Conteúdo Global: Compreendendo as Leis e Regulamentos de Zoneamento em Todo o Mundo
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
- Understand how zoning laws work around the world and how they shape land use, building types, e urban development. You’ll explore examples from cities like Nova Iorque, Cingapura, e Melbourne to see how zoning impacts real estate projects.
- Learn how to obtain permits and pass inspections across different global regions. You’ll gain insight into the application process, safety requirements, and how to meet environmental and building code standards in countries like Canadá, Dubai, e Japão.
- Discover key challenges in zoning, incluindo regional differences e restrictions in historical or environmentally sensitive areas, like Londres ou Kyoto. You’ll learn how to plan ahead and reduce risks in these situations.
- Explore best practices for managing global zoning laws, como working with local professionals, understanding local building codes, e keeping up with regulatory changes to stay compliant and improve project success.
A. Understanding Zoning Laws and Regulations Globally
Understanding Zoning Laws and Regulations Globally
Zoning laws define how land can be used and developed, and these regulations vary significantly across the world. Understanding local zoning laws is crucial for investors to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
- Estados Unidos: No U.S., zoning laws are managed at the municipal level, with areas designated for residential, commercial, industrial, or mixed-use purposes. In cities like Nova Iorque e Los Angeles, zoning regulations may also dictate building heights, parking requirements, and green space allocation.
- Cingapura: Em Cingapura, zoning regulations are part of the Master Plan, which designates specific areas for residential, commercial, and industrial use. The government tightly controls land use to ensure sustainable urban development, and any deviation from the Master Plan requires approval from the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA).
- Austrália: Em Austrália, zoning laws are controlled by local governments. Cities like Sydney e Melbourne have strict zoning regulations that dictate land use, building heights, and density. Investors must work with local councils to ensure compliance with zoning restrictions.
Challenges in Understanding Zoning Globally
- Regional Differences: Zoning laws differ widely between countries and even within cities. Investors must understand the specific zoning requirements in the area they are targeting.
- Environmental and Historical Protections: In global cities with historical or environmental protections, such as Kyoto ou Londres, zoning laws may restrict the types of developments allowed in certain areas.
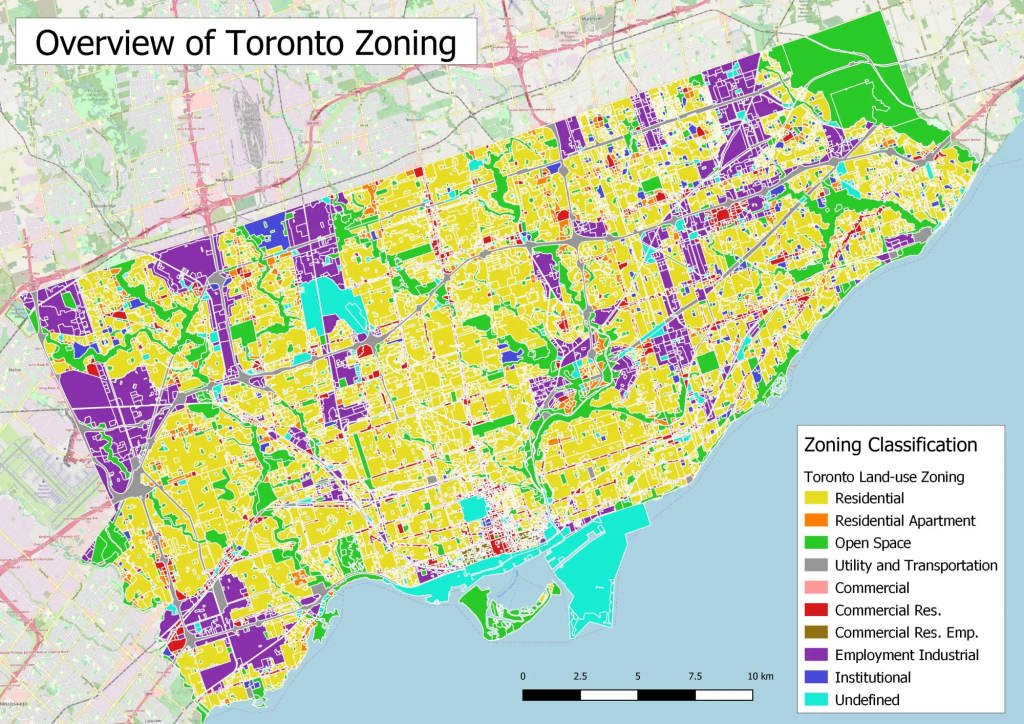
Figura: Diversidade nas leis de zoneamento de Toronto
Descrição:
A imagem fornece uma representação visual das leis de zoneamento de Toronto, categorizadas por diferentes tipos de uso do solo. Esses tipos incluem residencial, residencial para apartamentos, espaço aberto, serviços públicos e transporte, comercial, comercial residencial, industrial para empregos, institucional e zonas indefinidas. O mapa provavelmente destaca a distribuição dessas zonas por Toronto, oferecendo informações sobre o planejamento urbano e os padrões de desenvolvimento da cidade.
Principais conclusões:
- Zoneamento diversificado: As normas de zoneamento de Toronto exibem uma mistura de áreas residenciais, comerciais, industriais e espaços abertos, refletindo a paisagem urbana multifacetada da cidade.
- Áreas de Alta Diversidade: Regiões como Beaches e East York exibem uma rica mistura de tipos de zoneamento, incluindo áreas residenciais, industriais, espaços verdes e zonas comerciais.
- Áreas de baixa diversidade: Certas áreas de Toronto, especialmente a oeste da Yonge Street e ao sul da Allen Road, apresentam predominantemente habitações residenciais de baixa densidade, indicando menor diversidade de zoneamento.
- Importância dos centros comerciais: Centros comerciais regionais como Sherway Gardens, Yorkdale e Scarborough Town Center são polos de zoneamento diversificado devido à sua mistura de zonas comerciais, residenciais e industriais, juntamente com redes de transporte.
Aplicação da Informação:
Compreender a diversidade do zoneamento de Toronto é crucial para planejadores urbanos, incorporadores e formuladores de políticas. Isso oferece informações sobre os padrões de crescimento da cidade, as necessidades de infraestrutura e as áreas com potencial para desenvolvimento ou revitalização. Para investidores e empresas, esse conhecimento pode orientar decisões relacionadas a investimentos imobiliários, localização de negócios e compreensão dos padrões demográficos e econômicos de zonas específicas.
B. Navigating Permits and Inspections Globally
Navigating Permits and Inspections Globally
Obtaining permits and passing inspections are essential steps in real estate development globally. Different countries have their own regulations and processes for ensuring that developments comply with local laws.
- Estados Unidos: No U.S., developers must obtain building permits from local authorities before starting construction. In cities like São Francisco ou Chicago, permits are required for new construction, renovations, and changes in land use. Inspectors conduct regular site visits to ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards.
- Canadá: Em Canadá, the permit process varies by province and municipality. Cities like Toronto require detailed applications that include site plans, environmental impact assessments, and fire safety compliance before construction can begin.
- Dubai: Em Dubai, developers must obtain approvals from the Dubai Municipality and other relevant authorities before starting a project. Regular inspections ensure that construction adheres to local building codes and safety requirements, including fire safety and structural integrity.
Inspection Requirements Globally
- Permit Approvals: Globally, developers must secure various permits before breaking ground on a project. In Japão, for instance, developers must submit detailed site plans and comply with strict earthquake safety regulations before receiving building approval.
- On-Site Inspections: Throughout the construction process, local authorities conduct inspections to ensure that the building complies with safety standards. In Cingapura, inspectors check for compliance with building codes, fire safety, and environmental regulations at key stages of construction.
C. Best Practices for Navigating Zoning and Land Use Regulations Globally
Best Practices for Navigating Zoning and Land Use Regulations Globally
Navigating zoning laws and land use regulations requires a thorough understanding of local rules and proactive engagement with authorities.
- Work with Local Professionals: In global markets, partnering with local architects, planners, and legal experts is essential. In Hong Kong, for example, navigating zoning regulations requires close coordination with local professionals familiar with government land use plans.
- Understand Local Building Codes: Each country has its own building codes and standards. In cities like Nova Iorque ou Toronto, developers must ensure that their projects meet specific requirements for fire safety, accessibility, and structural integrity.
- Plan for Environmental and Historical ConsiderationsEm mercados como Kyoto ou Roma, zoning regulations may include additional requirements for preserving historical landmarks or protecting natural resources. Investors should factor these considerations into their project timelines and budgets.
- Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Zoning laws can change over time, particularly in rapidly developing cities like Dubai ou Xangai. Staying informed about local zoning and land use changes can help investors capitalize on new opportunities or avoid potential regulatory pitfalls.
Conclusão
Understanding zoning laws and land use regulations is essential for successful real estate investment, both in Europe and globally. By navigating permits and inspections effectively, working with local professionals, and staying informed about zoning changes, investors can ensure compliance and avoid costly delays. These best practices provide a roadmap for managing the legal and regulatory complexities of real estate development in any market.
Informações importantes da lição:
- Zoning laws determine land use, such as whether an area is for residential, commercial, ou industrial purposes. Countries like the U.S., Cingapura, e Austrália have detailed zoning systems, with rules that may also control building height, parking, e green space.
- Zoning requirements vary widely between countries and cities. In places like London or Kyoto, additional rules apply to preserve historical architecture e natural areas, limiting what can be built and how it’s designed.
- Understanding local zoning maps helps investors spot diverse land-use areas and growth potential. For example, Toronto’s zoning diversity offers a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial zones, especially near shopping centers and transport hubs.
- Permits are required before construction, and the process can be detailed. In São Francisco ou Toronto, developers must submit site plans, environmental assessments, e safety documents to get approval.
- Regular inspections during construction ensure that buildings meet local segurança, fire, e environmental standards. Cities like Singapore and Dubai conduct multiple inspections at different stages to maintain compliance.
Declaração de Encerramento:
Whether you’re a developer, investor, or planner, understanding zoning and permit processes globally helps you protect your investments, ensure legal compliance, and adapt your strategies to fit local needs. This knowledge is key for avoiding costly mistakes and building responsibly.