പ്രാദേശികം: EU-വിലെ വിലകൾ, വാങ്ങലുകൾ, പേയ്മെന്റുകൾ
പാഠ പഠന ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ:
ആമുഖം:
This section will help you understand how prices, purchasing power, and payments work within the EU. By exploring these concepts, you’ll learn to make smarter financial decisions, compare prices effectively, and manage inflation’s impact on purchasing power.
- Understand Prices and Purchasing Power: Learn how prices vary across EU countries and how inflation affects what you can buy with your money over time. This will help you make informed decisions when managing your budget.
- Calculate and Compare Prices: Gain skills to calculate unit prices, helping you determine the best value for different products and services. This will enable you to make more cost-effective purchases.
- Explore Consumer Rights in Online Purchases: Understand your rights as a consumer in the EU, including return policies, to shop confidently and safely.
- Identify Payment Methods and Security: Get familiar with different payment methods, exchange rates, and security measures to handle transactions safely across borders.
1.1 Understanding Prices and Purchasing Power in the EU
In the Eurozone and other parts of Europe, prices for goods and services can vary depending on the location, vendor, കൂടാതെ time of purchase. For example, the cost of the same product may differ when purchased in a local store, online, or in another EU country. Additionally, consumers must be aware of how പണപ്പെരുപ്പം affects the purchasing power of their money over time. As prices rise due to inflation, the same amount of money will buy fewer goods, affecting long-term financial planning.
ഉദാഹരണം: If the price of a grocery basket in Spain increases from €50 to €55 over the course of a year, this means that inflation has eroded the purchasing power of €50.
1.2 Calculating and Comparing Prices
It’s essential for EU consumers to understand how to calculate and compare prices, especially when unit prices are not immediately clear.
For instance, when buying products like groceries, consumers should be able to calculate the price per unit (e.g., per kilogram, liter, or item) to compare the value of different brands. Knowing that the same goods may be priced differently across the EU due to നികുതികൾ, shipping costs, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ customs duties when buying internationally is also critical.
For example, if a 1-liter bottle of olive oil costs €6 in Italy and €7.50 in France, calculating the price per liter helps determine which option offers better value.

ചിത്രം: Price Level Index for Food, Beverages, Clothing, and Footwear (2023, EU=100)
വിവരണം:
This table compares the price level index (PLI) for different categories—food and non-alcoholic beverages, alcoholic beverages and tobacco, clothing, കൂടാതെ footwear—across various countries in Europe and surrounding regions. The EU average PLI is set at 100, and values above or below this number indicate whether a country’s prices are higher or lower than the EU average. Countries like സ്വിറ്റ്സർലൻഡ് ഒപ്പം Iceland have the highest price levels, while countries like Turkey ഒപ്പം North Macedonia have the lowest. The coefficients of variation at the bottom show the relative differences in price levels for each category across the regions.
പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
- സ്വിറ്റ്സർലൻഡ് has the highest price levels across all categories, with food and non-alcoholic beverages ഒപ്പം alcoholic beverages having particularly high price indices.
- Turkey has the lowest price levels across the board, especially for footwear ഒപ്പം clothing.
- Alcoholic beverages and tobacco have the highest price variation between countries, as seen in the coefficients of variation.
- Food and non-alcoholic beverages show a broad range of pricing, with countries like Denmark ഒപ്പം Norway having higher price levels compared to the EU average.
- Price levels for clothing are relatively more uniform, with less variation compared to other categories.
വിവരങ്ങളുടെ പ്രയോഗം:
മനസ്സിലാക്കൽ price level index is essential for investors or businesses operating across borders. This data allows users to analyze cost-of-living differences between countries, which can affect consumption patterns, product pricing, and overall market strategy. Investors can use this data to determine potential market opportunities or challenges in different regions, particularly when evaluating purchasing power ഒപ്പം consumer spending behavior.
1.3 Managing Inflation, Opportunity Cost, and Sunk Cost
As inflation erodes the value of money, it’s important for consumers in the EU to take steps to protect their savings and manage the impact of inflation. This might involve moving money into interest-bearing accounts or investing in inflation-protected securities. Additionally, understanding that price is not the only criterion when making purchases—factors like quality, sustainability, and consumer rights also matter—can help consumers make more informed decisions.
The concept of ഒന്ന് തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുമ്പോൾ മറ്റൊന്ന് നഷ്ടമാകൽ is also key to making informed purchasing decisions. Opportunity cost refers to the value of what is given up when you decide to spend money on one item instead of another. For example, if you spend €200 on a new smartphone, that money is no longer available for other potential purchases, like a weekend trip or savings.
Additionally, it’s important to recognize the concept of sunk cost—money already spent that cannot be recovered. Sunk costs should not influence future purchasing decisions. For instance, continuing to pay for a gym membership you no longer use simply because you’ve already invested money in it is a common sunk cost fallacy.
1.4 Consumer Rights and Online Purchases in the EU
When making purchases, especially online, EU consumers benefit from strong consumer protection laws. For example, under EU law, consumers have the right to return goods purchased online within 14 days for a full refund, regardless of the reason. Companies are required to disclose important information about the product, including its price, return policies, and any applicable shipping or customs fees.
Knowing how to return purchases within legal timeframes, as well as understanding terms and conditions, allows consumers to shop with greater confidence, especially when buying across borders.
To avoid overspending and making unplanned purchases, it’s important to develop strategies like creating a shopping list, setting a budget, and resisting marketing pressures such as online pop-ups and flash sales. Being confident in saying no to unsatisfactory offers or sales tactics is essential in maintaining financial discipline.
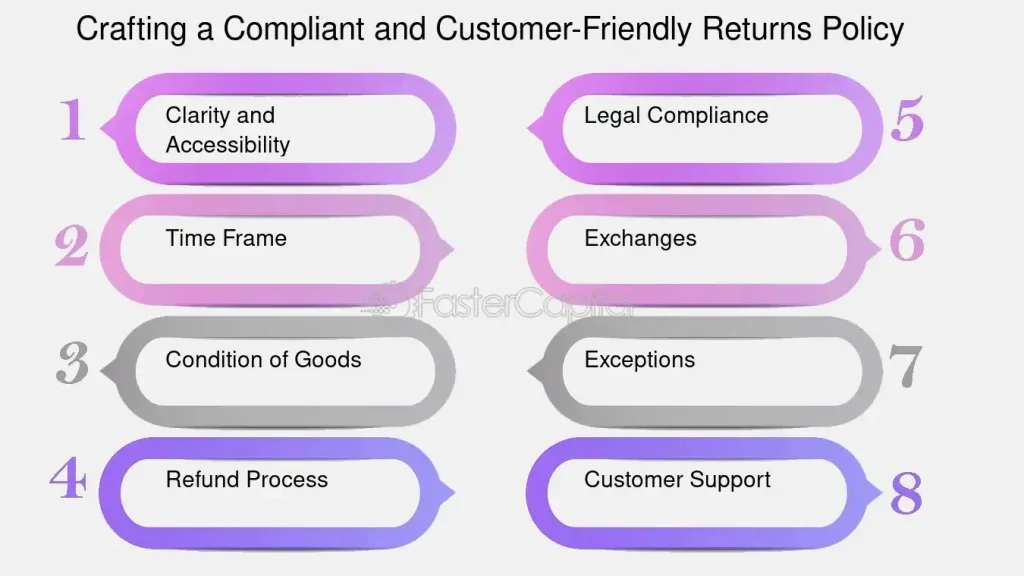
ചിത്രം: Crafting a Compliant and Customer-Friendly Returns Policy
വിവരണം:
This figure outlines the essential components of a compliant and customer-friendly returns policy. It includes key aspects such as clarity and accessibility (ensuring the policy is easy to understand), the time frame for returns, the condition of goods to be returned, and the refund process. Other components include ensuring legal compliance, guidelines for exchanges, identifying exceptions, and providing customer support to address any concerns during the return process. Together, these aspects ensure a balanced approach that protects both the business and the customer while simplifying the returns experience.
പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
- Clarity and accessibility make the policy easy for customers to find and understand.
- Clearly defined time frames help manage customer expectations for returns.
- Condition of goods must be specified to ensure only eligible items are returned.
- A straightforward refund process increases customer satisfaction.
- Legal compliance protects businesses from legal risks and ensures adherence to regulations.
വിവരങ്ങളുടെ പ്രയോഗം:
This framework helps businesses craft a returns policy that balances customer satisfaction with legal and business requirements. Investors or e-commerce entrepreneurs can use these components to ensure that their returns policies are both customer-friendly and compliant with relevant laws, improving customer trust and reducing potential disputes.
1.5 Payments and Handling Multiple Currencies in the EU
In a region as diverse as the EU, it’s common to deal with multiple currencies. Although the Euro is widely used, non-Eurozone countries have their own currencies, such as the Polish Zloty or the Danish Krone. Understanding how to calculate exchange rates and the associated ഫീസ് is important when making cross-border transactions.
For example, converting Euros to British Pounds when shopping in the UK involves calculating the exchange rate and any additional fees. If the exchange rate is €1 = £0.85, a purchase of £100 would cost approximately €117.65, plus any conversion fees imposed by the payment provider.
1.6 Sustainable and Smart Shopping Choices
Consumers in the EU are encouraged to consider sustainable alternatives to new purchases, such as buying second-hand അല്ലെങ്കിൽ refurbished products. The European Green Deal also emphasizes the importance of sustainability in purchasing decisions. Understanding how complementary products—such as accessories or maintenance services—affect the total cost of ownership can help avoid unexpected expenses.
For instance, buying an electric vehicle might include additional costs for charging infrastructure, which should be factored into the overall purchase decision.
1.7 Payment Methods and Security
In the EU, consumers have access to a variety of payment methods, including debit cards, credit cards, mobile wallets, കൂടാതെ bank transfers. Each method comes with its own risks and benefits. For instance, using a credit card can provide purchase protection but may incur interest charges if the balance is not paid off. It’s also essential to be aware of anti-money laundering regulations when using cash or transferring large sums of money.
EU consumers have the right to open a basic payment account regardless of their place of residence or financial situation. This allows them to make secure payments, even if they do not have access to full banking services. Understanding how to execute online payments securely by following digital security measures, such as two-factor authentication, is crucial in preventing fraud.
Consumers are encouraged to respect anti-money laundering rules, which require the reporting of large cash transactions and prohibit certain suspicious activities. Awareness of these rules ensures compliance and reduces the risk of financial fraud.
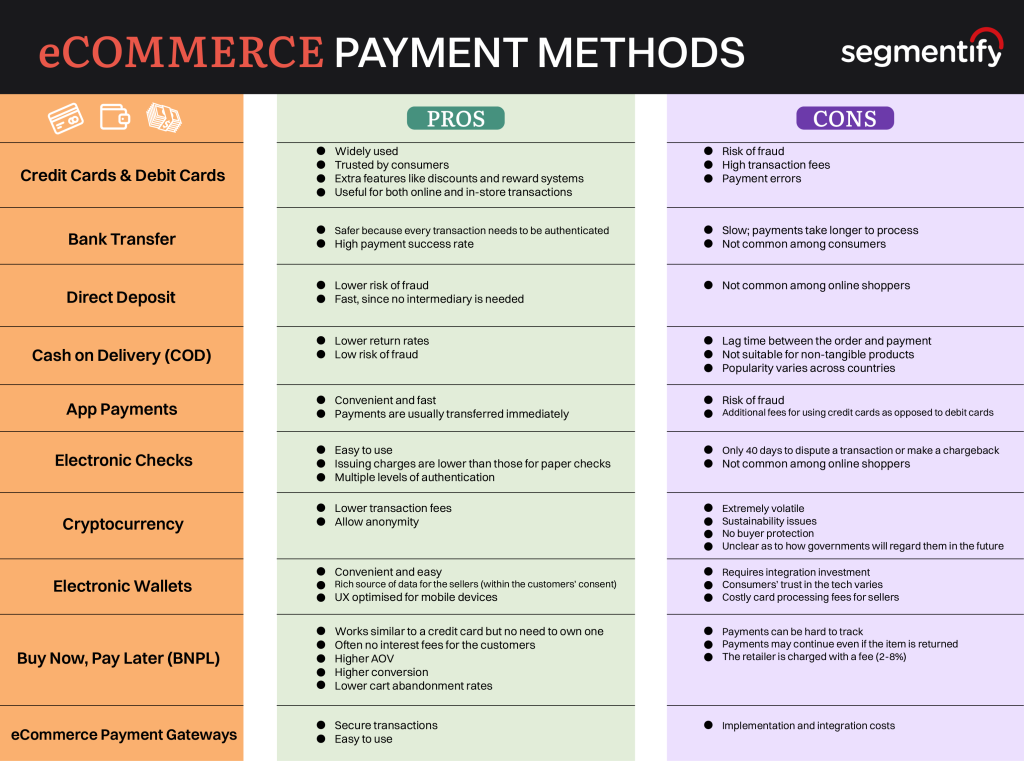
ചിത്രം: eCommerce Payment Methods: Pros and Cons
വിവരണം:
This figure compares various eCommerce payment methods by listing their pros ഒപ്പം cons. Payment methods such as Credit Cards & Debit Cards, Bank Transfer, Cash on Delivery (COD), കൂടാതെ Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) are categorized on the left. The pros include benefits like security, ease of use, and low transaction fees, while the cons mention risks such as fraud, high fees, and slower processing times. This chart helps businesses and users compare different payment options to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
- Credit and debit cards are widely used but come with high transaction fees and fraud risks.
- Bank transfers are more secure but are slower and less common for online shoppers.
- Cash on Delivery reduces fraud risk but is not practical for all types of goods.
- Cryptocurrency offers low transaction fees but is extremely volatile and lacks buyer protection.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) can boost conversion rates but poses tracking challenges for merchants.
വിവരങ്ങളുടെ പ്രയോഗം:
മനസ്സിലാക്കൽ advantages and disadvantages of different payment methods allows businesses to optimize their payment options for user experience ഒപ്പം security. By choosing the right mix of payment methods, companies can reduce fraud, increase transaction speed, and minimize fees, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and their eCommerce performance. Investors and business owners can use this data to better structure their online payment systems.
1.8 Tracking and Managing Payments
It’s important for consumers to keep track of their payments by checking receipts, bills, and invoices to ensure accuracy. In the EU, certain payments may incur ongoing costs, such as maintenance fees or subscriptions. Being aware of these and managing them effectively ensures that consumers are not caught off guard by unexpected renewals or costs.
For example, many subscription services automatically renew, so tracking the subscription’s end date and deciding whether to continue or cancel before renewal is essential.
It’s also important to keep receipts, especially for major purchases, in case issues arise later or for tax purposes. Monitoring payments and comparing them with bank statements or credit card bills can help consumers detect mistakes or fraudulent charges.
This section provides a comprehensive view of how consumers in the EU can make informed decisions about prices, purchases, and payments while considering consumer rights, opportunity cost, sunk cost, anti-money laundering regulations, ഒപ്പം sustainable alternatives. By understanding unit pricing, inflation, consumer rights, and sustainable alternatives, individuals can better navigate personal finance within the EU’s diverse economic landscape.
പ്രധാന പാഠ വിവരങ്ങൾ:
- Prices and Purchasing Power: Prices vary across EU countries and are affected by inflation, which reduces the buying power of your money. Understanding this helps you make better financial decisions and plan for inflation over time.
- Calculating Unit Prices: Knowing how to calculate unit prices (e.g., cost per kilogram or liter) allows you to compare the value of similar goods and choose the best option, whether shopping locally or across borders.
- Consumer Rights in Online Shopping: EU consumer protection laws allow you to return goods within 14 days for a full refund. Being aware of your rights can help you make safe and confident online purchases.
- Managing Multiple Currencies: When shopping across borders, understanding exchange rates and fees is essential for cost-effective transactions. For example, converting Euros to Pounds requires calculating the rate and additional fees to avoid overspending.
- Payment Methods and Security: Credit cards, bank transfers, and mobile wallets offer different benefits and risks. Understanding these options helps you select the safest and most convenient payment method for your needs. Awareness of anti-money laundering rules also keeps you compliant and secure.
- Sustainable Shopping Choices: Exploring second-hand or refurbished products is encouraged in the EU as part of sustainable consumption. Factoring in additional costs like maintenance can prevent unexpected expenses and support long-term financial goals.
സമാപന പ്രസ്താവന: This section equips you with essential knowledge about prices, payments, and consumer rights within the EU. By applying these concepts, you can improve your budgeting skills, make informed purchasing decisions, and manage your finances more effectively, whether at home or when shopping across borders.

