Lokalt: Administrere inntekt og forstå karriereveier
Læringsmål for leksjonen:
Introduksjon:
This section explores how managing income and career choices influences personal finances. Understanding different income sources, income management, and career growth will empower users to make better financial decisions and plan for financial stability.
- Identify various sources of income, such as earned and unearned income. Learn how different income sources, like wages, investments, or government benefits, impact financial planning and support financial transparency.
- Differentiate between gross and net income. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing earnings and deductions, which help in budgeting and comparing job offers effectively.
- Understand how to manage income fluctuations. This involves setting financial priorities, creating an emergency fund, and making confident decisions about expenses, which is crucial for financial resilience.
- Explore the impact of career choices on income potential. By understanding how different career paths influence long-term income growth, individuals can plan for major life events, such as starting a family or purchasing a home.
- Develop budgeting skills to balance income, expenses, and savings. Creating and adjusting a budget in response to changes in income and unexpected expenses will contribute to long-term financial security.
Introduksjon
Navigating income and careers is an essential part of personal financial management. Understanding where income comes from, how it is managed, and how career choices affect financial outcomes over time helps individuals make informed decisions for financial stability. This chapter covers different types of income, the role of career paths, and how to manage fluctuations in income effectively. It also provides strategies for budgeting and planning for unexpected expenses, all of which contribute to long-term financial success.
Sources of Income: Earned and Unearned
Income can come from various sources, and it’s important to understand the difference between earned income (from employment, self-employment, or entrepreneurship) and unearned income (from investments, rental properties, or government benefits). Earned income includes wages and salaries, while unearned income might include dividends, interest, eller pension payments.
Governments also offer benefits for those who meet certain requirements, such as unemployment benefits, disability payments, og retirement pensions. Understanding how to qualify for these benefits and declaring all sources of income to tax authorities is crucial for maintaining financial transparency.
Understanding Net and Gross Income
Gross income refers to the total income earned before deductions such as taxes, social security contributions, and other automatic deductions. Net income is what remains after all these deductions are made. These deductions may go toward building assets (such as retirement contributions) or paying expenses (such as health insurance).
It’s important to check payslips and income statements regularly to ensure that deductions and income match expectations. If there are discrepancies between expected and actual income, analyzing the cause helps clarify financial standing. Additionally, when comparing job offers or career changes, individuals should consider the full pay package, which may include benefits like insurance, retirement contributions, or bonuses.
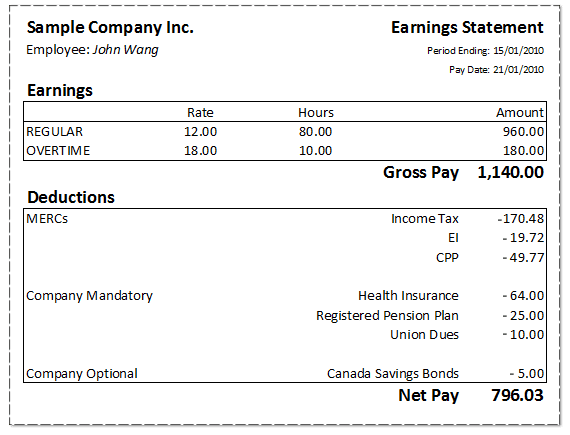
Figur: Earnings Statement Breakdown
Beskrivelse:
This image displays a sample Earnings Statement for an employee, detailing earnings, deductions, and the resulting net pay. The top half lists regular and overtime earnings, showing the employee’s hourly rate, total hours worked, and the gross pay (before deductions). The deductions include mandatory withholdings like Income Tax, EI (Employment Insurance), og CPP (Canada Pension Plan), along with company-provided health insurance og pensjonsordninger. There is also an optional deduction for Canada Savings Bonds. The final Net Pay is the employee’s take-home amount after all deductions.
Viktige takeaways:
- Gross pay is calculated based on hourly rate and hours worked, including overtime.
- Deductions include both government-required (taxes, EI, CPP) and company-provided benefits (health insurance, pension).
- Net pay is the final amount received after all deductions.
- Optional deductions can be voluntary savings contributions, like for Canada Savings Bonds.
- Understanding how deductions affect gross pay is important for financial planning.
Anvendelse av informasjon:
This image helps employees and learners understand the structure of an earnings statement and the impact of deductions on take-home pay. It’s useful for budgeting, tracking income, and analyzing benefits versus deductions. Investors can use this knowledge to assess company benefit offerings, while individuals can better manage their personal finances by understanding their net income.
Managing Income Fluctuations and Responsibility for Financial Decisions
Net income may fluctuate due to various reasons, such as overtime pay, bonuses, or changes in tax rates. For those in freelance eller self-employed roles, income may vary more significantly from month to month. It’s essential to monitor income carefully and set aside a portion of earnings for future expenses or emergencies.
Being confident in making independent decisions about income and expenditure is key to effective money management. This includes setting personal priorities when it comes to distinguishing between essential expenses (e.g., housing, food) and discretionary spending (e.g., vacations, entertainment). Accepting the responsibility of managing individual or household finances allows for greater financial security and planning.
For example, an individual may decide to allocate a portion of their income to an emergency fund to cover expenses in case of tap av jobb or other income disruptions. Knowing how much money is required to cover essential expenses for several months is a crucial part of building financial resilience.
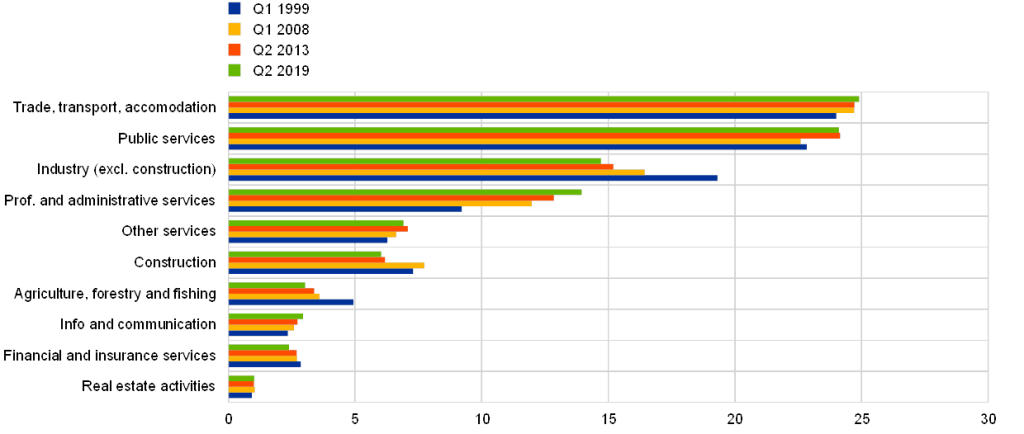
Figur: Comparison of Economic Sectors’ Growth in Euro Area (Q1 1998 – Q2 2018)
Beskrivelse:
This bar chart illustrates the economic growth across various sectors in the Euro Area over four distinct periods (Q1 1998, Q2 2008, Q2 2013, and Q2 2018). The sectors compared include retail trade, legal services, professional services, health, information technology, and manufacturing, among others. The chart uses color-coded bars to represent different periods, allowing a comparative view of sectoral changes over time. It highlights which sectors have grown or stagnated, providing insight into the economic evolution across industries.
Viktige takeaways:
- Professional and legal services showed steady growth across all periods, reflecting stability in these sectors.
- Information technology and professional services experienced significant increases from Q2 2008 to Q2 2018, highlighting their growing importance in the economy.
- Manufacturing and construction sectors saw fluctuations, indicating a more volatile pattern of growth.
- Sectors like arts and entertainment og sports showed slower growth compared to professional services, reflecting sector-specific challenges.
- De health sector displayed consistent growth, mirroring the rising demand for healthcare services.
Anvendelse av informasjon:
This chart can be applied by investors og policy makers to identify sectors with the highest growth potential and to assess economic health across industries. By analyzing the performance of key sectors, investors can better understand long-term trends and allocate resources efficiently. It also helps entrepreneurs og businesses to explore high-growth areas, such as information technology og professional services, for potential expansion opportunities.
Career Choices, Income Potential, and Life Stages
Different jobs and career paths provide varying levels of income over time. While some careers may offer a steady income, others, such as entrepreneurship, may offer higher income potential but with greater risk. It’s important for individuals to assess their current income needs and seek ways to generate sufficient income to cover these needs while also preparing for future financial stability.
As people progress through different life stages—such as entering the workforce, starting a family, or preparing for retirement—their income needs and financial priorities may change. Events such as marriage, having children, or purchasing a home can have a significant impact on both inntekt og expenditure, requiring individuals to adjust their financial plans accordingly.
Being confident in pursuing career choices and having the flexibility to consider job changes eller new business ideas can lead to better financial outcomes. However, individuals must also evaluate the risks and rewards associated with each path, ensuring they align with long-term financial goals.
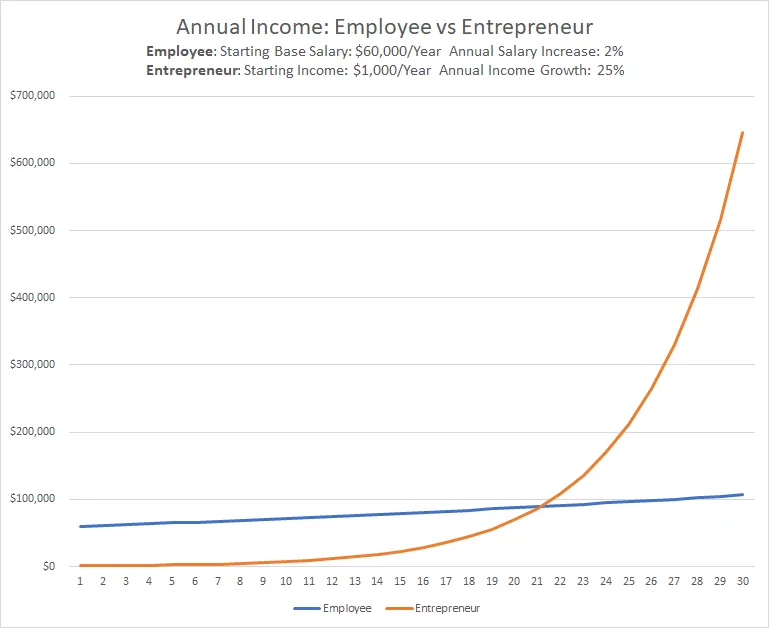
Figur: Annual Income: Employee vs Entrepreneur
Beskrivelse:
This line graph compares the annual income trajectories of an employee and an entrepreneur over 30 years. The employee starts with a base salary of $60,000 per year, with a modest annual salary increase of 2%. In contrast, the entrepreneur begins with a starting income of $1,000 per year, but with a 25% annual growth rate. The graph illustrates how the employee’s income increases steadily over time, while the entrepreneur’s income starts low but grows exponentially, surpassing the employee’s income after about 18 years and continuing to grow rapidly thereafter.
Viktige takeaways:
- Entrepreneurial income may start low but can increase exponentially with growth over time.
- Employee income is more predictable and stable, increasing gradually with annual salary increments.
- Around the 18-year mark, the entrepreneur’s income overtakes the employee’s income.
- The chart highlights the long-term financial potential of entrepreneurship compared to the more stable but slower-growing income of an employee.
Anvendelse av informasjon:
This chart can be used to illustrate the risks and rewards associated with entrepreneurship versus traditional employment. Investors and aspiring entrepreneurs can use this information to assess the potential long-term financial outcomes of each path. It highlights the importance of patience and investment in entrepreneurship, as it can lead to significantly higher income over time, despite early challenges.
Managing Expenses and Budgeting
A fundamental principle of personal finance is ensuring that expenditure does not exceed income. Creating a budsjett that includes both essential expenses (housing, food, utilities) and discretionary spending (entertainment, travel) helps individuals manage their finances effectively. Comparing actual expenses against budgeted amounts regularly ensures that spending stays on track.
For those with legal responsibility for managing other people’s finances, such as family members or dependents, it’s important to feel confident acting on their behalf. This responsibility requires careful management of their income and expenses to ensure that their financial needs are met.
If income or expenses fluctuate unexpectedly, it may be necessary to adjust the budget. For instance, an unexpected medical bill or job loss may require cutting back on discretionary spending or seeking alternative sources of income to cover the shortfall.
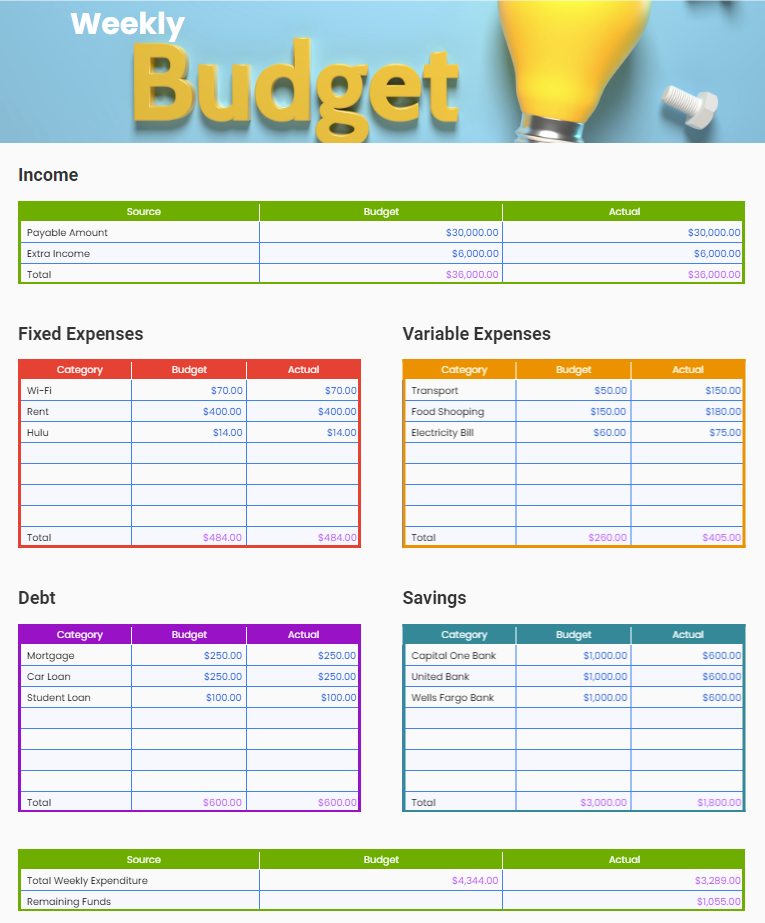
Figur: Weekly Budget
Beskrivelse:
This figure displays a weekly budget breakdown, showcasing various income sources, fixed and variable expenses, debt payments, and savings contributions. The income section lists total expected and actual income, which remains consistent at $36,000. The fixed expenses cover regular payments like rent, Wi-Fi, and Hulu, while variable expenses fluctuate, including items like transport and food shopping. The debt section lists payments like mortgages and loans, and the savings section shows contributions to different banks. The total weekly expenditure is compared against remaining funds, showing actual spending and savings.
Viktige takeaways:
- Income sources are consistent and provide a clear total for budgeting purposes.
- Fixed expenses are predictable, while variable expenses may fluctuate based on actual usage.
- Debt repayment is accounted for regularly, with categories like mortgage and student loans.
- Savings contributions vary, indicating potential adjustments in financial priorities.
- Remaining funds reflect the difference between total expenditures and actual income.
Anvendelse av informasjon:
This budget format helps users track their weekly financial health, ensuring they maintain control over income, expenses, and savings. By comparing budgeted amounts to actual spending, individuals can adjust their habits, optimize their savings, and manage debt efficiently, leading to better financial planning and decision-making.
Planning for Irregular and Unexpected Expenses
Life events such as marriage, childbirth, or purchasing a home often affect both inntekter og utgifter. Being prepared for these changes is key to maintaining financial stability. Additionally, it’s important to plan for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies or car repairs. Having an nødfond that can cover at least three to six months of living expenses is a good safety net.
For those facing unexpected expenses without sufficient savings, knowing the best payment options—such as using credit cards, loans, or installment plans—is critical. Each option comes with different costs and risks, so making informed decisions about how to finance these expenses ensures financial health.
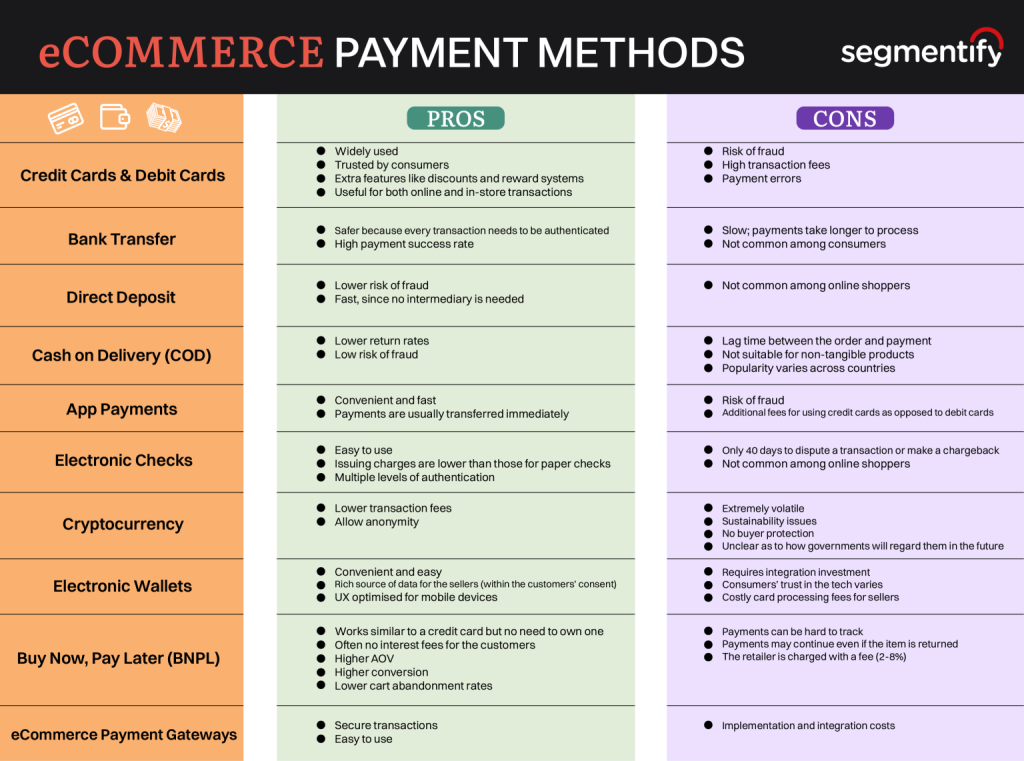
Figur: eCommerce Payment Methods
Beskrivelse:
This image presents a comparative analysis of various eCommerce payment methods. It categorizes payment options like Credit Cards, Bank Transfers, Direct Deposits, og Cryptocurrency into their pros og cons. Each payment method is evaluated based on factors such as fraud risk, transaction fees, processing time, og consumer trust. The chart is divided into two columns to clearly show the advantages and drawbacks of each method, making it easy to compare and understand.
Viktige takeaways:
- Credit and Debit Cards are widely used and trusted but come with high transaction fees og fraud risk.
- Bank Transfers are safer with high payment success rates, though slower in processing.
- Cryptocurrency provides lower transaction fees og anonymity, but its volatility is a significant concern.
- Buy Now, Pay Later models promote higher conversions og lower cart abandonment rates, but may result in payment tracking challenges.
- App Payments og Electronic Wallets offer convenience, especially for mobile users, but may face integration costs.
Anvendelse av informasjon:
Å forstå pros and cons of various eCommerce payment methods is crucial for businesses and consumers alike. Investors and entrepreneurs can leverage this knowledge to optimize payment options, reducing costs and improving user satisfaction. Additionally, eCommerce platforms can minimize fraud risks by selecting methods that prioritize security while ensuring convenience for their customers.
Confidence in Financial Decision-Making and Open Discussions
Being confident in managing income and expenditure is an essential life skill. This involves being able to set personal priorities, such as distinguishing between essential and discretionary spending, and making informed decisions about current and future financial needs.
Being comfortable discussing financial planning and management with significant others or partners ensures that household finances are transparent and well-managed. Open and honest discussions can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that both parties’ needs and goals are considered in financial planning.
For those with legal responsibility for managing the finances of others, it’s important to feel confident acting on their behalf, making budgeting decisions, and planning for their financial well-being. Open and honest discussions about finances with partners, family, or advisors can ensure that everyone’s needs are met while maintaining long-term financial stability.
Viktig informasjon om leksjoner:
- Sources of income include both earned and unearned forms. Earned income comes from jobs or self-employment, while unearned income is from investments or benefits. Knowing these sources helps in financial planning and meeting tax obligations.
- Gross income is the total earned before deductions, while net income is the amount left after deductions. Understanding both types of income helps individuals track their actual take-home pay, which is important for budgeting and financial decision-making.
- Income fluctuations require careful management to ensure that essential expenses are covered. Having an emergency fund and adjusting spending habits helps maintain financial stability during unpredictable times, such as job changes or economic downturns.
- Career choices can impact long-term income growth, with entrepreneurial paths offering higher potential returns, albeit with more risks. Traditional careers provide steady income, which can be useful for those seeking financial predictability.
- Creating and managing a budget helps individuals control their spending and ensure that their income is used efficiently. Regularly comparing actual spending with the budgeted amounts allows for necessary adjustments, helping individuals achieve financial goals.
- Planning for unexpected expenses is essential for maintaining financial stability. Building an emergency fund to cover at least three to six months of living expenses is a key strategy for managing unforeseen financial challenges.
Avsluttende uttalelse: Managing income, making career decisions, and budgeting effectively are critical skills for achieving financial stability. By understanding income types, planning for fluctuations, and adapting budgets, users can confidently navigate their financial journey and build a secure financial future.


