Global Content : Retail Properties Globally
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
- Understand how each commercial property type operates globally—from retail hubs in New York to logistics centers in Shanghai—highlighting the unique dynamics and revenue models behind each asset class.
- Compare international performance trends using real-world figures and data visuals that show vacancy rates, hotel occupancy, industrial development stages, and prime retail rents.
- Analyze benefits and challenges across sectors, such as high returns in luxury retail zones, or the impact of remote work on office demand, providing a balanced understanding of risk and reward.
- Identify how global events and regional policies—like e-commerce growth or tourism shifts—affect property values and investment strategies.
A. Retail Properties Globally
Retail property investments globally focus on shopping centers, high street retail, and standalone shops. Cities like New York, Dubai, e Hong Kong are known for their lucrative retail markets, where premium locations attract international luxury brands.
How it Works
Investors purchase or lease retail properties in high-traffic areas and lease them to retail businesses. Retail properties in major global cities command high rents, especially in high-demand areas like 5th Avenue in New York or Orchard Road in Singapore.
B. Office Properties Globally
Office properties are a mainstay of commercial real estate investment, particularly in business hubs like New York, Tokyo, e London. The global office market has been affected by the shift towards remote work, but demand remains strong in financial and tech centers.
How it Works
Investors buy or lease office buildings in major business districts and rent them to corporations. Office properties in global cities are typically leased on long-term contracts, providing stable cash flow.
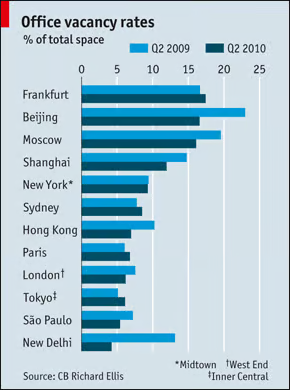
Figura: Office Vacancy Rates by City
Descrição:
Descrição:
This bar chart shows office vacancy rates as a percentage of total office space across global cities for two time periods: Q2 2009 e Q2 2010. Cities like Beijing, Frankfurt, e Moscow exhibit the highest vacancy rates, while Paris, London, e Tokyo report much lower rates. The data highlights year-over-year changes, with some cities experiencing increased vacancies, such as New Delhi, and others showing relative stability. This figure enables viewers to assess the state of office space utilization across major global cities during this period.
Principais conclusões:
- Beijing e Frankfurt reported some of the highest office vacancy rates during this period, exceeding 20%.
- New Delhi saw a notable increase in vacancy rates from Q2 2009 to Q2 2010.
- London e Paris maintained relatively low vacancy rates, reflecting steady demand for office space in these cities.
- The chart reflects the impact of economic conditions, as some markets, like Shanghai, saw reduced vacancies, signaling recovery or growth.
- Cities with high vacancy rates indicate oversupply or weakened demand, while lower rates suggest higher office space utilization.
Application of Information:
Understanding office vacancy rates is essential for real estate investors e corporate decision-makers looking to expand operations. High vacancy rates may signal an opportunity for negotiating lower rents or identifying underperforming areas, whereas low vacancy rates highlight prime investment locations with strong demand. This data is valuable for analyzing market health, particularly in times of economic recovery or stress, allowing investors to make more informed decisions.
C. Industrial Properties Globally
Industrial properties, including warehouses and manufacturing facilities, are essential for global trade and e-commerce. Cities like Los Angeles, Shanghai, e Dubai have thriving industrial real estate markets driven by logistics and distribution.
How it Works
Investors purchase or lease industrial properties and lease them to logistics and manufacturing companies. Industrial properties near major ports and transportation hubs are particularly valuable.
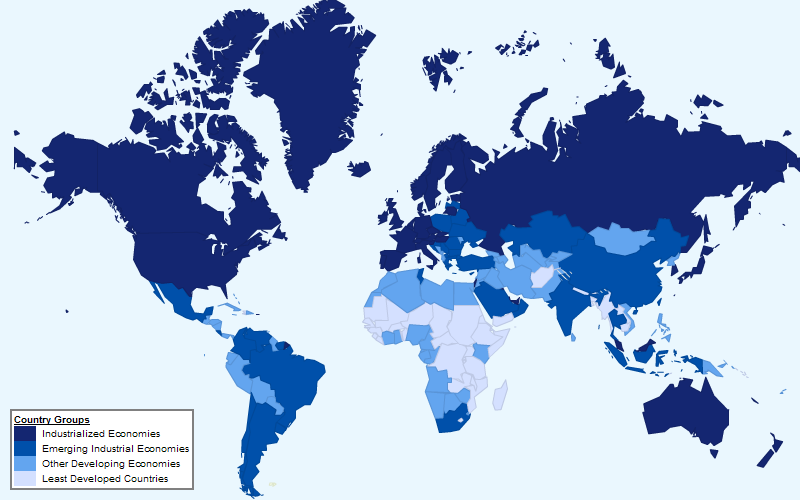
Figura: Country Groups by Stage of Industrialization
Descrição:
This map categorizes countries based on their stage of industrialization into four groups: Industrialized Economies, Emerging Industrial Economies, Other Developing Economies, e Least Developed Countries. Darker blue shades represent more advanced economies, while lighter shades signify less developed stages. For instance, countries in North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are shown as industrialized, while parts of Africa e South Asia fall under the least developed category. The map provides a clear visual breakdown of global industrial development patterns.
Principais conclusões:
- Industrialized economies (dark blue) include countries like the United States, Germany, e Japan, reflecting high levels of economic and industrial development.
- Emerging industrial economies (medium blue) include regions like China, India, e Brazil, indicating rapid industrial growth.
- Developing economies (light blue) are scattered across regions like South America and parts of Southeast Asia, showing moderate progress.
- Least developed countries (very light blue) are predominantly in Africa and parts of South Asia, highlighting economic and industrial challenges.
- The map provides a visual representation of economic disparities and the varying stages of development globally.
Application of Information:
This data is crucial for investors e business leaders to identify regions with potential for growth or requiring specific investment strategies. For instance, emerging industrial economies may offer opportunities for investment in infrastructure, technology, or manufacturing. Understanding these industrialization stages helps individuals and organizations align their investment strategies with regional economic conditions, ensuring better-informed decisions.
D. Hospitality Properties Globally
Hospitality properties are hotels, resorts, and serviced apartments in global tourist and business destinations like Paris, Dubai, e Las Vegas. The hospitality sector is heavily influenced by tourism and global events.
How it Works
Investors acquire hospitality properties and generate income through hotel room rentals, event hosting, and dining services. Demand is driven by both leisure and business travel.
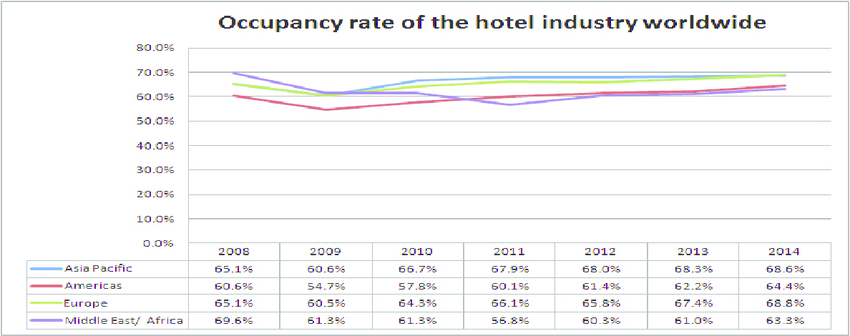
Figura: Occupancy Rate of the Hotel Industry Worldwide
Descrição:
This line chart depicts the occupancy rates of the hotel industry across different regions—Asia Pacific, Americas, Europe, e Middle East/Africa—from 2008 to 2014. The percentages represent the proportion of available hotel rooms that were occupied in each region during these years. The Middle East/Africa region started with the highest occupancy rate in 2008 (69.6%) but experienced a sharp decline, while Asia Pacific showed steady recovery after a dip in 2009. The Americas consistently reported the lowest occupancy rates but saw gradual improvement over the years. The chart provides insights into regional trends and the resilience of the hotel industry during this period.
Principais conclusões:
- Middle East/Africa had the highest occupancy rate in 2008 (69.6%) but saw a significant drop during the global economic downturn.
- Asia Pacific exhibited resilience with occupancy rates recovering after 2009, ending at 68.6% in 2014.
- O Americas consistently had the lowest occupancy rates, starting at 60.6% in 2008 but steadily climbing to 64.4% by 2014.
- Europe maintained steady occupancy levels, reflecting stability despite economic challenges.
- The data highlights the impact of global economic events on the hospitality industry and regional differences in recovery trajectories.
Application of Information:
This data helps hospitality investors e business planners identify regions with strong recovery trends, such as Asia Pacific, or more stable markets, like Europe. For those entering or expanding in the hospitality sector, understanding occupancy rate patterns can guide investment decisions and strategic planning, ensuring alignment with regional market resilience and demand trends.
Conclusão
Commercial real estate investment offers diverse opportunities across sectors like retail, office, industrial, and hospitality. In both Europe and globally, investors can benefit from high rental yields and capital appreciation but must be aware of challenges such as market saturation, economic cycles, and regulatory changes. Understanding the specific dynamics of each sector is key to making informed investment decisions.
Informações importantes da lição:
- Retail properties in cities like New York and Hong Kong generate high rental yields due to prime locations and luxury brand demand, but e-commerce continues to challenge traditional models, especially in non-core markets.
- Office properties em London, Tokyo, and New York remain lucrative when leased to high-quality tenants on long-term contracts, though vacancy rates reveal stress points in some cities due to shifts in work culture and corporate downsizing.
- Industrial properties are thriving in ports and trade hubs such as Los Angeles, Dubai, and Shanghai, fueled by e-commerce and global supply chain expansion. Industrialization stage maps help investors assess regional maturity and growth potential.
- Hospitality properties, especially in Paris, Las Vegas, and Dubai, offer strong returns tied to tourism cycles and global events, but are highly sensitive to economic downturns and regional instability. Regional occupancy data helps predict resilience and recovery speed.
- Visuals such as vacancy charts, industrialization maps, and hotel occupancy trends provide key insight for cross-border investment analysis, helping learners develop global awareness and assess opportunities based on both data and regional context.
Declaração de Encerramento:
Understanding global commercial real estate requires analyzing regional trends and adjusting investment strategies accordingly. While certain principles remain consistent, such as the value of prime locations or long-term leases, macro factors like industrialization, technology, and international tourism trends shape performance differently across the globe.