Local: Understanding Tax Obligations and Planning
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
Introdução:
This section emphasizes the importance of understanding tax obligations and planning for managing personal finances effectively. By exploring the basics of EU tax systems, this section aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed financial decisions while maximizing potential tax savings.
- Understand why taxes are collected and how they are used. By knowing the purpose behind tax collection, you’ll learn how taxes support public services and infrastructure, making you more aware of your role in sustaining society. This insight helps you appreciate tax contributions and their impact on national priorities.
- Recognize the consequences of failing to pay taxes. You’ll discover the potential penalties for tax evasion, such as fines, legal actions, and credit damage. This understanding encourages compliance with tax laws, avoiding severe financial and legal consequences.
- Learn to monitor and manage tax obligations. You’ll become familiar with different taxes, like income tax, VAT, and property tax, and learn how to use online tools to manage your tax responsibilities. This knowledge enables proactive tax management and helps avoid unexpected liabilities.
- Explore tax treatments of financial products. You’ll understand how taxes apply to mortgages, pensions, and savings. By knowing how these products are taxed, you can strategically plan to minimize tax burdens and maximize tax benefits over the long term.
- Integrate tax considerations into budgeting. You’ll learn how to factor in taxes when creating budgets and planning for savings, investments, and retirement. This strategic approach ensures that taxes are accounted for, contributing to overall financial stability.
Introdução
Tax planning is an essential part of managing personal finances effectively, ensuring compliance with tax obligations while maximizing opportunities for tax savings. This chapter explores the fundamentals of tax systems in the EU, including income tax, VAT, and corporate taxes, and provides insights into managing taxes on financial products like mortgages, pensions, and savings. By understanding the tax implications of financial decisions and utilizing online tax services, individuals can stay compliant and minimize tax liabilities. Strategic tax planning also plays a key role in long-term financial health, helping individuals integrate tax considerations into their budgeting and investment decisions.
Why Taxes Are Collected and How They Are Used
Taxes are mandatory financial charges imposed by governments to fund public services and infrastructure. Taxes support essential services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and social welfare programs. In the EU, tax revenues are also used to finance EU-wide initiatives such as environmental protection, research, and regional development. Understanding why taxes are collected helps citizens appreciate the role they play in maintaining a functioning society.
For example, income tax funds healthcare and education services, while value-added tax (VAT) on goods and services helps pay for transportation infrastructure and public safety.
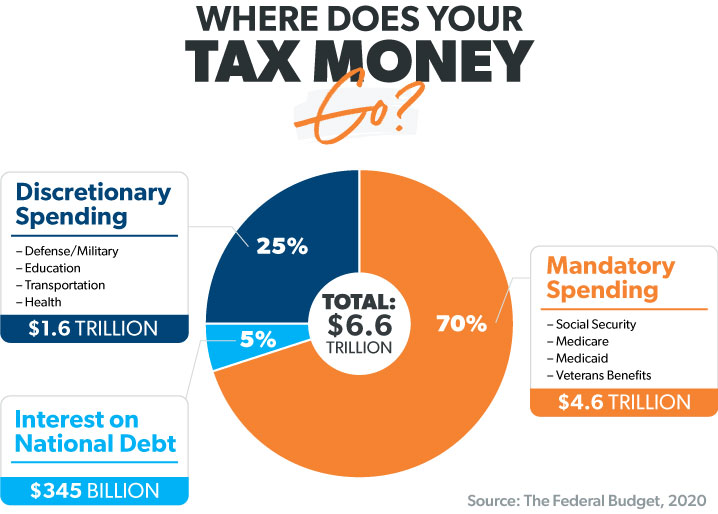
Figura: Where Does Your Tax Money Go?
Descrição:
The article from Ramsey Solutions breaks down the allocation of federal taxes collected by the IRS, which amounted to around $4.9 trillion in 2022. It explains the distribution of tax dollars across various government expenditures, including interest on government debt, mandatory spending on entitlement programs like Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, and Veterans Affairs benefits, as well as discretionary spending, which covers national defense, transportation, education, health, and more.
Principais vantagens:
- A portion of tax dollars is used to pay interest on the national debt.
- Mandatory spending includes significant entitlement programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
- Discretionary spending involves budget allocations that Congress debates annually, including defense, transportation, education, and health.
Aplicação de informações:
For individuals learning about personal finance, this breakdown provides insight into how government budgeting works and the importance of understanding where tax dollars are spent. It can inform decisions around political engagement and fiscal responsibility. For investors, knowing the areas of government spending can guide investment strategies, as sectors receiving significant funding may present investment opportunities. Understanding these allocations also helps taxpayers see the impact of their contributions on national priorities and services.
Consequences of Failing to Pay Taxes
Failure to pay taxes can result in severe legal and financial consequences. Individuals who do not comply with their tax obligations may face penalties such as fines, interest on unpaid taxes, and in extreme cases, legal action including imprisonment. Tax authorities across the EU are empowered to enforce tax laws rigorously, and not paying taxes can result in a damaged credit rating, wage garnishments, and the seizure of assets.
For example, in countries like Germany and France, tax evasion is a criminal offense, and those found guilty can face significant fines or even imprisonment.

Figura: The Consequences of Tax Evasion
Descrição:
The figure lists five significant consequences that individuals and businesses may face if they engage in tax evasion. These include financial penalties, garnished wages, seizure of assets, criminal charges, e damage to reputation. These outcomes highlight the serious legal and financial repercussions of failing to comply with tax regulations.
Principais vantagens:
- Financial penalties can be substantial, adding to the overall cost of evading taxes.
- Garnished wages allow authorities to recover owed taxes directly from income.
- Seizure of assets ensures that unpaid taxes are collected through property confiscation.
- Criminal charges may lead to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the evasion.
- Damage to reputation can affect personal and business relationships and opportunities.
Aplicação de informações:
Understanding these consequences encourages individuals and businesses to comply with tax laws and seek legal ways to optimize taxes instead of evading them. For investors, awareness of these risks helps in making informed decisions and encourages ethical financial practices to avoid severe legal and financial repercussions.
Checking and Monitoring Tax Obligations
It is essential for individuals to be aware of their tax obligations and to monitor them regularly. This includes understanding income tax, property tax, VAT, and any other taxes applicable based on one’s employment, property ownership, or consumption. Many EU countries provide online tax services to help individuals check their tax obligations, calculate the taxes they owe, and file their returns. Being aware of deferred tax obligations, such as taxes on pension withdrawals or investment gains, is also crucial for long-term planning.
For example, in Italy, online tax portals allow taxpayers to view their tax statements, track payments, and file annual returns, simplifying the tax management process.
Figura: e-Filing Portal Overview
Descrição:
The image shows the homepage of the e-Filing portal of the Income Tax Department of India, which allows users to manage various tax-related tasks online. Key features include options to e-verify returns, link Aadhaar, pay taxes, and check the status of Income Tax Returns (ITRs). The portal provides links to essential tools and updates, making tax filing and management more accessible for taxpayers.
Principais vantagens:
- e-Filing portal simplifies tax management, providing tools for e-verification, linking Aadhaar, and online tax payment.
- Quick access to essential features like ITR status, tax calendar, and PAN verification helps users stay updated.
- Latest updates section keeps users informed about new deadlines and requirements.
- User-friendly interface aims to streamline the process of managing taxes online.
Aplicação de informações:
This portal is useful for individuals and businesses to manage their tax compliance easily without needing to visit physical tax offices. Investors can use this platform to ensure they are up to date with their tax payments and filings, thus avoiding penalties and legal issues.
Understanding Basic Taxes (Income Tax, VAT, etc.)
Every EU country collects various types of taxes, and it’s important to understand the basic ones, including:
- Income tax: Charged on personal earnings from employment, investments, or business activities.
- Value-added tax (VAT): Applied to the purchase of goods and services. VAT rates differ across EU countries, but it is a standard consumption tax across the region.
- Corporate tax: Levied on the profits of businesses, impacting individuals who own or invest in companies.
For instance, income tax rates in the EU vary widely, with countries like Belgium and Sweden imposing some of the highest rates, while countries like Bulgaria and Hungary have flat and lower income tax rates. Understanding these differences helps individuals make informed decisions, especially for long-term financial planning.
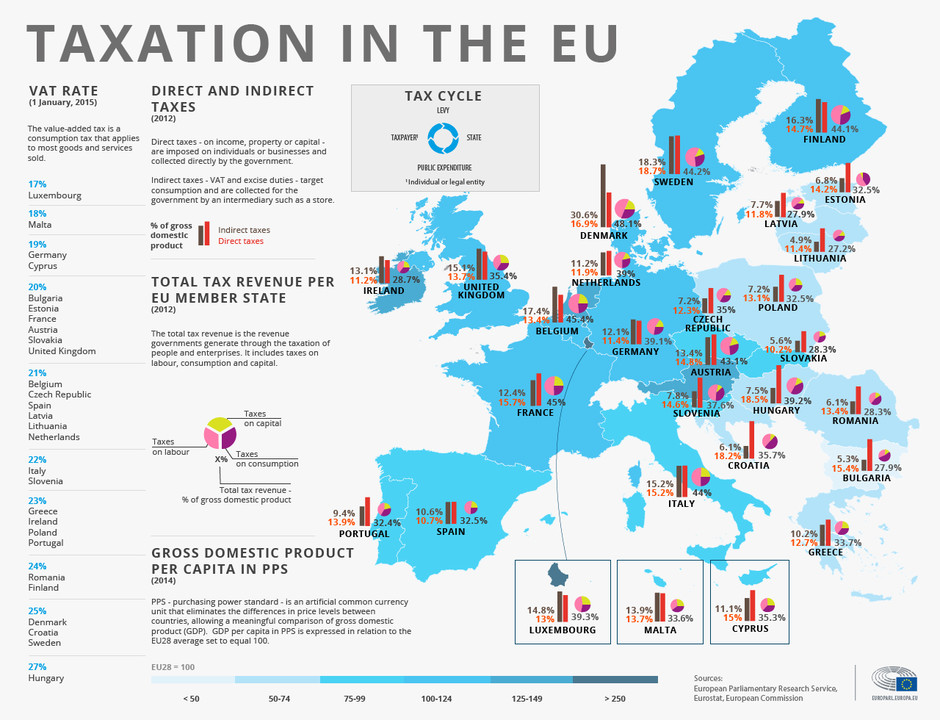
Figure: Taxation in the EU
Descrição:
The image displays a detailed overview of taxation across the European Union (EU), highlighting VAT rates, direct and indirect taxes, and the tax revenue as a percentage of GDP for each member state. It illustrates how different countries generate revenue from taxes on labor, capital, and consumption. The map uses graphical indicators to show variations in tax revenue, providing a comparison of tax structures across nations.
Principais vantagens:
- VAT rates vary across EU countries, with the lowest in Luxembourg (17%) and the highest in Hungary (27%).
- Tax revenue as a percentage of GDP indicates the overall tax burden, showing how different countries rely on taxation.
- Direct vs. indirect taxes are represented, illustrating which countries lean more towards direct (income-based) or indirect (consumption-based) taxation.
- GDP per capita (PPS) information shows economic disparity across the EU, providing context to tax policies.
Aplicação de informações:
Understanding taxation structures in the EU helps investors evaluate economic environments for business expansion or investment. Knowing VAT rates and tax revenue sources allows individuals and companies to make informed decisions about cost structures e potential returns when operating in different EU nations.
Tax Treatments of Financial Products (Mortgages, Pensions, Savings)
Different financial products such as mortgages, pensions, e savings often receive varying tax treatments in the EU. For example, interest payments on mortgages may be tax-deductible in some countries, while pension contributions might qualify for tax deferrals until retirement. Understanding how these products are taxed helps individuals maximize tax benefits and avoid unnecessary tax burdens.
For instance, in countries like the Netherlands, mortgage interest payments are tax-deductible, reducing the taxable income of homeowners, while in other countries, pension contributions may be deferred until withdrawal.
Managing Taxes and Budgeting
Incorporating tax obligations into personal budgeting and long-term financial plans is essential for financial stability. Individuals need to take into account income taxes, VAT, and other taxes when planning their annual budgets, making long-term investment decisions, or saving for retirement. This also involves keeping track of tax refunds and ensuring that any overpaid taxes are claimed back in a timely manner.
For example, if a person in Spain is saving for retirement, they might consider pension products that offer tax deferral benefits, helping reduce their current taxable income and allowing them to invest more for the future.
Figure: Financial Obligations and Misc. Payments
Descrição:
The figure shows a table listing different financial obligations, including long-term savings, retirement contributions, credit card payments, and additional income tax. It also includes a section for miscellaneous payments, where users can add other types of payments not covered in the previous section. Each row allows for the entry of values, with totals calculated at the bottom, helping individuals track their expenses and savings.
Principais vantagens:
- Financial tracking is simplified by categorizing different types of payments and obligations.
- Retirement contributions and savings are clearly listed to help users plan for the future.
- Credit card and additional taxes sections emphasize the importance of managing regular financial commitments.
- Miscellaneous payment slots provide flexibility for users to add unique expenses that may not fit standard categories.
Aplicação de informações:
This table is useful for anyone looking to organize and manage their finances by keeping track of essential obligations and miscellaneous payments. By regularly updating and reviewing these sections, users can ensure their expenses do not exceed their income and plan for long-term financial stability.
Utilizing Online Tax Services
Most EU tax administrations provide online services that simplify the process of managing taxes. These platforms allow taxpayers to file tax returns, pay taxes, monitor outstanding obligations, and access tax documents. Individuals should become familiar with these tools to efficiently manage their tax responsibilities. These services can often save time and reduce errors, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
For example, in France, taxpayers can use the impots.gouv.fr platform to manage their taxes entirely online, from filing returns to paying any owed amounts.
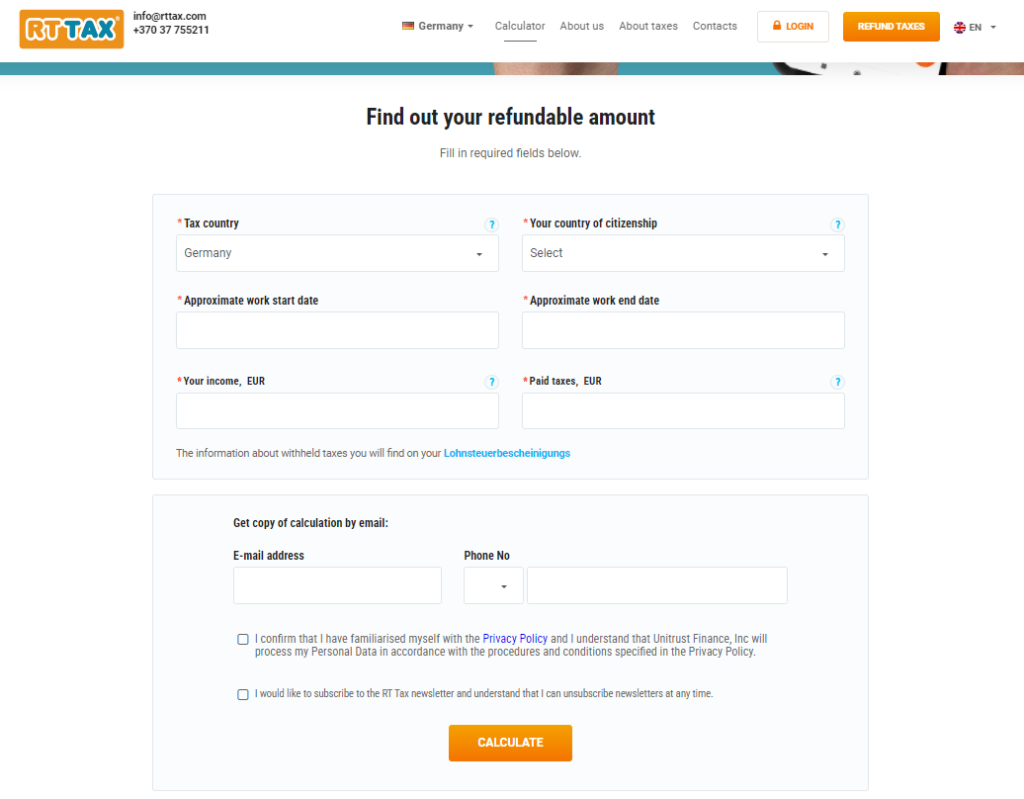
Accepting the Importance of Paying Taxes
It is important to acknowledge that paying taxes is a fundamental civic responsibility. By contributing to tax revenues, individuals help support the public services that benefit society as a whole, including healthcare, infrastructure, and education. Accepting the importance of paying taxes ensures that citizens play their part in maintaining a functioning economy and government, while also protecting themselves from legal consequences.

Figura: Where Does Your Tax Money Go?
Descrição:
The article from Ramsey Solutions breaks down the allocation of federal taxes collected by the IRS, which amounted to around $4.9 trillion in 2022. It explains the distribution of tax dollars across various government expenditures, including interest on government debt, mandatory spending on entitlement programs like Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, and Veterans Affairs benefits, as well as discretionary spending, which covers national defense, transportation, education, health, and more.
Principais vantagens:
- A portion of tax dollars is used to pay interest on the national debt.
- Mandatory spending includes significant entitlement programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
- Discretionary spending involves budget allocations that Congress debates annually, including defense, transportation, education, and health.
Aplicação de informações:
For individuals learning about personal finance, this breakdown provides insight into how government budgeting works and the importance of understanding where tax dollars are spent. It can inform decisions around political engagement and fiscal responsibility. For investors, knowing the areas of government spending can guide investment strategies, as sectors receiving significant funding may present investment opportunities. Understanding these allocations also helps taxpayers see the impact of their contributions on national priorities and services.
Principais informações da lição:
- Taxes support essential public services. Taxes fund healthcare, education, infrastructure, and social welfare programs, contributing to the overall well-being of society. Recognizing this helps you understand the broader impact of your tax payments on public services and initiatives, enhancing civic responsibility.
- Failure to pay taxes has severe consequences. Not paying taxes can result in financial penalties, asset seizures, wage garnishments, and even legal action. Understanding these consequences encourages you to comply with tax regulations and seek legal ways to optimize tax payments.
- Monitoring tax obligations helps prevent issues. Regularly checking tax obligations, using online tools, and keeping track of deferred taxes are critical steps in staying compliant. This proactive approach prevents surprises and helps you manage taxes efficiently, ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties.
- Tax treatments vary by financial product. Mortgages, pensions, and savings have different tax implications across the EU. By understanding these differences, you can make better financial decisions, choosing products that align with your tax strategy and financial goals.
- Tax-efficient budgeting leads to long-term stability. Incorporating taxes into your budget and financial planning ensures you’re prepared for all obligations. This approach allows for better savings, informed investment decisions, and sustainable financial health.
- Online tax services simplify compliance. Digital tax platforms provide tools for filing returns, paying taxes, and accessing documents easily. Utilizing these services can save time, reduce errors, and ensure timely compliance, making tax management more convenient and less stressful.
Declaração de encerramento: Understanding tax obligations and planning effectively is crucial for financial success. By recognizing the importance of taxes, complying with regulations, and using strategic planning, you can maintain financial stability and contribute positively to society. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions, ensuring that tax considerations are seamlessly integrated into your financial planning.