Local (European-Specific) Content : Contracts and Agreements in Europe
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
- Understanding Contracts and Agreements is essential for secure real estate transactions. You’ll learn how agreements differ across countries like France, Germany, e Spain, and why it’s important to include key clauses about duration, termination, e maintenance responsibilities.
- Knowing the Real Estate Transaction Process helps you prepare for each step. This section breaks down the flow of a real estate purchase, from property search to closing, and explains how buyers, sellers, and agents work together to complete the deal.
- Recognizing Landlord-Tenant Laws in Europe protects both investors and tenants. You’ll discover how countries like Germany, France, e Italy manage evictions, tenant rights, e rental regulations, especially during challenging times such as winter bans or legal disputes.
- Fair Housing Laws ensure equal access to housing. You’ll understand how EU directives and national laws like the Equality Act in the U.K. e AGG in Germany help prevent discrimination and promote fairness in rental practices.
- Applying Best Practices gives investors an advantage. You’ll learn why working with legal professionals, understanding local laws, e negotiating clear contracts are critical for long-term success in European real estate markets.
18.1 Contracts and Agreements in Europe
The Importance of Contracts and Agreements
Contracts and agreements are fundamental to every real estate transaction. In Europe, legally binding contracts protect both buyers and sellers, as well as landlords and tenants. They ensure that all parties understand their rights and obligations and provide a legal framework for resolving disputes.
Key Considerations for Contracts and Agreements in Europe
Contracts in real estate, whether for purchasing a property or leasing it, must adhere to the specific legal requirements of each country. European countries like Germany, France, e Spain have distinct laws governing real estate transactions, which vary in terms of documentation, taxes, and terms.
- Purchase Agreements: When purchasing real estate in Europe, the purchase agreement outlines the terms of the sale, including the purchase price, payment method, and any contingencies. In France, for example, real estate transactions are finalized through a compromis de vente, a preliminary contract that legally binds both parties. In Germany, a notary is required to certify the contract to make it legally enforceable.
- Rental Agreements: Rental agreements define the terms of the lease, including the rent amount, duration of the lease, and responsibilities of both landlord and tenant. In Germany, rental contracts are typically long-term and heavily regulated, with provisions that protect tenant rights. In Spain, rental contracts often include clauses about rent increases, security deposits, and property maintenance responsibilities.
- Important Clauses: Contracts in Europe must clearly specify critical terms, such as:
- Duration: Specify the start and end date of the agreement.
- Termination: Include clauses regarding how and when the contract can be terminated.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Define who is responsible for repairs and routine maintenance, especially in countries like Italy e France, where tenant and landlord responsibilities are legally defined.
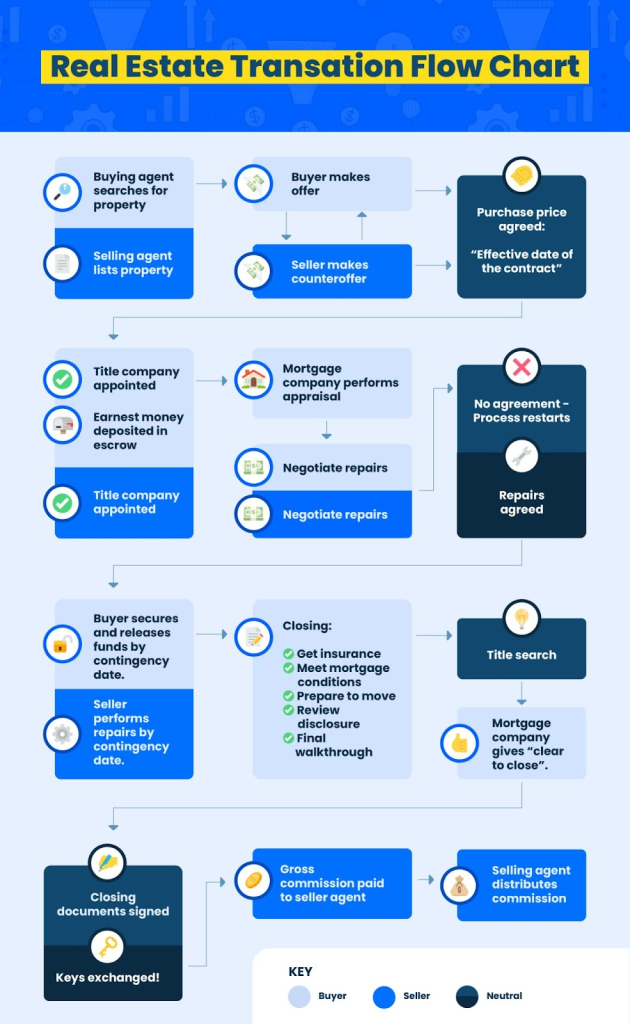
Figure: Real Estate Transaction Flow Chart
Descrição:
This flowchart illustrates the step-by-step process of a real estate transaction from the initial property search to the final exchange of keys. It begins with the buyer’s agent searching for properties and the selling agent listing properties, followed by offers, counteroffers, and agreement on a purchase price. The chart includes key milestones such as title search, mortgage appraisal, repair negotiations, and meeting mortgage conditions. The process concludes with the closing phase, where funds are secured, documents signed, and the keys exchanged. The chart uses a color-coded key to distinguish actions taken by the buyer, seller, or neutral entities.
Principais conclusões:
- Real estate transactions involve multiple stakeholders, including buyers, sellers, agents, title companies, and mortgage companies.
- Key steps include offer negotiation, appraisal, repair agreements, and title search.
- The process emphasizes the importance of mortgage approval and ensuring all conditions are met before closing.
- The chart highlights the role of contingency dates for securing funds and making necessary repairs.
- The transaction concludes with document signing, commission payment, and the transfer of property ownership.
Application of Information:
Understanding this flowchart can help buyers, sellers, and agents navigate real estate transactions efficiently. Investors can use it to streamline the process, ensuring they are prepared for key milestones such as appraisals and inspections. For first-time buyers, this provides clarity on the steps involved in purchasing property and helps them anticipate challenges like negotiation and closing costs.
18.2 Landlord-Tenant Laws in Europe
Eviction Process and Tenant Rights in Europe
Tenant rights are strongly protected in many European countries, making eviction a legally complex process. Each country has its own specific regulations regarding the grounds for eviction, tenant notice periods, and court involvement.
- Germany: In Germany, tenants have significant protections against eviction. Landlords can only terminate a rental contract under specific circumstances, such as the owner requiring the property for personal use. Even in these cases, landlords must provide tenants with notice periods of up to nine months, depending on how long the tenant has lived in the property.
- France: In France, evicting a tenant for non-payment of rent is a lengthy process, often taking several months. French law requires landlords to send formal notices and, if necessary, file a court order to proceed with the eviction. Winter eviction bans, known as the trêve hivernale, protect tenants from being evicted during the cold months (November to March).
- Italy: In Italy, the eviction process for non-payment of rent or violation of lease terms also requires a formal legal procedure. Landlords must file a claim in court, and the process can take several months. Similar to France, Italy offers protections during winter months, making it difficult to evict tenants during specific periods.
Fair Housing Laws in Europe
Fair housing laws in Europe aim to protect tenants from discrimination in housing, ensuring that all individuals have equal access to housing regardless of race, religion, gender, or socioeconomic status.
- European Union Directives: The EU has established several directives that prohibit discrimination in housing. These laws ensure that landlords cannot deny housing based on race, ethnicity, or nationality, among other protected characteristics.
- Country-Specific Regulations: Each country implements fair housing regulations slightly differently. In the U.K., for example, the Equality Act 2010 prohibits discrimination in property rentals, sales, and management. In Germany, the General Equal Treatment Act (AGG) protects tenants from discrimination during the rental application process and throughout their tenancy.
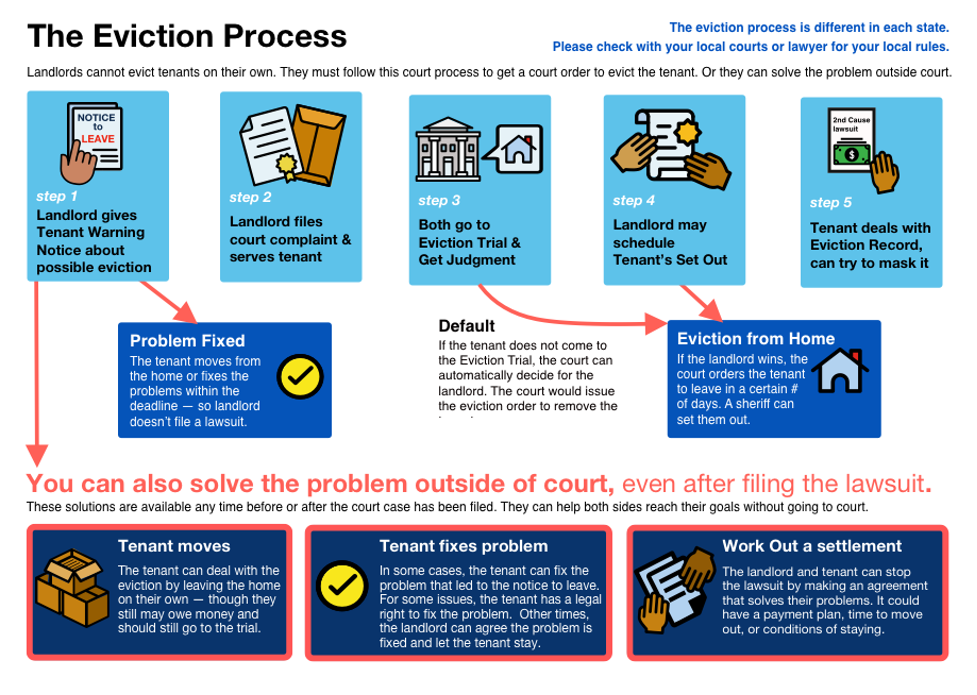
Figura: The Eviction Process
Descrição:
This figure outlines the eviction process that landlords must follow to legally evict tenants. It includes five key steps: (1) issuing a warning notice to the tenant, (2) filing a court complaint, (3) attending the eviction trial to obtain a judgment, (4) scheduling a tenant’s set-out if needed, and (5) managing the eviction record. The chart also highlights alternative solutions to avoid court, such as tenants moving, fixing problems, or negotiating settlements. It emphasizes that laws may differ by state, so it is critical to verify local regulations.
Principais conclusões:
- Eviction requires legal steps: Landlords cannot evict tenants on their own; they must follow proper legal processes.
- Key steps include warnings, court filings, and potential trials to resolve disputes and issue judgments.
- Tenants can avoid court by resolving issues (e.g., paying rent or fixing lease violations).
- Eviction records can impact tenants long-term, but solutions like record masking may be available.
- The process emphasizes fair resolution through court or alternative solutions to protect both parties.
Application of Information:
This data is useful for landlords and tenants to understand their legal rights and responsibilities during eviction. For landlords, it ensures compliance with laws to avoid legal disputes. For tenants, it provides insights into resolving issues before court involvement and the potential long-term effects of eviction records. Investors and property managers can also use this to ensure ethical and lawful handling of tenant disputes, preserving reputation and tenant relations.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit Tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
18.3 Best Practices and Advice for European Investors
When investing in real estate in Europe, following best practices can help navigate legal complexities and ensure smooth transactions and property management.
- Understand Local Laws: Real estate laws differ across European countries, so it’s essential to work with local legal professionals to ensure compliance. For example, in Spain, understanding local property tax laws and the legalities around short-term rentals is crucial for investors.
- Use Legal Professionals: Always involve a notary or real estate lawyer when dealing with contracts, especially in countries like Germany e France, where legal documents must be notarized or certified.
- Know Tenant Rights: Being familiar with tenant rights and regulations regarding rent control, lease terms, and eviction processes is vital for landlords. Understanding these laws ensures that landlords remain compliant with local tenant protection regulations.
- Negotiate Fair Terms: Whether buying or renting, negotiating clear, fair terms is important. In countries like Italy ou the Netherlands, including clauses that detail maintenance responsibilities and rent adjustment mechanisms can help avoid future disputes.
Figura: Real Estate Investment Checklist
Descrição:
This figure provides a checklist of critical factors to consider when evaluating a real estate investment. It emphasizes analyzing the location’s benefits to assess growth potential and market appeal. Calculating potential rental yield helps investors estimate the return on investment by comparing rental income to property costs. Assessing the property’s condition ensures any necessary repairs are accounted for before purchase. Studying market trends allows investors to understand current and future conditions that may influence profitability, while evaluating long-term growth prospects ensures the property aligns with investment goals.
Principais conclusões:
- Location is critical: Properties in high-demand or growing areas provide better investment potential.
- Rental income is a key factor: Calculating potential yield helps determine profitability.
- Property condition impacts costs: Ensuring the property is in good shape reduces unexpected expenses.
- Market knowledge is essential: Understanding trends allows investors to make informed decisions.
- Long-term potential matters: Growth prospects help ensure sustainable returns on investment.
Application of Information:
This checklist is a practical tool for real estate investors e students of finance. It can help users identify and evaluate the best investment opportunities, ensuring profitability and minimizing risks. By focusing on location, market trends, and future growth, users can make smarter financial decisions and build a successful real estate portfolio.
Informações importantes da lição:
- Contracts and Agreements must follow local legal rules. Countries like France require preliminary contracts (compromis de vente), while Germany mandates notarization. Contracts should include clear clauses on lease duration, termination rules, e maintenance duties to prevent future conflicts.
- Real Estate Transactions involve multiple steps and people. From offers and negotiations to title searches e mortgage approvals, understanding the transaction flow helps investors stay organized and avoid delays during the buying process.
- Landlord-Tenant Laws in Europe protect renters, especially from unfair eviction. In Germany, eviction can only happen under specific legal grounds. In France e Italy, the eviction process can take months and often pauses in the winter. Following the law ensures fairness and avoids costly legal disputes.
- Fair Housing Regulations prevent discrimination. EU directives and national laws like the Equality Act (U.K.) e AGG (Germany) make it illegal to deny housing based on race, religion, or background. Knowing these laws helps maintain ethical rental practices.
- Best Practices for European Investors include hiring local legal experts, learning country-specific regulations, e negotiating fair contract terms. In countries like Spain, understanding local property tax rules and rental restrictions is essential for compliance and long-term success.
Declaração de Encerramento:
Clear contracts, legal awareness, and thoughtful planning make European real estate investing more secure and profitable. These practices help investors navigate local laws, protect tenant rights, and make smart, ethical investment decisions.