Global: finansinės strategijos skolų valdymui ir skubiam taupymui
Pamokos mokymosi tikslai:
Įvadas:
This section explores different types of financial accounts and how they can be used for managing debt, saving for emergencies, and planning for long-term financial stability. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each account, you can make smarter financial decisions tailored to your needs.
- Understand the features of various financial accounts like checking accounts, savings accounts, money market accounts, and CDs. You will learn how each account functions and which is best suited for specific financial goals, such as managing daily expenses or building emergency savings.
- Learn how to effectively build an emergency fund by understanding the recommended savings amount and how to achieve it gradually. This knowledge will help you maintain financial stability in case of unexpected events, like job loss or medical emergencies.
- Explore tools and services provided by financial institutions that aid in debt management and emergency savings. This includes budgeting tools, automatic transfers, and debt consolidation options, helping you make better use of available financial services.
A. Types of Accounts and Financial Services
Understanding the different types of financial accounts and services available is key to effective debt management and long-term financial planning. Various accounts offer different benefits depending on an individual’s financial goals, whether it’s saving for emergencies, managing daily expenses, or investing for the future. The most common types of accounts include:
- Checking accounts: These are used for day-to-day financial transactions, such as paying bills and receiving income. Checking accounts offer easy access to funds but usually offer little or no interest.
- Savings accounts: These accounts are designed for storing money that is not needed for immediate expenses. They typically offer higher interest rates than checking accounts, making them ideal for building emergency funds.
- Money market accounts: These are hybrid accounts that offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts but may have minimum balance requirements. They often provide limited check-writing capabilities, offering both liquidity and growth.
- Indėlių sertifikatai (CD): CDs are time-based deposit accounts that offer fixed interest rates over a set period. They provide higher interest returns, but the money is locked in for a certain term, making them less flexible for emergency use.
- Credit accounts: Credit cards and lines of credit are financial products that allow users to borrow money up to a pre-approved limit. These accounts can be useful for managing unexpected expenses but can quickly become costly due to high interest rates if not repaid promptly.
Choosing the right type of account for specific financial needs helps individuals balance liquidity and growth, ensuring they have access to emergency funds while also planning for long-term financial stability.

Paveikslėlis: Compare Account Types
Aprašymas:
The figure compares three types of accounts: Savings Account, Money Market Account, and Certificates of Deposit (CD). It highlights differences in interest rates, opening deposit requirements, and ongoing balance requirements for each. It also guides users on which account might suit their financial goals, depending on factors like flexibility, long-term savings, and the need for a guaranteed return.
Svarbiausios išvados:
- Savings accounts are flexible, with low minimum requirements, suitable for those starting an emergency fund.
- Money market accounts may offer higher interest rates than savings accounts but could require higher opening deposits and balances.
- Indėlių sertifikatai (CD) provide a guaranteed return over a fixed term but require funds to be locked for a specific period.
- Account choice depends on your financial goals, such as saving for the short term or aiming for higher returns over time.
- Multiple accounts can be beneficial for managing various financial goals simultaneously.
Informacijos taikymas:
Understanding the features of each account type helps users decide where to allocate their savings for maximum benefit. By comparing interest rates, deposit requirements, and account flexibility, individuals can choose the best option to meet their financial objectives. This knowledge is especially useful for planning short-term savings and long-term investment strategies.
B. Emergency Funds and Financial Planning
An skubios pagalbos fondas is a crucial component of financial planning, serving as a safety net for unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent home repairs. The goal of an emergency fund is to ensure that individuals do not need to rely on high-cost credit or loans when faced with sudden financial challenges. Experts typically recommend saving enough to cover three to six months of living expenses in an easily accessible account, such as a savings account arba money market account.
Building an emergency fund involves setting aside a portion of income regularly, even if it starts small. The key is to prioritize consistent contributions to this fund until it reaches an adequate level.
For example, if an individual’s monthly living expenses (rent, utilities, food, and transportation) total $2,000, a fully funded emergency fund would be $6,000 to $12,000. This ensures they can maintain financial stability for several months in the event of a loss of income.
Finansinis planavimas extends beyond just saving for emergencies. It involves creating a comprehensive plan that includes long-term savings, debt repayment strategies, and investment goals. By integrating emergency funds into a broader financial plan, individuals can stay prepared for both short-term needs and future aspirations, such as home ownership, education, or retirement.
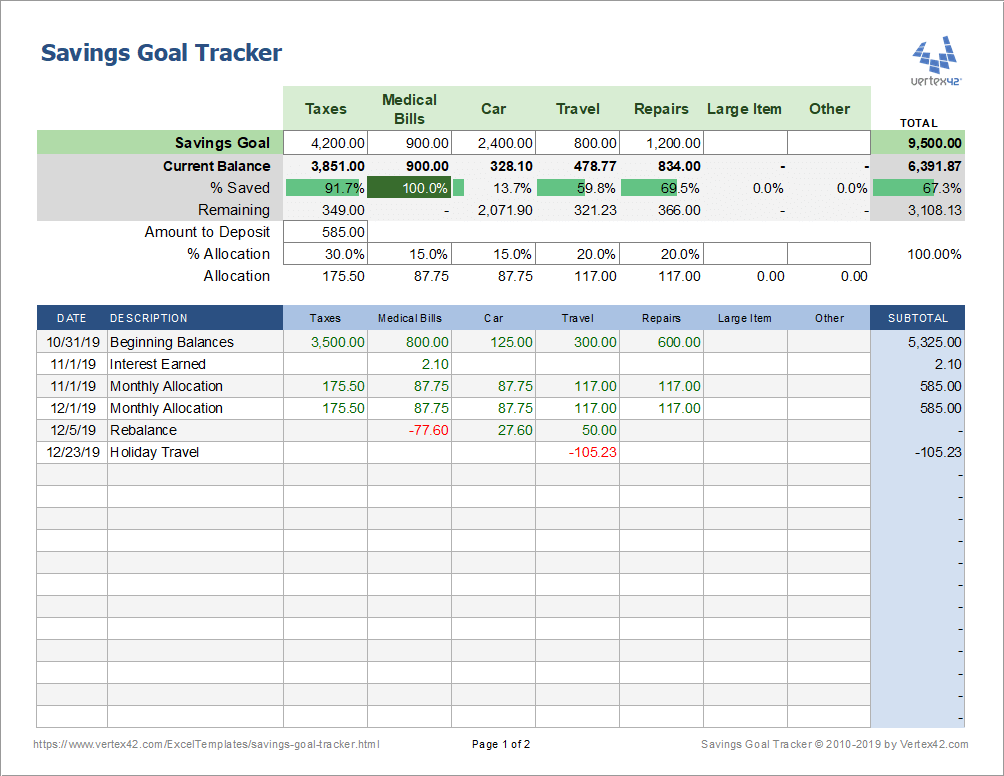
Paveikslėlis: Savings Goal Tracker
Aprašymas:
The figure is a savings goal tracker that helps users monitor and manage multiple savings categories such as taxes, medical bills, car expenses, travel, and repairs. It shows each category’s goal, current balance, and the percentage saved, along with the remaining amount to be saved. The tracker also provides a breakdown of contributions and adjustments over time, allowing users to see how their savings grow and where they may need to allocate more funds.
Svarbiausios išvados:
- Savings allocation can be managed across different goals, making it easier to track progress for multiple objectives.
- Percentage saved provides a clear view of how close each goal is to being achieved.
- Balance tracking over time helps users see how their savings grow and identify patterns in their contributions.
- Adjustments like rebalancing can be made to ensure funds are appropriately distributed.
Informacijos taikymas:
This tracker can be used to set and achieve savings goals by breaking them down into manageable categories. Users can monitor their progress, adjust contributions, and ensure they are on track to meet each goal. This practical tool promotes better financial planning and budgeting, especially for individuals who are saving for multiple future expenses.
C. Using Financial Services for Debt and Emergency Management
Many financial institutions offer services and tools to help individuals manage debt and build emergency funds. These services can include:
- Budgeting tools: Most banks and credit unions offer digital tools or apps to help individuals track their income, expenses, and savings. These tools provide insights into spending habits and can help allocate more money toward emergency savings arba debt repayment.
- Automatic transfers: Setting up automatic transfers from checking accounts to savings accounts ensures regular contributions to an emergency fund without requiring constant effort or oversight.
- Debt management services: Financial institutions may offer debt consolidation loans arba credit counseling services to help individuals manage and reduce their debt burden. These services can make it easier to repay existing debt and free up funds for emergency savings.
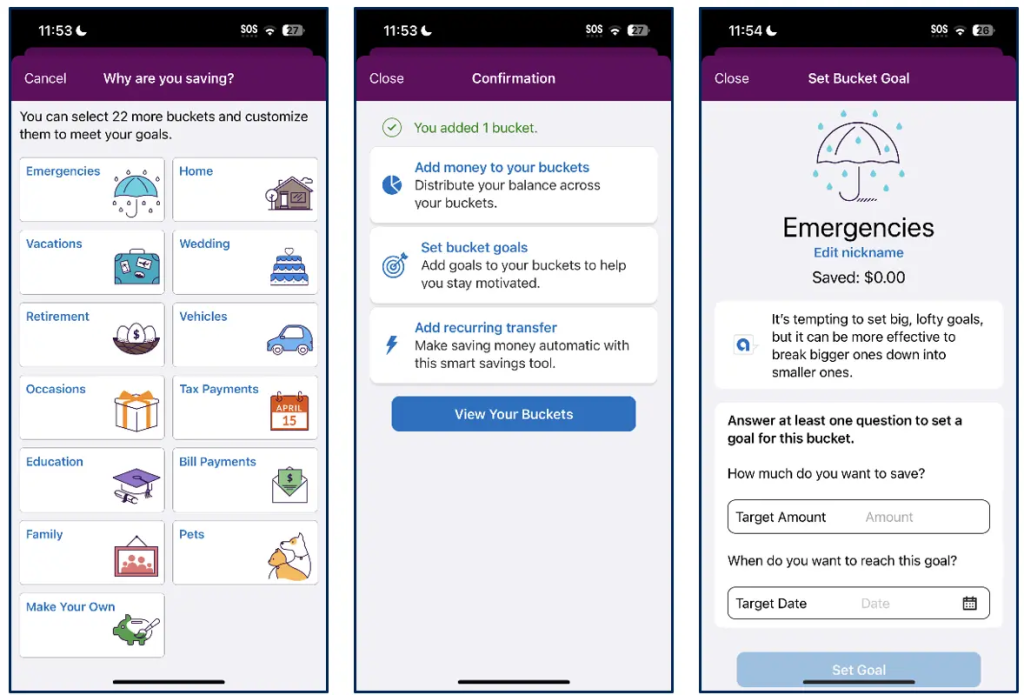
Paveikslėlis: Savings Buckets in a Mobile App
Aprašymas:
The image displays three screens from a mobile app that helps users organize and set goals for their savings. The first screen shows various categories, called “buckets,” that users can choose for their savings, such as emergencies, vacations, and bill payments. The second screen confirms the addition of a new bucket and provides options for managing it, including setting goals and enabling automatic transfers. The third screen shows a specific bucket (for emergencies), where users can define a target amount and set a timeline to achieve their goal.
Svarbiausios išvados:
- Savings buckets help users categorize and plan their savings, making it easier to manage multiple financial goals.
- Tikslų nustatymas allows users to specify a target amount and timeframe, keeping them focused and motivated.
- Automatic transfers make it convenient for users to save regularly without manual effort.
- Customization enables users to create and name their own buckets, adding flexibility to their savings plan.
Informacijos taikymas:
This feature helps users effectively organize their savings by breaking down financial goals into manageable parts. It encourages regular savings habits through automatic transfers and provides clarity on progress by setting specific targets. Investors and savers can use this approach to plan for short-term and long-term financial objectives, ensuring a structured and disciplined saving strategy.
Pagrindinė pamokos informacija:
- Different account types serve unique purposes in financial planning. Checking accounts are ideal for daily transactions, while savings accounts help store funds for emergencies. Money market accounts offer both growth and liquidity, and CDs provide fixed returns over time but require funds to be locked in.
- Emergency funds act as a financial safety net. By regularly setting aside money, even in small amounts, you can gradually build a fund that covers three to six months of living expenses. This fund prevents the need to rely on high-cost credit in emergencies.
- Budgeting tools offered by banks can track income, expenses, and savings, guiding you to allocate funds more efficiently toward debt repayment and emergency savings. Using automatic transfers makes saving consistent and effortless, helping you reach your goals without manual oversight.
- Debt management services can include credit counseling, consolidation loans, or customized repayment plans, making it easier to manage existing debt. These services free up funds that can be directed toward emergency savings or other financial goals.
- Using savings buckets in digital banking apps can help you organize your savings into categories like emergencies, vacations, or home repairs. This clear structure makes it easier to see your progress and maintain focus on multiple goals simultaneously.
Baigiamasis pareiškimas: Understanding how to use different financial accounts and services effectively can enhance your ability to manage debt and save for emergencies. By applying these strategies, you can build a solid foundation for both immediate needs and long-term financial success.

