Local: Introdução às Bolsas de Valores Europeias
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
- Introdução: This section introduces you to the European stock exchanges, highlighting their structure e regulatory environment. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone interested in the European financial markets.
- Gain an understanding of MiFID II and its role in enhancing transparency e investor protection across the European Union. This knowledge is vital for navigating the complex regulatory landscape of European markets.
- Learn about the major European stock exchanges such as Euronext, London Stock Exchange, e Deutsche Börse. Recognize the importance of these exchanges in the global financial ecosystem and how they contribute to economic activity in Europe.
- Understand the function of the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and its impact on ensuring efficient market operation and investor protection across Europe. This will help you appreciate the cohesive regulatory framework governing European financial markets.
- Explore the various investor protections available within European markets, including country-specific regulations and compensation schemes. This knowledge will empower you to invest more confidently and securely in these markets.
1.1 Introduction to European Stock Exchanges
In Europe, stock markets operate under a distinct regulatory environment. One of the key regulations that impact European financial markets is MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II), which aims to enhance transparency and strengthen investor protection across the European Union.
Major European stock exchanges include:
- Euronext, a cross-border exchange operating in cities like Amsterdam, Brussels, and Paris.
- O London Stock Exchange (LSE), a major financial hub, especially before Brexit.
- Deutsche Börse, based in Frankfurt, Germany, which hosts the DAX index, listing 30 of Germany’s largest companies.
These markets are regulated by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), which ensures that investors are protected and financial markets operate efficiently.
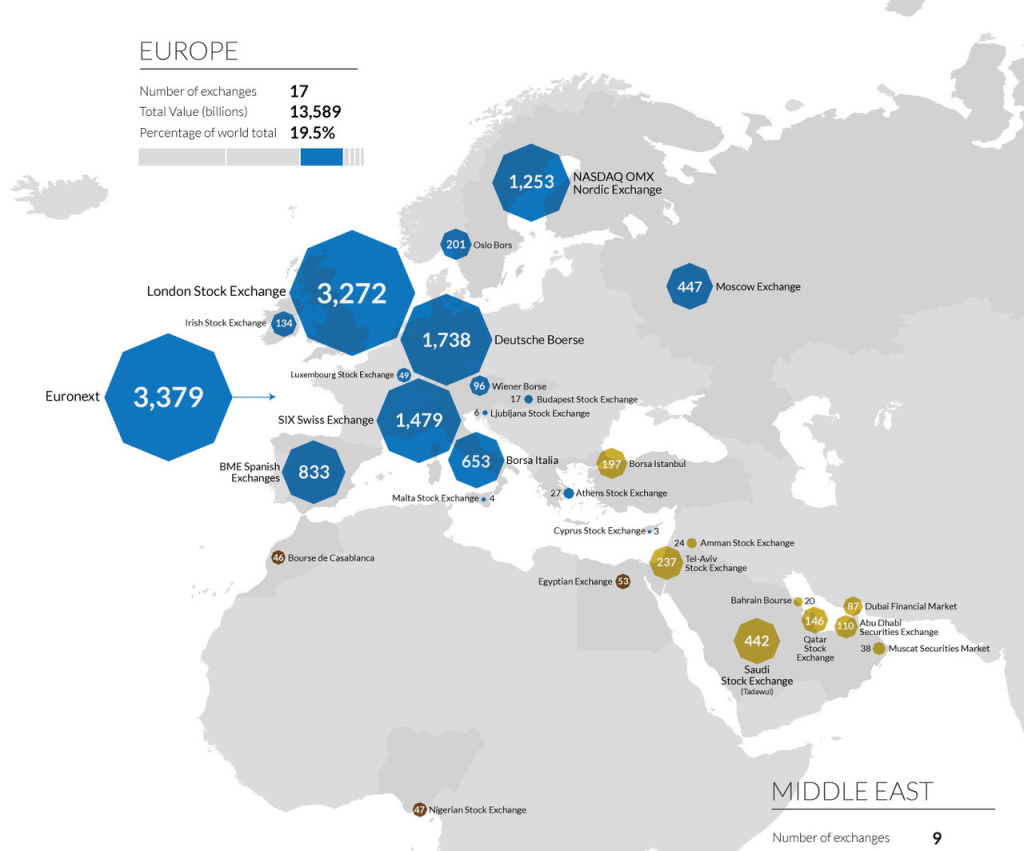
Figura: Map of European and Middle Eastern Stock Exchanges by Market Cap
Descrição:
This map illustrates the distribution and market capitalization of stock exchanges across Europe and the Middle East. Each exchange is represented by a hexagonal shape, with the size reflecting its total market cap in billions. Key exchanges such as Euronext, London Stock Exchange, and Deutsche Börse stand out due to their larger market caps, while smaller exchanges are also labeled but with smaller hexagons. The total number of exchanges, their combined value, and their percentage contribution to the world market are displayed for Europe and the Middle East.
Principais conclusões:
- Europa has a total of 17 exchanges, contributing 19.5% to the global market cap.
- Largest exchanges in Europe include Euronext (3,379 billion), London Stock Exchange (3,272 billion), and Deutsche Börse (1,738 billion).
- Middle Eastern exchanges are smaller in comparison, with Saudi Stock Exchange (442 billion) being the largest in the region.
- O geographical spread emphasizes the dominance of major European financial hubs.
Aplicação da Informação:
This map aids users in understanding the regional distribution e relative size of stock exchanges in Europe and the Middle East. It can guide investors in recognizing key financial centers and evaluating regional market significance, which is crucial for diversificação e risk assessment in international investing. The visualization also highlights where larger liquidity pools exist, which is useful for decision-making regarding market entry and strategy formulation.
1.2 A Strong Foundation for Success
Local: Overview of European Investor Protections
In Europe, investors benefit from extensive protections to ensure that markets operate transparently and fairly. These protections are enforced by various regulations, often coordinated by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
Each country in Europe may also have its own specific regulations to ensure the safety and fairness of its markets.
- MiFID II: One of the most significant regulations governing the European financial markets is MiFID II, which was designed to increase transparency, improve investor protections, and reduce conflicts of interest between investors and financial firms. MiFID II requires financial firms to provide clear, detailed information about the risks and costs associated with investments.
- Country-Specific Protections: While ESMA oversees many aspects of European markets, each country has its regulatory body that enforces local laws:
- In the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) ensures financial markets function well for consumers, even post-Brexit.
- Em Alemanha, the BaFin (Federal Financial Supervisory Authority) regulates banks and financial institutions to protect investors.
- França has the Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF), which ensures that investors receive clear, accurate information and monitors financial transactions to prevent fraud.
- In the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) ensures financial markets function well for consumers, even post-Brexit.
- Investor Compensation Schemes: Many European countries also offer investor compensation schemes that provide a safety net if an investment firm fails. For example, in the UK, the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) protects investments up to a certain amount, helping individuals recoup losses if a firm becomes insolvent.
- Cross-Border Protections: Investors operating in more than one European market benefit from a coordinated regulatory approach, as ESMA works to standardize rules across the European Union, ensuring a smooth and secure experience for investors across borders.
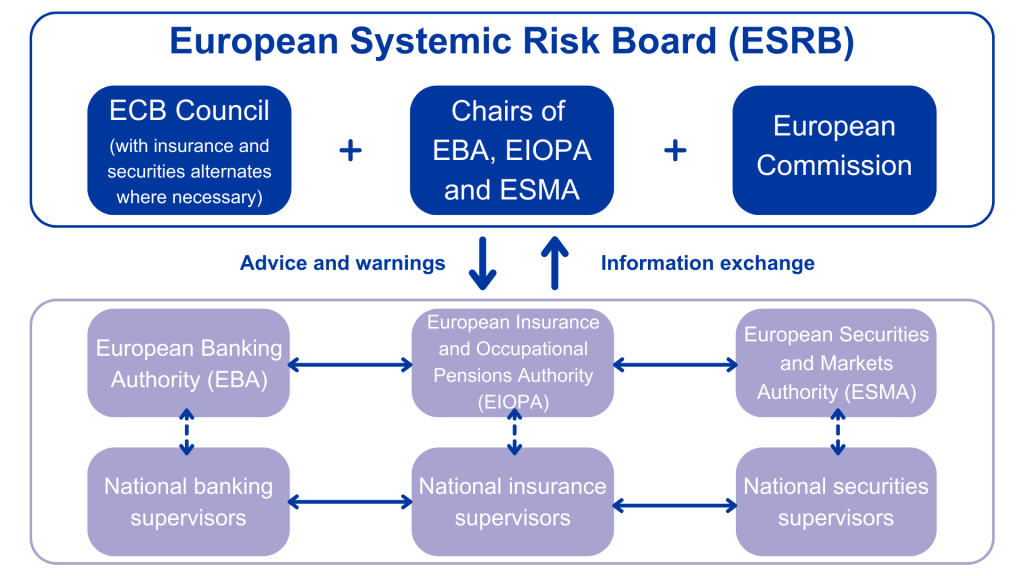
Figura: European Systemic Risk Board (ESRB) Structure
Descrição:
This diagram shows the organizational structure and information flow within the European Systemic Risk Board (ESRB), which includes the European Central Bank (ECB) Council, Chairs of European Supervisory Authorities (EBA, EIOPA, and ESMA), and the European Commission. It depicts how advice, warnings, and information exchange occur between the ESRB and national supervisors across banking, insurance, pensions, and securities markets.
Principais conclusões:
- ESRB involves collaboration among ECB Council, supervisory authorities, and the European Commission.
- It serves as the central hub for systemic risk management in Europe, covering banking, insurance, pensions, and securities markets.
- Information exchange e warnings flow between ESRB and national supervisors, enhancing regulatory oversight and stability.
- National supervisors ensure local implementation of guidelines and advice from ESRB.
Aplicação da Informação:
Understanding the structure of the ESRB helps investors and analysts appreciate how systemic risk is managed in Europe, fostering financial stability. This information is useful for evaluating regulatory frameworks and their implications for European financial markets. It also aids in assessing the risk management strategies of European financial institutions.
1.3 Beyond Chance: Understanding the Stock Market
Local: European Stock Market Structure
The European stock market is a diverse and complex system composed of multiple stock exchanges across the continent. Each country has its own stock exchanges, some of which have joined to form larger, cross-border markets. Understanding how these markets work is crucial for any investor looking to engage in European stocks.
- Euronext: Euronext is the largest pan-European exchange, operating in countries like França, Netherlands, Belgium, e Portugal. It allows companies from various industries to list their shares, providing a central hub for European investors. As an investor, you can access a broad range of stocks and financial products, making Euronext a key part of the European financial landscape.
- Deutsche Börse: Based in Frankfurt, Germany, Deutsche Börse is one of Europe’s most important stock exchanges. It hosts the DAX Index, which includes 30 of the largest and most liquid German companies, providing a snapshot of the German economy and an essential market for investors interested in European stocks.
- London Stock Exchange (LSE): Although Londres is no longer part of the European Union, the London Stock Exchange remains a critical global financial hub. Investors from Europe still actively trade on the LSE due to its liquidity and wide range of listed companies. The FTSE 100 Index is its flagship index, tracking the largest companies listed on the exchange.
- BME (Bolsas y Mercados Españoles): Spain’s stock exchange, based in Madrid, is part of the broader European market. The IBEX 35 Index tracks the top 35 companies in Spain and is a key indicator of the Spanish market’s health.
These exchanges function under a harmonized regulatory framework coordinated by ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority). This ensures that investors can operate in these different markets with a sense of security and consistency in regulatory practices.
Informações importantes da lição:
- European stock exchanges operate under a strict regulatory framework highlighted by MiFID II, aimed at improving market transparency e protection for investors. This ensures a more secure investment environment across Europe.
- Major exchanges such as Euronext, the London Stock Exchange, e Deutsche Börse play pivotal roles in Europe’s financial markets, offering diverse investment opportunities and contributing significantly to the European and global economies.
- O European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) oversees the regulation of European financial markets, ensuring that they operate efficiently and transparently while providing necessary investor protections.
- Country-specific protections e cross-border regulatory cooperation enhance the security of investments within Europe. These measures protect investors from potential losses and promote a stable financial environment.
- Understanding the structure and regulations of European stock exchanges is crucial for anyone involved in international investing, as it affects decision-making related to market entry, investment diversification, and risk assessment.
Declaração de Encerramento:
Grasping the intricate details of European stock exchanges and their regulatory environments equips you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions, fostering a safer and more profitable investing experience.


