Vietinis: asmeniniai finansai Europoje
Pamokos mokymosi tikslai:
Įvadas:
This section covers personal finance in Europe, focusing on managing money wisely, understanding different forms of money, and dealing with legal tender and exchange rates. By gaining these skills, you will be able to make informed financial decisions that suit your personal goals and the European financial environment.
- Understand Personal Finance in Europe: Learn how personal finance in Europe is shaped by different currencies, legal systems, and financial practices. This will help you manage your money effectively across the Eurozone and non-Eurozone countries.
- Recognize Different Forms of Money and Legal Tender: Grasp the different forms of money used in Europe, including cash, digital payments, and cryptocurrency. Understand how legal tender works to ensure seamless financial transactions.
- Identify the Pros and Cons of Money Types: Understand the advantages and disadvantages of cash, debit/credit cards, digital payments, and cryptocurrency. Knowing this will help you make better choices based on your financial needs and circumstances.
- Calculate and Manage Exchange Rates and Fees: Learn how to calculate exchange rates, including fees, to maximize the value of your money when making cross-border transactions in Europe.
- Enhance Financial Safety: Gain practical tips for securely storing cash, protecting digital payments, and managing cryptocurrency wallets. This knowledge will improve your financial safety in daily transactions.
1.1 Introduction to Personal Finance in Europe
Personal finnce in Europe involves managing money wisely, understanding the financial systems, and making informed decisions about saving, spending, and investing. The Euro (€) is the common currency in the Eurozone, but countries outside the Eurozone use their national currencies. In such a diverse financial environment, knowing how to handle different forms of money and understanding the legal frameworks around them is essential for both personal and cross-border financial management.
1.2 Forms of Money, Legal Tender, and Safe Storage
In Europe, money takes various forms, including grynieji pinigai, digital paymentsir cryptocurrency. Understanding that money can exist in these different forms is essential for making informed decisions. Cash is still widely used, particularly in Southern Europe, while digital payments dominate in Northern Europe. Cryptocurrency is growing but remains less common due to its volatility.
Legal tender refers to money that must be accepted for transactions. In the Eurozone, the Euro is the official currency, while non-Eurozone countries use their national currencies. It’s important to know the accepted currency in a country and how to handle payments when traveling or conducting business across borders.
Ensuring money is stored safely is a key financial responsibility. For cash, this involves keeping it secure or depositing it in a bank. For digital payments, secure platforms and two-factor authentication should be used to prevent fraud. Understanding how to safely manage cryptocurrency through secure wallets is also becoming increasingly important.
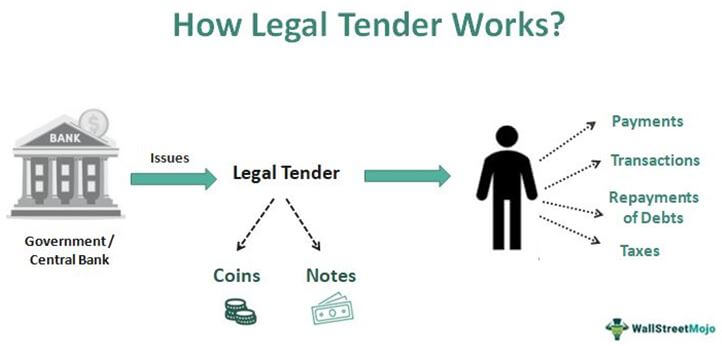
Paveikslėlis: How Legal Tender Works
Aprašymas:
This figure explains the process of legal tender issuance and its use in an economy. It shows how governments or central banks issue legal tender, which comes in the form of coins ir notes (paper money). Legal tender is then used by individuals for various financial transactions such as payments, repaying debts, paying taxes, and conducting everyday transactions. The diagram highlights the direct link between the central authority that issues money and the public, who use it for daily financial needs.
Svarbiausios išvados:
- Legal tender refers to coins and notes issued by the government or central bank.
- It is used by individuals for payments, transactions, debt repaymentsir taxes.
- Legal tender forms the backbone of a country’s monetary system, allowing for smooth economic transactions.
- Coins and notes are widely accepted as a means of exchange in a given economy.
Informacijos taikymas:
Understanding how legal tender works is crucial for both investors and individuals learning about finance. It provides a foundation for understanding how monetary systems operate, and why coins and notes are essential tools for conducting economic transactions. For investors, knowledge of legal tender helps in comprehending broader economic concepts like monetary policy ir infliacija, which directly impact the financial markets.
1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Forms of Money
Each form of money has its pros and cons:
- Cash: Convenient for small transactions and universally accepted, but it’s easy to lose and can be stolen.
- Debit/Credit Cards: Secure and widely accepted, but transaction fees may apply, especially for foreign payments.
- Digital Payments: Fast and easy, but reliant on technology and subject to exchange rate fluctuations.
- Cryptocurrency: Offers privacy and decentralization, but it’s volatile and not widely accepted for everyday transactions.
Making the right choice depends on understanding the context and financial situation. For example, when traveling, using a combination of cash and cards helps balance convenience and safety.

1.4 Currency Handling and Counterfeit Money
Europeans must be aware of how to handle both genuine and counterfeit notes. The European Central Bank incorporates several security features into Euro notes, such as watermarks, hologramsir raised printing to help identify genuine currency. It’s important to know how to check these features when handling cash.
Occasionally, notes and coins become obsolete due to redesigns or the removal of certain denominations. Knowing how to exchange obsolete currency within the designated time frame is essential. When counterfeit money is suspected, the proper course of action is to report it to local authorities or a bank.
1.5 Exchange Rates and Handling Multiple Currencies
Exchange rates fluctuate and vary between providers. When converting currencies, individuals must understand how to apply exchange rates and the associated fees and commissions. Various currency converter tools are available to help calculate conversions and ensure the best possible rates.
1.6 Example: How to Calculate Exchange Rates
Let’s say you are traveling from the Eurozone to the UK, and you need to convert Euros (€) to British Pounds (£). Suppose thùe exchange rate is €1 = £0.85, meaning 1 Euro equals 0.85 British Pounds. Here’s how you would calculate:
- If you have €500 and want to convert it to British Pounds, the calculation is:
€500×0.85=£425
So, you would receive £425 for your €500.
Now, consider that some currency exchange services may charge a transaction fee of 2%. To calculate how much you will receive after the fee:
- First, calculate the fee:
500×0.02=€10500 \times 0.02 = €10500×0.02=€10
This means you’ll pay €10 in fees. - Subtract the fee from the original amount:
€500−€10=€490€500 – €10 = €490€500−€10=€490 - Now, convert the remaining amount (€490) to British Pounds:
€490×0.85=£416.50€490 \times 0.85 = £416.50€490×0.85=£416.50
After the fee, you would receive £416.50 for your €500.
This example illustrates how fees and exchange rates affect the final amount of money you receive when converting currencies.
1.7 Managing Exchange Rates and Fees
When making cross-border transactions, such as sending remittances or purchasing goods abroad, it’s crucial to factor in both the exchange rate and transaction fees. Monitoring exchange rates and timing transactions effectively can help maximize value. It’s also important to compare rates from different providers to ensure you get the best deal.
Having the confidence to handle transactions in different currencies, whether for travel or international purchases, is vital in a connected European economy. By comparing exchange rates and minimizing fees, individuals can make more informed and cost-effective financial decisions.
Pagrindinė pamokos informacija:
- Personal Finance in Europe involves understanding various currencies, legal frameworks, and financial tools to make informed decisions. This knowledge helps individuals manage money wisely across different European regions.
- Forms of Money like cash, digital payments, and cryptocurrency offer different benefits and drawbacks. Cash is convenient for small purchases but risky if lost or stolen. Cards are secure but may involve fees. Digital payments are fast but dependent on technology, and cryptocurrency provides privacy but is volatile and less accepted.
- Legal Tender is crucial for everyday transactions, including paying for goods, services, and taxes. Coins and banknotes issued by a country’s central authority are considered legal tender, ensuring smooth economic exchanges.
- Handling Currency Exchange involves knowing exchange rates and factoring in fees. For example, when converting euros to British pounds, understanding how rates and fees impact the final amount helps manage cross-border transactions effectively.
- Security in Financial Transactions is essential for protecting money, whether it’s cash, digital payments, or cryptocurrency. Safe storage, secure platforms, and two-factor authentication help maintain financial safety.
Baigiamasis pareiškimas: Managing personal finance in Europe requires an understanding of money forms, legal tender, and exchange rates. By applying this knowledge, you can make confident financial decisions, handle cross-border transactions effectively, and protect your finances from potential risks. This foundation is essential for achieving financial stability and success in Europe.