Global: Market Capitalization and Enterprise Value
수업 학습 목표:
- Understand the concept of 시가총액, how it is calculated, and its role in categorizing companies into large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap. This knowledge is crucial for gauging a company’s size and its comparative scale within the industry.
- 에 대한 학습 Enterprise Value (EV) and how it provides a more comprehensive measure of a company’s total value by including debt and cash. This measure is essential for deeper financial analysis, especially in mergers and acquisitions.
- Differentiate between 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치, recognizing how each metric serves different purposes in investment analysis. This distinction is vital for making informed investment decisions and for understanding the financial health and true worth of a company.
- Explore how these financial metrics are applied in real-world scenarios, such as in the evaluation of company size, investment analysis, and strategic decision-making. This practical application reinforces the theoretical knowledge and aids in better investment planning.
소개
When evaluating a company, two of the most important metrics investors use are 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치. These measures provide insight into a company’s size, value, and financial health, helping investors assess its worth in the marketplace. Understanding the differences between these two metrics is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This section introduces 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치, explains their differences, and demonstrates how to use them in investment analysis.
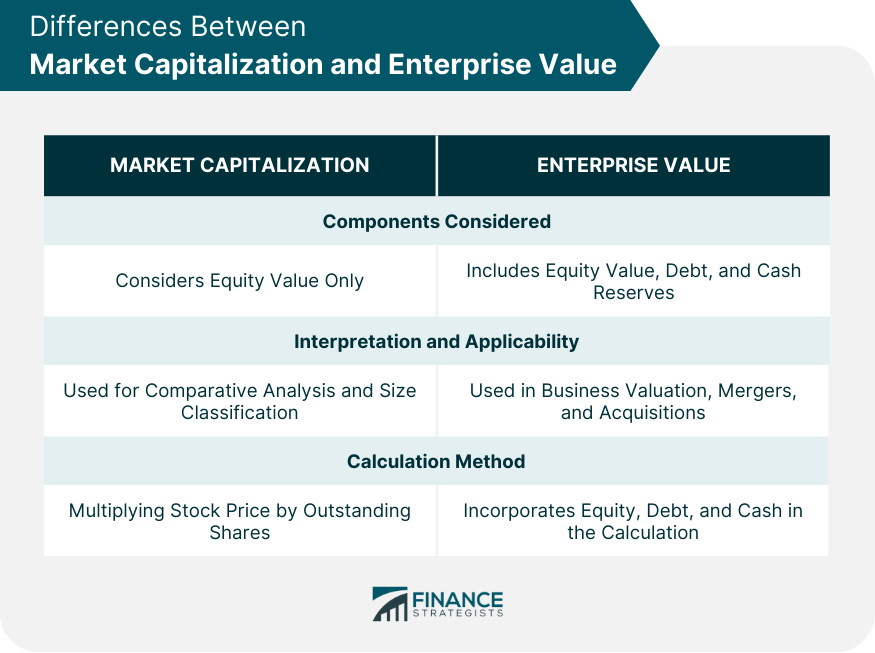
수치: Differences Between Market Capitalization and Enterprise Value
설명:
This table presents a comparison between 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치, highlighting three main areas of distinction: components considered, interpretation and applicability, 그리고 calculation method. 시가총액 considers only the 자산 가치, making it useful for comparative analysis and sizing a company. It is calculated by multiplying the stock price by outstanding shares. 기업 가치, on the other hand, provides a broader view by incorporating equity value, debt, and cash reserves, and is more applicable in business valuation, mergers, and acquisitions.
주요 시사점:
- 시가총액 를 나타냅니다 total equity value and is widely used for stock comparison.
- 기업 가치 provides a more comprehensive measure of a company’s value by including debt and cash reserves.
- 그만큼 calculation ~의 시가총액 is straightforward, while 기업 가치 requires incorporating additional factors like debt and cash.
정보의 응용:
Investors can use 시가총액 to understand the size of a company in terms of equity, while 기업 가치 offers a more accurate picture of the total value, particularly useful in mergers and acquisitions. Understanding the difference helps in evaluating financial health and making better 투자 결정.
A. Market Capitalization
시가총액, often referred to as “market cap,” is the total value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock. It is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of shares outstanding. Market capitalization is a quick way to gauge the size of a company and its relative importance in the market.
- Formula: Market Capitalization = Stock Price × Total Shares Outstanding.
For example, if a company has 1 million shares outstanding and its current stock price is $50, its market capitalization is $50 million. Investors use market capitalization to categorize companies into different classes:
- Large-cap: Companies with a market cap over $10 billion.
- Mid-cap: Companies with a market cap between $2 billion and $10 billion.
- Small-cap: Companies with a market cap below $2 billion.
Market capitalization reflects a company’s equity value but does not consider its debt or cash reserves. While it’s a useful measure of size, it provides only a partial view of the company’s total value.
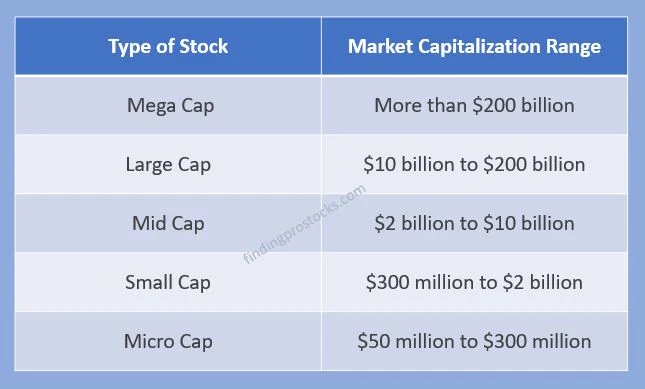
수치: Type of Stock by Market Capitalization Range
설명:
This table categorizes different types of stocks based on their 시가총액. The types are divided into Mega Cap, Large Cap, Mid Cap, Small Cap, 그리고 Micro Cap, with corresponding ranges of market capitalization values. Mega Cap stocks have a market cap of over $200 billion, while Large Cap stocks fall between $10 billion 그리고 $200 billion. Mid Cap stocks range from $2 billion 에게 $10 billion, Small Cap stocks from $300 million 에게 $2 billion, 그리고 Micro Cap stocks from $50 million 에게 $300 million.
주요 시사점:
- Mega Cap stocks represent the largest companies, generally stable with extensive global influence.
- Large Cap stocks are established companies with significant market share.
- Mid Cap stocks have potential for growth, balancing risk and return.
- Small Cap stocks are typically younger companies, offering higher growth potential but increased volatility.
- Micro Cap stocks are often the smallest companies, involving the highest risk but potential for high returns.
정보의 응용:
Understanding market capitalization categories can help investors assess a company’s size, stability, 그리고 growth potential. This information is crucial for 포트폴리오 다양화, allowing investors to align their investments with 위험 감수 그리고 financial goals.
B. Enterprise Value
Enterprise value (EV) is a more comprehensive measure of a company’s total value, as it includes not only the market capitalization but also the company’s debt and subtracts cash on hand. Enterprise value represents the amount of money required to buy the entire company, including both its equity and its debt obligations, making it a better indicator of the company’s true value.
- Formula: Enterprise Value = Market Capitalization + Total Debt – Cash and Cash Equivalents.
Enterprise value accounts for all the capital invested in a company, giving investors a clearer picture of its worth, especially when comparing companies with different capital structures. For instance, two companies may have similar market capitalizations, but if one has substantial debt and the other does not, their enterprise values will differ significantly.
For example, if a company has a market cap of $50 million, $10 million in debt, and $5 million in cash, the enterprise value would be:
- EV = $50 million (market cap) + $10 million (debt) – $5 million (cash) = $55 million.
By factoring in debt and cash, enterprise value gives a more accurate representation of what it would cost to acquire the company.
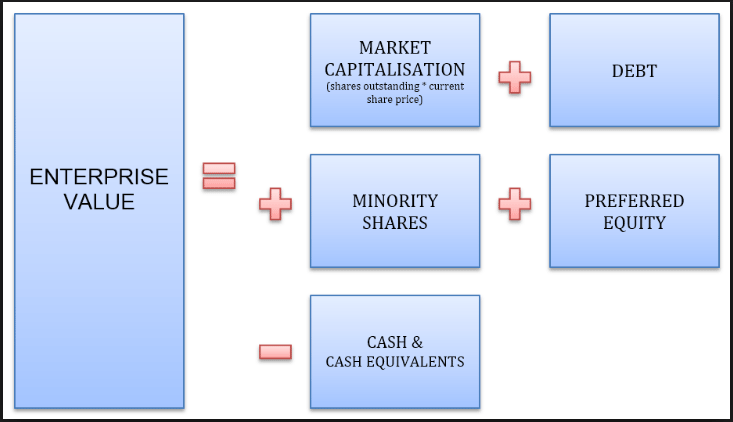
수치: 기업 가치 공식
설명:
This figure illustrates the formula for calculating Enterprise Value (EV), which represents a company’s total value. The formula includes 시가총액 (total shares outstanding multiplied by current share price), 빚, Minority Shares, 그리고 Preferred Equity. It subtracts Cash & Cash Equivalents from the total. This approach gives a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s valuation by considering debt and available cash, beyond just market capitalization.
주요 시사점:
- 기업 가치 provides a holistic measure of a company’s value, considering both 형평성 그리고 빚.
- 시가총액 only represents equity value, while EV adjusts for cash, debt, and other components.
- 빚 그리고 preferred equity add to a company’s valuation, while 현금 is subtracted as it can be used to pay off debt.
- EV is often used in mergers and acquisitions to assess a company’s total worth.
정보의 응용:
Understanding 기업 가치 helps investors evaluate a company’s overall value, including debt obligations, making it useful for valuation 그리고 comparison purposes. It provides insights into a company’s capital structure, allowing investors to make informed decisions in scenarios like acquisitions, takeovers, or when considering a company’s financial health.
C. Differences between Market Capitalization and Enterprise Value
While both 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치 provide insights into a company’s size and value, they serve different purposes in investment analysis.
- 시가총액 only considers the company’s equity value, making it a simple metric to understand but limited in scope. It does not factor in the company’s debt or cash reserves, which can have a significant impact on its true value.
- 기업 가치 offers a more complete picture of a company’s worth by including debt and subtracting cash. This makes EV a better metric when comparing companies with different capital structures or evaluating potential acquisitions.
For instance, if two companies have the same market capitalization but one has significant debt, the company with higher debt will have a larger enterprise value. This is important for investors looking to understand the company’s total value, including its liabilities.
D. Using Market Capitalization and Enterprise Value in Investment Analysis
Both 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치 are essential tools in investment analysis, but they are used for different purposes.
- 시가총액: Investors use market capitalization to categorize companies and compare their relative sizes. Large-cap companies are often seen as more stable and less risky, while small-cap companies may offer higher growth potential but come with greater risk. Market capitalization is also used in calculating stock market indices like the S&P 500.
- 기업 가치: EV is particularly useful when analyzing a company for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) or for comparing companies with varying amounts of debt. It provides a clearer picture of a company’s total value, especially when you want to understand the cost to acquire a company or compare it with another company that has a different capital structure. EV is often used in valuation ratios like EV/EBITDA (enterprise value to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization), which helps compare companies on a more apples-to-apples basis.
For example, if you are comparing two companies in the same industry, one with a lot of debt and one without, enterprise value provides a more accurate comparison than market capitalization alone.
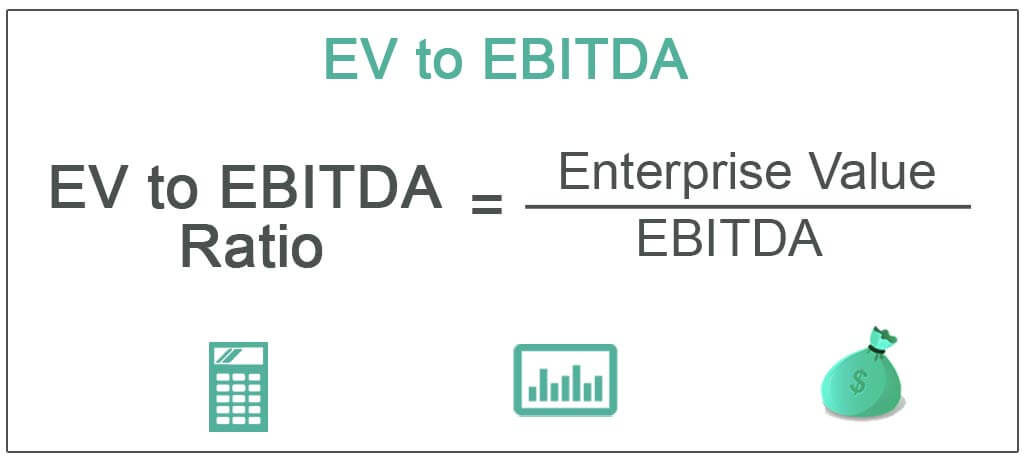
수치: EV to EBITDA Ratio
설명:
The figure shows the calculation of the EV to EBITDA Ratio, which is a widely used financial metric to assess a company’s valuation. It is calculated by dividing the Enterprise Value (EV) by the Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA). This ratio is often used to compare the value of different companies, considering both their operating earnings and their capital structure.
주요 시사점:
- EV to EBITDA helps investors evaluate a company’s valuation, considering both equity and debt.
- It provides insights into how much investors are willing to pay for each unit of EBITDA, a measure of core profitability.
- It is frequently used in mergers and acquisitions to determine if a company is undervalued or overvalued.
- ㅏ lower EV/EBITDA ratio can indicate that a company is more attractive or potentially undervalued, while a higher ratio suggests overvaluation or higher growth expectations.
정보의 응용:
그만큼 EV to EBITDA Ratio is useful for comparing companies of different sizes within the same industry. It helps investors identify undervalued investment opportunities and determine the profitability potential of a business relative to its valuation. It is especially valuable for private equity 그리고 venture capital investors, as it offers a clear view of a company’s earnings potential without the impact of financing or accounting decisions.
결론
시가총액 그리고 기업 가치 are both critical tools for understanding a company’s size and worth, but they serve different functions. Market capitalization offers a straightforward view of a company’s equity value, while enterprise value gives a more comprehensive measure that includes debt and cash, making it a better indicator of the company’s total value. By using both metrics, investors can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial standing, compare it with peers, and make more informed investment decisions.
주요 수업 정보:
- 시가총액 is a basic yet essential metric for estimating the size of a company by multiplying its stock price by its total outstanding shares. This measurement helps categorize companies into different market cap classes (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap).
- Enterprise Value (EV) offers a holistic view of a company’s valuation by incorporating debt and cash, making it a crucial metric for comprehensive financial analysis and better reflective of a company’s total market value.
- The comparison between 시가총액 그리고 기업 가치 highlights their unique roles in financial analysis, with market cap focusing on equity value and EV providing a broader perspective by including debt and cash holdings.
- Understanding these concepts aids investors in making informed decisions, particularly in scenarios involving mergers, acquisitions, or when assessing the financial stability and growth potential of a company.
마무리 진술:
Grasping the concepts of Market Capitalization and Enterprise Value equips investors with the necessary tools to perform accurate company valuations and make informed investment decisions. This knowledge is foundational for anyone involved in financial markets, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of company valuation beyond just stock prices.

