Local: Como funciona o mercado de ações?
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
- Introdução: Gain a fundamental understanding of how stock markets work in Europe, including the distinctions between exchange-based e over-the-counter (OTC) trading environments. This knowledge is crucial for anyone participating in or studying European financial markets.
- Aprenda sobre o regulatory frameworks such as MiFID II that govern these markets. Understanding these regulations helps ensure compliance and informs investment strategies within Europe.
- Explore the concept of fractional ownership through investment vehicles like UCITS (Undertakings for the Collective Investment in Transferable Securities). Recognizing how these funds work provides investors with opportunities for diversification and risk management.
- Understand the dynamics of supply and demand for stocks in Europe, influenced by EU-specific regulations, monetary policies, and broader economic factors. This insight is vital for making informed investment decisions.
3.1 How Does the Stock Market Work?
In Europe, stock exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) markets operate under distinct regulatory frameworks, with variations across EU countries. Stock exchanges such as Euronext, the London Stock Exchange (LSE), e Deutsche Börse are heavily regulated by both national authorities and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA). These exchanges provide a transparent, regulated environment where shares of companies are traded publicly.
OTC markets, on the other hand, allow for the direct trading of securities between two parties without the use of an exchange. In the EU, OTC markets are less strictly regulated than exchanges, but they are still subject to oversight under MiFID II, which aims to increase transparency and protect investors. Despite being less visible than traditional exchanges, OTC trading is vital for certain financial instruments, including bonds and derivatives. The level of regulation for OTC trading can vary between EU countries, but MiFID II ensures a common standard across member states.
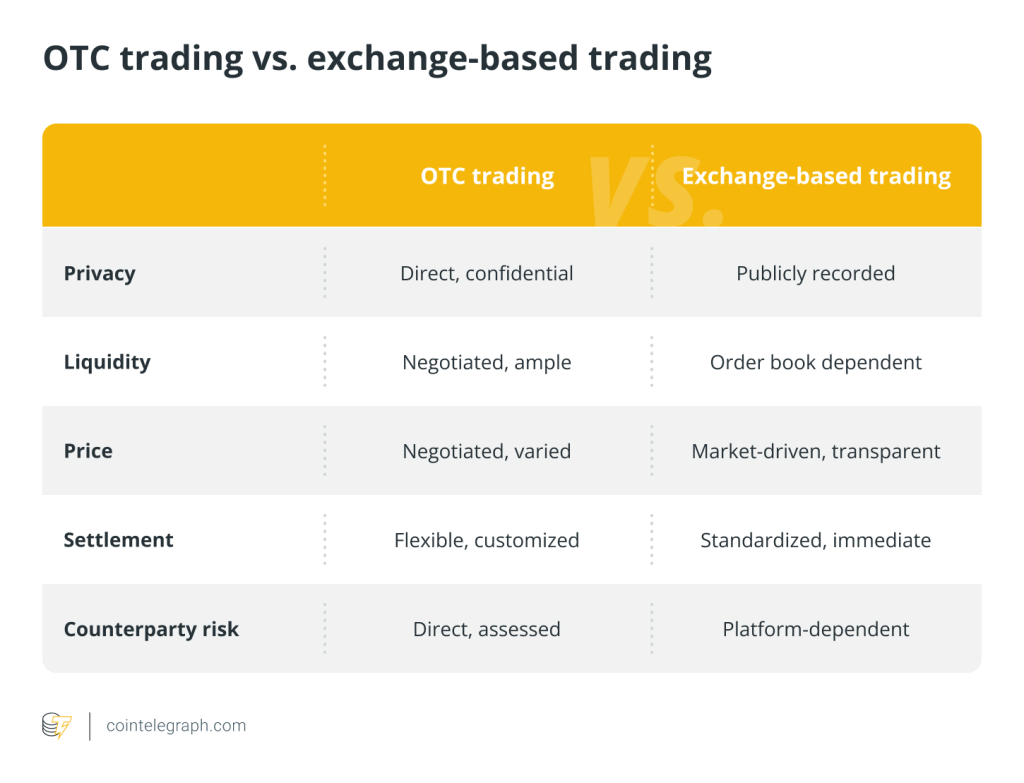
Figura: OTC Trading vs. Exchange-Based Trading
Descrição:
The image presents a comparison between Over-the-Counter (OTC) trading e exchange-based trading across five aspects: privacy, liquidity, price, settlement, e counterparty risk. OTC trading is characterized by direct and confidential transactions, negotiated liquidity and prices, flexible settlement, and direct counterparty risk assessment. In contrast, exchange-based trading involves publicly recorded transactions, liquidity based on order books, market-driven prices, standardized settlement, and platform-dependent counterparty risk.
Principais vantagens:
- Privacy: OTC offers direct and confidential transactions, while exchange-based trading is publicly recorded.
- Liquidity: OTC has negotiated and ample liquidity, whereas exchange-based trading relies on order books.
- Price: OTC prices are negotiated and varied, while exchange-based trading has transparent, market-driven prices.
- Settlement: OTC allows flexible and customized settlements, unlike the standardized, immediate settlements of exchanges.
- Counterparty risk: OTC involves direct risk assessment, whereas exchanges depend on platform-based risk management.
Aplicação de informações:
Understanding the differences between OTC and exchange-based trading helps investors decide the best approach based on their trading goals, tolerância de risco, e liquidity needs. This knowledge is valuable for traders evaluating where to buy or sell assets, considering factors like privacy, price flexibility, e settlement terms.
3.2 Ações como propriedade fracionária
In Europe, investors benefit from specific investment products that provide exposure to fractional ownership in companies. One of the most significant examples is UCITS (Undertakings for the Collective Investment in Transferable Securities), a regulatory framework that allows the creation of investment funds widely used across the EU. UCITS funds pool investors’ money to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, and other securities.
UCITS products are highly regulated, ensuring that investors have access to safe, transparent, and liquid investment vehicles. These funds must comply with strict guidelines imposed by ESMA and national financial authorities, making them a preferred choice for European investors. UCITS are particularly attractive to retail investors because they offer diversification, professional management, and a high degree of investor protection.

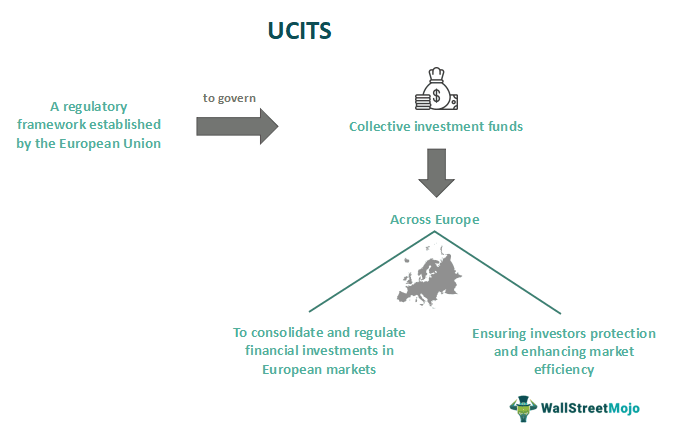
Figura: UCITS (Undertakings for the Collective Investment in Transferable Securities)
Descrição:
The image illustrates the UCITS framework, which is a regulatory system established by the European Union to manage collective investment funds across Europe. It emphasizes the consolidation and regulation of financial investments in European markets while ensuring investor protection and enhancing market efficiency. The framework governs investment funds to maintain a consistent and secure financial environment throughout Europe.
Principais vantagens:
- UCITS is a regulatory framework created by the European Union.
- It governs collective investment funds across Europe, ensuring consistent regulation.
- The main objectives are to protect investors, enhance market efficiency, e regulate financial investments.
- UCITS funds offer transparency, liquidity, and safety, making them popular among European investors.
Aplicação de informações:
Entendendo o UCITS framework helps investors identify regulated investment opportunities in Europe. It provides insights into the benefits of investing in UCITS funds, which are known for their safety, transparency, e consistent regulation. This information is useful for investors seeking secure and regulated options in the European financial market.
3.3 Companies, Supply, and Demand for Stock

The supply and demand for stocks in Europe are shaped not only by general market forces but also by EU-specific regulations and policies. For instance, MiFID II and national regulatory frameworks govern key aspects of trading, such as short-selling, margin requirements, and trade transparency. These regulations help maintain orderly markets and ensure investor protection across the EU.
European monetary policies also play a role in influencing stock market supply and demand. For example, actions taken by the European Central Bank (ECB), such as adjusting interest rates or implementing quantitative easing, can directly affect liquidity in the market. Additionally, national policies, such as tax incentives for long-term investments or pension fund regulations, impact how companies issue stock and how investors respond in terms of buying and selling shares.
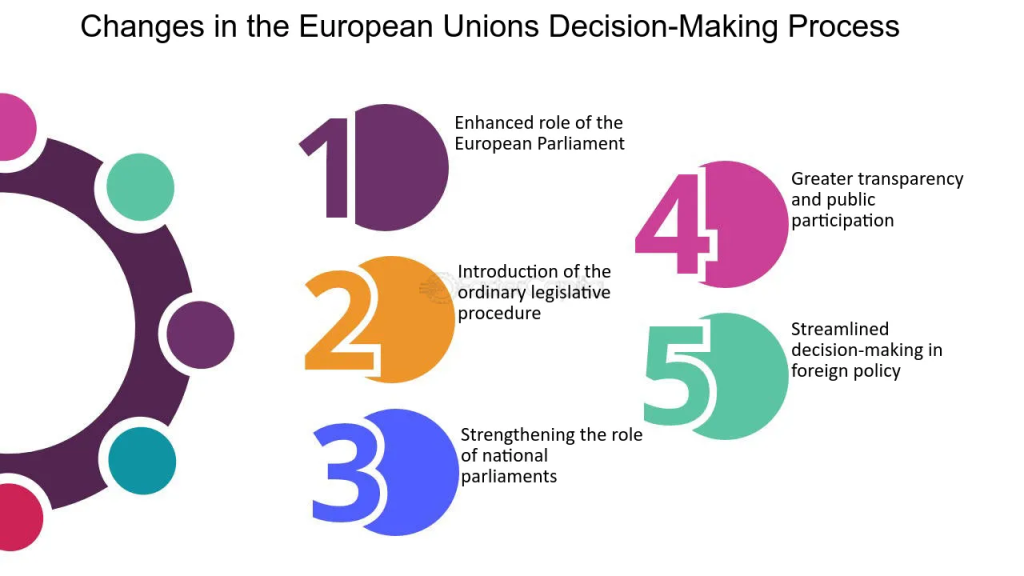
Figura: Changes in the European Union’s Decision-Making Process
Descrição:
The image outlines five significant changes in the European Union’s decision-making process. These include the enhanced role of the European Parliament, the introduction of the ordinary legislative procedure, strengthening the role of national parliaments, increasing transparency and public participation, and the streamlining of decision-making in foreign policy. Each step aims to improve efficiency, inclusivity, and accountability in EU governance.
Principais vantagens:
- Enhanced role of the European Parliament aims to increase its influence in the decision-making process.
- O ordinary legislative procedure helps standardize and simplify law-making.
- National parliaments play a more significant role in shaping EU policies.
- The changes encourage greater transparency and public participation in EU decision-making.
- There is a focus on streamlining foreign policy decisions to enhance responsiveness.
Aplicação de informações:
Understanding these changes in the EU’s decision-making process helps investors and businesses comprehend the evolving regulatory environment. For those involved in European markets, this knowledge is crucial for navigating policy impacts, anticipating legislative shifts, and aligning strategies with the EU’s governance framework.
Principais informações da lição:
- European stock markets operate through both regulated exchanges e OTC markets, each with its own set of rules and characteristics. Exchanges offer a transparent trading environment, while OTC markets provide flexibility and privacy.
- Regulatory frameworks like MiFID II play a critical role in ensuring transparency and protecting investors in European markets. They standardize practices across EU countries, making it easier to navigate the investment landscape.
- UCITS funds offer a highly regulated, transparent, and liquid investment option in Europe, making them attractive to investors looking for diversified and managed investment solutions.
- O supply and demand for stocks are significantly shaped by regulatory and monetary policies. For instance, decisions by the European Central Bank can directly influence market liquidity and stock prices.
Declaração de encerramento
By understanding the operational mechanisms of stock markets in Europe, the regulatory environment, and investment frameworks like UCITS, you are better equipped to engage with the European financial markets effectively. This foundational knowledge helps in crafting strategies that align with regulatory requirements and market conditions, enhancing investment success in Europe.