Stock Characteristics
Lesson Learning Objectives:
Introduction: This section delves into the various characteristics of stocks such as value, growth, size,
and liquidity. Understanding these attributes is crucial for making informed investment decisions and
building a diversified portfolio.
1. Understand Different Stock Characteristics: Gain a solid understanding of various stock
characteristics like value, growth, size, and liquidity to make better-informed investment
decisions.
2. Distinguish Between Value and Growth Stocks: Learn how value stocks and growth stocks
differ in terms of financial performance, growth potential, and returns to investors.
3. Grasp Key Stock Aspects: Understand the significance of stock liquidity, stock splits,
preferred stocks, buybacks, mergers and acquisitions, and spinoffs in determining your
investment strategy.

Figure: The infographic emphasizes the considerations when evaluating stock performance. It highlights the importance of using specific criteria to assess stocks, understanding the alignment of an asset with individual goals, and the significance of capital in the decision-making process. It’s crucial for investors to regularly evaluate their portfolio and ensure that each asset aligns with their broader financial and investment objectives.
Source: Custom Infographic
8.1 Value, Growth, Size, Liquidity, and More
Understanding different stock characteristics can help investors make more informed decisions and build a diversified portfolio.

Figure: The infographic focuses on the concept of “Favorable Asset Utilization.” It defines favorable asset utilization as the ratio of revenue earned for each dollar of assets a company owns. The infographic also emphasizes that different industries have different favorable ratios, and like the operating margin, this ratio is a measure of efficiency over time.
Source: Custom Infographic
- Value stocks: These stocks are considered undervalued compared to their financial performance, often trading at lower price-to-earnings ratios. Value stocks may offer the potential for long-term appreciation.
- Growth stocks: These stocks represent companies with higher-than-average growth potential. They often have higher price-to-earnings ratios and may not pay dividends, as profits are reinvested in the business.
- Size: Stocks can be classified based on market capitalization (market cap), which represents the total value of a company’s outstanding shares. Stocks can be categorized as small-cap, mid-cap, or large-cap. Market cap is important because it can indicate the stability, growth potential, and risk profile of a company.
- Liquidity: The ease with which a stock can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price. More liquid stocks tend to have higher trading volumes and tighter bid-ask spreads.
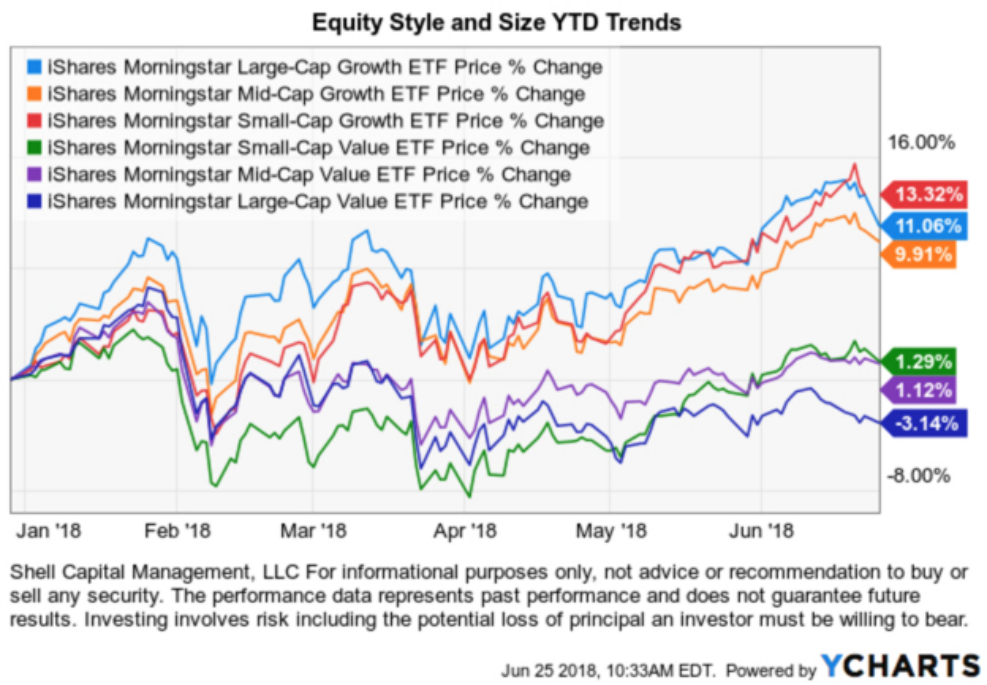
Figure title: ETF Performance Based on Company Size and Characteristics
Source: Asymmetry Observations
Description: The graph presents the performance trends of various ETFs, which represent distinctive stock characteristics based on company size and nature—either “Growth” or “Value”. It visually demonstrates the fluctuations and differences in returns among small, mid, and large-cap companies under these two categories over time.
Key takeaways:
- Equity Styles: The ETFs are categorized by their focus on either Growth or Value characteristics.
- Company Size Matters: The graph represents three main segments—small, mid, and large-cap companies. Performance varies within these segments.
- Variable Performance: The trajectory of each ETF shows that their returns can be quite diverse, depending on prevailing business conditions and the economic cycle.
Application: For investors, understanding the distinctions and performance patterns among these ETFs is crucial. It aids in making informed decisions on asset allocation—whether to lean more towards growth or value, and the ideal company size to invest in. This insight can potentially enhance returns and manage risk more effectively in diverse market conditions.
8.2 Other Stock Information:
- Stock splits: A corporate action in which a company increases the number of its outstanding shares while proportionally decreasing the stock’s price. This makes the stock more accessible to a broader range of investors.
- Preferred stocks: A type of stock that has characteristics of both stocks and bonds. Preferred stockholders receive dividends before common stockholders and have priority in the event of liquidation.
- Buybacks: A corporate action in which a company repurchases its own shares, reducing the number of outstanding shares and potentially increasing the stock’s value.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Transactions in which companies combine or one company acquires another, potentially affecting the value of the stocks involved.
- Spinoffs: A corporate action in which a company creates a new, independent company by separating a business segment or subsidiary.
8.4 Investing in Penny Stocks

Figure title: Understanding Penny Stocks and Their Dynamics
Source: FutureCaps
Description: The infographic provides a comprehensive overview of penny stocks, which are stocks that trade at a very low price and have a low market capitalization. Typically, in India, penny stocks trade at around Rs 0.05 to Rs 10 per share and are ultra micro-cap companies with a market capitalization of less than Rs. 50 crore. The infographic delves into the advantages and risks associated with investing in penny stocks, emphasizing the potential for significant returns if chosen wisely but also highlighting the inherent risks due to their volatile nature.
Key takeaways:
- Penny Stocks Definition: Stocks with a very low price and market capitalization, typically trading between Rs 0.05 to Rs 10 per share in India.
- Advantages: Penny stocks are not widely known, offering potential opportunities for investors willing to research their fundamentals.
- Risks: These stocks often lack transparent fundamentals, have low trading volumes, and can be manipulated by market operators.
- Regulatory Risks: Penny stocks might face regulatory actions from stock exchanges, including trading suspensions.
- Potential for High Returns: If chosen wisely, some penny stocks can become future multibaggers, offering substantial returns.
Application: For investors looking to diversify their portfolio and are willing to take on higher risks for potentially higher returns, penny stocks can be an option. However, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research, diversify investments across multiple penny stocks, and be wary of overly positive research reports. Setting strict stop-loss limits and regularly monitoring the performance of these stocks is also essential to mitigate potential losses.
Penny stocks are low-priced stocks, typically trading below $5 per share. They are often associated with smaller market cap, less established companies and can be highly speculative. Due to their volatility, lack of liquidity, and potential for manipulation, we do not recommend penny stocks for beginners.
Key Takeaways:
Closing Statement: The understanding of stock characteristics is pivotal in navigating the stock market
and making informed decisions. Each characteristic provides a unique lens through which to evaluate
potential investments, thereby playing a crucial role in building a diversified and robust portfolio.
1. Stocks can be classified into value stocks and growth stocks, with value stocks often being
undervalued compared to their financial performance, and growth stocks representing
companies with higher-than-average growth potential.
2. The size of a stock, denoted by market capitalization, indicates the stability, growth
potential, and risk profile of a company, categorized into small-cap, mid-cap, or large-cap.
3. Stock liquidity, the ease of buying or selling a stock without affecting its price, is an essential
factor to consider when investing, with more liquid stocks having higher trading volumes and
tighter bid-ask spreads.
4. Other significant stock information like stock splits, preferred stocks, buybacks, mergers
and acquisitions, and spinoffs can substantially influence the stock’s value and your
investment strategy.
