Globalne: Wybór kariery i zrozumienie dochodów
Cele lekcji:
Wstęp:
This section covers the importance of making informed decisions about career choices, understanding different types of income, and analyzing compensation and benefits in the workplace. By learning about income sources, vocational training, and the gig economy, users can better plan for financial stability.
- Explore job and career options by considering factors like income potential, job stability, and personal interests. Knowing how to assess different career paths helps users align their choices with personal and financial goals.
- Understand different types of income, including earned and unearned income. This knowledge is useful for managing finances, maximizing earnings, and complying with tax regulations.
- Learn how to evaluate total compensation packages, including salary and benefits. This helps users make better comparisons when choosing between job offers and assess the long-term value of different benefits.
- Compare vocational training and college education as two distinct paths to employment. Understanding the benefits and challenges of each helps users choose the best option based on personal career goals and financial situations.
- Analyze the gig economy and entrepreneurship as alternative career paths. Users will learn about the benefits, challenges, and financial responsibilities associated with these flexible but uncertain work environments.
A. Choosing Jobs and Careers
When selecting a job or career, it’s important to evaluate various factors, such as income potential, job stability, I personal interests. Some careers may offer steady and reliable income but less flexibility, while others may provide higher income potential with more risk. Balancing personal passion with the realities of job market demand and future financial stability is key to making informed career choices.
In a global context, When selecting a job or career, it’s important to evaluate various factors, such as income potential, job stability, I personal interests. Some careers may offer steady and reliable income but less flexibility, while others may provide higher income potential with more risk. Balancing personal passion with the realities of job market demand and future financial stability is key to making informed career choices .should also consider the impact of geography, industry trends, I economic conditions on job availability and compensation. For example, tech industries might offer higher salaries and more job security in certain regions, while traditional industries may face declines due to automation or economic shifts.

B. Income Types: Earned and Unearned
Earned income comes from employment Lub self-employment and includes wages, salaries, and bonuses. Unearned income, on the other hand, comes from sources such as investments, rental properties, Lub interest on savings accounts.
Many people supplement their primary income with secondary income streams, such as freelance work or investments, to achieve financial security. Understanding the implikacje podatkowe I financial management of both earned and unearned income is crucial to maximizing income while ensuring compliance with local tax laws.
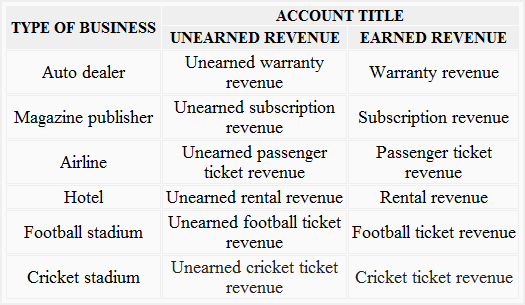
Postać: Types of Business and Unearned vs. Earned Revenue
Opis:
This table categorizes different types of businesses, such as auto dealers, airlines, and football stadiums, based on the distinction between unearned revenue I earned revenue. It highlights examples of unearned revenue (such as unearned subscription revenue for a magazine publisher) and their corresponding earned revenue once the service or product has been provided (e.g., subscription revenue after the service has been delivered). This comparison shows how businesses transition revenue from unearned to earned as services are rendered or goods are delivered.
Najważniejsze wnioski:
- Unearned revenue refers to money received by a business before providing a service or product.
- Earned revenue is recorded once the business has delivered the goods or services.
- Examples across industries include unearned warranty revenue for auto dealers and unearned passenger ticket revenue for airlines.
- Businesses in industries such as hospitality, sports, and publishing regularly deal with transitioning unearned revenue into earned revenue.
Zastosowanie informacji:
Understanding the distinction between unearned I earned revenue is crucial for investors and analysts when evaluating a company’s financial health. Unearned revenue represents a future obligation for the company, while earned revenue reflects actual performance. This information is useful for making informed investment decisions, as it indicates how much revenue a company has yet to earn and how efficiently it transitions this revenue to earned status.
C. Understanding Compensation and Benefits in the Workplace
Compensation goes beyond just salary—it includes korzyści such as health insurance, retirement contributions, bonuses, I stock options. When comparing job offers, it’s important to consider the entire compensation package. For instance, a job with a lower base salary but generous benefits may provide greater long-term value than a higher salary with few benefits.
Benefits like retirement plans Lub company-sponsored insurance can make a significant difference in overall financial security, so it’s essential to evaluate these offerings carefully. Workplace perks such as flexible working hours, paid leave, and professional development opportunities also play an important role in job satisfaction and career growth.
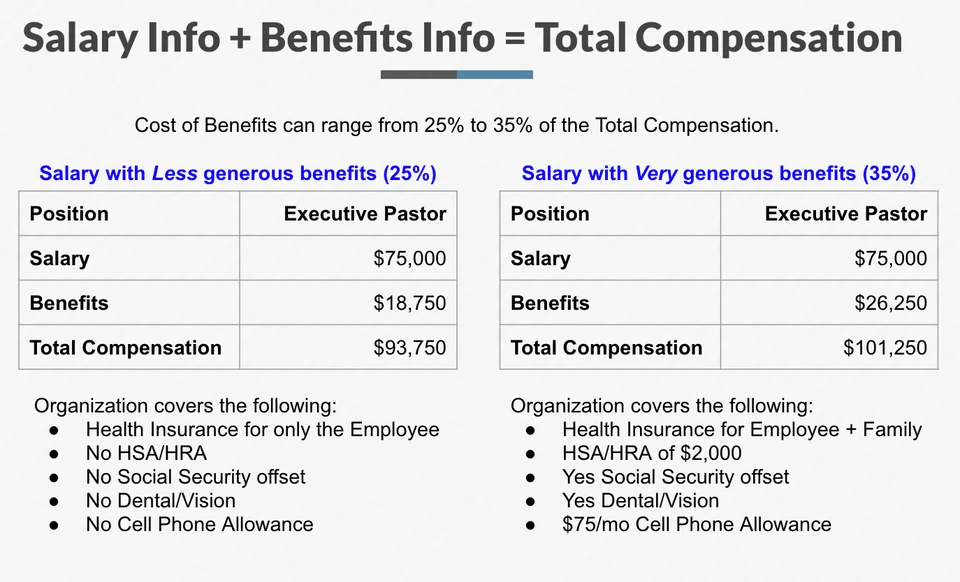
Postać: Salary Info + Benefits Info = Total Compensation
Opis:
This figure compares two compensation packages for the same position—Executive Pastor—with different benefit levels. The first column shows a salary of $75,000 with less generous benefits, totaling $93,750 in compensation when factoring in 25% benefit costs. The second column shows a more generous benefit plan at 35%, with the total compensation rising to $101,250. The image also lists the specific types of benefits covered in each scenario, such as health insurance, HSA/HRA, dental/vision, and cell phone allowances.
Najważniejsze wnioski:
- Total compensation includes both salary and benefits, which can range from 25% to 35% of total compensation.
- Benefits can significantly affect overall compensation, even when the base salary remains the same.
- Examples of benefits include health insurance, dental/vision coverage, HSA/HRA, I cell phone allowances.
- A more generous benefits plan leads to a higher total compensation package, adding significant value beyond just salary.
Zastosowanie informacji:
Understanding the difference between salary and total compensation helps both employees and employers make informed decisions. For investors, this information is essential when analyzing labor costs in companies, as benefits can represent a significant portion of employee expenses. Evaluating total compensation packages allows for a more comprehensive understanding of labor costs and competitiveness in the job market.
D. Vocational Training vs. College Education
One major decision individuals face is whether to pursue vocational training or a college degree. Vocational training typically offers a faster and more direct path to employment, with hands-on training for specific trades like plumbing, carpentry, or technical fields. It often comes with lower education costs and allows individuals to enter the workforce sooner.
On the other hand, a college education may open doors to a broader range of career opportunities and higher-paying positions, particularly in fields like engineering, healthcare, Lub business. However, it often requires a longer time commitment and greater financial investment.
Choosing between these two paths depends on an individual’s career goals, financial situation, and the job market demand in their chosen field.
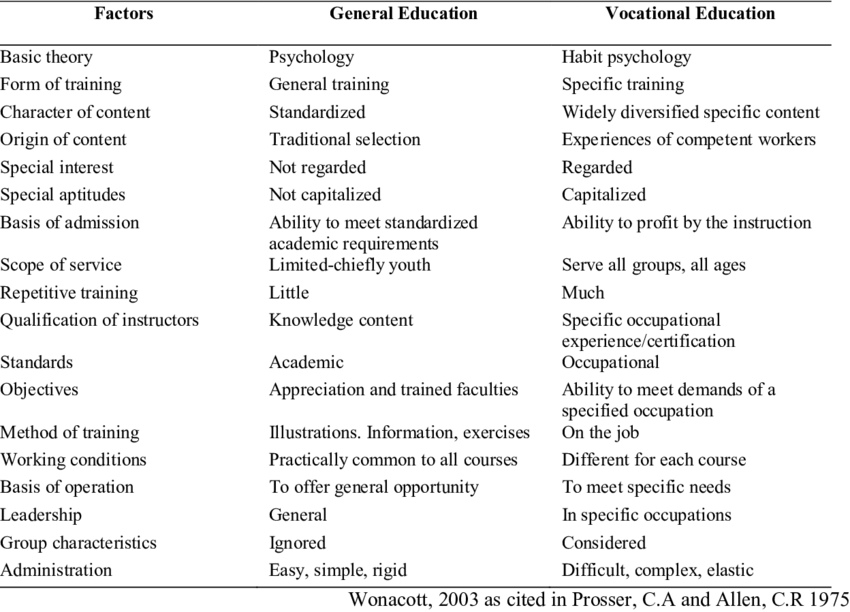
Postać: Comparison Between General Education and Vocational Education
Opis:
This figure compares General Education I Vocational Education across various factors such as training methods, content type, instructor qualifications, and student qualifications. General education emphasizes standardized content and academic theory, while vocational education focuses on specialized training and practical experience designed for specific occupations. The figure also contrasts the working conditions and objectives, where general education is often youth-focused and standardized, while vocational education serves all age groups with a focus on immediate job readiness.
Najważniejsze wnioski:
- General Education is broad, focusing on standardized academic content, while Vocational Education targets specific skills for direct employment.
- Vocational education is more practical, often involving hands-on or on-the-job training.
- Qualification of instructors differs: general education requires academic knowledge, whereas vocational education demands practical, job-specific experience.
- Ten scope of service for general education is typically limited to youth, while vocational education caters to all groups and ages.
Zastosowanie informacji:
This comparison highlights the distinct paths individuals can take in education based on their career goals. For investors and policymakers, understanding the differences between general and vocational education can guide decisions about resource allocation and workforce development. Focusing on vocational education could address immediate labor market needs by providing students with job-ready skills tailored to specific industries.
E. Entrepreneurship as a Career Choice
Entrepreneurship is an increasingly popular career choice, offering the potential for high income I personal freedom. However, it also comes with financial risk and uncertainty. Entrepreneurs must be prepared to invest time and resources into building a business, often without guaranteed income in the early stages.
Starting a business requires a thorough understanding of financial management, market analysis, I business planning. Entrepreneurs also need to be aware of regulations, taxes, I legal requirements in their country or region. While entrepreneurship can provide significant financial rewards and personal satisfaction, individuals must be prepared for the challenges I risks involved.

Figure: The Marketing Research Process
Opis:
The figure outlines the five steps of the Marketing Research Process. It begins with Identifying the problem, where the goals, objectives, and research questions are determined. Next, it moves to Developing the research plan, where information is gathered, methods are selected, and responsibilities are assigned. The third step is Conducting research, involving data collection through primary and secondary methods. In the fourth step, Analyze and report findings, data is formatted and analyzed to draw conclusions and recommendations. Finally, Taking action involves implementing the findings, adjusting the plan, and making decisions based on the research.
Najważniejsze wnioski:
- Identifying the problem is crucial to guiding the research effort.
- Ten research plan ensures all necessary methods and tools are chosen for data collection.
- Conducting research involves both primary and secondary data collection techniques.
- Analyzing and reporting is key for interpreting results and making recommendations.
- Taking action involves using the insights to make decisions and adjustments.
Zastosowanie informacji:
This marketing research process is fundamental for businesses and investors to make data-driven decisions. Understanding how to go from identifying a problem to taking action ensures efficient use of resources and targeted marketing strategies. Investors can apply this structured approach to analyze market trends, customer needs, and opportunities to optimize their investment decisions.
F. The Gig Economy
The rise of the gig economy has transformed the way people work. Gig workers, such as freelancers, independent contractors, I ride-share drivers, enjoy greater flexibility and control over their work schedules. However, gig workers often lack access to traditional employment benefits like health insurance I retirement contributions, and their income may be less stable.
Gig workers must manage their income and expenses carefully to account for fluctuations in earnings and the lack of a safety net. It’s also important for gig workers to save for taxes and plan for future expenses, as they are often responsible for paying their own income tax I self-employment tax.
The gig economy can provide a valuable source of additional income or serve as a full-time career path for those seeking flexibility. However, individuals must be prepared to navigate its financial challenges.

Postać: Gig Economy Pros and Cons
Opis:
This figure outlines the advantages and disadvantages of working in the gig economy. On the pros side, workers benefit from greater flexibility, more variety in tasks, increased independence, and a better work-life balance. However, the cons highlight irregular income, complex taxes, the absence of korzyści, I fewer professional connections. The visual split between pros and cons emphasizes the balance individuals must consider when deciding to participate in the gig economy.
Najważniejsze wnioski:
- Elastyczność I independence are significant advantages in the gig economy, allowing workers to control their schedules.
- Irregular income I complex tax situations make financial management more challenging.
- Gig workers often miss out on korzyści like health insurance and retirement plans.
- Professional connections may be harder to build due to fewer long-term relationships with companies.
Zastosowanie informacji:
This data is crucial for individuals considering a transition to the gig economy or investors looking to understand the dynamics of gig work. For financial planning, gig workers need to be prepared for irregular income and manage taxes carefully. This analysis can help potential gig workers weigh the pros and cons of this flexible but uncertain work environment.
Najważniejsze informacje dotyczące lekcji:
- Career choices depend on various factors, including income potential, stability, and personal passion. Balancing these elements helps users make well-informed decisions that align with their financial and personal goals. For example, some roles offer high income but come with more risk, while others provide steady income but less flexibility.
- Earned and unearned income have distinct sources and tax implications. Earned income comes from employment or self-employment, while unearned income comes from investments or rental properties. Understanding how to manage both types of income ensures financial growth and compliance with tax laws.
- Total compensation includes more than just salary. Benefits like health insurance, retirement contributions, and bonuses significantly impact overall earnings. Evaluating the full compensation package helps users make more informed decisions about job offers and long-term financial planning.
- Vocational training offers faster paths to employment, while college education may provide broader opportunities. Choosing between these options depends on an individual’s career goals, financial situation, and the job market demand. Vocational training can be ideal for specific skills, while college education may lead to higher-paying roles in fields like engineering or healthcare.
- The gig economy and entrepreneurship offer flexibility but come with income instability. Individuals in the gig economy must manage irregular income, plan for taxes, and compensate for the lack of traditional benefits. Understanding the pros and cons of gig work helps users decide whether it fits their financial needs and lifestyle.
Oświadczenie końcowe: This section equips users with the knowledge to make informed decisions about careers, income, and compensation. By understanding these concepts, users can better navigate career choices, manage different income types, and evaluate financial opportunities, whether through traditional employment, entrepreneurship, or gig work. This foundation sets the stage for financial growth and long-term stability.

