Історія фондового ринку
Ключові цілі навчання:
Вступ: This section delves into the historical events and trends of the stock market, offering a lens to better understand market dynamics and make informed investment decisions. The historical analysis will unveil patterns and influences that shape the market landscape.
- Gain a Deep Understanding of Stock Market History: Discern market trends, economic cycles, and the influence of historical events on financial markets.
- Learn About Notable Market Crashes: Зрозумійте causes, impacts, і recovery patterns of significant market crashes throughout history.
- Understand Historical Business Cycles: Learn about various historical business cycles, their characteristics, and the factors that led to their commencement and termination.
- Recognize the Influence of External Events: Understand the impact of external events, like wars or pandemics, on market performance and economic cycles.
- Appreciate the Importance of Studying Market History: Realize how studying market history aids in making more informed investment decisions.
Understanding the history of the stock market is essential for investors, as it can provide valuable insights into market trends, economic cycles, and the impact of historical events on financial markets. By studying market history, investors can develop a better understanding of the factors that can influence the performance of their investments and make more informed decisions.
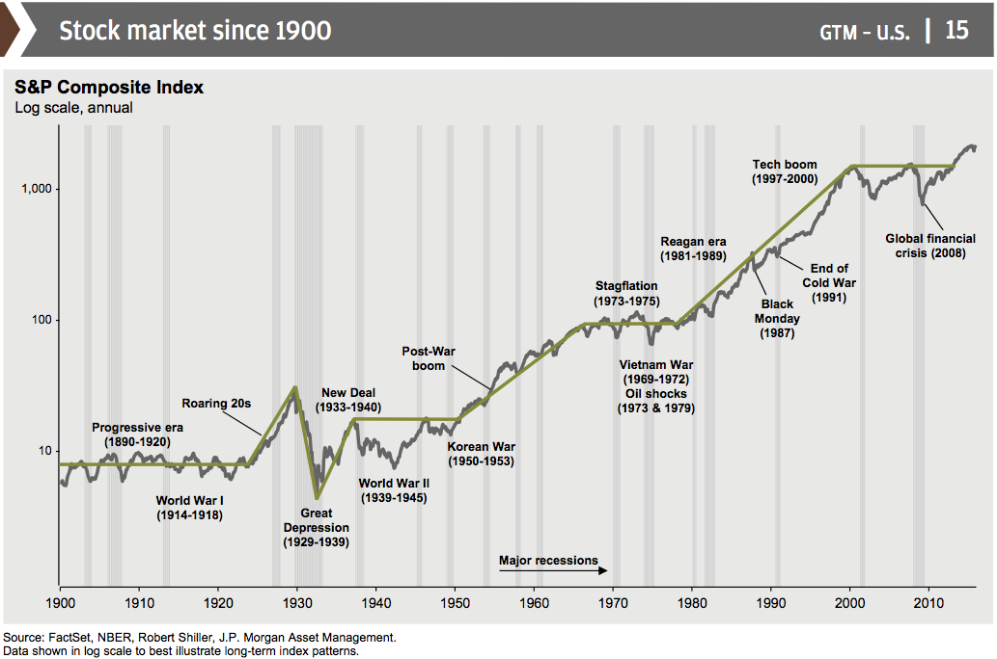
Figure title: Stock Market Since 1900
Джерело: Бізнес-інсайдер
опис:
The image provides a historical overview of the stock market as represented by the S&P Composite Index, plotted on a logarithmic scale to better illustrate long-term index patterns.
Various significant historical events and periods are marked along the timeline, including:
- Great Depression (1929-1939): A period of severe economic downturn.
- World Wars: World War I (1914-1918) and World War II (1939-1945).
- Roaring 20s: A period of economic prosperity during the 1920s.
- New Deal (1933-1940): A series of programs and projects instituted during the Great Depression.
- Korean War (1950-1953): A conflict between North Korea (with the support of China and the Soviet Union) and South Korea (with the principal support of the United States).
- Vietnam War (1969-1972): A long, costly armed conflict that pitted the communist regime of North Vietnam and its southern allies, known as the Viet Cong, against South Vietnam and its principal ally, the United States.
- Oil Shocks (1973 & 1979): Two significant oil price shocks due to geopolitical events.
- Stagflation (1973-1975): A situation in which the inflation rate is high, the economic growth rate slows, and unemployment remains steadily high.
- End of Cold War (1981): The period marking the end of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union.
- Black Monday (1987): A severe stock market crash that occurred on October 19, 1987.
- Global Financial Crisis (2008): A severe worldwide economic crisis that occurred in the late 2000s.
Ключові висновки:
- The stock market has experienced various ups and downs corresponding to major historical events.
- Economic policies, geopolitical events, and global crises significantly impact the stock market.
- The logarithmic scale helps to visualize long-term trends in the stock market.
Застосування: This historical overview provides a contextual understanding of the stock market’s behavior over more than a century. By studying the impact of historical events on the stock market, investors, financial analysts, and students can better understand market dynamics and potentially make more informed decisions in their financial endeavors.
5.1 Historical Market Crashes
Назва рисунка: Understanding Stock Market Crashes
Джерело: Investopedia
опис:
A stock market crash is characterized by a rapid and often unexpected drop in stock prices. This can be triggered by major catastrophic events, economic crises, or the collapse of speculative bubbles. Public panic can exacerbate the crash, leading to even steeper declines. Notable stock market crashes have occurred during events like the 1929 Great Depression, Black Monday in 1987, the 2001 dotcom bubble burst, the 2008 financial crisis, and the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic.
Ключові висновки:
- Definition: A stock market crash is a sudden and significant drop in stock prices, often triggered by panic selling, economic downturns, or external events.
- Impact: Such crashes can have profound economic implications, potentially leading to recessions or depressions.
- Historical Crashes: Notable crashes include the 1929 crash that led to the Great Depression, Black Monday in 1987, and the crash during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic.
Prevention: Measures like trading curbs or circuit breakers have been implemented to halt trading during severe market declines, aiming to stabilize the market.
застосування: For investors, understanding the causes and effects of stock market crashes is crucial. Recognizing the signs leading up to a potential crash can help in making informed decisions about when to buy or sell. Additionally, being aware of preventive measures like circuit breakers can provide some reassurance during volatile market periods. Diversifying investments and not putting all funds into equities can also be a prudent strategy to mitigate the impacts of potential crashes.
Market crashes are significant and rapid declines in the value of financial markets, often driven by a combination of economic, political, and psychological factors.
Here are five notable market crashes throughout history:
The Wall Street Crash of 1929: Triggered by speculative excesses during the 1920s, the crash marked the beginning of the Great Depression. Stock prices fell by nearly 90% over the next three years, and the economy took more than a decade to recover. Safe-haven assets like gold and government bonds performed relatively well during this period, while stocks and real estate suffered.
The 1987 Black Monday Crash: On October 19, 1987, stock markets around the world experienced a sudden and severe drop in value, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average falling 22.6% in a single day. The exact cause remains unclear, but factors such as computerized trading, market psychology, and global economic concerns contributed to the crash. The market rebounded relatively quickly, with most major indexes regaining their pre-crash levels within two years.
The Dot-Com Bubble Burst (2000-2002): The overvaluation of technology and internet-based companies led to a market bubble, which burst in 2000. The Nasdaq Composite, heavily weighted towards technology stocks, lost 78% of its value over the next two years. Traditional value stocks and bonds performed relatively well during this period, while tech stocks suffered significant losses.
The 2008 Global Financial Crisis: Triggered by the collapse of the US housing market and the proliferation of subprime mortgages, the crisis led to a severe global recession. Stock markets lost approximately 50% of their value, and many financial institutions faced bankruptcy. Government bonds and other safe-haven assets performed well during this time, while stocks, real estate, and commodities experienced sharp declines.
The 2020 COVID-19 Market Crash: The rapid global spread of the COVID-19 pandemic led to widespread economic disruption, causing markets to plunge in March 2020. Central banks and governments implemented stimulus measures, leading to a swift recovery in the following months. Technology and healthcare stocks performed well during this period, while sectors like travel and energy struggled.

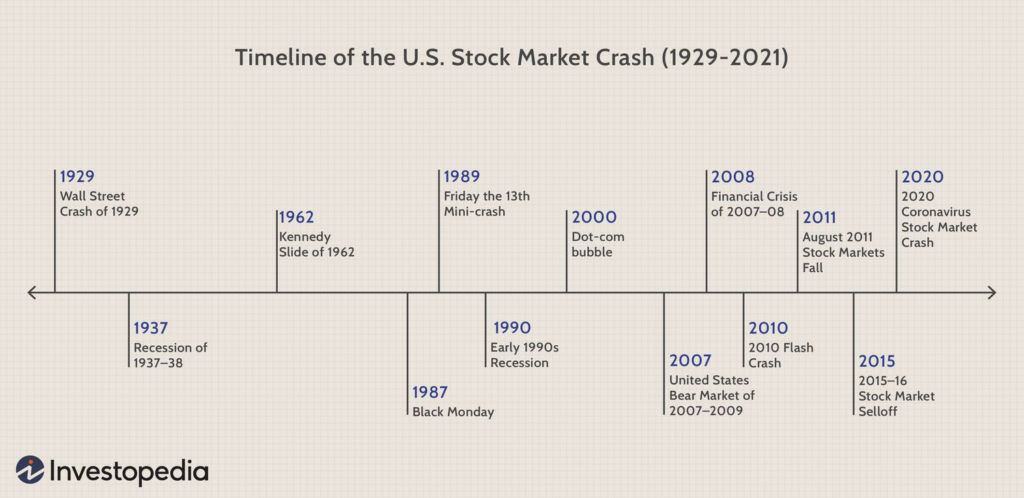
Назва рисунка: Major US Stock Market Crashes: A Timeline
Джерело: Investopedia
-
- 1929 Wall Street Crash:
- Also known as the Great Crash, this was a major stock market crash that occurred in late October 1929. It led to the Great Depression.
- Industries impacted: Almost every sector was affected, but banks and financial institutions were the hardest hit.
- Learning for Investors: Diversification is crucial. Relying heavily on stock market investments without diversification can lead to significant losses.
- 1929 Wall Street Crash:
-
- 1937 Recession of 1937-1938:
- This economic downturn was caused by policy retractions and fiscal tightening, coming shortly after the Great Depression.
- Industries impacted: Manufacturing industries suffered the most.
- Learning for Investors: Market recoveries can be fragile. Ensure a balanced portfolio to weather unforeseen economic shocks.
- 1937 Recession of 1937-1938:
-
- 1962 Kennedy Slide:
- A sharp stock market decline in mid-1962 which was partly attributed to anti-trust actions against US steel companies by the Kennedy administration.
- Industries impacted: Steel companies and related industries.
- Learning for Investors: Political and governmental decisions can have immediate impacts on specific sectors.
- 1962 Kennedy Slide:
- 1989 Friday the 13th Market Crash:
-
-
- A sudden and severe stock market crash that occurred on October 13, 1989, due to a failed leveraged buyout of United Airlines.
- Industries impacted: Airline and transportation industries.
- Learning for Investors: External events, even unrelated to the broader economy, can have ripple effects in the stock market.
-
- 1990 Early 1990s Recession:
-
-
- This recession was a result of oil price shocks, falling home prices, and broader economic stagnation.
- Industries impacted: Energy, real estate, and banking.
- Learning for Investors: Global events, like oil price fluctuations, can influence domestic markets significantly.
-
- 2000 Dot-com Bubble:
-
-
- An intense speculative bubble around internet-based companies (dot-coms) which burst in the early 2000s.
- Industries impacted: Technology and internet-based startups.
- Learning for Investors: Beware of investing heavily in over-hyped sectors without substantial underlying value.
-
-
- 2007 United States Bear Market of 2007-2009:
- Primarily caused by the subprime mortgage crisis, leading to the global financial crisis.
- Industries impacted: Banking, real estate, and finance.
- Learning for Investors: Real estate isn’t always a safe bet. It’s crucial to be cautious of industries showing signs of overheating.
- 2007 United States Bear Market of 2007-2009:
- 2010 Flash Crash:
-
-
- A trillion-dollar stock market crash occurring within minutes on May 6, 2010.
- Industries impacted: Broad impact, but particularly the futures market.
- Learning for Investors: Algorithmic trading can lead to rapid market fluctuations. Always have a risk management strategy in place.
-
- 2011 August 2011 Stock Market Falls:
-
-
- Driven by the US credit rating downgrade by Standard & Poor’s.
- Industries impacted: Widespread impact, especially financial institutions.
- Learning for Investors: External evaluations, like credit ratings, can influence investor sentiments heavily.
-
- 2015-2016 Stock Market Selloff:
-
- Primarily driven by concerns over China’s economic slowdown.
- Industries impacted: Global markets, with an emphasis on commodities.
- Learning for Investors: Globalization means economic issues in one country can impact markets worldwide.
- 2020 Coronavirus Stock Market Crash:
- Caused by the global pandemic of the COVID-19 virus, leading to unprecedented economic shutdowns.
- Industries impacted: Travel, hospitality, and offline retail were hardest hit, while tech and healthcare sectors saw growth.
- Learning for Investors: Black swan events, unpredictable in nature, can lead to dramatic market shifts. Having a diverse portfolio can mitigate risks.
5.2 Four Historical Business Cycles
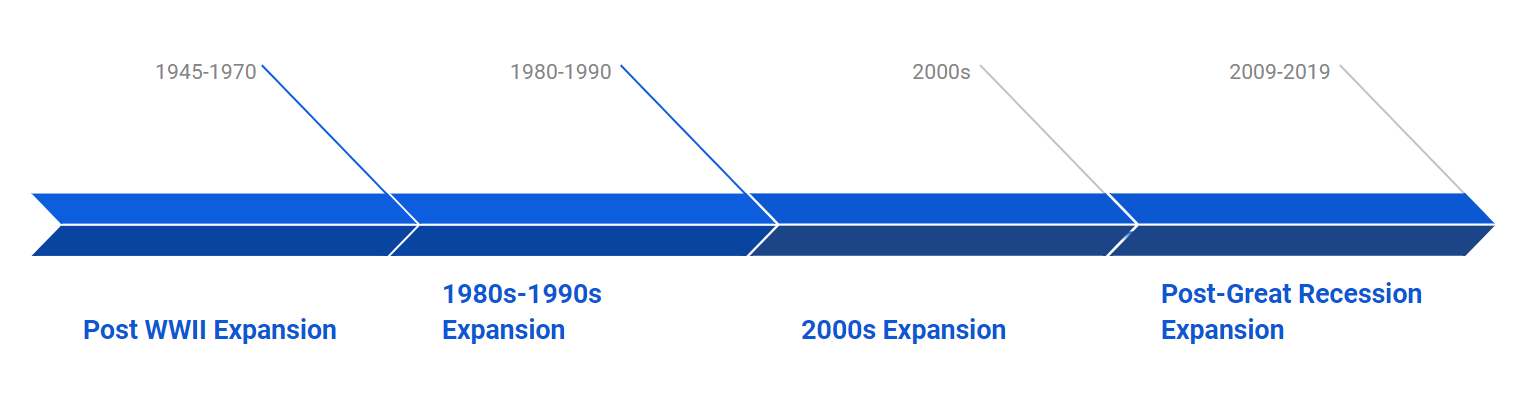
малюнок: The infographic provides a timeline highlighting various expansion periods in the U.S. economy. It starts with the “Post WWII Expansion” from 1945-1970, followed by the “1980s-1990s Expansion,” then the “2000s Expansion,” and finally the “Post-Great Recession Expansion” from 2009-2019. Each period is distinctly marked, offering a clear visual representation of the economic growth phases in the U.S. over the decades. Recognizing these expansion periods can help users understand the cyclical nature of economic growth and the factors that drive it.
Джерело: Інфографіка на замовлення
The Post-WWII Expansion (1945-1970): This period saw rapid economic growth and technological advancements, including the development of computers and telecommunications. The cycle ended with the 1970s stagflation, a period of high inflation and stagnant growth.
The 1980s-1990s Expansion: After a period of high inflation and economic stagnation in the 1970s, the global economy experienced a prolonged expansion during the 1980s and 1990s. The rise of personal computers, the internet, and globalization contributed to economic growth. The cycle ended with the dot-com bubble bursting in 2000.
The 2000s Expansion: Following the dot-com bubble burst, the global economy experienced a period of growth driven by housing markets and easy credit conditions. The cycle ended with the 2008 global financial crisis, which was triggered by the collapse of the US housing market and the spread of subprime mortgages.
The Post-Great Recession Expansion (2009-2019): After the 2008 financial crisis, central banks implemented aggressive monetary policies, and governments introduced fiscal stimulus measures to revive economic growth. Technological advancements in sectors such as e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy contributed to the expansion. The cycle ended with the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent global economic slowdown.
Назва рисунка: Increase in Value of $1 Invested in the U.S. Stock Market (1870-2020)
Джерело: Morningstar
опис: This graph traces the journey of a single dollar invested in the U.S. stock market between 1870 and 2020. While capturing various market crashes and significant events, it highlights the predominant upward trend. However, periods of pronounced volatility and downturns are evident, underscoring the market’s unpredictable nature.
Ключові висновки:
- The long-term trend of the stock market has been upward.
- Several market crashes and significant events have been captured over this 150-year span.
- Even though the trend is upwards, intense volatility and substantial downturns have occurred.
- Maintaining investments through these downturns has historically resulted in net gains.
застосування: To harness the market’s long-term upward trajectory, investors must weather its volatile phases without panic-selling. This graph emphasizes the importance of liquidity management, ensuring that investors aren’t forced to liquidate assets during unfavorable market conditions. It reiterates the classic investing mantra: “It’s not about timing the market, but time in the market.”
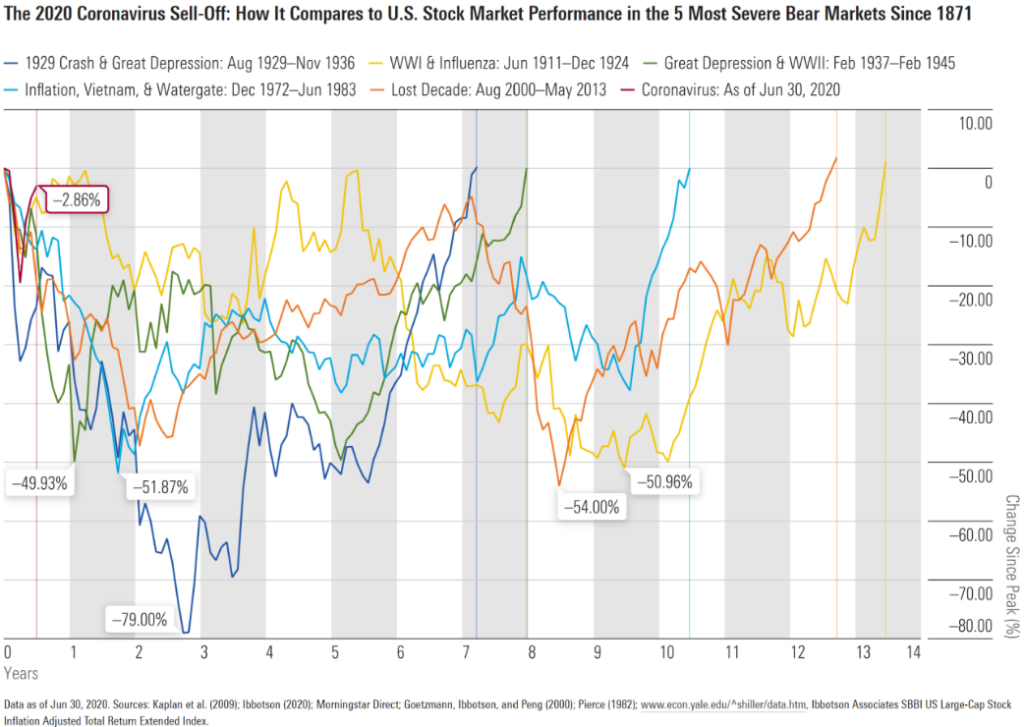
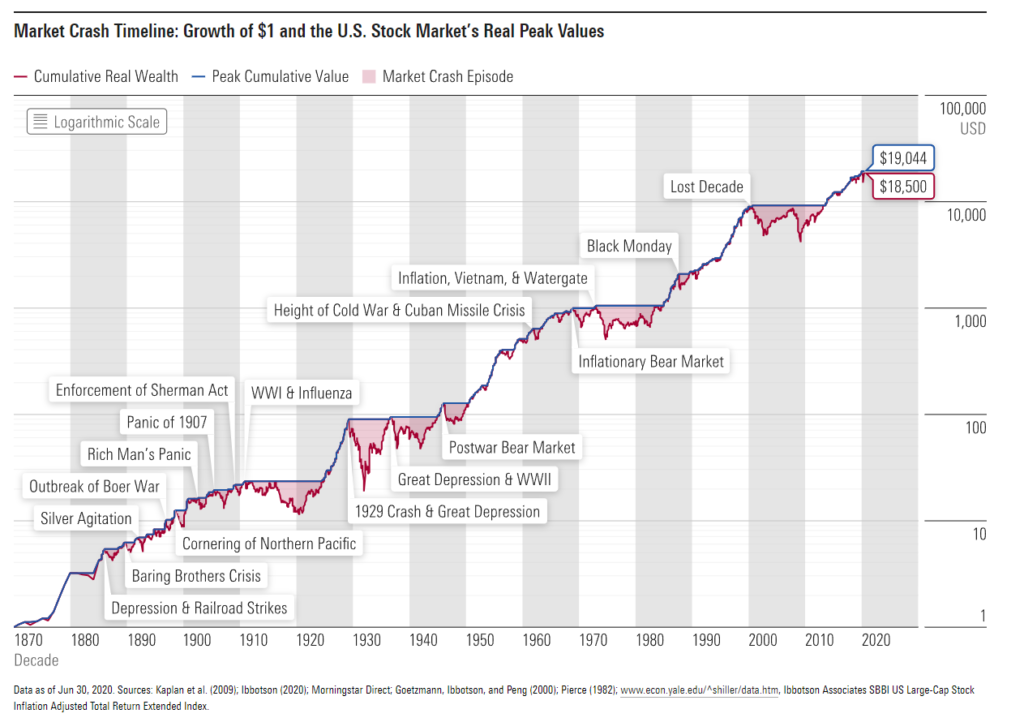
Назва рисунка: U.S. Stock Market Performance Across Various Market Crashes (1911-2020)
Джерело: Morningstar
опис: The graph illustrates the performance of the U.S. stock market through notable market crashes from 1911 to 2020. These crashes range from events like the 1929 Crash and Great Depression, WW1 & the Influenza outbreak, the era of the Great Depression combined with WW2, the turbulent times of inflation, Vietnam War & Watergate, to the Lost Decade and the recent Coronavirus crash. Each event, marked by significant market drops, reveals the market’s resilience as it eventually rebounds.
Ключові висновки:
- Market crashes, though disruptive, have occurred regularly throughout the past century for varied reasons.
- The resilience of the stock market is evident as it has historically rebounded after significant downturns.
- Each market crash event provides unique insights into the interplay of global events and market dynamics.
The long-term trend of the market, despite these crashes, tends to be positive.
застосування: Investors can use this historical perspective to develop a long-term view, understanding that downturns, while concerning, are a part of the market’s cycle. It highlights the significance of being patient and well-informed, as reacting impulsively during a market crash can potentially lead to missed opportunities during recovery.
Ключові висновки:
Заключне слово: The historical lens provided in this section equips investors with a broader understanding, enabling them to foresee potential market trends and make well-informed decisions. The past, with its cycles and dramatic market events, serves as a valuable teacher for navigating the financial markets of today and tomorrow.
- The history of the stock market offers invaluable insights into market trends, economic cycles, and the effects of historical events on financial arenas.
- Market crashes are typically caused by a blend of economic, political, and psychological factors, and studying them helps anticipate potential market risks.
- Notable market crashes like the Wall Street Crash of 1929, 1987 Black Monday Crash, Dot-Com Bubble Burst, 2008 Global Financial Crisis, і 2020 COVID-19 Market Crash are significant learning points.
- Various notable business cycles in history, such as the Post-WWII Expansion, the 1980s-1990s Expansion, the 2000s Expansion, і Post-Great Recession Expansion offer lessons for understanding market dynamics.
- Studying these cycles and crashes equips investors with knowledge to navigate future market fluctuations and make informed decisions.
