expenses related to investing. This knowledge will help you maximize your returns and navigate the financial landscape more effectively.
28.1 Managing Taxes and Fees in Stock Trading
Introduction to Taxes and Fees
Taxes and fees are an inevitable part of stock trading and investing. Understanding and managing them effectively can have a significant impact on your overall returns.
세금의 종류:
- Capital gains tax: Levied on the profit made from selling stocks, bonds, or other investments
- Dividend tax: Applied to dividend income received from stocks
Types of Fees:
- Brokerage fees: Commissions or fees charged by your broker for executing trades
- Account maintenance fees: Ongoing fees charged by your broker for maintaining your account
- Fund management fees: Fees charged by mutual funds and ETFs for managing the investment portfolio
28.2 Strategies to Reduce or Manage Tax

수치: A business professional using a computer to meticulously fill out an individual income tax return form online. The image highlights the modern approach to tax filing, emphasizing the convenience and efficiency of digital tax submissions.
원천: iStock사진
- Hold investments for the long term: Capital gains tax rates are generally lower for investments held for more than one year. By holding stocks for the long term, you can potentially pay a lower tax rate on your profits.
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts: In many countries, there are tax-advantaged accounts such as IRAs or 401(k)s in the United States, which allow for tax-deferred or tax-free growth on investments.
- Harvest tax losses: Selling stocks that have declined in value can help offset capital gains, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Reinvest dividends: Reinvesting dividends in additional shares can defer taxes on those dividends, allowing your investments to grow more efficiently.
28.3 Managing Fees and Expenses in Investing

수치: A prominent sign displaying the word “FEES” against a blurred background. The image underscores the concept of financial charges, emphasizing the importance of being aware of additional costs in transactions.
원천: iStock사진
- Choose low-cost brokers and investment platforms: Compare brokerage fees and account maintenance fees to find a platform that offers the lowest overall costs.
- Invest in low-cost funds: When investing in mutual funds or ETFs, choose funds with low expense ratios to minimize management fees.
- Diversify with commission-free investments: Some brokers offer commission-free trading on specific stocks or ETFs, which can help reduce your trading costs.
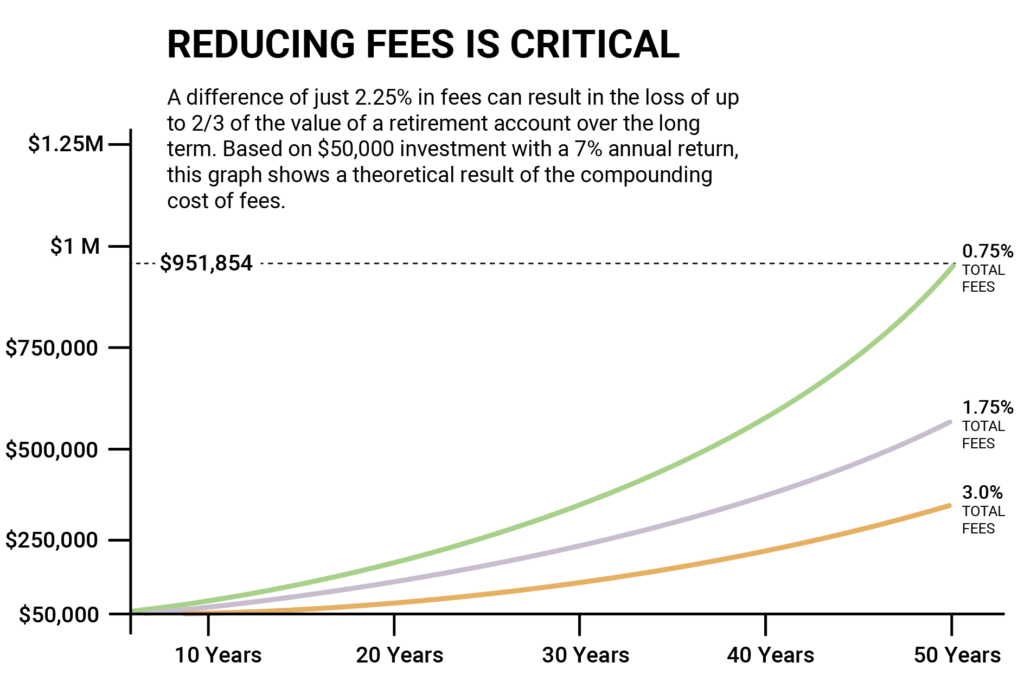
Figure title: The Impact of Management Fees on Investment Portfolio Growth
원천: One Day In July
설명: The figure vividly illustrates how varying levels of management fees can significantly affect the growth of an investment portfolio over time. It showcases three scenarios with fees of 0.75%, 1.75%, and 3%, starting from an initial investment of $50,000 and assuming a 7% annual growth rate.
주요 시사점:
- 복합 효과: The compounding nature of fees means that even a small difference in fee percentage can lead to a large divergence in final portfolio value.
- Fee Variations: A 0.75% fee leads to a portfolio worth $951,854, while a 3% fee reduces the portfolio value to only two-thirds of that amount.
- Long-Term Consequences: The effects of high fees are most dramatic when considered over a long-term investment horizon, severely eroding the power of compound interest in your favor.
애플리케이션: For investors, understanding the long-term impact of fees is crucial. Minimizing management fees can be a straightforward way to boost net returns and make the most of compound growth over time.
주요 시사점:
마무리 진술: The section demystifies the financial obligations accompanying stock trading, empowering you with strategies to minimize taxes and fees. This knowledge is crucial for maximizing your post-tax returns and ensuring a larger portion of your earnings remains invested.
- Taxes in Stock Trading include capital gains tax on profits and dividend tax on dividend income. Awareness and effective management of these taxes are vital for maximizing post-tax returns.
- Fees in Investing range from brokerage fees for trade execution to fund management fees in mutual funds and ETFs. Being conscious of these fees and choosing cost-effective options can significantly impact overall returns.
- Strategies to Reduce or Manage Tax include holding investments long-term, using 세금 우대 계좌, harvesting tax losses, and reinvesting dividends. Each strategy offers a way to defer, reduce, or manage tax implications.
- To Manage Fees, opt for low-cost brokers, invest in funds with low expense ratios, and diversify with commission-free investments. These steps ensure you keep a larger portion of your returns, making your investment journey more fruitful and satisfying.
