محليًا: الأسهم الفردية - اختيار الرابحين والخاسرين
أهداف تعلم الدرس:
- Understand European tax rules ذات صلة ب الأسهم الفردية، مثل wealth tax و ضريبة الأرباح الرأسمالية, so you can better plan your investments and avoid unexpected tax costs.
- Learn how country-specific regulations, like financial transaction taxes و reporting requirements, can affect your investment costs and decision-making when picking stocks in Europe.
- Explore the challenges of cross-border investing within Europe, including how توجيه أسواق الأدوات المالية (MiFID II) creates shared rules while national differences still matter. This helps you invest more confidently across borders.
- Recognize how investor protections, especially those from هيئة الأوراق المالية والأسواق الأوروبية, help keep your investments safe and ensure you’re informed about the المخاطر والفوائد of buying stocks.
- Gain insight into favorable asset utilization, a way to measure how well companies use their assets to make money, which can help you compare different stock opportunities more effectively.
9.1 Individual Stocks - Picking the Winners and Losers
When investing in individual stocks in Europe, investors must consider the البيئة التنظيمية and specific الآثار المترتبة على الضرائب in their respective countries. Stock-picking in the European Union is influenced by a variety of laws and regulations designed to protect investors and ensure market stability.
- Wealth Tax: Some European countries impose a wealth tax on high-net-worth individuals, which may affect investments in individual stocks. For example, countries like فرنسا و إسبانيا have wealth taxes, requiring investors to pay a percentage of their total wealth, including stock holdings, above a certain threshold. This can reduce overall returns for wealthier investors.
- ضريبة الأرباح الرأسمالية: Different EU countries have varying levels of ضريبة الأرباح الرأسمالية on profits from individual stock investments. Some countries, like ألمانيا, tax capital gains on investments held for less than a year at a higher rate, while others, like بلجيكا, do not tax capital gains on stocks for individuals.
- Regulations on Stock Investments: Certain European countries have additional regulations concerning stock-picking. For instance, in إيطاليا و فرنسا, stricter reporting requirements and financial transaction taxes (FTTs) are imposed on stock trades, impacting the overall cost of investing in individual stocks.
- Cross-Border Investments: European investors may also need to comply with additional regulations when investing in stocks across EU borders. While the توجيه أسواق الأدوات المالية (MiFID II) harmonizes many regulations across the EU, there may still be specific national rules that investors must follow when purchasing individual stocks from other European countries.
- حماية المستثمرين: ال هيئة الأوراق المالية والأسواق الأوروبية (ESMA) provides guidelines and frameworks to ensure investor protection when trading individual stocks. These regulations aim to increase transparency and reduce risks, ensuring that investors are well-informed about the risks and rewards of their stock investments.

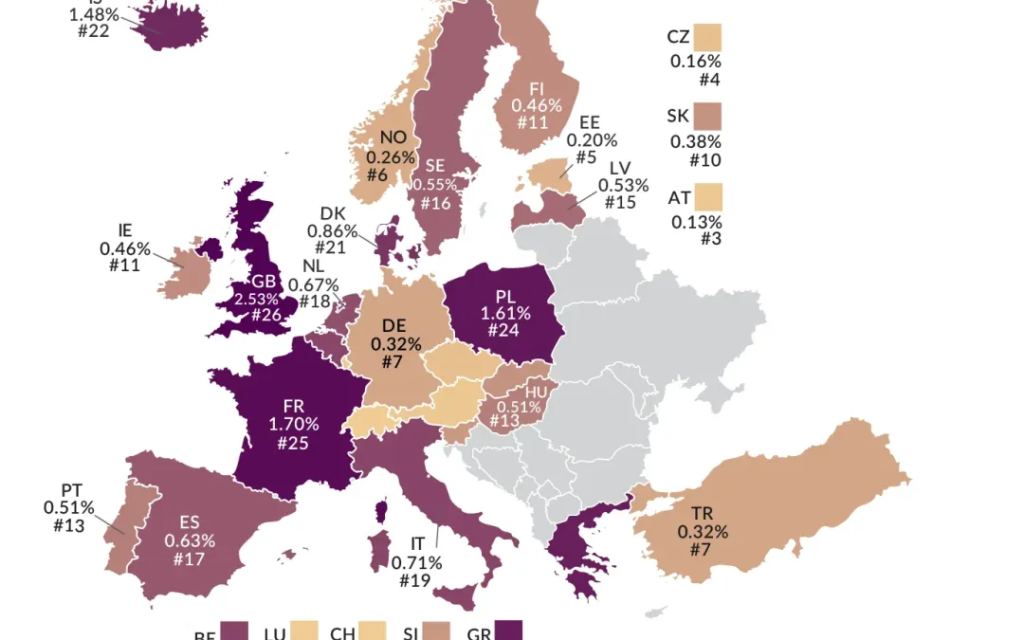
شكل: Capital Gains Tax Rates in Europe
وصف:
هذه الخريطة توضح معدلات ضريبة مكاسب رأس المال across different European countries. The color gradient indicates the tax rate, ranging from low to high. على سبيل المثال،, فرنسا (1.70%), ألمانيا (0.32%), and the المملكة المتحدة (2.53%) exhibit different rates, highlighting variations in capital gains taxation across the region. Each country is also ranked based on its tax rate, providing a comparative view of the capital gains tax landscape in Europe.
الماخذ الرئيسية:
- فرنسا has one of the highest capital gains tax rates in Europe at 1.70%.
- ألمانيا و ديك رومى have relatively low capital gains tax rates, both at 0.32%.
- ال المملكة المتحدة shows a significantly higher rate at 2.53%, placing it among the highest in Europe.
- إيطاليا و إسبانيا have moderate rates at 0.71% و 0.63%, ، على التوالى.
- The map emphasizes the disparity in capital gains taxation within Europe, which can affect investment decisions.
تطبيق المعلومات:
Investors can use this information to optimize their investment strategies based on the معدلات ضريبة مكاسب رأس المال in different European countries. Understanding these rates is crucial for التخطيط الضريبي, especially for cross-border investors looking to تعظيم العائدات while minimizing tax liabilities. This knowledge can also guide real estate and stock investments, helping investors select more favorable tax jurisdictions.
معلومات الدرس الرئيسية:
- Wealth tax في بلدان مثل فرنسا و إسبانيا means that high-net-worth individuals may pay extra taxes on their stock holdings. This can reduce total investment returns and should be considered when building a portfolio in these countries.
- ضريبة الأرباح الرأسمالية varies across Europe. Some countries, like بلجيكا, do not tax capital gains for individuals, while others, like ألمانيا, tax them at higher rates if the investment is sold within a year. Knowing this can help you plan when and where to sell your stocks.
- Stock regulations and transaction costs are higher in some countries, such as إيطاليا و فرنسا, where there are financial transaction taxes (FTTs) and extra reporting rules. These costs can lower your returns if not accounted for.
- الاستثمارات عبر الحدود in the EU benefit from shared rules under توجيه أسواق الأدوات المالية (MiFID II), but each country may still have additional regulations. Being aware of these differences is important for investors looking to buy stocks across European countries.
- Investor protection through organizations like هيئة الأوراق المالية والأسواق الأوروبية ensures better الشفافية and safer investing environments. These protections give investors more confidence and help prevent losses due to unclear or unfair practices.
كلمة الختام:
Choosing individual stocks in Europe means thinking beyond company performance. Taxes, rules, and cross-border complexities all influence your final returns. This section shows how to manage those factors wisely so your investments work better for you.