Global Content: Understanding Zoning Laws and Regulations Globally
Lesson Learning Objectives:
- Understand how zoning laws work around the world and how they shape land use, building typesir urban development. You’ll explore examples from cities like New York, Singaporeir Melbourne to see how zoning impacts real estate projects.
- Learn how to obtain permits and pass inspections across different global regions. You’ll gain insight into the application process, safety requirements, and how to meet environmental and building code standards in countries like Kanada, Dubaiir Japan.
- Discover key challenges in zoning, including regional differences ir restrictions in historical or environmentally sensitive areas, like London arba Kyoto. You’ll learn how to plan ahead and reduce risks in these situations.
- Explore best practices for managing global zoning laws, such as working with local professionals, understanding local building codesir keeping up with regulatory changes to stay compliant and improve project success.
A. Understanding Zoning Laws and Regulations Globally
Understanding Zoning Laws and Regulations Globally
Zoning laws define how land can be used and developed, and these regulations vary significantly across the world. Understanding local zoning laws is crucial for investors to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
- United States: In the U.S., zoning laws are managed at the municipal level, with areas designated for residential, commercial, industrial, or mixed-use purposes. In cities like New York ir Los Angeles, zoning regulations may also dictate building heights, parking requirements, and green space allocation.
- Singapore: In Singapore, zoning regulations are part of the Master Plan, which designates specific areas for residential, commercial, and industrial use. The government tightly controls land use to ensure sustainable urban development, and any deviation from the Master Plan requires approval from the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA).
- Australija: In Australija, zoning laws are controlled by local governments. Cities like Sydney ir Melbourne have strict zoning regulations that dictate land use, building heights, and density. Investors must work with local councils to ensure compliance with zoning restrictions.
Challenges in Understanding Zoning Globally
- Regional Differences: Zoning laws differ widely between countries and even within cities. Investors must understand the specific zoning requirements in the area they are targeting.
- Environmental and Historical Protections: In global cities with historical or environmental protections, such as Kyoto arba London, zoning laws may restrict the types of developments allowed in certain areas.
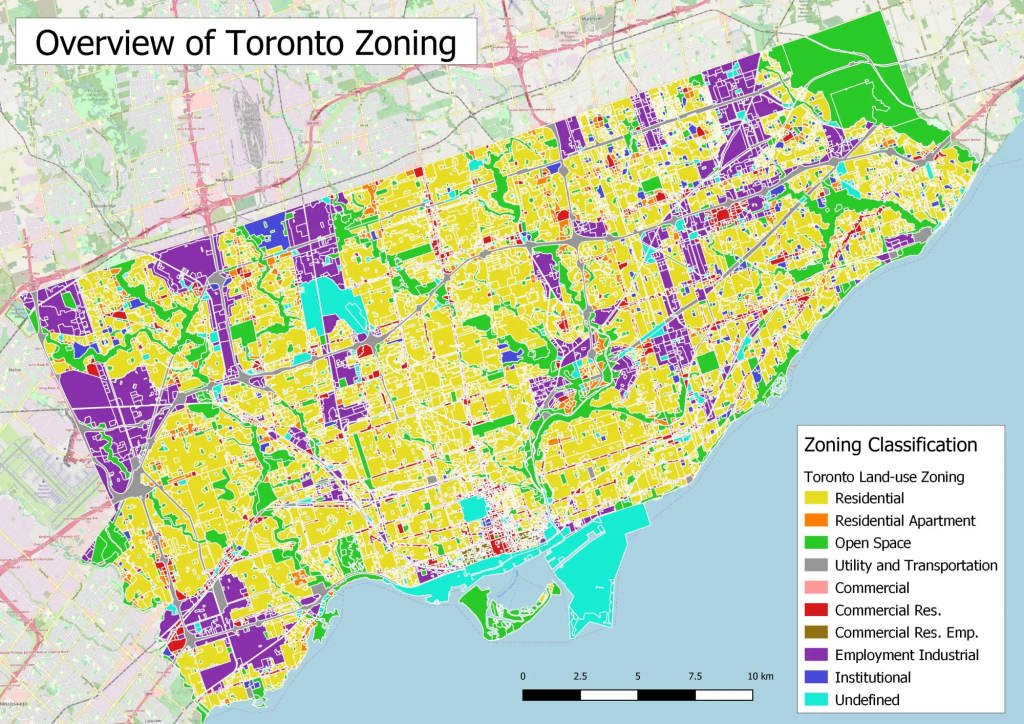
Paveikslėlis: Toronto Zoning By-Law Diversity
Aprašymas:
The image provides a visual representation of Toronto’s zoning by-laws, categorized by different land-use types. These types include residential, residential apartment, open space, utility and transportation, commercial, commercial residential, employment industrial, institutional, and undefined zones. The map likely highlights the distribution of these zones across Toronto, offering insights into the city’s urban planning and development patterns.
Svarbiausios išvados:
- Diverse Zoning: Toronto’s zoning by-laws exhibit a mix of residential, commercial, industrial, and open spaces, reflecting the city’s multifaceted urban landscape.
- High Diversity Areas: Regions such as the Beaches and East York showcase a rich mix of zoning types, including residential, industrial, green spaces, and commercial pockets.
- Low Diversity Areas: Certain parts of Toronto, especially west of Yonge Street and south of Allen Road, predominantly feature low-density residential housing, indicating less zoning diversity.
- Significance of Shopping Centers: Regional shopping centers like Sherway Gardens, Yorkdale, and Scarborough Town Center are hubs of diverse zoning due to their mix of commercial, residential, and industrial zones, coupled with transportation networks.
Application of Information:
Understanding Toronto’s zoning diversity is crucial for urban planners, developers, and policymakers. It offers insights into the city’s growth patterns, infrastructure needs, and areas of potential development or redevelopment. For investors and businesses, this knowledge can guide decisions related to property investments, business locations, and understanding the demographic and economic patterns of specific zones.
B. Navigating Permits and Inspections Globally
Navigating Permits and Inspections Globally
Obtaining permits and passing inspections are essential steps in real estate development globally. Different countries have their own regulations and processes for ensuring that developments comply with local laws.
- United States: In the U.S., developers must obtain building permits from local authorities before starting construction. In cities like San Francisco arba Chicago, permits are required for new construction, renovations, and changes in land use. Inspectors conduct regular site visits to ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards.
- Kanada: In Kanada, the permit process varies by province and municipality. Cities like Toronto require detailed applications that include site plans, environmental impact assessments, and fire safety compliance before construction can begin.
- Dubai: In Dubai, developers must obtain approvals from the Dubai Municipality and other relevant authorities before starting a project. Regular inspections ensure that construction adheres to local building codes and safety requirements, including fire safety and structural integrity.
Inspection Requirements Globally
- Permit Approvals: Globally, developers must secure various permits before breaking ground on a project. In Japan, for instance, developers must submit detailed site plans and comply with strict earthquake safety regulations before receiving building approval.
- On-Site Inspections: Throughout the construction process, local authorities conduct inspections to ensure that the building complies with safety standards. In Singapore, inspectors check for compliance with building codes, fire safety, and environmental regulations at key stages of construction.
C. Best Practices for Navigating Zoning and Land Use Regulations Globally
Best Practices for Navigating Zoning and Land Use Regulations Globally
Navigating zoning laws and land use regulations requires a thorough understanding of local rules and proactive engagement with authorities.
- Work with Local Professionals: In global markets, partnering with local architects, planners, and legal experts is essential. In Hong Kong, for example, navigating zoning regulations requires close coordination with local professionals familiar with government land use plans.
- Understand Local Building Codes: Each country has its own building codes and standards. In cities like New York arba Toronto, developers must ensure that their projects meet specific requirements for fire safety, accessibility, and structural integrity.
- Plan for Environmental and Historical Considerations: In markets like Kyoto arba Rome, zoning regulations may include additional requirements for preserving historical landmarks or protecting natural resources. Investors should factor these considerations into their project timelines and budgets.
- Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Zoning laws can change over time, particularly in rapidly developing cities like Dubai arba Shanghai. Staying informed about local zoning and land use changes can help investors capitalize on new opportunities or avoid potential regulatory pitfalls.
Išvada
Understanding zoning laws and land use regulations is essential for successful real estate investment, both in Europe and globally. By navigating permits and inspections effectively, working with local professionals, and staying informed about zoning changes, investors can ensure compliance and avoid costly delays. These best practices provide a roadmap for managing the legal and regulatory complexities of real estate development in any market.
Pagrindinė pamokos informacija:
- Zoning laws determine land use, such as whether an area is for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes. Countries like the U.S., Singaporeir Australija have detailed zoning systems, with rules that may also control building height, parkingir green space.
- Zoning requirements vary widely between countries and cities. In places like London or Kyoto, additional rules apply to preserve historical architecture ir natural areas, limiting what can be built and how it’s designed.
- Understanding local zoning maps helps investors spot diverse land-use areas and growth potential. For example, Toronto’s zoning diversity offers a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial zones, especially near shopping centers and transport hubs.
- Permits are required before construction, and the process can be detailed. In San Francisco arba Toronto, developers must submit site plans, environmental assessmentsir safety documents to get approval.
- Regular inspections during construction ensure that buildings meet local safety, fireir environmental standards. Cities like Singapore and Dubai conduct multiple inspections at different stages to maintain compliance.
Baigiamasis pareiškimas:
Whether you’re a developer, investor, or planner, understanding zoning and permit processes globally helps you protect your investments, ensure legal compliance, and adapt your strategies to fit local needs. This knowledge is key for avoiding costly mistakes and building responsibly.